Three Americans were charged this week with stealing more than $400 million in a November 2022 SIM-swapping attack. The U.S. government did not name the victim organization, but there is every indication that the money was stolen from the now-defunct cryptocurrency exchange FTX, which had just filed for bankruptcy on that same day.
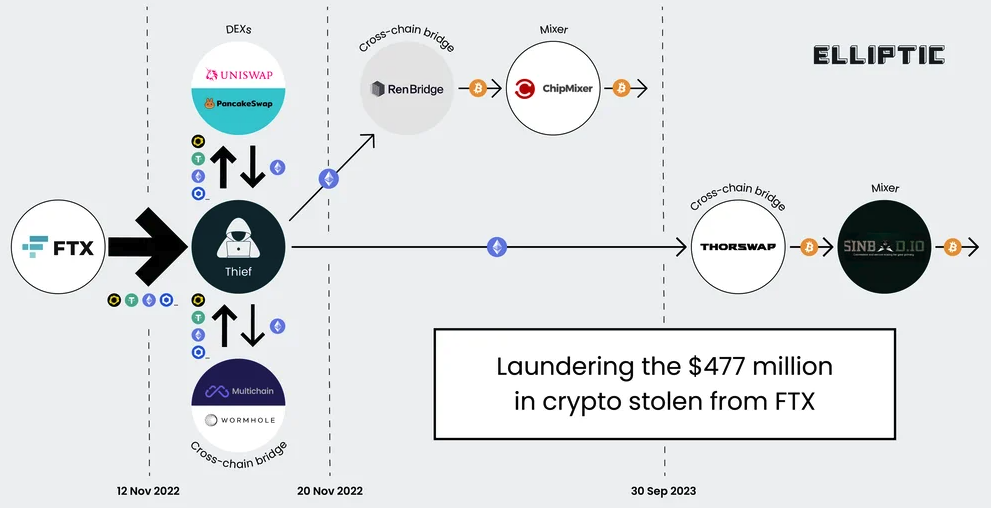
A graphic illustrating the flow of more than $400 million in cryptocurrencies stolen from FTX on Nov. 11-12, 2022. Image: Elliptic.co.
An indictment unsealed this week and first reported on by Ars Technica alleges that Chicago man Robert Powell, a.k.a. “R,” “R$” and “ElSwapo1,” was the ringleader of a SIM-swapping group called the “Powell SIM Swapping Crew.” Colorado resident Emily “Em” Hernandez allegedly helped the group gain access to victim devices in service of SIM-swapping attacks between March 2021 and April 2023. Indiana resident Carter Rohn, a.k.a. “Carti,” and “Punslayer,” allegedly assisted in compromising devices.
In a SIM-swapping attack, the crooks transfer the target’s phone number to a device they control, allowing them to intercept any text messages or phone calls sent to the victim, including one-time passcodes for authentication or password reset links sent via SMS.
The indictment states that the perpetrators in this heist stole the $400 million in cryptocurrencies on Nov. 11, 2022 after they SIM-swapped an AT&T customer by impersonating them at a retail store using a fake ID. However, the document refers to the victim in this case only by the name “Victim 1.”
Wired’s Andy Greenberg recently wrote about FTX’s all-night race to stop a $1 billion crypto heist that occurred on the evening of November 11:
“FTX’s staff had already endured one of the worst days in the company’s short life. What had recently been one of the world’s top cryptocurrency exchanges, valued at $32 billion only 10 months earlier, had just declared bankruptcy. Executives had, after an extended struggle, persuaded the company’s CEO, Sam Bankman-Fried, to hand over the reins to John Ray III, a new chief executive now tasked with shepherding the company through a nightmarish thicket of debts, many of which it seemed to have no means to pay.”
“FTX had, it seemed, hit rock bottom. Until someone—a thief or thieves who have yet to be identified—chose that particular moment to make things far worse. That Friday evening, exhausted FTX staffers began to see mysterious outflows of the company’s cryptocurrency, publicly captured on the Etherscan website that tracks the Ethereum blockchain, representing hundreds of millions of dollars worth of crypto being stolen in real time.”
