The homepage of Stark Industries Solutions.
Two weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022, a large, mysterious new Internet hosting firm called Stark Industries Solutions materialized and quickly became the epicenter of massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on government and commercial targets in Ukraine and Europe. An investigation into Stark Industries reveals it is being used as a global proxy network that conceals the true source of cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns against enemies of Russia.
At least a dozen patriotic Russian hacking groups have been launching DDoS attacks since the start of the war at a variety of targets seen as opposed to Moscow. But by all accounts, few attacks from those gangs have come close to the amount of firepower wielded by a pro-Russia group calling itself “NoName057(16).”
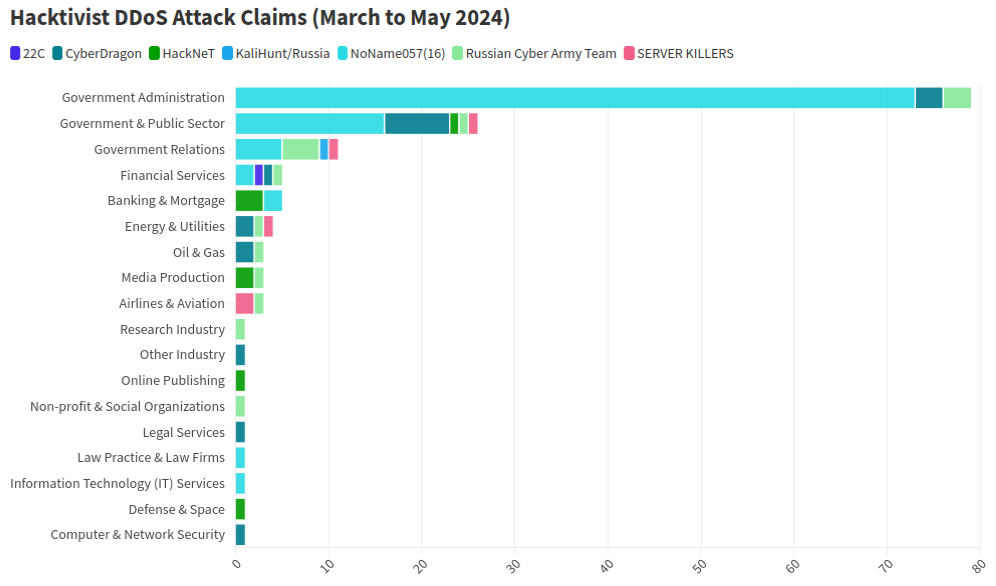
This graphic comes from a recent report from NETSCOUT about DDoS attacks from Russian hacktivist groups.
As detailed by researchers at Radware, NoName has effectively gamified DDoS attacks, recruiting hacktivists via its Telegram channel and offering to pay people who agree to install a piece of software called DDoSia. That program allows NoName to commandeer the host computers and their Internet connections in coordinated DDoS campaigns, and DDoSia users with the most attacks can win cash prizes.
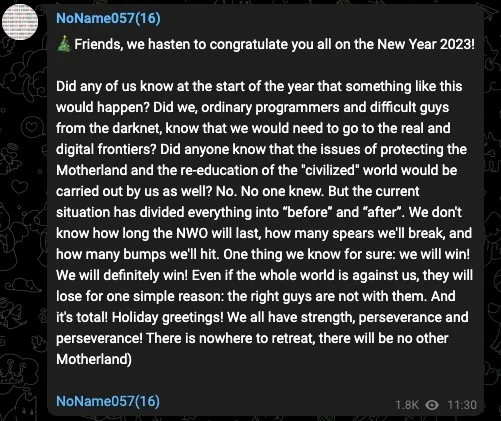
The NoName DDoS group advertising on Telegram. Image: SentinelOne.com.
A report from the security firm Team Cymru found the DDoS attack infrastructure used in NoName campaigns is assigned to two interlinked hosting providers: MIRhosting and Stark Industries. MIRhosting is a hosting provider founded in The Netherlands in 2004. But Stark Industries Solutions Ltd was incorporated on February 10, 2022, just two weeks before the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Security experts say that not long after the war started, Stark began hosting dozens of proxy services and free virtual private networking (VPN) services, which are designed to help users shield their Internet usage and location from prying eyes.
Proxy providers allow users to route their Internet and Web browsing traffic through someone else’s computer. From a website’s perspective, the traffic from a proxy network user appears to originate from the rented IP address, not from the proxy service customer.
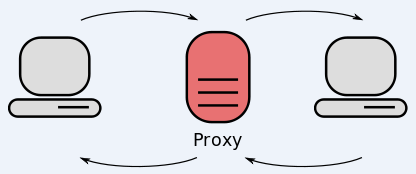
These services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence — but they are also massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity because they can make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source.
What’s more, many proxy services do not disclose how they obtain access to the proxies they are renting out, and in many cases the access is obtained through the dissemination of malicious software that turns the infected system into a traffic relay — usually unbeknownst to the legitimate owner of the Internet connection. Other proxy services will allow users to make money by renting out their Internet connection to anyone.
Spur.us is a company that tracks VPNs and proxy services worldwide. Spur finds that Stark Industries (AS44477) currently is home to at least 74 VPN services, and 40 different proxy services. As we’ll see in the final section of this story, just one of those proxy networks has over a million Internet addresses available for rent across the globe.
