
For many Aussies, identity theft was always something that happened to other people. People on TV, usually. But the recent spate of data breaches at Optus, Medibank and Energy Australia has made many of us pay far more attention than ever to one of the fastest growing crimes in our country.
According to the Department of Home Affairs, 1 in 4 Aussies will be the victim of identity theft over the course of their lives with an annual economic impact of more than $2 billion. And with the financial fallout from the recent data breaches only just starting to be counted, these statistics will no doubt increase dramatically next year.
Identity theft is when a cybercriminal gains access to your personal information to steal money or gain other benefits. Armed with your personal info, they can apply for real identity documents in your name but with another person’s photograph. This enables them to then apply for loans or benefits in your name, sign up for memberships or even apply for credit cards.
And it goes without saying that the financial and emotional fallout from identity theft can be huge. Since the Optus and Medibank hacking stories broke just a few months ago, there has been multiple stories of Aussie families who have had their identities stolen and who are in a world of pain. This Melbourne family who have had over $40,000 stolen from ATM withdrawals alone is just one example.
Your personal information is any piece of information or data that can confirm who you are or how to find you. It may be a single piece of information, or several pieces used together. It’s often referred to as personally identifiable information (PII). So, it includes your name, parents’ name, address, date of birth, phone numbers, email address, usernames/passwords or passphrases, bank account details, school or university attended, location check-ins even RSVPS for events.
Every time you register with a new shopping site or social media platform, you will be asked to share some personally identifiable information. However, what you share may be stolen or even misused – just think about the recent list of Australian companies who had their customers’ private information stolen by hackers. So that’s why you need to ensure you are only sharing your information with trusted online sites and take every possible step to protect your personal information online.
While there are no guarantees in life, there are steps you can take to ensure your online identity is as safe as possible. Here are my top 5 tips:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or 2 Factor Authentication (2FA) is a no-brainer because it makes a hacker’s life a lot harder. In short, it requires the user to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or app. This might be a text, email or even a code generated by an authentication app. So, even if a hacker has your password and username, they still need that final piece of information before they can get their hands on your account!
Now this may take a bit of work to set up but using a unique and complex password on every account is one of the best things you can do to protect your online identity. And here’s the rationale – if you use the same password on all your accounts and your login details are stolen then hackers have access to all the accounts that are accessed with that password. Yikes!!! So, a unique password for each account is a great measure. I love using a password manager to make this process a little easier. Not only do they generate complex passwords, but they remember them too! All you need to do is remember your Master Password which needs to be extremely complex!!!
Updates are most commonly about addressing security weaknesses. And yes, I know they can be a pain but if you ignore them, you are essentially making it easier for hackers to find their way into your life via weak spots. And don’t forget to ensure your security software remains updated too!
I always recommend keeping a backup of all your important info in case something goes wrong. This should include all your photos, key documents and all your personally identifiable information. A hard drive works well but saving to the cloud is also a good option. I once dropped a hard drive and lost treasured family photos, so the cloud is my personal preference.
We all know knowledge is power so investing in top notch security and identity monitoring software will help keep you ahead of threats. McAfee+, McAfee’s new all in one privacy, identity and device protection solution is a fantastic way for Aussies to protect themselves online. It features identity monitoring and a password manager but also an unlimited VPN, a file shredder, protection score and parental controls. And the Rolls Royce version called McAfee+ Advanced, also offers subscribers additional identity protections including access to licensed restoration experts who can help you repair your identity and credit, in case you’re affected by a data breach. It also gives subscribers access to lost wallet protection which help you cancel and replace your ID, credit cards if they are lost or stolen.
Public, unsecured Wi-Fi can make life so much easier when you’re out and about but it’s also a tried and tested way for scammers to access your personal information. Unsecured Wi-Fi is free Wi-Fi that is available in public places such as libraries, cafes, or shopping centres. So, instead of using Wi-Fi, just use the data in your phone plan. Or alternatively invest in a Virtual Private Network (VPN) that cleverly encrypts everything you share on your device.
