On Jan. 9, 2024, U.S. authorities arrested a 19-year-old Florida man charged with wire fraud, aggravated identity theft, and conspiring with others to use SIM-swapping to steal cryptocurrency. Sources close to the investigation tell KrebsOnSecurity the accused was a key member of a criminal hacking group blamed for a string of cyber intrusions at major U.S. technology companies during the summer of 2022.
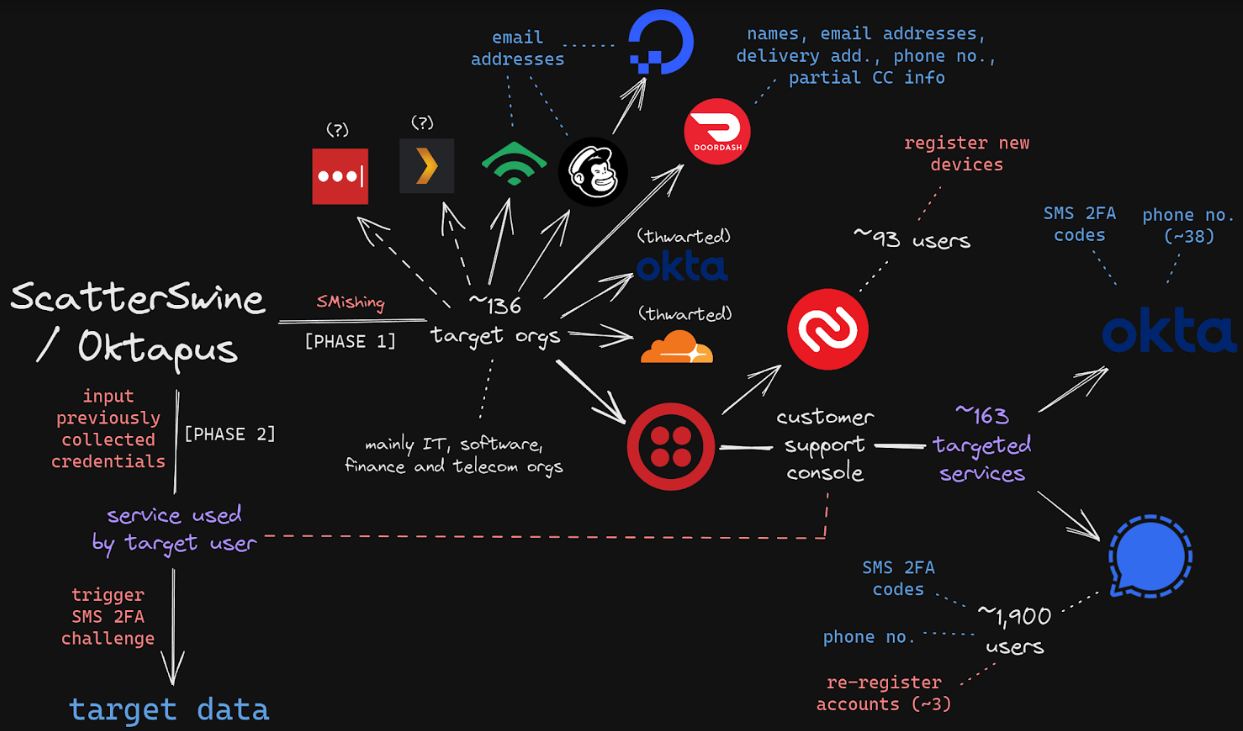
A graphic depicting how 0ktapus leveraged one victim to attack another. Image credit: Amitai Cohen of Wiz.
Prosecutors say Noah Michael Urban of Palm Coast, Fla., stole at least $800,000 from at least five victims between August 2022 and March 2023. In each attack, the victims saw their email and financial accounts compromised after suffering an unauthorized SIM-swap, wherein attackers transferred each victim’s mobile phone number to a new device that they controlled.