Raymond Dijkxhoorn operates a hosting firm in The Netherlands called Prolocation. He also co-runs SURBL, an anti-abuse service that flags domains and Internet address ranges that are strongly associated with spam and cybercrime activity, including DDoS.
Dijkxhoorn said last year SURBL heard from multiple people who said they operated VPN services whose web resources were included in SURBL’s block lists.
“We had people doing delistings at SURBL for domain names that were suspended by the registrars,” Dijkhoorn told KrebsOnSecurity. “And at least two of them explained that Stark offered them free VPN services that they were reselling.”
Dijkxhoorn added that Stark Industries also sponsored activist groups from Ukraine.
“How valuable would it be for Russia to know the real IPs from Ukraine’s tech warriors?” he observed.
Richard Hummel is threat intelligence lead at NETSCOUT. Hummel said when he considers the worst of all the hosting providers out there today, Stark Industries is consistently near or at the top of that list.
“The reason is we’ve had at least a dozen service providers come to us saying, ‘There’s this network out there inundating us with traffic,'” Hummel said. “And it wasn’t even DDoS attacks. [The systems] on Stark were just scanning these providers so fast it was crashing some of their services.”
Hummel said NoName will typically launch their attacks using a mix of resources rented from major, legitimate cloud services, and those from so-called “bulletproof” hosting providers like Stark. Bulletproof providers are so named when they earn or cultivate a reputation for ignoring any abuse complaints or police reports about activity on their networks.
Combining bulletproof providers with legitimate cloud hosting, Hummel said, likely makes NoName’s DDoS campaigns more resilient because many network operators will hesitate to be too aggressive in blocking Internet addresses associated with the major cloud services.
“What we typically see here is a distribution of cloud hosting providers and bulletproof hosting providers in DDoS attacks,” he said. “They’re using public cloud hosting providers because a lot of times that’s your first layer of network defense, and because [many companies are wary of] over-blocking access to legitimate cloud resources.”
But even if the cloud provider detects abuse coming from the customer, the provider is probably not going to shut the customer down immediately, Hummel said.
“There is usually a grace period, and even if that’s only an hour or two, you can still launch a large number of attacks in that time,” he said. “And then they just keep coming back and opening new cloud accounts.”
Stark Industries is incorporated at a mail drop address in the United Kingdom. UK business records list an Ivan Vladimirovich Neculiti as the company’s secretary. Mr. Neculiti also is named as the CEO and founder of PQ Hosting Plus S.R.L. (aka Perfect Quality Hosting), a Moldovan company formed in 2019 that lists the same UK mail drop address as Stark Industries.

Ivan Neculiti, as pictured on LinkedIn.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Neculiti said PQ Hosting established Stark Industries as a “white label” of its brand so that “resellers could distribute our services using our IP addresses and their clients would not have any affairs with PQ Hosting.”
“PQ Hosting is a company with over 1,000+ of [our] own physical servers in 38 countries and we have over 100,000 clients,” he said. “Though we are not as large as Hetzner, Amazon and OVH, nevertheless we are a fast growing company that provides services to tens of thousands of private customers and legal entities.”
Asked about the constant stream of DDoS attacks whose origins have traced back to Stark Industries over the past two years, Neculiti maintained Stark hasn’t received any official abuse reports about attacks coming from its networks.
“It was probably some kind of clever attack that we did not see, I do not rule out this fact, because we have a very large number of clients and our Internet channels are quite large,” he said. “But, in this situation, unfortunately, no one contacted us to report that there was an attack from our addresses; if someone had contacted us, we would have definitely blocked the network data.”
DomainTools.com finds Ivan V. Neculiti was the owner of war[.]md, a website launched in 2008 that chronicled the history of a 1990 armed conflict in Moldova known as the Transnistria War and the Moldo-Russian war.

An ad for war.md, circa 2009.
Transnistria is a breakaway pro-Russian region that declared itself a state in 1990, although it is not internationally recognized. The copyright on that website credits the “MercenarieS TeaM,” which was at one time a Moldovan IT firm. Mr. Neculiti confirmed personally registering this domain.
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence reports that an Ivan V. Neculiti registered multiple online accounts under the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru. Cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 shows this email address is tied to the username “dfyz” on more than a half-dozen Russian language cybercrime forums since 2008. The user dfyz on Searchengines[.]ru in 2008 asked other forum members to review war.md, and said they were part of the MercenarieS TeaM.
Back then, dfyz was selling “bulletproof servers for any purpose,” meaning the hosting company would willfully ignore abuse complaints or police inquiries about the activity of its customers.
DomainTools reports there are at least 33 domain names registered to dfyz_bk@bk.ru. Several of these domains have Ivan Neculiti in their registration records, including tracker-free[.]cn, which was registered to an Ivan Neculiti at dfyz_bk@bk.ru and referenced the MercenarieS TeaM in its original registration records.
Dfyz also used the nickname DonChicho, who likewise sold bulletproof hosting services and access to hacked Internet servers. In 2014, a prominent member of the Russian language cybercrime community Antichat filed a complaint against DonChicho, saying this user scammed them and had used the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru.
The complaint said DonChicho registered on Antichat from the Transnistria Internet address 84.234.55[.]29. Searching this address in Constella reveals it has been used to register just five accounts online that have been created over the years, including one at ask.ru, where the user registered with the email address neculitzy1@yandex.ru. Constella also returns for that email address a user by the name “Ivan” at memoraleak.com and 000webhost.com.