The indictment says the $400 million was stolen over several hours between November 11 and 12, 2022. Tom Robinson, co-founder of the blockchain intelligence firm Elliptic, said the attackers in the FTX heist began to drain FTX wallets on the evening of Nov. 11, 2022 local time, and continuing until the 12th of November.
Robinson said Elliptic is not aware of any other crypto heists of that magnitude occurring on that date.
“We put the value of the cryptoassets stolen at $477 million,” Robinson said. “The FTX administrators have reported overall losses due to “unauthorized third-party transfers” of $413 million – the discrepancy is likely due to subsequent seizure and return of some of the stolen assets. Either way, it’s certainly over $400 million, and we are not aware of any other thefts from crypto exchanges on this scale, on this date.”
The SIM-swappers allegedly responsible for the $400 million crypto theft are all U.S. residents. But there are some indications they had help from organized cybercriminals based in Russia. In October 2023, Elliptic released a report that found the money stolen from FTX had been laundered through exchanges with ties to criminal groups based in Russia.
“A Russia-linked actor seems a stronger possibility,” Elliptic wrote. “Of the stolen assets that can be traced through ChipMixer, significant amounts are combined with funds from Russia-linked criminal groups, including ransomware gangs and darknet markets, before being sent to exchanges. This points to the involvement of a broker or other intermediary with a nexus in Russia.”
Nick Bax, director of analytics at the cryptocurrency wallet recovery firm Unciphered, said the flow of stolen FTX funds looks more like what his team has seen from groups based in Eastern Europe and Russian than anything they’ve witnessed from US-based SIM-swappers.
“I was a bit surprised by this development but it seems to be consistent with reports from CISA [the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency] and others that “Scattered Spider” has worked with [ransomware] groups like ALPHV/BlackCat,” Bax said.
CISA’s alert on Scattered Spider says they are a cybercriminal group that targets large companies and their contracted information technology (IT) help desks.
“Scattered Spider threat actors, per trusted third parties, have typically engaged in data theft for extortion and have also been known to utilize BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware alongside their usual TTPs,” CISA said, referring to the group’s signature “Tactics, Techniques an Procedures.”
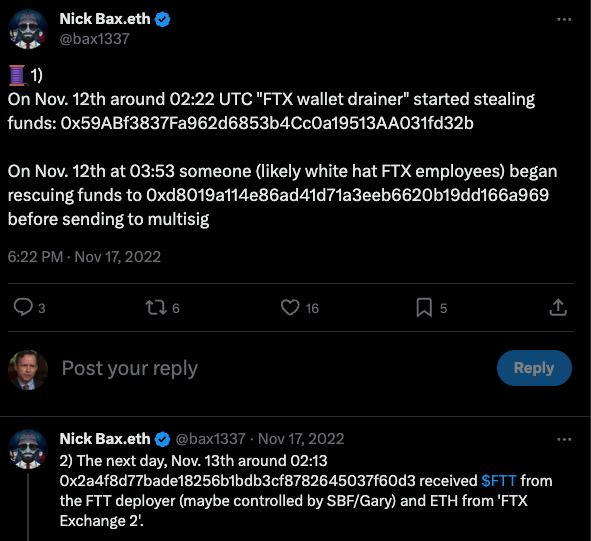
Nick Bax, posting on Twitter/X in Nov 2022 about his research on the $400 million FTX heist.
Earlier this week, KrebsOnSecurity published a story noting that a Florida man recently charged with being part of a SIM-swapping conspiracy is thought to be a key member of Scattered Spider, a hacking group also known as 0ktapus. That group has been blamed for a string of cyber intrusions at major U.S. technology companies during the summer of 2022.
Financial claims involving FTX’s bankruptcy proceedings are being handled by the financial and risk consulting giant Kroll. In August 2023, Kroll suffered its own breach after a Kroll employee was SIM-swapped. According to Kroll, the thieves stole user information for multiple cryptocurrency platforms that rely on Kroll services to handle bankruptcy proceedings.
