The data privacy company Onerep.com bills itself as a Virginia-based service for helping people remove their personal information from almost 200 people-search websites. However, an investigation into the history of onerep.com finds this company is operating out of Belarus and Cyprus, and that its founder has launched dozens of people-search services over the years.
Onerep’s “Protect” service starts at $8.33 per month for individuals and $15/mo for families, and promises to remove your personal information from nearly 200 people-search sites. Onerep also markets its service to companies seeking to offer their employees the ability to have their data continuously removed from people-search sites.
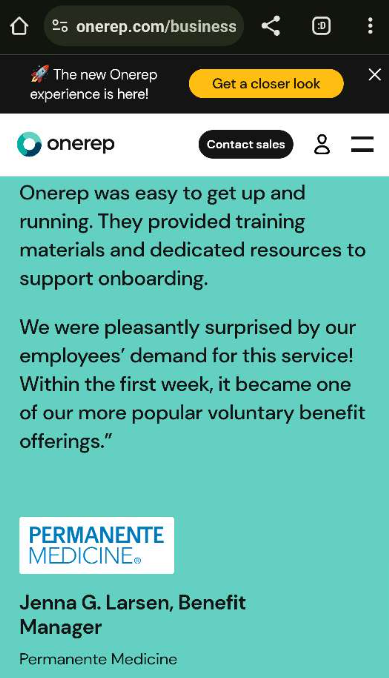
A testimonial on onerep.com.
Customer case studies published on onerep.com state that it struck a deal to offer the service to employees of Permanente Medicine, which represents the doctors within the health insurance giant Kaiser Permanente. Onerep also says it has made inroads among police departments in the United States.
But a review of Onerep’s domain registration records and that of its founder reveal a different side to this company. Onerep.com says its founder and CEO is Dimitri Shelest from Minsk, Belarus, as does Shelest’s profile on LinkedIn. Historic registration records indexed by DomainTools.com say Mr. Shelest was a registrant of onerep.com who used the email address dmitrcox2@gmail.com.
A search in the data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence for the name Dimitri Shelest brings up the email address dimitri.shelest@onerep.com. Constella also finds that Dimitri Shelest from Belarus used the email address d.sh@nuwber.com, and the Belarus phone number +375-292-702786.
Nuwber.com is a people search service whose employees all appear to be from Belarus, and it is one of dozens of people-search companies that Onerep claims to target with its data-removal service. Onerep.com’s website disavows any relationship to Nuwber.com, stating quite clearly, “Please note that OneRep is not associated with Nuwber.com.”
However, there is an abundance of evidence suggesting Mr. Shelest is in fact the founder of Nuwber. Constella found that Minsk telephone number (375-292-702786) has been used multiple times in connection with the email address dmitrcox@gmail.com. Recall that Onerep.com’s domain registration records in 2018 list the email address dmitrcox2@gmail.com.
It appears Mr. Shelest sought to reinvent his online identity in 2015 by adding a “2” to his email address. The Belarus phone number tied to Nuwber.com shows up in the domain records for comversus.com, and DomainTools says this domain is tied to both dmitrcox@gmail.com and dmitrcox2@gmail.com. Other domains that mention both email addresses in their WHOIS records include careon.me, docvsdoc.com, dotcomsvdot.com, namevname.com, okanyway.com and tapanyapp.com.
Onerep.com CEO and founder Dimitri Shelest, as pictured on the “about” page of onerep.com.
A search in DomainTools for the email address dmitrcox@gmail.com shows it is associated with the registration of at least 179 domain names, including dozens of mostly now-defunct people-search companies targeting citizens of Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Israel, Italy, Japan, Latvia and Mexico, among others.
Those include nuwber.fr, a site registered in 2016 which was identical to the homepage of Nuwber.com at the time. DomainTools shows the same email and Belarus phone number are in historic registration records for nuwber.at, nuwber.ch, and nuwber.dk (all domains linked here are to their cached copies at archive.org, where available).
Update, March 21, 11:15 a.m. ET: Mr. Shelest has provided a lengthy response to the findings in this story. In summary, Shelest acknowledged maintaining an ownership stake in Nuwber, but said there was “zero cross-over or information-sharing with OneRep.” Mr. Shelest said any other old domains that may be found and associated with his name are no longer being operated by him.