Constella finds that the password most frequently used by the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru was “filecast,” and that there are more than 90 email addresses associated with this password. Among them are roughly two dozen addresses with the name “Neculiti” in them, as well as the address support@donservers[.]ru.
Intel 471 says DonChicho posted to several Russian cybercrime forums that support@donservers[.]ru was his address, and that he logged into cybercrime forums almost exclusively from Internet addresses in Tiraspol, the capital of Transnistria. A review of DonChicho’s posts shows this person was banned from several forums in 2014 for scamming other users.
Cached copies of DonChicho’s vanity domain (donchicho[.]ru) show that in 2009 he was a spammer who peddled knockoff prescription drugs via Rx-Promotion, once one of the largest pharmacy spam moneymaking programs for Russian-speaking affiliates.
Mr. Neculiti told KrebsOnSecurity he has never used the nickname DonChicho.
“I may assure you that I have no relation to DonChicho nor to his bulletproof servers,” he said.
Below is a mind map that shows the connections between the accounts mentioned above.
Earlier this year, NoName began massively hitting government and industry websites in Moldova. A new report from Arbor Networks says the attacks began around March 6, when NoName alleged the government of Moldova was “craving for Russophobia.”
“Since early March, more than 50 websites have been targeted, according to posted ‘proof’ by the groups involved in attacking the country,” Arbor’s ASERT Team wrote. “While NoName seemingly initiated the ramp of attacks, a host of other DDoS hacktivists have joined the fray in claiming credit for attacks across more than 15 industries.”
The German independent news outlet Correctiv.org last week published a scathing investigative report on Stark Industries and MIRhosting, which notes that Ivan Neculiti operates his hosting companies with the help of his brother, Yuri.
The report points out that Stark Industries continues to host a Russian disinformation news outlet called “Recent Reliable News” (RRN) that was sanctioned by the European Union in 2023 for spreading links to propaganda blogs and fake European media and government websites.
“The website was not running on computers in Moscow or St. Petersburg until recently, but in the middle of the EU, in the Netherlands, on the computers of the Neculiti brothers,” Correctiv reporters wrote.
“After a request from this editorial team, a well-known service was installed that hides the actual web host,” the report continues. “Ivan Neculiti announced that he had blocked the associated access and server following internal investigations. “We very much regret that we are only now finding out that one of our customers is a sanctioned portal,” said the company boss. However, RRN is still accessible via its servers.”
Correctiv also points to a January 2023 report from the Ukrainian government, which found servers from Stark Industries Solutions were used as part of a cyber attack on the Ukrainian news agency “Ukrinform”. Correctiv notes the notorious hacker group Sandworm — an advanced persistent threat (APT) group operated by a cyberwarfare unit of Russia’s military intelligence service — was identified by Ukrainian government authorities as responsible for that attack.
Public records indicate MIRhosting is based in The Netherlands and is operated by 37-year old Andrey Nesterenko, whose personal website says he is an accomplished concert pianist who began performing publicly at a young age.
DomainTools says mirhosting[.]com is registered to Mr. Nesterenko and to Innovation IT Solutions Corp, which lists addresses in London and in Nesterenko’s stated hometown of Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.
This is interesting because according to the book Inside Cyber Warfare by Jeffrey Carr, Innovation IT Solutions Corp. was responsible for hosting StopGeorgia[.]ru, a hacktivist website for organizing cyberattacks against Georgia that appeared at the same time Russian forces invaded the former Soviet nation in 2008. That conflict was thought to be the first war ever fought in which a notable cyberattack and an actual military engagement happened simultaneously.
Responding to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, Mr. Nesterenko said he couldn’t say whether his network had ever hosted the StopGeorgia website back in 2008 because his company didn’t keep records going back that far. But he said Stark Industries Solutions is indeed one of MIRhsoting’s colocation customers.
“Our relationship is purely provider-customer,” Nesterenko said. “They also utilize multiple providers and data centers globally, so connecting them directly to MIRhosting overlooks their broader network.”
“We take any report of malicious activity seriously and are always open to information that can help us identify and prevent misuse of our infrastructure, whether involving Stark Industries or any other customer,” Nesterenko continued. “In cases where our services are exploited for malicious purposes, we collaborate fully with Dutch cyber police and other relevant authorities to investigate and take appropriate measures. However, we have yet to receive any actionable information beyond the article itself, which has not provided us with sufficient detail to identify or block malicious actors.”
In December 2022, security firm Recorded Future profiled the phishing and credential harvesting infrastructure used for Russia-aligned espionage operations by a group dubbed Blue Charlie (aka TAG-53), which has targeted email accounts of nongovernmental organizations and think tanks, journalists, and government and defense officials.
Recorded Future found that virtually all the Blue Charlie domains existed in just ten different ISPs, with a significant concentration located in two networks, one of which was MIRhosting. Both Microsoft and the UK government assess that Blue Charlie is linked to the Russian threat activity groups variously known as Callisto Group, COLDRIVER, and SEABORGIUM.
Mr. Nesterenko took exception to a story on that report from The Record, which is owned by Recorded Future.
“We’ve discussed its contents with our customer, Stark Industries,” he said. “We understand that they have initiated legal proceedings against the website in question, as they firmly believe that the claims made are inaccurate.”
Recorded Future said they updated their story with comments from Mr. Neculiti, but that they stand by their reporting.
Mr. Nesterenko’s LinkedIn profile says he was previously the foreign region sales manager at Serverius-as, a hosting company in The Netherlands that remains in the same data center as MIRhosting.