The government says Urban went by the aliases “Sosa” and “King Bob,” among others. Multiple trusted sources told KrebsOnSecurity that Sosa/King Bob was a core member of a hacking group behind the 2022 breach at Twilio, a company that provides services for making and receiving text messages and phone calls. Twilio disclosed in Aug. 2022 that an intrusion had exposed a “limited number” of Twilio customer accounts through a sophisticated social engineering attack designed to steal employee credentials.
Shortly after that disclosure, the security firm Group-IB published a report linking the attackers behind the Twilio intrusion to separate breaches at more than 130 organizations, including LastPass, DoorDash, Mailchimp, and Plex. Multiple security firms soon assigned the hacking group the nickname “Scattered Spider.”
Group-IB dubbed the gang by a different name — 0ktapus — which was a nod to how the criminal group phished employees for credentials. The missives asked users to click a link and log in at a phishing page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page. Those who submitted credentials were then prompted to provide the one-time password needed for multi-factor authentication.

A booking photo of Noah Michael Urban released by the Volusia County Sheriff.
0ktapus used newly-registered domains that often included the name of the targeted company, and sent text messages urging employees to click on links to these domains to view information about a pending change in their work schedule. The phishing sites used a Telegram instant message bot to forward any submitted credentials in real-time, allowing the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
0ktapus often leveraged information or access gained in one breach to perpetrate another. As documented by Group-IB, the group pivoted from its access to Twilio to attack at least 163 of its customers. Among those was the encrypted messaging app Signal, which said the breach could have let attackers re-register the phone number on another device for about 1,900 users.
Also in August 2022, several employees at email delivery firm Mailchimp provided their remote access credentials to this phishing group. According to an Aug. 12 blog post, the attackers used their access to Mailchimp employee accounts to steal data from 214 customers involved in cryptocurrency and finance.
On August 25, 2022, the password manager service LastPass disclosed a breach in which attackers stole some source code and proprietary LastPass technical information, and weeks later LastPass said an investigation revealed no customer data or password vaults were accessed.
However, on November 30, 2022 LastPass disclosed a far more serious breach that the company said leveraged data stolen in the August breach. LastPass said criminal hackers had stolen encrypted copies of some password vaults, as well as other personal information.
In February 2023, LastPass disclosed that the intrusion involved a highly complex, targeted attack against a DevOps engineer who was one of only four LastPass employees with access to the corporate vault. In that incident, the attackers exploited a security vulnerability in a Plex media server that the employee was running on his home network, and succeeded in installing malicious software that stole passwords and other authentication credentials. The vulnerability exploited by the intruders was patched back in 2020, but the employee never updated his Plex software.
As it happens, Plex announced its own data breach one day before LastPass disclosed its initial August intrusion. On August 24, 2022, Plex’s security team urged users to reset their passwords, saying an intruder had accessed customer emails, usernames and encrypted passwords.
A review of thousands of messages that Sosa and King Bob posted to several public forums and Discord servers over the past two years shows that the person behind these identities was mainly focused on two things: Sim-swapping, and trading in stolen, unreleased rap music recordings from popular artists.
Indeed, those messages show Sosa/King Bob was obsessed with finding new “grails,” the slang term used in some cybercrime discussion channels to describe recordings from popular artists that have never been officially released. It stands to reason that King Bob was SIM-swapping important people in the music industry to obtain these files, although there is little to support this conclusion from the public chat records available.
“I got the most music in the com,” King Bob bragged in a Discord server in November 2022. “I got thousands of grails.”
King Bob’s chats show he was particularly enamored of stealing the unreleased works of his favorite artists — Lil Uzi Vert, Playboi Carti, and Juice Wrld. When another Discord user asked if he has Eminem grails, King Bob said he was unsure.
“I have two folders,” King Bob explained. “One with Uzi, Carti, Juicewrld. And then I have ‘every other artist.’ Every other artist is unorganized as fuck and has thousands of random shit.”
King Bob’s posts on Discord show he quickly became a celebrity on Leaked[.]cx, one of most active forums for trading, buying and selling unreleased music from popular artists. The more grails that users share with the Leaked[.]cx community, the more their status and access on the forum grows.