About 2 months ago, I embarked on a project to clean up my online life. I’m working through the list of sites I have accounts with and am closing those I no longer use, I’m also doing a huge password audit to ensure they are all unique to each site and are super complex, thanks to my password manager. Now, I’m not quite done yet, but things are in better shape than they were. Why not consider doing the same? With the holiday season fast approaching, why not dedicate a little of your poolside time to practicing a little cyber hygiene.
Till next time, keep those identities safe!
Alex
The post The Best Way To Protect Your Online Identity appeared first on McAfee Blog.
It’s all fun and games over the holidays, but is your young gamer safe from the darker side of the action?
The post ‘Tis the season for gaming: Keeping children safe (and parents sane) appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
Millions of people likely just received an email or snail mail notice saying they’re eligible to claim a class action payment in connection with the 2017 megabreach at consumer credit bureau Equifax. Given the high volume of reader inquiries about this, it seemed worth pointing out that while this particular offer is legit (if paltry), scammers are likely to soon capitalize on public attention to the settlement money.

One reader’s copy of their Equifax Breach Settlement letter. They received a check for $6.97.
In 2017, Equifax disclosed a massive, extended data breach that led to the theft of Social Security Numbers, dates of birth, addresses and other personal information on nearly 150 million people. Following a public breach response perhaps best described as a giant dumpster fire, the big-three consumer credit reporting bureau was quickly hit with nearly two dozen class-action lawsuits.
In exchange for resolving all outstanding class action claims against it, Equifax in 2019 agreed to a settlement that includes up to $425 million to help people affected by the breach.
Affected consumers were eligible to apply for at least three years of credit monitoring via all three major bureaus simultaneously, including Equifax, Experian and TransUnion. Or, if you didn’t want to take advantage of the credit monitoring offers, you could opt for a cash payment of up to $125.
The settlement also offered reimbursement for the time you may have spent remedying identity theft or misuse of your personal information caused by the breach, or purchasing credit monitoring or credit reports. This was capped at 20 total hours at $25 per hour ($500), with total cash reimbursement payments not to exceed $20,000 per consumer.
Those who did file a claim probably started receiving emails or other communications earlier this year from the Equifax Breach Settlement Fund, which has been messaging class participants about methods of collecting their payments.
How much each recipient receives appears to vary quite a bit, but probably most people will have earned a payment on the smaller end of that $125 scale — like less than $10. Those who received higher amounts likely spent more time documenting actual losses and/or explaining how the breach affected them personally.
So far this week, KrebsOnSecurity has received at least 20 messages from readers seeking more information about these notices. Some readers shared copies of letters they got in the mail along with a paper check from the Equifax Breach Settlement Fund (see screenshot above).
Others said they got emails from the Equifax Breach Settlement domain that looked like an animated greeting card offering instructions on how to redeem a virtual prepaid card.
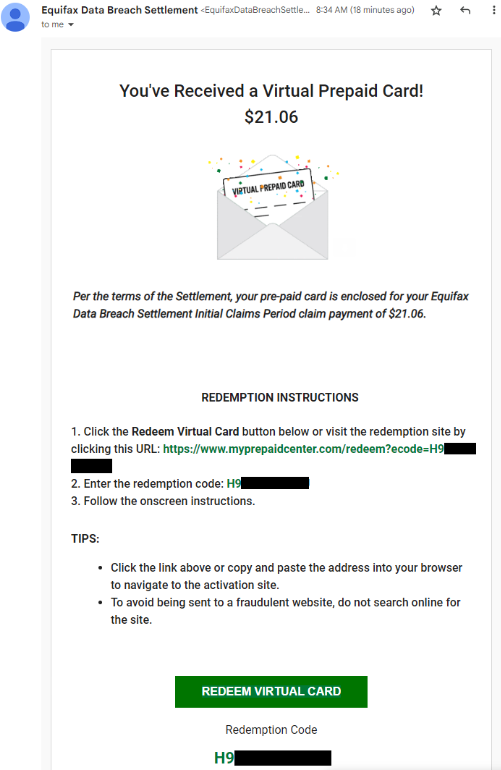
If you received one of these settlement emails and are wary about clicking the included links (good for you, by the way), copy the redemption code and paste it into the search box at myprepaidcenter.com/redeem. Successfully completing the card application requires accepting a prepaid MasterCard agreement (PDF).