In February, the Dutch police took 13 servers offline that were used by the infamous LockBit ransomware group, which had originally bragged on its darknet website that its home base was in The Netherlands. Sources tell KrebsOnSecurity the servers seized by the Dutch police were located in Serverius’ data center in Dronten, which is also shared by MIRhosting.
Serverius-as did not respond to requests for comment. Nesterenko said MIRhosting does use one of Serverius’s data centers for its operations in the Netherlands, alongside two other data centers, but that the recent incident involving the seizure of servers has no connection to MIRhosting.
“We are legally prohibited by Dutch law and police regulations from sharing information with third parties regarding any communications we may have had,” he said.
A February 2024 report from security firm ESET found Serverius-as systems were involved in a series of targeted phishing attacks by Russia-aligned groups against Ukrainian entities throughout 2023. ESET observed that after the spearphishing domains were no longer active, they were converted to promoting rogue Internet pharmacy websites.
A review of the Internet address ranges recently added to the network operated by Stark Industries Solutions offers some insight into its customer base, usage, and maybe even true origins. Here is a snapshot (PDF) of all Internet address ranges announced by Stark Industries so far in the month of May 2024 (this information was graciously collated by the network observability platform Kentik.com).
Those records indicate that the largest portion of the IP space used by Stark is in The Netherlands, followed by Germany and the United States. Stark says it is connected to roughly 4,600 Internet addresses that currently list their ownership as Comcast Cable Communications.
A review of those address ranges at spur.us shows all of them are connected to an entity called Proxyline, which is a sprawling proxy service based in Russia that currently says it has more than 1.6 million proxies globally that are available for rent.

Proxyline dot net.
Reached for comment, Comcast said the Internet address ranges never did belong to Comcast, so it is likely that Stark has been fudging the real location of its routing announcements in some cases.
Stark reports that it has more than 67,000 Internet addresses at Santa Clara, Calif.-based EGIhosting. Spur says the Stark addresses involving EGIhosting all map to Proxyline as well. EGIhosting did not respond to requests for comment.
EGIhosting manages Internet addresses for the Cyprus-based hosting firm ITHOSTLINE LTD (aka HOSTLINE-LTD), which is represented throughout Stark’s announced Internet ranges. Stark says it has more than 21,000 Internet addresses with HOSTLINE. Spur.us finds Proxyline addresses are especially concentrated in the Stark ranges labeled ITHOSTLINE LTD, HOSTLINE-LTD, and Proline IT.
Stark’s network list includes approximately 21,000 Internet addresses at Hockessin, De. based DediPath, which abruptly ceased operations without warning in August 2023. According to a phishing report released last year by Interisle Consulting, DediPath was the fourth most common source of phishing attacks in the year ending Oct. 2022. Spur.us likewise finds that virtually all of the Stark address ranges marked “DediPath LLC” are tied to Proxyline.

Image: Interisle Consulting.
A large number of the Internet address ranges announced by Stark in May originate in India, and the names that are self-assigned to many of these networks indicate they were previously used to send large volumes of spam for herbal medicinal products, with names like HerbalFarm, AdsChrome, Nutravo, Herbzoot and Herbalve.
The anti-spam organization SpamHaus reports that many of the Indian IP address ranges are associated with known “snowshoe spam,” a form of abuse that involves mass email campaigns spread across several domains and IP addresses to weaken reputation metrics and avoid spam filters.
It’s not clear how much of Stark’s network address space traces its origins to Russia, but big chunks of it recently belonged to some of the oldest entities on the Russian Internet (a.k.a. “Runet”).
For example, many Stark address ranges were most recently assigned to a Russian government entity whose full name is the “Federal State Autonomous Educational Establishment of Additional Professional Education Center of Realization of State Educational Policy and Informational Technologies.”
A review of Internet address ranges adjacent to this entity reveals a long list of Russian government organizations that are part of the Federal Guard Service of the Russian Federation. Wikipedia says the Federal Guard Service is a Russian federal government agency concerned with tasks related to protection of several high-ranking state officials, including the President of Russia, as well as certain federal properties. The agency traces its origins to the USSR’s Ninth Directorate of the KGB, and later the presidential security service.
Stark recently announced the address range 213.159.64.0/20 from April 27 to May 1, and this range was previously assigned to an ancient ISP in St. Petersburg, RU called the Computer Technologies Institute Ltd.
According to a post on the Russian language webmaster forum searchengines[.]ru, the domain for Computer Technologies Institute — ctinet[.]ru — is the seventh-oldest domain in the entire history of the Runet.
Curiously, Stark also lists large tracts of Internet addresses (close to 48,000 in total) assigned to a small ISP in Kharkiv, Ukraine called NetAssist. Reached via email, the CEO of NetAssist Max Tulyev confirmed his company provides a number of services to PQ Hosting.
“We colocate their equipment in Warsaw, Madrid, Sofia and Thessaloniki, provide them IP transit and IPv4 addresses,” Tulyev said. “For their size, we receive relatively low number of complains to their networks. I never seen anything about their pro-Russian activity or support of Russian hackers. It is very interesting for me to see proofs of your accusations.”
Spur.us mapped the entire infrastructure of Proxyline, and found more than one million proxies across multiple providers, but by far the biggest concentration was at Stark Industries Solutions. The full list of Proxyline address ranges (.CSV) shows two other ISPs appear repeatedly throughout the list. One is Kharkiv, Ukraine based ITL LLC, also known as Information Technology Laboratories Group, and Integrated Technologies Laboratory.