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment for this story from Kroll, the FBI, the prosecuting attorneys, and Sullivan & Cromwell, the law firm handling the FTX bankruptcy. This story will be updated in the event any of them respond.
Attorneys for Mr. Powell said they do not know who Victim 1 is in the indictment, as the government hasn’t shared that information yet. Powell’s next court date is a detention hearing on Feb. 2, 2024.
Update, Feb. 3, 12:19 p.m. ET: The FBI declined a request to comment.
Authorities in Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States this week levied financial sanctions against a Russian man accused of stealing data on nearly 10 million customers of the Australian health insurance giant Medibank. 33-year-old Aleksandr Ermakov allegedly stole and leaked the Medibank data while working with one of Russia’s most destructive ransomware groups, but little more is shared about the accused. Here’s a closer look at the activities of Mr. Ermakov’s alleged hacker handles.

Aleksandr Ermakov, 33, of Russia. Image: Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
The allegations against Ermakov mark the first time Australia has sanctioned a cybercriminal. The documents released by the Australian government included multiple photos of Mr. Ermakov, and it was clear they wanted to send a message that this was personal.
It’s not hard to see why. The attackers who broke into Medibank in October 2022 stole 9.7 million records on current and former Medibank customers. When the company refused to pay a $10 million ransom demand, the hackers selectively leaked highly sensitive health records, including those tied to abortions, HIV and alcohol abuse.
The U.S. government says Ermakov and the other actors behind the Medibank hack are believed to be linked to the Russia-backed cybercrime gang REvil.
“REvil was among the most notorious cybercrime gangs in the world until July 2021 when they disappeared. REvil is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation and generally motivated by financial gain,” a statement from the U.S. Department of the Treasury reads. “REvil ransomware has been deployed on approximately 175,000 computers worldwide, with at least $200 million paid in ransom.”
The sanctions say Ermakov went by multiple aliases on Russian cybercrime forums, including GustaveDore, JimJones, and Blade Runner. A search on the handle GustaveDore at the cyber intelligence platform Intel 471 shows this user created a ransomware affiliate program in November 2021 called Sugar (a.k.a. Encoded01), which focused on targeting single computers and end-users instead of corporations.
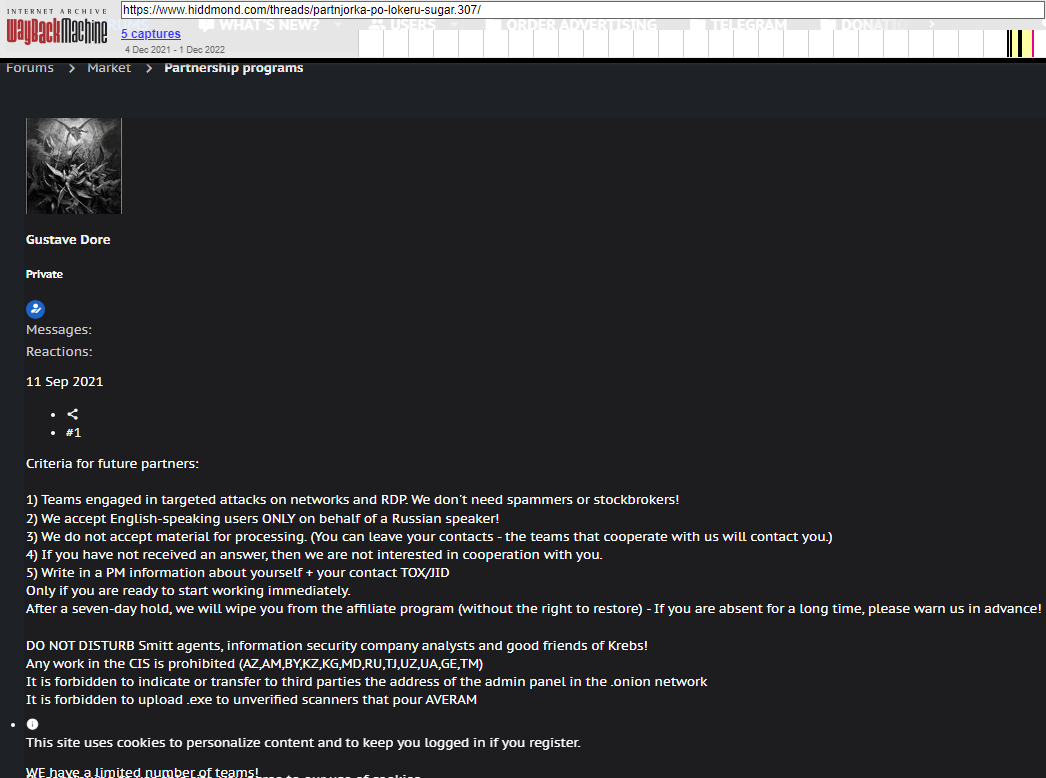
An ad for the ransomware-as-a-service program Sugar posted by GustaveDore warns readers against sharing information with security researchers, law enforcement, or “friends of Krebs.”