The website for the settlement — equifaxbreachsettlement.com — also includes a lookup tool that lets visitors check whether they were affected by the breach; it requires your last name and the last six digits of your Social Security Number.
But be aware that phishers and other scammers are likely to take advantage of increased public awareness of the payouts to snooker people. Tim Helming, security evangelist at DomainTools.com, today flagged several new domains that mimic the name of the real Equifax Breach Settlement website and do not appear to be defensively registered by Equifax, including equifaxbreechsettlement[.]com, equifaxbreachsettlementbreach[.]com, and equifaxsettlements[.]co.
In February 2020, the U.S. Justice Department indicted four Chinese officers of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) for perpetrating the 2017 Equifax hack. DOJ officials said the four men were responsible for carrying out the largest theft of sensitive personal information by state-sponsored hackers ever recorded.
Equifax surpassed Wall Street’s expectations in its most recent quarterly earnings: The company reported revenues of $1.24 billion for the quarter ending September 2022.
Of course, most of those earnings come from Equifax’s continued legal ability to buy and sell eye-popping amounts of financial and personal data on U.S. consumers. As one of the three major credit bureaus, Equifax collects and packages information about your credit, salary, and employment history. It tracks how many credit cards you have, how much money you owe, and how you pay your bills. Each company creates a credit report about you, and then sells this report to businesses who are deciding whether to give you credit.
Americans currently have no legal right to opt out of this data collection and trade. But you can and also should freeze your credit, which by the way can make your credit profile less profitable for companies like Equifax — because they make money every time some potential creditor wants a peek inside your financial life. Also, it’s probably a good idea to freeze the credit of your children and/or dependents as well. It’s free on both counts.
Give yourself peace of mind and help create a safe online space for your child using Android or iOS parental controls
The post How to set up parental controls on your child’s new smartphone appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
The time has come for your child to receive their first smartphone. Before handing it over, however, make sure to help them use their new gadget safely and responsibly.
The post Help! My kid has asked Santa for a smartphone appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
Microsoft has released its final monthly batch of security updates for 2022, fixing more than four dozen security holes in its various Windows operating systems and related software. The most pressing patches include a zero-day in a Windows feature that tries to flag malicious files from the Web, a critical bug in PowerShell, and a dangerous flaw in Windows 11 systems that was detailed publicly prior to this week’s Patch Tuesday.

The security updates include patches for Azure, Microsoft Edge, Office, SharePoint Server, SysInternals, and the .NET framework. Six of the update bundles earned Microsoft’s most dire “critical” rating, meaning they fix vulnerabilities that malware or malcontents can use to remotely commandeer an unpatched Windows system — with little to no interaction on the part of the user.
The bug already seeing exploitation is CVE-2022-44698, which allows attackers to bypass the Windows SmartScreen security feature. The vulnerability allows attackers to craft documents that won’t get tagged with Microsoft’s “Mark of the Web,” despite being downloaded from untrusted sites.
“This means no Protected View for Microsoft Office documents, making it easier to get users to do sketchy things like execute malicious macros, said Greg Wiseman, product manager at security firm Rapid7. This is the second Mark of the Web flaw Microsoft has patched in as many months; both were first publicly detailed over the past two months on Twitter by security researcher Will Dormann.
Publicly disclosed (but not actively exploited for now) is CVE-2022-44710, which is an elevation of privilege flaw in the DirectX graphics component of Windows 11.
Another notable critical bug is CVE-2022-41076, a remote code execution flaw in PowerShell — a key component of Windows that makes it easier to automate system tasks and configurations.
Kevin Breen at Immersive Labs said while Microsoft doesn’t share much detail about CVE-2022-41076 apart from the designation ‘Exploitation More Likely,’ they also note that successful exploitation requires an attacker to take additional actions to prepare the target environment.