The second is a related hosting company in Miami, called Green Floid LLC. Green Floid featured in a 2017 scoop by CNN, which profiled the company’s owner and quizzed him about Russian troll farms using proxy networks on Green Floid and its parent firm ITL to mask disinformation efforts tied to the Kremlin’s Internet Research Agency (IRA). At the time, the IRA was using Facebook and other social media networks to spread videos showing police brutality against African Americans in an effort to encourage protests across the United States.

Doug Madory, director of Internet analysis at Kentik, was able to see at a high level the top sources and destinations for traffic traversing Stark’s network.
“Based on our aggregate NetFlow, we see Iran as the top destination (35.1%) for traffic emanating from Stark (AS44477),” Madory said. “Specifically, the top destination is MTN Irancell, while the top source is Facebook. This data supports the theory that AS44477 houses proxy services as Facebook is blocked in Iran.”
On April 30, the security firm Malwarebytes explored an extensive malware operation that targets corporate Internet users with malicious ads. Among the sites used as lures in that campaign were fake Wall Street Journal and CNN websites that told visitors they were required to install a WSJ or CNN-branded browser extension (malware). Malwarebytes found a domain name central to that operation was hosted at Internet addresses owned by Stark Industries.
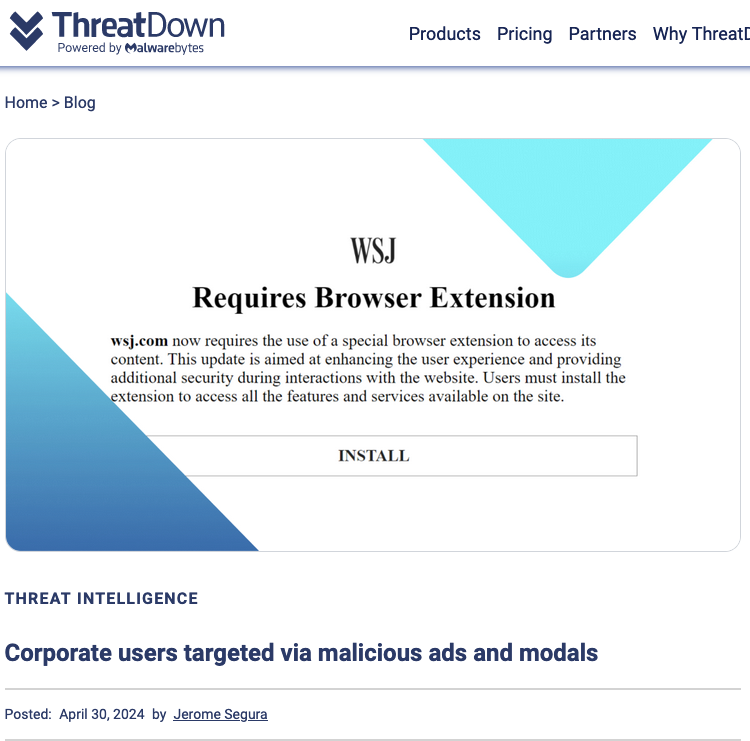
Image: threatdown.com
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) today levied fines totaling nearly $200 million against the four major carriers — including AT&T, Sprint, T-Mobile and Verizon — for illegally sharing access to customers’ location information without consent.
![]()
The fines mark the culmination of a more than four-year investigation into the actions of the major carriers. In February 2020, the FCC put all four wireless providers on notice that their practices of sharing access to customer location data were likely violating the law.
The FCC said it found the carriers each sold access to its customers’ location information to ‘aggregators,’ who then resold access to the information to third-party location-based service providers.
“In doing so, each carrier attempted to offload its obligations to obtain customer consent onto downstream recipients of location information, which in many instances meant that no valid customer consent was obtained,” an FCC statement on the action reads. “This initial failure was compounded when, after becoming aware that their safeguards were ineffective, the carriers continued to sell access to location information without taking reasonable measures to protect it from unauthorized access.”
The FCC’s findings against AT&T, for example, show that AT&T sold customer location data directly or indirectly to at least 88 third-party entities. The FCC found Verizon sold access to customer location data (indirectly or directly) to 67 third-party entities. Location data for Sprint customers found its way to 86 third-party entities, and to 75 third-parties in the case of T-Mobile customers.
The commission said it took action after Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) sent a letter to the FCC detailing how a company called Securus Technologies had been selling location data on customers of virtually any major mobile provider to law enforcement officials.
That same month, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that LocationSmart — a data aggregation firm working with the major wireless carriers — had a free, unsecured demo of its service online that anyone could abuse to find the near-exact location of virtually any mobile phone in North America.
The carriers promised to “wind down” location data sharing agreements with third-party companies. But in 2019, reporting at Vice.com showed that little had changed, detailing how reporters were able to locate a test phone after paying $300 to a bounty hunter who simply bought the data through a little-known third-party service.
Sen. Wyden said no one who signed up for a cell plan thought they were giving permission for their phone company to sell a detailed record of their movements to anyone with a credit card.
“I applaud the FCC for following through on my investigation and holding these companies accountable for putting customers’ lives and privacy at risk,” Wyden said in a statement today.
The FCC fined Sprint and T-Mobile $12 million and $80 million respectively. AT&T was fined more than $57 million, while Verizon received a $47 million penalty. Still, these fines represent a tiny fraction of each carrier’s annual revenues. For example, $47 million is less than one percent of Verizon’s total wireless service revenue in 2023, which was nearly $77 billion.