In November 2020, Intel 471 analysts concluded that GustaveDore’s alias JimJones “was using and operating several different ransomware strains, including a private undisclosed strain and one developed by the REvil gang.”
In 2020, GustaveDore advertised on several Russian discussion forums that he was part of a Russian technology firm called Shtazi, which could be hired for computer programming, web development, and “reputation management.” Shtazi’s website remains in operation today.

A Google-translated version of Shtazi dot ru. Image: Archive.org.
The third result when one searches for shtazi[.]ru in Google is an Instagram post from a user named Mikhail Borisovich Shefel, who promotes Shtazi’s services as if it were also his business. If this name sounds familiar, it’s because in December 2023 KrebsOnSecurity identified Mr. Shefel as “Rescator,” the cybercriminal identity tied to tens of millions of payment cards that were stolen in 2013 and 2014 from big box retailers Target and Home Depot, among others.
How close was the connection between GustaveDore and Mr. Shefel? The Treasury Department’s sanctions page says Ermakov used the email address ae.ermak@yandex.ru. A search for this email at DomainTools.com shows it was used to register just one domain name: millioner1[.]com. DomainTools further finds that a phone number tied to Mr. Shefel (79856696666) was used to register two domains: millioner[.]pw, and shtazi[.]net.
The December 2023 story here that outed Mr. Shefel as Rescator noted that Shefel recently changed his last name to “Lenin” and had launched a service called Lenin[.]biz that sells physical USSR-era Ruble notes bearing the image of Vladimir Lenin, the founding father of the Soviet Union. The Instagram account for Mr. Shefel includes images of stacked USSR-era Ruble notes, as well as multiple links to Shtazi.