The last cache of Leaked dot cx indexed by the archive.org on Jan. 11, 2024.
And King Bob shared a large number of his purloined tunes with this community. Still others he tried to sell. It’s unclear how many of those sales were ever consummated, but it is not unusual for a prized grail to sell for anywhere from $5,000 to $20,000.
In mid-January 2024, several Leaked[.]cx regulars began complaining that they hadn’t seen King Bob in a while and were really missing his grails. On or around Jan. 11, the same day the Justice Department unsealed the indictment against Urban, Leaked[.]cx started blocking people who were trying to visit the site from the United States.
Days later, frustrated Leaked[.]cx users speculated about what could be the cause of the blockage.
“Probs blocked as part of king bob investigation i think?,” wrote the user “Plsdontarrest.” “Doubt he only hacked US artists/ppl which is why it’s happening in multiple countries.”
On Sept. 21, 2022, KrebsOnSecurity told the story of a “Foreshadow,” the nickname chosen by a Florida teenager who was working for a SIM-swapping crew when he was abducted, beaten and held for a $200,000 ransom. A rival SIM-swapping group claimed that Foreshadow and his associates had robbed them of their fair share of the profits from a recent SIM-swap.
In a video released by his abductors on Telegram, a bloodied, battered Foreshadow was made to say they would kill him unless the ransom was paid.
As I wrote in that story, Foreshadow appears to have served as a “holder” — a term used to describe a low-level member of any SIM-swapping group who agrees to carry out the riskiest and least rewarding role of the crime: Physically keeping and managing the various mobile devices and SIM cards that are used in SIM-swapping scams.
KrebsOnSecurity has since learned that Foreshadow was a holder for a particularly active SIM-swapper who went by “Elijah,” which was another nickname that prosecutors say Urban used.

Shortly after Foreshadow’s hostage video began circulating on Telegram and Discord, multiple known actors in the SIM-swapping space told everyone in the channels to delete any previous messages with Foreshadow, claiming he was fully cooperating with the FBI.
This was not the first time Sosa and his crew were hit with violent attacks from rival SIM-swapping groups. In early 2022, a video surfaced on a popular cybercrime channel purporting to show attackers hurling a brick through a window at an address that matches the spacious and upscale home of Urban’s parents in Sanford, Fl.
“Brickings” are among the “violence-as-a-service” offerings broadly available on many cybercrime channels. SIM-swapping and adjacent cybercrime channels are replete with job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
A number of these classified ads are in service of performing brickings, where someone is hired to visit a specific address and toss a brick through the target’s window. Other typical IRL job offers involve tire slashings and even drive-by shootings.
Sosa was known to be a top member of the broader cybercriminal community online known as “The Com,” wherein hackers boast loudly about high-profile exploits and hacks that almost invariably begin with social engineering — tricking people over the phone, email or SMS into giving away credentials that allow remote access to corporate internal networks.
Sosa also was active in a particularly destructive group of accomplished criminal SIM-swappers known as “Star Fraud.” Cyberscoop’s AJ Vicens reported last year that individuals within Star Fraud were likely involved in the high-profile Caesars Entertainment an MGM Resorts extortion attacks.
“ALPHV, an established ransomware-as-a-service operation thought to be based in Russia and linked to attacks on dozens of entities, claimed responsibility for Caesars and MGM attacks in a note posted to its website earlier this month,” Vicens wrote. “Experts had said the attacks were the work of a group tracked variously as UNC 3944 or Scattered Spider, which has been described as an affiliate working with ALPHV made up of people in the United States and Britain who excel at social engineering.”
In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity published data taken from the Telegram channels for Star Fraud and two other SIM-swapping groups showing these crooks focused on SIM-swapping T-Mobile customers, and that they collectively claimed access to T-Mobile on 100 separate occasions over a 7-month period in 2022.