The fine amounts vary because they were calculated based in part on the number of days that the carriers continued sharing customer location data after being notified that doing so was illegal (the agency also considered the number of active third-party location data sharing agreements). The FCC notes that AT&T and Verizon each took more than 320 days from the publication of the Times story to wind down their data sharing agreements; T-Mobile took 275 days; Sprint kept sharing customer location data for 386 days.
Update, 6:25 p.m. ET: Clarified that the FCC launched its investigation at the request of Sen. Wyden.
Nikita Kislitsin, formerly the head of network security for one of Russia’s top cybersecurity firms, was arrested last week in Kazakhstan in response to 10-year-old hacking charges from the U.S. Department of Justice. Experts say Kislitsin’s prosecution could soon put the Kazakhstan government in a sticky diplomatic position, as the Kremlin is already signaling that it intends to block his extradition to the United States.

Nikita Kislitsin, at a security conference in Russia.
Kislitsin is accused of hacking into the now-defunct social networking site Formspring in 2012, and conspiring with another Russian man convicted of stealing tens of millions of usernames and passwords from LinkedIn and Dropbox that same year.
In March 2020, the DOJ unsealed two criminal hacking indictments against Kislitsin, who was then head of security at Group-IB, a cybersecurity company that was founded in Russia in 2003 and operated there for more than a decade before relocating to Singapore.
Prosecutors in Northern California indicted Kislitsin in 2014 for his alleged role in stealing account data from Formspring. Kislitsin also was indicted in Nevada in 2013, but the Nevada indictment does not name his alleged victim(s) in that case.
However, documents unsealed in the California case indicate Kislitsin allegedly conspired with Yevgeniy Nikulin, a Russian man convicted in 2020 of stealing 117 million usernames and passwords from Dropbox, Formspring and LinkedIn in 2012. Nikulin is currently serving a seven-year sentence in the U.S. prison system.
As first reported by Cyberscoop in 2020, a trial brief in the California investigation identified Nikulin, Kislitsin and two alleged cybercriminals — Oleg Tolstikh and Oleksandr Vitalyevich Ieremenko — as being present during a 2012 meeting at a Moscow hotel, where participants allegedly discussed starting an internet café business.
A 2010 indictment out of New Jersey accuses Ieremenko and six others with siphoning nonpublic information from the U.S. Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) and public relations firms, and making $30 million in illegal stock trades based on the proprietary information they stole.
[The U.S. Secret Service has an outstanding $1 million reward for information leading to the arrest of Ieremenko (Александр Витальевич Еременко), who allegedly went by the hacker handles “Zl0m” and “Lamarez.”]
Kislitsin was hired by Group-IB in January 2013, nearly six months after the Formspring hack. Group-IB has since moved its headquarters to Singapore, and in April 2023 the company announced it had fully exited the Russian market.
In a statement provided to KrebsOnSecurity, Group-IB said Mr. Kislitsin is no longer an employee, and that he now works for a Russian organization called FACCT, which stands for “Fight Against Cybercrime Technologies.”
“Dmitry Volkov, co-founder and CEO, sold his stake in Group-IB’s Russia-based business to the company’s local management,” the statement reads. “The stand-alone business in Russia has been operating under the new brand FACCT ever since and will continue to operate as a separate company with no connection to Group-IB.”
FACCT says on its website that it is a “Russian developer of technologies for combating cybercrime,” and that it works with clients to fight targeted attacks, data leaks, fraud, phishing and brand abuse. In a statement published online, FACCT said Kislitsin is responsible for developing its network security business, and that he remains under temporary detention in Kazakhstan “to study the basis for extradition arrest at the request of the United States.”
“According to the information we have, the claims against Kislitsin are not related to his work at FACCT, but are related to a case more than 10 years ago when Nikita worked as a journalist and independent researcher,” FACCT wrote.
From 2006 to 2012, Kislitsin was editor-in-chief of “Hacker,” a popular Russian-language monthly magazine that includes articles on information and network security, programming, and frequently features interviews with and articles penned by notable or wanted Russian hackers.
“We are convinced that there are no legal grounds for detention on the territory of Kazakhstan,” the FACCT statement continued. “The company has hired lawyers who have been providing Nikita with all the necessary assistance since last week, and we have also sent an appeal to the Consulate General of the Russian Federation in Kazakhstan to assist in protecting our employee.”
FACCT indicated that the Kremlin has already intervened in the case, and the Russian government claims Kislitsin is wanted on criminal charges in Russia and must instead be repatriated to his homeland.
“The FACCT emphasizes that the announcement of Nikita Kislitsin on the wanted list in the territory of the Russian Federation became known only today, June 28, 6 days after the arrest in Kazakhstan,” FACCT wrote. “The company is monitoring developments.”
The Kremlin followed a similar playbook in the case of Aleksei Burkov, a cybercriminal who long operated two of Russia’s most exclusive underground hacking forums. Burkov was arrested in 2015 by Israeli authorities, and the Russian government fought Burkov’s extradition to the U.S. for four years — even arresting and jailing an Israeli woman on phony drug charges to force a prisoner swap.
That effort ultimately failed: Burkov was sent to America, pleaded guilty, and was sentenced to nine years in prison.

Alexei Burkov, seated second from right, attends a hearing in Jerusalem in 2015. Image: Andrei Shirokov / Tass via Getty Images.