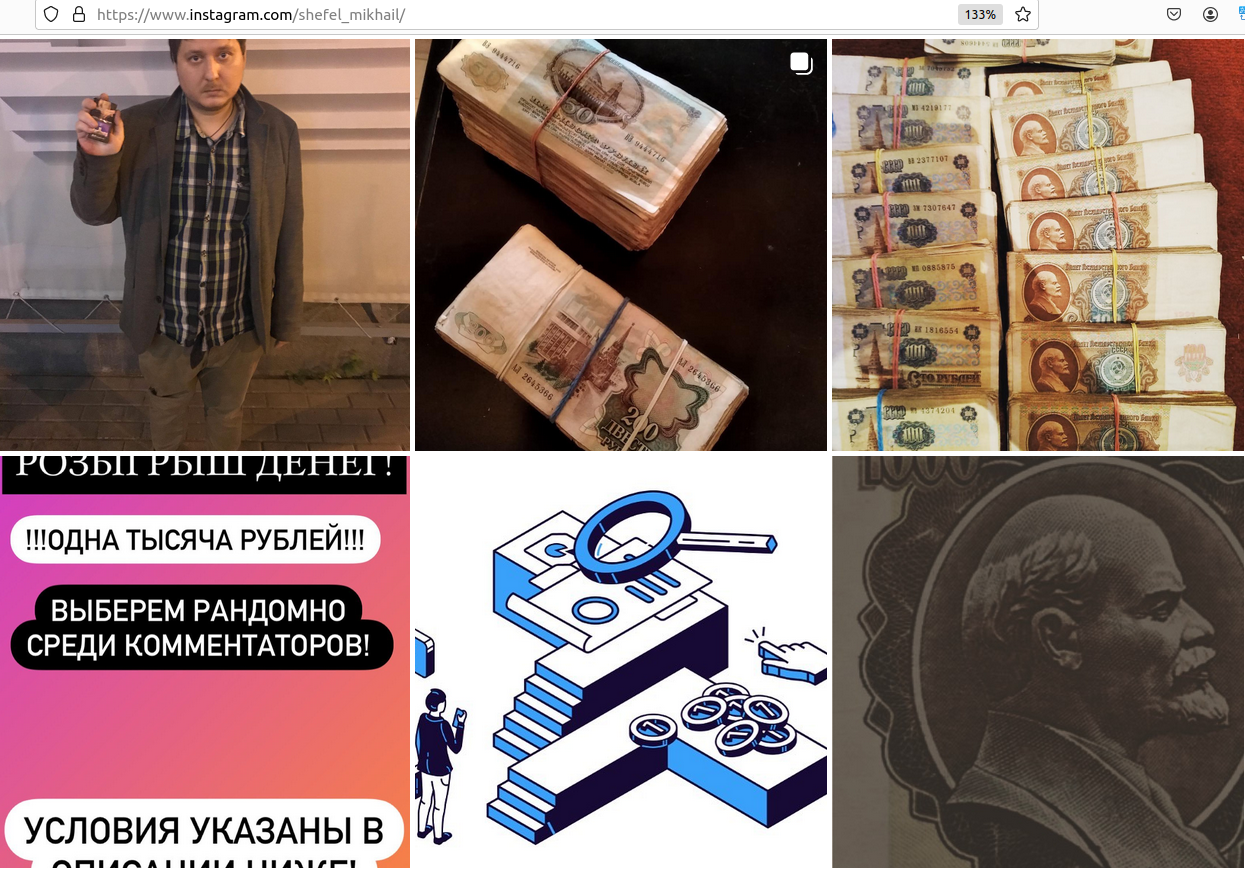
The Instagram account of Mikhail Borisovich Shefel, aka MikeMike aka Rescator.
Intel 471’s research revealed Ermakov was affiliated in some way with REvil because the stolen Medibank data was published on a blog that had one time been controlled by REvil affiliates who carried out attacks and paid an affiliate fee to the gang.
But by the time of the Medibank hack, the REvil group had mostly scattered after a series of high-profile attacks led to the group being disrupted by law enforcement. In November 2021, Europol announced it arrested seven REvil affiliates who collectively made more than $230 million worth of ransom demands since 2019. At the same time, U.S. authorities unsealed two indictments against a pair of accused REvil cybercriminals.
“The posting of Medibank’s data on that blog, however, indicated a connection with that group, although the connection wasn’t clear at the time,” Intel 471 wrote. “This makes sense in retrospect, as Ermakov’s group had also been a REvil affiliate.”
It is easy to dismiss sanctions like these as ineffective, because as long as Mr. Ermakov remains in Russia he has little to fear of arrest. However, his alleged role as an apparent top member of REvil paints a target on him as someone who likely possesses large sums of cryptocurrency, said Patrick Gray, the Australian co-host and founder of the security news podcast Risky Business.
“I’ve seen a few people poo-poohing the sanctions…but the sanctions component is actually less important than the doxing component,” Gray said. “Because this guy’s life just got a lot more complicated. He’s probably going to have to pay some bribes to stay out of trouble. Every single criminal in Russia now knows he is a vulnerable 33 year old with an absolute ton of bitcoin. So this is not a happy time for him.”