“I get it,” Shelest wrote. “My affiliation with a people search business may look odd from the outside. In truth, if I hadn’t taken that initial path with a deep dive into how people search sites work, Onerep wouldn’t have the best tech and team in the space. Still, I now appreciate that we did not make this more clear in the past and I’m aiming to do better in the future.” The full statement is available here (PDF).
Original story:
Historic WHOIS records for onerep.com show it was registered for many years to a resident of Sioux Falls, SD for a completely unrelated site. But around Sept. 2015 the domain switched from the registrar GoDaddy.com to eNom, and the registration records were hidden behind privacy protection services. DomainTools indicates around this time onerep.com started using domain name servers from DNS provider constellix.com. Likewise, Nuwber.com first appeared in late 2015, was also registered through eNom, and also started using constellix.com for DNS at nearly the same time.
Listed on LinkedIn as a former product manager at OneRep.com between 2015 and 2018 is Dimitri Bukuyazau, who says their hometown is Warsaw, Poland. While this LinkedIn profile (linkedin.com/in/dzmitrybukuyazau) does not mention Nuwber, a search on this name in Google turns up a 2017 blog post from privacyduck.com, which laid out a number of reasons to support a conclusion that OneRep and Nuwber.com were the same company.
“Any people search profiles containing your Personally Identifiable Information that were on Nuwber.com were also mirrored identically on OneRep.com, down to the relatives’ names and address histories,” Privacyduck.com wrote. The post continued:
“Both sites offered the same immediate opt-out process. Both sites had the same generic contact and support structure. They were – and remain – the same company (even PissedConsumer.com advocates this fact: https://nuwber.pissedconsumer.com/nuwber-and-onerep-20160707878520.html).”
“Things changed in early 2016 when OneRep.com began offering privacy removal services right alongside their own open displays of your personal information. At this point when you found yourself on Nuwber.com OR OneRep.com, you would be provided with the option of opting-out your data on their site for free – but also be highly encouraged to pay them to remove it from a slew of other sites (and part of that payment was removing you from their own site, Nuwber.com, as a benefit of their service).”
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Bukuyazau declined to answer questions, such as whether he ever worked at Nuwber.com. However, Constella Intelligence finds two interesting email addresses for employees at nuwber.com: d.bu@nuwber.com, and d.bu+figure-eight.com@nuwber.com, which was registered under the name “Dzmitry.”
PrivacyDuck’s claims about how onerep.com appeared and behaved in the early days are not readily verifiable because the domain onerep.com has been completely excluded from the Wayback Machine at archive.org. The Wayback Machine will honor such requests if they come directly from the owner of the domain in question.
Still, Mr. Shelest’s name, phone number and email also appear in the domain registration records for a truly dizzying number of country-specific people-search services, including pplcrwlr.in, pplcrwlr.fr, pplcrwlr.dk, pplcrwlr.jp, peeepl.br.com, peeepl.in, peeepl.it and peeepl.co.uk.
The same details appear in the WHOIS registration records for the now-defunct people-search sites waatpp.de, waatp1.fr, azersab.com, and ahavoila.com, a people-search service for French citizens.
A search on the email address dmitrcox@gmail.com suggests Mr. Shelest was previously involved in rather aggressive email marketing campaigns. In 2010, an anonymous source leaked to KrebsOnSecurity the financial and organizational records of Spamit, which at the time was easily the largest Russian-language pharmacy spam affiliate program in the world.
Spamit paid spammers a hefty commission every time someone bought male enhancement drugs from any of their spam-advertised websites. Mr. Shelest’s email address stood out because immediately after the Spamit database was leaked, KrebsOnSecurity searched all of the Spamit affiliate email addresses to determine if any of them corresponded to social media accounts at Facebook.com (at the time, Facebook allowed users to search profiles by email address).
That mapping, which was done mainly by generous graduate students at my alma mater George Mason University, revealed that dmitrcox@gmail.com was used by a Spamit affiliate, albeit not a very profitable one. That same Facebook profile for Mr. Shelest is still active, and it says he is married and living in Minsk [Update, Mar. 16: Mr. Shelest’s Facebook account is no longer active].
Scrolling down Mr. Shelest’s Facebook page to posts made more than ten years ago show him liking the Facebook profile pages for a large number of other people-search sites, including findita.com, findmedo.com, folkscan.com, huntize.com, ifindy.com, jupery.com, look2man.com, lookerun.com, manyp.com, peepull.com, perserch.com, persuer.com, pervent.com, piplenter.com, piplfind.com, piplscan.com, popopke.com, pplsorce.com, qimeo.com, scoutu2.com, search64.com, searchay.com, seekmi.com, selfabc.com, socsee.com, srching.com, toolooks.com, upearch.com, webmeek.com, and many country-code variations of viadin.ca (e.g. viadin.hk, viadin.com and viadin.de).