Arkady Bukh is a U.S. attorney who has represented dozens of accused hackers from Russia and Eastern Europe who were extradited to the United States over the years. Bukh said Moscow is likely to turn the Kislitsin case into a diplomatic time bomb for Kazakhstan, which shares an enormous border and a great deal of cultural ties with Russia. A 2009 census found that Russians make up about 24 percent of the population of Kazakhstan.
“That would put Kazakhstan at a crossroads to choose between unity with Russia or going with the West,” Bukh said. “If that happens, Kazakhstan may have to make some very unpleasant decisions.”
Group-IB’s exodus from Russia comes as its former founder and CEO Ilya Sachkov remains languishing in a Russian prison, awaiting a farcical trial and an inevitable conviction on charges of treason. In September 2021, the Kremlin issued treason charges against Sachkov, although it has so far refused to disclose any details about the allegations.
Sachkov’s pending treason trial has been the subject of much speculation among denizens of Russian cybercrime forums, and the consensus seems to be that Sachkov and Group-IB were seen as a little too helpful to the DOJ in its various investigations involving top Russian hackers.
Indeed, since its inception in 2003, Group-IB’s researchers have helped to identify, disrupt and even catch a number of high-profile Russian hackers, most of whom got busted after years of criminal hacking because they made the unforgivable mistake of stealing from their own citizens.
When the indictments against Kislitsin were unsealed in 2020, Group-IB issued a lengthy statement attesting to his character and saying they would help him with his legal defense. As part of that statement, Group-IB noted that “representatives of the Group-IB company and, in particular, Kislitsin, in 2013, on their own initiative, met with employees of the US Department of Justice to inform them about the research work related to the underground, which was carried out by Kislitsin in 2012.”
We learned some remarkable new details this week about the recent supply-chain attack on VoIP software provider 3CX. The lengthy, complex intrusion has all the makings of a cyberpunk spy novel: North Korean hackers using legions of fake executive accounts on LinkedIn to lure people into opening malware disguised as a job offer; malware targeting Mac and Linux users working at defense and cryptocurrency firms; and software supply-chain attacks nested within earlier supply chain attacks.
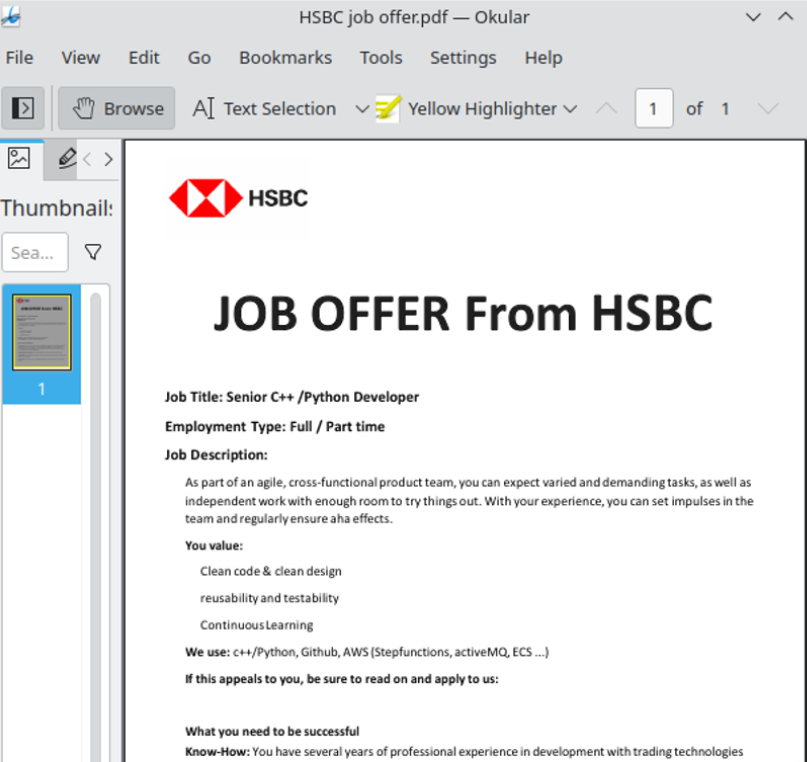
Researchers at ESET say this job offer from a phony HSBC recruiter on LinkedIn was North Korean malware masquerading as a PDF file.
In late March 2023, 3CX disclosed that its desktop applications for both Windows and macOS were compromised with malicious code that gave attackers the ability to download and run code on all machines where the app was installed. 3CX says it has more than 600,000 customers and 12 million users in a broad range of industries, including aerospace, healthcare and hospitality.
3CX hired incident response firm Mandiant, which released a report on Wednesday that said the compromise began in 2022 when a 3CX employee installed a malware-laced software package distributed via an earlier software supply chain compromise that began with a tampered installer for X_TRADER, a software package provided by Trading Technologies.
“This is the first time Mandiant has seen a software supply chain attack lead to another software supply chain attack,” reads the April 20 Mandiant report.
Mandiant found the earliest evidence of compromise uncovered within 3CX’s network was through the VPN using the employee’s corporate credentials, two days after the employee’s personal computer was compromised.
“Eventually, the threat actor was able to compromise both the Windows and macOS build environments,” 3CX said in an April 20 update on their blog.
Mandiant concluded that the 3CX attack was orchestrated by the North Korean state-sponsored hacking group known as Lazarus, a determination that was independently reached earlier by researchers at Kaspersky Lab and Elastic Security.