Update, Feb. 21, 1:10 p.m. ET: The Russian security firm F.A.C.C.T reports that Ermakov has been arrested in Russia, and charged with violating domestic laws that prohibit the creation, use and distribution of malicious computer programs.
“During the investigation, several defendants were identified who were not only promoting their ransomware, but also developing custom-made malicious software, creating phishing sites for online stores, and driving user traffic to fraudulent schemes popular in Russia and the CIS,” F.A.C.C.T. wrote. “Among those detained was the owner of the nicknames blade_runner, GistaveDore, GustaveDore, JimJones.”
Google continues to struggle with cybercriminals running malicious ads on its search platform to trick people into downloading booby-trapped copies of popular free software applications. The malicious ads, which appear above organic search results and often precede links to legitimate sources of the same software, can make searching for software on Google a dicey affair.
Google says keeping users safe is a top priority, and that the company has a team of thousands working around the clock to create and enforce their abuse policies. And by most accounts, the threat from bad ads leading to backdoored software has subsided significantly compared to a year ago.
But cybercrooks are constantly figuring out ingenious ways to fly beneath Google’s anti-abuse radar, and new examples of bad ads leading to malware are still too common.
For example, a Google search earlier this week for the free graphic design program FreeCAD produced the following result, which shows that a “Sponsored” ad at the top of the search results is advertising the software available from freecad-us[.]org. Although this website claims to be the official FreeCAD website, that honor belongs to the result directly below — the legitimate freecad.org.
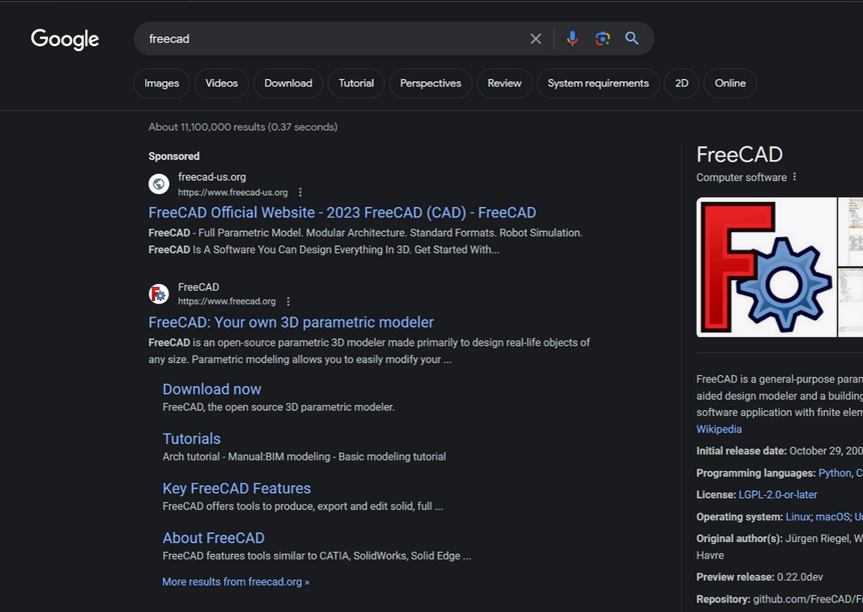
How do we know freecad-us[.]org is malicious? A review at DomainTools.com show this domain is the newest (registered Jan. 19, 2024) of more than 200 domains at the Internet address 93.190.143[.]252 that are confusingly similar to popular software titles, including dashlane-project[.]com, filezillasoft[.]com, keepermanager[.]com, and libreofficeproject[.]com.
Some of the domains at this Netherlands host appear to be little more than software review websites that steal content from established information sources in the IT world, including Gartner, PCWorld, Slashdot and TechRadar.
Other domains at 93.190.143[.]252 do serve actual software downloads, but none of them are likely to be malicious if one visits the sites through direct navigation. If one visits openai-project[.]org and downloads a copy of the popular Windows desktop management application Rainmeter, for example, the file that is downloaded has the same exact file signature as the real Rainmeter installer available from rainmeter.net.