The SIM-swapping groups were able to switch targeted phone numbers to another device on demand because they constantly phished T-Mobile employees into giving up credentials to employee-only tools. In each of those cases the goal was the same: Phish T-Mobile employees for access to internal company tools, and then convert that access into a cybercrime service that could be hired to divert any T-Mobile user’s text messages and phone calls to another device.
Allison Nixon, chief research officer at the New York cybersecurity consultancy Unit 221B, said the increasing brazenness of many Com members is a function of how long it has taken federal authorities to go after guys like Sosa.
“These incidents show what happens when it takes too long for cybercriminals to get arrested,” Nixon said. “If governments fail to prioritize this source of threat, violence originating from the Internet will affect regular people.”
The Daytona Beach News-Journal reports that Urban was arrested Jan. 9 and his trial is scheduled to begin in the trial term starting March 4 in Jacksonville. The publication said the judge overseeing Urban’s case denied bail because the defendant was a strong flight risk.
At Urban’s arraignment, it emerged that he had no fixed address and had been using an alias to stay at an Airbnb. The judge reportedly said that when a search warrant was executed at Urban’s residence, the defendant was downloading programs to delete computer files.
What’s more, the judge explained, despite telling authorities in May that he would not have any more contact with his co-conspirators and would not engage in cryptocurrency transactions, he did so anyway.
Urban entered a plea of not guilty. Urban’s court-appointed attorney said her client would have no comment at this time.
Prosecutors charged Urban with eight counts of wire fraud, one count of conspiracy to commit wire fraud, and five counts of aggravated identity theft. According to the government, if convicted Urban faces up to 20 years in federal prison on each wire fraud charge. He also faces a minimum mandatory penalty of two years in prison for the aggravated identity offenses, which will run consecutive to any other prison sentence imposed.
Google continues to struggle with cybercriminals running malicious ads on its search platform to trick people into downloading booby-trapped copies of popular free software applications. The malicious ads, which appear above organic search results and often precede links to legitimate sources of the same software, can make searching for software on Google a dicey affair.
Google says keeping users safe is a top priority, and that the company has a team of thousands working around the clock to create and enforce their abuse policies. And by most accounts, the threat from bad ads leading to backdoored software has subsided significantly compared to a year ago.
But cybercrooks are constantly figuring out ingenious ways to fly beneath Google’s anti-abuse radar, and new examples of bad ads leading to malware are still too common.
For example, a Google search earlier this week for the free graphic design program FreeCAD produced the following result, which shows that a “Sponsored” ad at the top of the search results is advertising the software available from freecad-us[.]org. Although this website claims to be the official FreeCAD website, that honor belongs to the result directly below — the legitimate freecad.org.
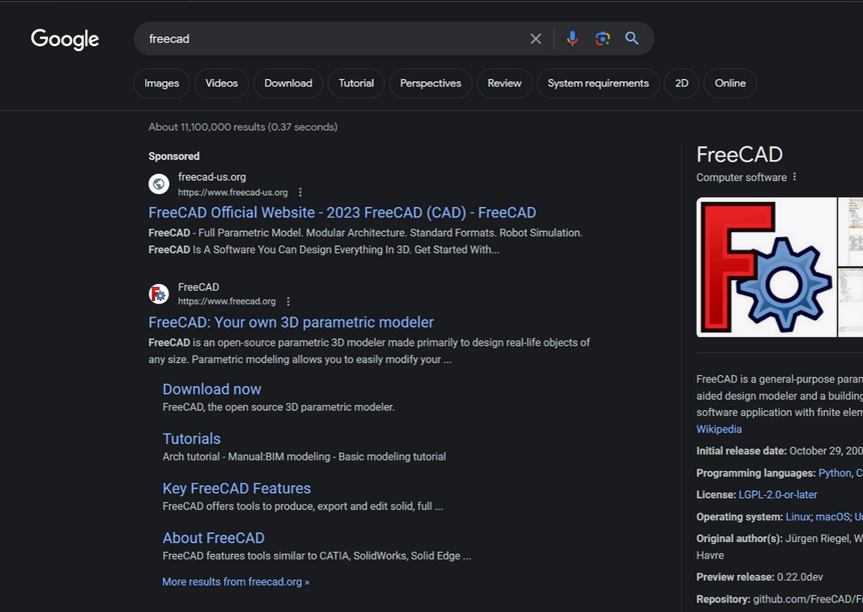
How do we know freecad-us[.]org is malicious? A review at DomainTools.com show this domain is the newest (registered Jan. 19, 2024) of more than 200 domains at the Internet address 93.190.143[.]252 that are confusingly similar to popular software titles, including dashlane-project[.]com, filezillasoft[.]com, keepermanager[.]com, and libreofficeproject[.]com.