“What actions are required is not clear; however, we do know that exploitation requires an authenticated user level of access,” Breen said. “This combination suggests that the exploit requires a social engineering element, and would likely be seen in initial infections using attacks like MalDocs or LNK files.”
Speaking of malicious documents, Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative highlights CVE-2022-44713, a spoofing vulnerability in Outlook for Mac.
“We don’t often highlight spoofing bugs, but anytime you’re dealing with a spoofing bug in an e-mail client, you should take notice,” ZDI’s Dustin Childs wrote. “This vulnerability could allow an attacker to appear as a trusted user when they should not be. Now combine this with the SmartScreen Mark of the Web bypass and it’s not hard to come up with a scenario where you receive an e-mail that appears to be from your boss with an attachment entitled “Executive_Compensation.xlsx”. There aren’t many who wouldn’t open that file in that scenario.”
Microsoft also released guidance on reports that certain software drivers certified by Microsoft’s Windows Hardware Developer Program were being used maliciously in post-exploitation activity.
Three different companies reported evidence that malicious hackers were using these signed malicious driver files to lay the groundwork for ransomware deployment inside victim organizations. One of those companies, Sophos, published a blog post Tuesday detailing how the activity was tied to the Russian ransomware group Cuba, which has extorted an estimated $60 million from victims since 2019.
Of course, not all scary and pressing security threats are Microsoft-based. Also on Tuesday, Apple released a bevy of security updates to iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS and Safari, including a patch for a newly discovered zero-day vulnerability that could lead to remote code execution.
Anyone responsible for maintaining Fortinet or Citrix remote access products probably needs to update, as both are dealing with active attacks on just-patched flaws.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today (indexed by severity and other metrics) check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.
InfraGard, a program run by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to build cyber and physical threat information sharing partnerships with the private sector, this week saw its database of contact information on more than 80,000 members go up for sale on an English-language cybercrime forum. Meanwhile, the hackers responsible are communicating directly with members through the InfraGard portal online — using a new account under the assumed identity of a financial industry CEO that was vetted by the FBI itself.
On Dec. 10, 2022, the relatively new cybercrime forum Breached featured a bombshell new sales thread: The user database for InfraGard, including names and contact information for tens of thousands of InfraGard members.
The FBI’s InfraGard program is supposed to be a vetted Who’s Who of key people in private sector roles involving both cyber and physical security at companies that manage most of the nation’s critical infrastructures — including drinking water and power utilities, communications and financial services firms, transportation and manufacturing companies, healthcare providers, and nuclear energy firms.
“InfraGard connects critical infrastructure owners, operators, and stakeholders with the FBI to provide education, networking, and information-sharing on security threats and risks,” the FBI’s InfraGard fact sheet reads.
In response to information shared by KrebsOnSecurity, the FBI said it is aware of a potential false account associated with the InfraGard Portal and that it is actively looking into the matter.
“This is an ongoing situation, and we are not able to provide any additional information at this time,” the FBI said in a written statement.
KrebsOnSecurity contacted the seller of the InfraGard database, a Breached forum member who uses the handle “USDoD” and whose avatar is the seal of the U.S. Department of Defense.
USDoD said they gained access to the FBI’s InfraGard system by applying for a new account using the name, Social Security Number, date of birth and other personal details of a chief executive officer at a company that was highly likely to be granted InfraGard membership.
The CEO in question — currently the head of a major U.S. financial corporation that has a direct impact on the creditworthiness of most Americans — told KrebsOnSecurity they were never contacted by the FBI seeking to vet an InfraGard application.
USDoD told KrebsOnSecurity their phony application was submitted in November in the CEO’s name, and that the application included a contact email address that they controlled — but also the CEO’s real mobile phone number.
“When you register they said that to be approved can take at least three months,” USDoD said. “I wasn’t expected to be approve[d].”