Domaintools.com finds that all of the domains mentioned in the last paragraph were registered to the email address dmitrcox@gmail.com.
Mr. Shelest has not responded to multiple requests for comment. KrebsOnSecurity also sought comment from onerep.com, which likewise has not responded to inquiries about its founder’s many apparent conflicts of interest. In any event, these practices would seem to contradict the goal Onerep has stated on its site: “We believe that no one should compromise personal online security and get a profit from it.”
Max Anderson is chief growth officer at 360 Privacy, a legitimate privacy company that works to keep its clients’ data off of more than 400 data broker and people-search sites. Anderson said it is concerning to see a direct link between between a data removal service and data broker websites.
“I would consider it unethical to run a company that sells people’s information, and then charge those same people to have their information removed,” Anderson said.
Last week, KrebsOnSecurity published an analysis of the people-search data broker giant Radaris, whose consumer profiles are deep enough to rival those of far more guarded data broker resources available to U.S. police departments and other law enforcement personnel.
That story revealed that the co-founders of Radaris are two native Russian brothers who operate multiple Russian-language dating services and affiliate programs. It also appears many of the Radaris founders’ businesses have ties to a California marketing firm that works with a Russian state-run media conglomerate currently sanctioned by the U.S. government.

KrebsOnSecurity will continue investigating the history of various consumer data brokers and people-search providers. If any readers have inside knowledge of this industry or key players within it, please consider reaching out to krebsonsecurity at gmail.com.
Update, March 15, 11:35 a.m. ET: Many readers have pointed out something that was somehow overlooked amid all this research: The Mozilla Foundation, the company that runs the Firefox Web browser, has launched a data removal service called Mozilla Monitor that bundles OneRep. That notice says Mozilla Monitor is offered as a free or paid subscription service.
“The free data breach notification service is a partnership with Have I Been Pwned (“HIBP”),” the Mozilla Foundation explains. “The automated data deletion service is a partnership with OneRep to remove personal information published on publicly available online directories and other aggregators of information about individuals (“Data Broker Sites”).”
In a statement shared with KrebsOnSecurity.com, Mozilla said they did assess OneRep’s data removal service to confirm it acts according to privacy principles advocated at Mozilla.
“We were aware of the past affiliations with the entities named in the article and were assured they had ended prior to our work together,” the statement reads. “We’re now looking into this further. We will always put the privacy and security of our customers first and will provide updates as needed.”
The U.S. government agency in charge of improving the nation’s cybersecurity posture is ordering all federal agencies to take new measures to restrict access to Internet-exposed networking equipment. The directive comes amid a surge in attacks targeting previously unknown vulnerabilities in widely used security and networking appliances.

Under a new order from the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), federal agencies will have 14 days to respond to any reports from CISA about misconfigured or Internet-exposed networking equipment. The directive applies to any networking devices — such as firewalls, routers and load balancers — that allow remote authentication or administration.
The order requires federal departments to limit access so that only authorized users on an agency’s local or internal network can reach the management interfaces of these devices. CISA’s mandate follows a slew of recent incidents wherein attackers exploited zero-day flaws in popular networking products to conduct ransomware and cyber espionage attacks on victim organizations.
Earlier today, incident response firm Mandiant revealed that since at least October 2022, Chinese cyber spies have been exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in many email security gateway (ESG) appliances sold by California-based Barracuda Networks to hoover up email from organizations using these devices.
Barracuda was alerted to the exploitation of a zero-day in its products in mid-May, and two days later the company pushed a security update to address the flaw in all affected devices. But last week, Barracuda took the highly unusual step of offering to replace compromised ESGs, evidently in response to malware that altered the systems in such a fundamental way that they could no longer be secured remotely with software updates.
According to Mandiant, a previously unidentified Chinese hacking group was responsible for exploiting the Barracuda flaw, and appeared to be searching through victim organization email records for accounts “belonging to individuals working for a government with political or strategic interest to [China] while this victim government was participating in high-level, diplomatic meetings with other countries.”
When security experts began raising the alarm about a possible zero-day in Barracuda’s products, the Chinese hacking group altered their tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) in response to Barracuda’s efforts to contain and remediate the incident, Mandiant found.