Some of the domains at this Netherlands host appear to be little more than software review websites that steal content from established information sources in the IT world, including Gartner, PCWorld, Slashdot and TechRadar.
Other domains at 93.190.143[.]252 do serve actual software downloads, but none of them are likely to be malicious if one visits the sites through direct navigation. If one visits openai-project[.]org and downloads a copy of the popular Windows desktop management application Rainmeter, for example, the file that is downloaded has the same exact file signature as the real Rainmeter installer available from rainmeter.net.
But this is only a ruse, says Tom Hegel, principal threat researcher at the security firm Sentinel One. Hegel has been tracking these malicious domains for more than a year, and he said the seemingly benign software download sites will periodically turn evil, swapping out legitimate copies of popular software titles with backdoored versions that will allow cybercriminals to remotely commander the systems.
“They’re using automation to pull in fake content, and they’re rotating in and out of hosting malware,” Hegel said, noting that the malicious downloads may only be offered to visitors who come from specific geographic locations, like the United States. “In the malicious ad campaigns we’ve seen tied to this group, they would wait until the domains gain legitimacy on the search engines, and then flip the page for a day or so and then flip back.”
In February 2023, Hegel co-authored a report on this same network, which Sentinel One has dubbed MalVirt (a play on “malvertising”). They concluded that the surge in malicious ads spoofing various software products was directly responsible for a surge in malware infections from infostealer trojans like IcedID, Redline Stealer, Formbook and AuroraStealer.
Hegel noted that the spike in malicious software-themed ads came not long after Microsoft started blocking by default Office macros in documents downloaded from the Internet. He said the volume of the current malicious ad campaigns from this group appears to be relatively low compared to a year ago.
“It appears to be same campaign continuing,” Hegel said. “Last January, every Google search for ‘Autocad’ led to something bad. Now, it’s like they’re paying Google to get one out of every dozen of searches. My guess it’s still continuing because of the up-and-down [of the] domains hosting malware and then looking legitimate.”
Several of the websites at this Netherlands host (93.190.143[.]252) are currently blocked by Google’s Safebrowsing technology, and labeled with a conspicuous red warning saying the website will try to foist malware on visitors who ignore the warning and continue.
But it remains a mystery why Google has not similarly blocked more than 240+ other domains at this same host, or else removed them from its search index entirely. Especially considering there is nothing else but these domains hosted at that Netherlands IP address, and because they have all remained at that address for the past year.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, Google said maintaining a safe ads ecosystem and keeping malware off of its platforms is a priority across Google.
“Bad actors often employ sophisticated measures to conceal their identities and evade our policies and enforcement, sometimes showing Google one thing and users something else,” Google said in a written statement. “We’ve reviewed the ads in question, removed those that violated our policies, and suspended the associated accounts. We’ll continue to monitor and apply our protections.”
Google says it removed 5.2 billion ads in 2022, and restricted more than 4.3 billion ads and suspended over 6.7 million advertiser accounts. The company’s latest ad safety report says Google in 2022 blocked or removed 1.36 billion advertisements for violating its abuse policies.
Some of the domains referenced in this story were included in Sentinel One’s February 2023 report, but dozens more have been added since, such as those spoofing the official download sites for Corel Draw, Github Desktop, Roboform and Teamviewer.