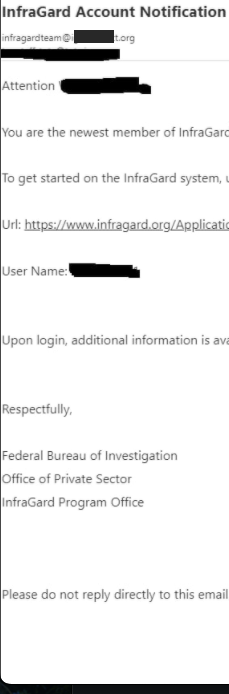 But USDoD said that in early December, their email address in the name of the CEO received a reply saying the application had been approved (see redacted screenshot to the right). While the FBI’s InfraGard system requires multi-factor authentication by default, users can choose between receiving a one-time code via SMS or email.
But USDoD said that in early December, their email address in the name of the CEO received a reply saying the application had been approved (see redacted screenshot to the right). While the FBI’s InfraGard system requires multi-factor authentication by default, users can choose between receiving a one-time code via SMS or email.
“If it was only the phone I will be in [a] bad situation,” USDoD said. “Because I used the person[‘s] phone that I’m impersonating.”
USDoD said the InfraGard user data was made easily available via an Application Programming Interface (API) that is built into several key components of the website that help InfraGard members connect and communicate with each other.
USDoD said after their InfraGard membership was approved, they asked a friend to code a script in Python to query that API and retrieve all available InfraGard user data.
“InfraGard is a social media intelligence hub for high profile persons,” USDoD said. “They even got [a] forum to discuss things.”
To prove they still had access to InfraGard as of publication time Tuesday evening, USDoD sent a direct note through InfraGard’s messaging system to an InfraGard member whose personal details were initially published as a teaser on the database sales thread.
That InfraGard member, who is head of security at a major U.S. technology firm, confirmed receipt of USDoD’s message but asked to remain anonymous for this story.
USDoD acknowledged that their $50,000 asking price for the InfraGard database may be a tad high, given that it is a fairly basic list of people who are already very security-conscious. Also, only about half of the user accounts contain an email address, and most of the other database fields — like Social Security Number and Date of Birth — are completely empty.
“I don’t think someone will pay that price, but I have to [price it] a bit higher to [negotiate] the price that I want,” they explained.
While the data exposed by the infiltration at InfraGard may be minimal, the user data might not have been the true end game for the intruders.
USDoD said they were hoping the imposter account would last long enough for them to finish sending direct messages as the CEO to other executives using the InfraGuard messaging portal. USDoD shared the following redacted screenshot from what they claimed was one such message, although they provided no additional context about it.
USDoD said in their sales thread that the guarantor for the transaction would be Pompompurin, the administrator of the cybercrime forum Breached. By purchasing the database through the forum administrator’s escrow service, would-be buyers can theoretically avoid getting ripped off and ensure the transaction will be consummated to the satisfaction of both parties before money exchanges hands.
Pompompurin has been a thorn in the side of the FBI for years. Their Breached forum is widely considered to be the second incarnation of RaidForums, a remarkably similar English-language cybercrime forum shuttered by the U.S. Department of Justice in April. Prior to its infiltration by the FBI, RaidForums sold access to more than 10 billion consumer records stolen in some of the world’s largest data breaches.
In November 2021, KrebsOnSecurity detailed how Pompompurin abused a vulnerability in an FBI online portal designed to share information with state and local law enforcement authorities, and how that access was used to blast out thousands of hoax email messages — all sent from an FBI email and Internet address.
Update, 10:58 p.m. ET: Updated the story after hearing from the financial company CEO whose identity was used to fool the FBI into approving an InfraGard membership. That CEO said they were never contacted by the FBI.
Update, 11:15 p.m. ET: The FBI just confirmed that it is aware of a potential false account associated with the InfraGard portal. The story now includes their full statement.
This is a developing story. Updates will be noted here with timestamps.
Cybersecurity has changed dramatically since the dawn of firewalls in the 1980s. But despite all the upheaval and innovation, they have stood the test of time. The basic concept of allowing “good” traffic to flow and blocking the bad stuff remains essential. Of course, it looks much different now than in the era of Care Bears and Cabbage Patch Kids.