Mandiant said the attackers will continue to change their tactics and malware, “especially as network defenders continue to take action against this adversary and their activity is further exposed by the infosec community.”
Meanwhile, this week we learned more details about the ongoing exploitation of a zero-day flaw in a broad range of virtual private networking (VPN) products made by Fortinet — devices many organizations rely on to facilitate remote network access for employees.
On June 11, Fortinet released a half-dozen security updates for its FortiOS firmware, including a weakness that researchers said allows an attacker to run malware on virtually any Fortinet SSL VPN appliance. The researchers found that just being able to reach the management interface for a vulnerable Fortinet SSL VPN appliance was enough to completely compromise the devices.
“This is reachable pre-authentication, on every SSL VPN appliance,” French vulnerability researcher Charles Fol tweeted. “Patch your #Fortigate.”
In details published on June 12, Fortinet confirmed that one of the vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-27997) is being actively exploited. The company said it discovered the weakness in an internal code audit that began in January 2023 — when it learned that Chinese hackers were exploiting a different zero-day flaw in its products.
Shodan.io, the search engine made for finding Internet of Things devices, reports that there are currently more than a half-million vulnerable Fortinet devices reachable via the public Internet.
The new cybersecurity directive from CISA orders agencies to remove any networking device management interfaces from the internet by making them only accessible from an internal enterprise network (CISA recommends an isolated management network). CISA also says agencies should “deploy capabilities, as part of a Zero Trust Architecture, that enforce access control to the interface through a policy enforcement point separate from the interface itself (preferred action).”

Security experts say CISA’s directive highlights the reality that cyberspies and ransomware gangs are making it increasingly risky for organizations to expose any devices to the public Internet, because these groups have strong incentives to probe such devices for previously unknown security vulnerabilities.
The most glaring example of this dynamic can be seen in the frequency with which ransomware groups have discovered and pounced on zero-day flaws in widely-used file transfer applications. One ransomware gang in particular — Cl0p — has repeatedly exploited zero day bugs in various file transfer appliances to extort tens of millions of dollars from hundreds of ransomware victims.
On February 2, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that attackers were exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in the GoAnywhere file transfer appliance by Fortra. By the time security updates were available to fix the vulnerability, Cl0p had already used it to steal data from more than a hundred organizations running Fortra’s appliance.
According to CISA, on May 27, Cl0p began exploiting a previously unknown flaw in MOVEit Transfer, a popular Internet-facing file transfer application. MOVEit parent Progress Software has since released security updates to address the weakness, but Cl0p claims to have already used it to compromise hundreds of victim organizations. TechCrunch has been tracking the fallout from victim organizations, which range from banks and insurance providers to universities and healthcare entities.
The always on-point weekly security news podcast Risky Business has recently been urging organizations to jettison any and all FTP appliances, noting that Cl0p (or another crime gang) is likely to visit the same treatment on other FTP appliance vendors.
But that sound advice doesn’t exactly scale for mid-tier networking devices like Barracuda ESGs or Fortinet SSL VPNs, which are particularly prominent in small to mid-sized organizations.
“It’s not like FTP services, you can’t tell an enterprise [to] turn off the VPN [because] the productivity hit of disconnecting the VPN is terminal, it’s a non-starter,” Risky Business co-host Adam Boileau said on this week’s show. “So how to mitigate the impact of having to use a domain-joined network appliance at the edge of your network that is going to get zero-day in it? There’s no good answer.”
Risky Business founder Patrick Gray said the COVID-19 pandemic breathed new life into entire classes of networking appliances that rely on code which was never designed with today’s threat models in mind.
“In the years leading up to the pandemic, the push towards identity-aware proxies and zero trust everything and moving away from this type of equipment was gradual, but it was happening,” Gray said. “And then COVID-19 hit and everybody had to go work from home, and there really was one option to get going quickly — which was to deploy VPN concentrators with enterprise features.”
Gray said the security industry had been focused on building the next generation of remote access tools that are more security-hardened, but when the pandemic hit organizations scrambled to cobble together whatever they could.
“The only stuff available in the market was all this old crap that is not QA’d properly, and every time you shake them CVEs fall out,” Gray remarked, calling the pandemic, “a shot in the arm” to companies like Fortinet and Barracuda.
“They sold so many VPNs through the pandemic and this is the hangover,” Gray said. “COVID-19 extended the life of these companies and technologies, and that’s unfortunate.”