This October 2023 report on the FreeCAD user forum came from a user who reported downloading a copy of the software from freecadsoft[.]com after seeing the site promoted at the top of a Google search result for “freecad.” Almost a month later, another FreeCAD user reported getting stung by the same scam.
“This got me,” FreeCAD forum user “Matterform” wrote on Nov. 19, 2023. “Please leave a report with Google so it can flag it. They paid Google for sponsored posts.”
Sentinel One’s report didn’t delve into the “who” behind this ongoing MalVirt campaign, and there are precious few clues that point to attribution. All of the domains in question were registered through webnic.cc, and several of them display a placeholder page saying the site is ready for content. Viewing the HTML source of these placeholder pages shows many of the hidden comments in the code are in Cyrillic.
Trying to track the crooks using Google’s Ad Transparency tools didn’t lead far. The ad transparency record for the malicious ad featuring freecad-us[.]org (in the screenshot above) shows that the advertising account used to pay for the ad has only run one previous ad through Google search: It advertised a wedding photography website in New Zealand.
The apparent owner of that photography website did not respond to requests for comment, but it’s also likely his Google advertising account was hacked and used to run these malicious ads.
A Canadian man who says he’s been falsely charged with orchestrating a complex e-commerce scam is seeking to clear his name. His case appears to involve “triangulation fraud,” which occurs when a consumer purchases something online — from a seller on Amazon or eBay, for example — but the seller doesn’t actually own the item for sale. Instead, the seller purchases the item from an online retailer using stolen payment card data. In this scam, the unwitting buyer pays the scammer and receives what they ordered, and very often the only party left to dispute the transaction is the owner of the stolen payment card.
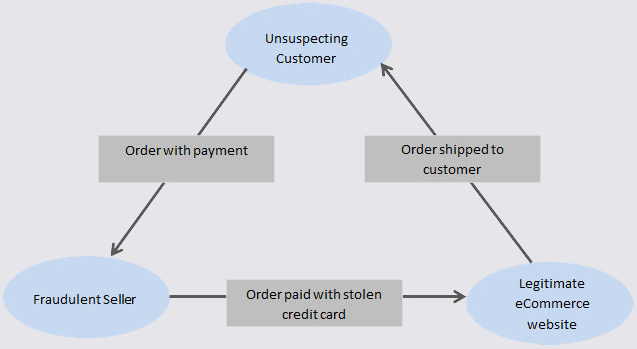
Triangulation fraud. Image: eBay Enterprise.
Timothy Barker, 56, was until recently a Band Manager at Duncan’s First Nation, a First Nation in northwestern Alberta, Canada. A Band Manager is responsible for overseeing the delivery of all Band programs, including community health services, education, housing, social assistance, and administration.
Barker told KrebsOnSecurity that during the week of March 31, 2023 he and the director of the Band’s daycare program discussed the need to purchase items for the community before the program’s budget expired for the year.
“There was a rush to purchase items on the Fiscal Year 2023 timeline as the year ended on March 31,” Barker recalled.
Barker said he bought seven “Step2 All Around Playtime Patio with Canopy” sets from a seller on Amazon.ca, using his payment card on file to pay nearly $2,000 for the items.
On the morning of April 7, Barker’s Facebook account received several nasty messages from an Ontario woman he’d never met. She demanded to know why he’d hacked her Walmart account and used it to buy things that were being shipped to his residence. Barker shared a follow-up message from the woman, who later apologized for losing her temper.
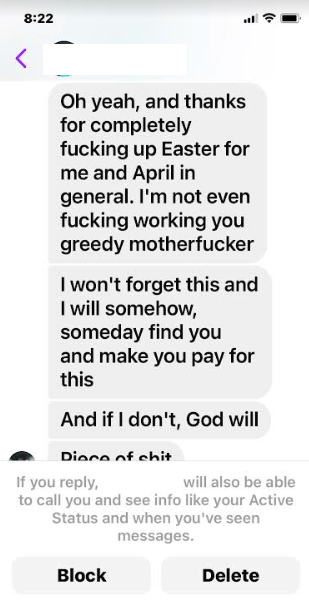
One of several messages from the Ontario woman whose Walmart account was used to purchase the goods that Barker ordered from Amazon.