But this is only a ruse, says Tom Hegel, principal threat researcher at the security firm Sentinel One. Hegel has been tracking these malicious domains for more than a year, and he said the seemingly benign software download sites will periodically turn evil, swapping out legitimate copies of popular software titles with backdoored versions that will allow cybercriminals to remotely commander the systems.
“They’re using automation to pull in fake content, and they’re rotating in and out of hosting malware,” Hegel said, noting that the malicious downloads may only be offered to visitors who come from specific geographic locations, like the United States. “In the malicious ad campaigns we’ve seen tied to this group, they would wait until the domains gain legitimacy on the search engines, and then flip the page for a day or so and then flip back.”
In February 2023, Hegel co-authored a report on this same network, which Sentinel One has dubbed MalVirt (a play on “malvertising”). They concluded that the surge in malicious ads spoofing various software products was directly responsible for a surge in malware infections from infostealer trojans like IcedID, Redline Stealer, Formbook and AuroraStealer.
Hegel noted that the spike in malicious software-themed ads came not long after Microsoft started blocking by default Office macros in documents downloaded from the Internet. He said the volume of the current malicious ad campaigns from this group appears to be relatively low compared to a year ago.
“It appears to be same campaign continuing,” Hegel said. “Last January, every Google search for ‘Autocad’ led to something bad. Now, it’s like they’re paying Google to get one out of every dozen of searches. My guess it’s still continuing because of the up-and-down [of the] domains hosting malware and then looking legitimate.”
Several of the websites at this Netherlands host (93.190.143[.]252) are currently blocked by Google’s Safebrowsing technology, and labeled with a conspicuous red warning saying the website will try to foist malware on visitors who ignore the warning and continue.
But it remains a mystery why Google has not similarly blocked more than 240+ other domains at this same host, or else removed them from its search index entirely. Especially considering there is nothing else but these domains hosted at that Netherlands IP address, and because they have all remained at that address for the past year.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, Google said maintaining a safe ads ecosystem and keeping malware off of its platforms is a priority across Google.
“Bad actors often employ sophisticated measures to conceal their identities and evade our policies and enforcement, sometimes showing Google one thing and users something else,” Google said in a written statement. “We’ve reviewed the ads in question, removed those that violated our policies, and suspended the associated accounts. We’ll continue to monitor and apply our protections.”
Google says it removed 5.2 billion ads in 2022, and restricted more than 4.3 billion ads and suspended over 6.7 million advertiser accounts. The company’s latest ad safety report says Google in 2022 blocked or removed 1.36 billion advertisements for violating its abuse policies.
Some of the domains referenced in this story were included in Sentinel One’s February 2023 report, but dozens more have been added since, such as those spoofing the official download sites for Corel Draw, Github Desktop, Roboform and Teamviewer.
This October 2023 report on the FreeCAD user forum came from a user who reported downloading a copy of the software from freecadsoft[.]com after seeing the site promoted at the top of a Google search result for “freecad.” Almost a month later, another FreeCAD user reported getting stung by the same scam.
“This got me,” FreeCAD forum user “Matterform” wrote on Nov. 19, 2023. “Please leave a report with Google so it can flag it. They paid Google for sponsored posts.”
Sentinel One’s report didn’t delve into the “who” behind this ongoing MalVirt campaign, and there are precious few clues that point to attribution. All of the domains in question were registered through webnic.cc, and several of them display a placeholder page saying the site is ready for content. Viewing the HTML source of these placeholder pages shows many of the hidden comments in the code are in Cyrillic.
Trying to track the crooks using Google’s Ad Transparency tools didn’t lead far. The ad transparency record for the malicious ad featuring freecad-us[.]org (in the screenshot above) shows that the advertising account used to pay for the ad has only run one previous ad through Google search: It advertised a wedding photography website in New Zealand.
The apparent owner of that photography website did not respond to requests for comment, but it’s also likely his Google advertising account was hacked and used to run these malicious ads.