Mandiant found the compromised 3CX software would download malware that sought out new instructions by consulting encrypted icon files hosted on GitHub. The decrypted icon files revealed the location of the malware’s control server, which was then queried for a third stage of the malware compromise — a password stealing program dubbed ICONICSTEALER.
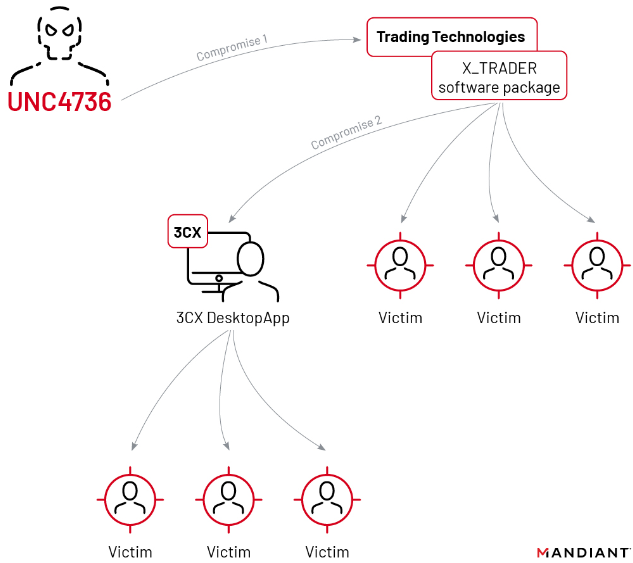
The double supply chain compromise that led to malware being pushed out to some 3CX customers. Image: Mandiant.
Meanwhile, the security firm ESET today published research showing remarkable similarities between the malware used in the 3CX supply chain attack and Linux-based malware that was recently deployed via fake job offers from phony executive profiles on LinkedIn. The researchers said this was the first time Lazarus had been spotted deploying malware aimed at Linux users.
As reported in a series last summer here, LinkedIn has been inundated this past year by fake executive profiles for people supposedly employed at a range of technology, defense, energy and financial companies. In many cases, the phony profiles spoofed chief information security officers at major corporations, and some attracted quite a few connections before their accounts were terminated.
Mandiant, Proofpoint and other experts say Lazarus has long used these bogus LinkedIn profiles to lure targets into opening a malware-laced document that is often disguised as a job offer. This ongoing North Korean espionage campaign using LinkedIn was first documented in August 2020 by ClearSky Security, which said the Lazarus group operates dozens of researchers and intelligence personnel to maintain the campaign globally.
Microsoft Corp., which owns LinkedIn, said in September 2022 that it had detected a wide range of social engineering campaigns using a proliferation of phony LinkedIn accounts. Microsoft said the accounts were used to impersonate recruiters at technology, defense and media companies, and to entice people into opening a malicious file. Microsoft found the attackers often disguised their malware as legitimate open-source software like Sumatra PDF and the SSH client Putty.
Microsoft attributed those attacks to North Korea’s Lazarus hacking group, although they’ve traditionally referred to this group as “ZINC“. That is, until earlier this month, when Redmond completely revamped the way it names threat groups; Microsoft now references ZINC as “Diamond Sleet.”
The ESET researchers said they found a new fake job lure tied to an ongoing Lazarus campaign on LinkedIn designed to compromise Linux operating systems. The malware was found inside of a document that offered an employment contract at the multinational bank HSBC.
“A few weeks ago, a native Linux payload was found on VirusTotal with an HSBC-themed PDF lure,” wrote ESET researchers Peter Kalnai and Marc-Etienne M.Leveille. “This completes Lazarus’s ability to target all major desktop operating systems. In this case, we were able to reconstruct the full chain, from the ZIP file that delivers a fake HSBC job offer as a decoy, up until the final payload.”
ESET said the malicious PDF file used in the scheme appeared to have a file extension of “.pdf,” but that this was a ruse. ESET discovered that the dot in the filename wasn’t a normal period but instead a Unicode character (U+2024) representing a “leader dot,” which is often used in tables of contents to connect section headings with the page numbers on which those sections begin.
“The use of the leader dot in the filename was probably an attempt to trick the file manager into treating the file as an executable instead of a PDF,” the researchers continued. “This could cause the file to run when double-clicked instead of opening it with a PDF viewer.”
ESET said anyone who opened the file would see a decoy PDF with a job offer from HSBC, but in the background the executable file would download additional malware payloads. The ESET team also found the malware was able to manipulate the program icon displayed by the malicious PDF, possibly because fiddling with the file extension could cause the user’s system to display a blank icon for the malware lure.
Kim Zetter, a veteran Wired.com reporter and now independent security journalist, interviewed Mandiant researchers who said they expect “many more victims” will be discovered among the customers of Trading Technologies and 3CX now that news of the compromised software programs is public.
“Mandiant informed Trading Technologies on April 11 that its X_Trader software had been compromised, but the software maker says it has not had time to investigate and verify Mandiant’s assertions,” Zetter wrote in her Zero Day newsletter on Substack. For now, it remains unclear whether the compromised X_Trader software was downloaded by people at other software firms.
If there’s a silver lining here, the X_Trader software had been decommissioned in April 2020 — two years before the hackers allegedly embedded malware in it.
“The company hadn’t released new versions of the software since that time and had stopped providing support for the product, making it a less-than-ideal vector for the North Korean hackers to infect customers,” Zetter wrote.