“If this is not the person who did this to me, I’m sorry, I’m pissed,” the lady from Ontario said. “This order is being delivered April 14th to the address above. If not you, then someone who has the same name. Now I feel foolish.”
On April 12, 2023, before the Amazon purchases had even arrived at his home, Barker received a call from an investigator with the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP), who said Barker urgently needed to come down to the local RCMP office for an interview related to “an investigation.” Barker said the officer wouldn’t elaborate at the time on the nature of the investigation, and that he told the officer he was in Halifax for several days but could meet after his return home.
According to Barker, the investigator visited his home anyway the following day and began questioning his wife, asking about his whereabouts, his work, and when he might return home.
On April 14, six boxes arrived to partially fulfill his Amazon order; another box was delayed, and the Amazon.ca seller he’d purchased from said the remaining box was expected to ship the following week. Barker said he was confused because all six boxes came from Walmart instead of Amazon, and the shipping labels had his name and address on them but carried a contact phone number in Mexico.
Three days later, the investigator called again, demanding he submit to an interview.
“He then asked where my wife was and what her name is,” Barker said. “He wanted to know her itinerary for the day. I am now alarmed and frightened — this doesn’t feel right.”
Barker said he inquired with a local attorney about a consultation, but that the RCMP investigator showed up at his house before he could speak to the lawyer. The investigator began taking pictures of the boxes from his Amazon order.
“The [investigator] derisively asked why would anyone order so many play sets?” Barker said. “I started to give the very logical answer that we are helping families improve their children’s home life and learning for toddlers when he cut me off and gave the little speech about giving a statement after my arrest. He finally told me that he believes that I used someone’s credit card in Ontario to purchase the Walmart products.”
Eager to clear his name, Barker said he shared with the police copies of his credit card bills and purchase history at Amazon. But on April 21, the investigator called again to say he was coming to arrest Barker for theft.
“He said that if I was home at five o’clock then he would serve the papers at the house and it would go easy and I wouldn’t have to go to the station,” Barker recalled. “If I wasn’t home, then he would send a search team to locate me and drag me to the station. He said he would kick the door down if I didn’t answer my phone. He said he had every right to break our door down.”
Barker said he briefly conferred with an attorney about how to handle the arrest. Later that evening, the RCMP arrived with five squad cars and six officers.
“I asked if handcuffs were necessary – there is no danger of violence,” Barker said. “I was going to cooperate. His response was to turn me around and cuff me. He walked me outside and stood me beside the car for a full 4 or 5 minutes in full view of all the neighbors.”

Barker believes he and the Ontario woman are both victims of triangulation fraud, and that someone likely hacked the Ontario woman’s Walmart account and added his name and address as a recipient.
But he says he has since lost his job as a result of the arrest, and now he can’t find new employment because he has a criminal record. Barker’s former employer — Duncan’s First Nation — did not respond to requests for comment.
“In Canada, a criminal record is not a record of conviction, it’s a record of charges and that’s why I can’t work now,” Barker said. “Potential employers never find out what the nature of it is, they just find out that I have a criminal arrest record.”
Barker said that right after his arrest, the RCMP called the Ontario woman and told her they’d solved the crime and arrested the perpetrator.
“They even told her my employer had put me on administrative leave,” he said. “Surely, they’re not allowed to do that.”
Contacted by KrebsOnSecurity, the woman whose Walmart account was used to fraudulently purchase the child play sets said she’s not convinced this was a case of triangulation fraud. She declined to elaborate on why she believed this, other than to say the police told her Barker was a bad guy.
“I don’t think triangulation fraud was used in this case,” she said. “My actual Walmart.ca account was hacked and an order was placed on my account, using my credit card. The only thing Mr. Barker did was to order the item to be delivered to his address in Alberta.”