Today’s workers, data, and applications are everywhere, and firewalls must be as well. There’s no longer just one finite space to defend. With the recent explosion of hybrid work and the rapid transition to multi-cloud environments, it’s imperative that firewalls evolve alongside a business — and be ready for whatever’s next.
So, can your firewall grow with you? Or is it stuck in the age of Hair Bands and He-Man?
The past few years have brought about a keen focus on resilience — remaining strong, yet adaptable in the face of unexpected and even unfathomable challenges. But an organization cannot persevere without security being at the forefront of any resilience strategy.
96% of executives consider security resilience highly important to their business.
– Cisco Security Outcomes Report
Firewalls are a critical foundation for building powerful, resilient security infrastructure. Yet contemporary firewalls have to be and do more than one thing. Cisco Secure Firewall delivers world-class security controls wherever you need them, with unified visibility and consistent policy management and enforcement.
As a worldwide leader in networking and security, Cisco is better positioned than any other vendor to incorporate effective firewall controls into your infrastructure — anywhere your data and applications reside. According to a study conducted on behalf of Cisco by Forrester Research, Cisco Secure Firewall customers can:
Cisco Secure Firewall delivers on several key aspects necessary for security resilience: visibility, flexibility, intelligence, integration, and unified controls. Together, they enable organizations to close gaps, see and detect threats faster, and adapt quickly to change.
Watch video: Cisco Secure Firewall Overview
With most of today’s internet traffic being encrypted, security measures can become obsolete without the ability to see into all traffic, encrypted or not. While decryption is commonplace, it is simply not feasible in many cases, and can have serious impacts on network performance. With its Encrypted Visibility Engine, Cisco Secure Firewall leverages deep packet inspection (DPI) to identify potentially malicious applications in encrypted traffic without offloading to another appliance and degrading performance.
Due to a highly distributed network and workforce, as well as constantly maturing attacks, the ability to see into every corner of your ecosystem is crucial. Cisco Secure Firewall blends multiple technologies to detect and block more threats in more places. By combining traditional firewall capabilities with URL filtering, application visibility and control, malware defense, and Snort 3 intrusion prevention, organizations gain robust protection against even the most sophisticated threats.
Cisco offers a wide variety of firewalls for defending the different areas of your network — including physical, virtual, and cloud-native — as well as cloud-delivered. We can secure businesses and offices of all types and sizes, from the data center to the cloud.
Cisco Secure also provides flexible firewall management options, enabling you to deploy and operate your security architecture in a way that is tailored to the unique requirements of your NetOps, SecOps, and DevOps teams. No matter which firewall models you choose or environments you operate in (physical or virtual), you can use a single, simplified application to manage all your firewalls from one place.
The threat landscape changes every day, and our defenses must change with it. Cisco Talos is one of the largest and most trusted threat intelligence groups in the world. Its in-depth insight into global threats, and advanced research and analysis, enable us to quickly incorporate protections for new threats into our products via hourly updates. That way, Cisco customers are continuously safeguarded from both known and unknown threats.
“When the Log4j vulnerability was discovered, we were protected before we even completed our patching,” said Paul Smith, network administrator at Marian University. “As a result of automated hourly updates from Talos, Cisco Secure Firewall had an early detection signature, so it was already blocking the concerning traffic from infiltrating our network.”
Another differentiator for Cisco Secure Firewall is that it’s part of an integrated security ecosystem. With Cisco SecureX, organizations can correlate data from multiple technologies and unleash XDR capabilities for a centralized, automated response to threats.
“At the end of the day, it’s about protecting the data, and we do that with the integration of [Cisco] Secure Endpoint, Umbrella, and Secure Firewall, which combine to protect the networks, endpoints, workstations, and servers — and all of this can be correlated easily within SecureX.”
– Elliott Bujan, IT Security Manager, Marine Credit Union
The new Cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center leverages the cloud to facilitate agile, simplified operations for a distributed, hybrid network. It provides efficiency at scale by allowing security teams to swiftly deploy and update policies across their environment with just a few clicks, as well as take coordinated actions to prioritize, investigate, and remediate threats within a single pane of glass. And with a cloud-delivered management center, Cisco regularly updates its software behind the scenes, which reduces risk, maintains compliance, and gives your team more time to focus on other priorities.