Barker shared with this author all of the documentation he gave to the RCMP, including screenshots of his Amazon.ca account showing that the items in dispute were sold by a seller named “Adavio,” and that the merchant behind this name was based in Turkey.
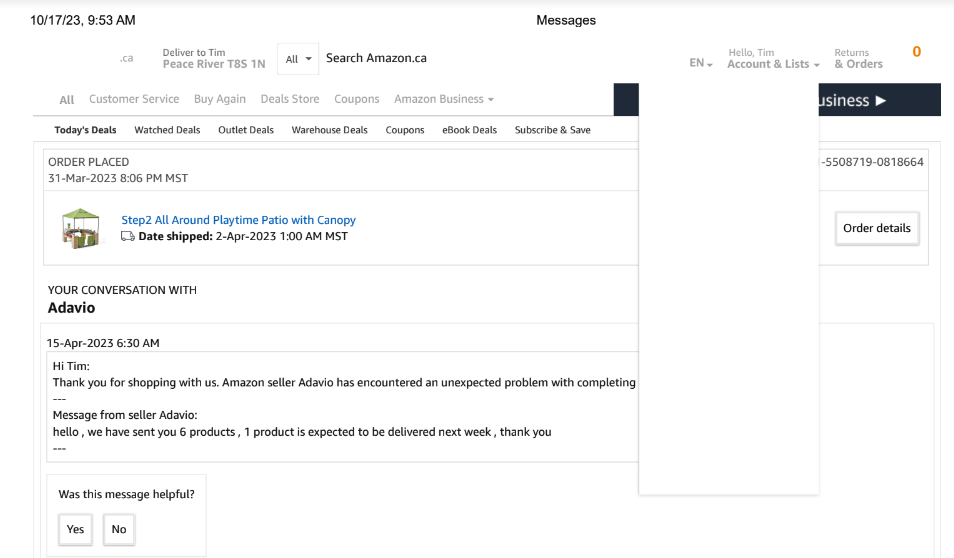
That Adavio account belongs to a young computer engineering student and “SEO expert” based in Adana, Turkey who did not respond to requests for comment.
Amazon.ca said it conducted an investigation and found that Mr. Barker never filed a complaint about the seller or transaction in question. The company noted that Adavio currently has a feedback rating of 4.5 stars out of 5.
“Amazon works hard to provide customers with a great experience and it’s our commitment to go above and beyond to make things right for customers,” Amazon.ca said in a written statement. “If a customer has an issue with an order, they may flag to Amazon through our Customer Service page.”
Barker said when he went to file a complaint with Amazon last year he could no longer find the Adavio account on the website, and that the site didn’t have a category for the type of complaint he wanted to file.
When he first approached KrebsOnSecurity about his plight last summer, Barker said he didn’t want any media attention to derail the chances of having his day in court, and confronting the RCMP investigator with evidence proving that he was being wrongfully prosecuted and maligned.
But a week before his court date arrived at the end of November 2023, prosecutors announced the charges against him would be stayed, meaning they had no immediate plans to prosecute the case further but that the investigation could still be reopened at some point in the future.
The RCMP declined to comment for this story, other than to confirm they had issued a stay of proceedings in the case.
Barker says the stay has left him in legal limbo — denying him the ability to clear his name, while giving the RCMP a free pass for a botched investigation. He says he has considered suing the investigating officer for defamation, but has been told by his attorney that the bar for success in such cases against the government is extremely high.
“I’m a 56-year-old law-abiding citizen, and I haven’t broken any laws,” Barker said, wondering aloud who would be stupid enough to use someone else’s credit card and have the stolen items shipped directly to their home.
“Their putting a stay on the proceedings without giving any evidence or explanation allows them to cover up bad police work,” he said. “It’s all so stupid.”
Triangulation fraud is hardly a new thing. KrebsOnSecurity first wrote about it from an e-commerce vendor’s perspective in 2015, but the scam predates that story by many years and is now a well-understood problem. The Canadian authorities should either let Mr. Barker have his day in court, or drop the charges altogether.