Additionally, Cisco Secure Firewall dynamically shares policies driven by intelligence from Cisco Secure Workload, which uses microsegmentation to prevent lateral movement of attackers throughout a network. This allows security policies to be harmonized across both the network and application environments, boosting efficacy and fostering collaboration between teams.
These are just some examples of what makes up a comprehensive, modernized firewall. But Cisco is not stopping there. We continue to innovate to meet evolving business needs. For example, the new enterprise-class 3100 Series firewalls are specially designed for hybrid work, supporting more end users with high-performance remote access for increased organizational flexibility.
Additionally, Cisco Secure Firewall serves as a key component of advanced security strategies including XDR, SASE, and zero trust, helping businesses keep pace with accelerating digital transformation. According to Cisco’s most recent Security Outcomes Report, organizations with mature XDR, SASE, and zero trust implementations all boast significantly higher levels of security resilience.
Fuel and energy retailer, Ampol, uses a variety of Cisco technologies, including Secure Firewall, to segment and safeguard its network. “Cisco was an integral part of our success during COVID-19 as we were able to serve customers without interruption in stores,” said Amir Yassa, senior project specialist at Ampol. “Deploying our retail resilience project, mostly comprised of Cisco products, enabled us to reduce our IT-related incidents by 90%, thus enabling us to serve our customers better now and into the future.”
Is your firewall keeping up with future demands, or is it still stuck in the 80s teasing its hair? If it’s the latter, we can help. Visit cisco.com/go/firewall and learn how to refresh your firewall.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels

Payment applications make splitting restaurant bills, taxi fares, and household expenses so much easier. Without having to tally totals at the table or fumble with crumpled bills, you and your companions can spend less stress and more time on the fun at hand.
There are various payment apps available, and the company that may first come to mind is PayPal. PayPal is regarded as a safe platform where security and strong encryption are a priority; however, a recent and advanced phishing scam is putting PayPal users at risk of giving up large sums of money and their personally identifiable information (PII).1
Let’s look at this “triple-pronged” PayPal phishing scam and review some tips to help you identify and proceed should you encounter it.
The typical part of this three-sided scam is the phishing email component. According to one source, the phishing email comes from a legitimate-looking PayPal service email address. Luckily, the typos, odd punctuation, extra spaces, and grammar errors in the body of the email give away that it is a phishing attempt. Remember, phishing emails are often worded poorly or have errors. Large companies, especially ones like PayPal, have teams of content experts vetting all automated messages for such mistakes, so several mistakes in an email should set off your alarm bells. Proceed with caution and do not click on any links in the message.
The email also included wording that encouraged the user to act quickly or be charged a lot of money. That’s another trademark of phishing emails: urgency. Take a deep breath and make sure to reread carefully all emails that “require” a quick response. Don’t be scared by dire consequences. Phishers rely on people to rush and not give themselves time to listen to their better judgement.
The PayPal phishing email included a support phone number that claimed it was toll free. In actuality, it was an international phone number. So, if the recipient of the phishing email didn’t quite believe the message but wanted to follow up, the scam could catch them with what’s called a one-ring phone scam.2 This occurs when someone unknowingly calls an international phone number and then gets charged by their phone company for the long-distance call.
The best way to avoid one-ring phone scams is to never call a number you don’t recognize. Always go to an organization’s official website to find their contact information.
The third dimension of this PayPal scam was the international phone number in the phishing email connected the caller directly with the scammer who posed as the PayPal fraud department. The “customer service representative” then asked prying personal and financial questions to glean enough PII to break into a PayPal account or compromise the caller’s identity. This is the most damaging part of the scam. An excellent customer support team may be able to reimburse you your lost money; however, once your personal details are in nefarious hands, you can’t take them back.
In addition to never calling numbers you haven’t verified, never give out passwords and never give out more personal information than you need to. Even in legitimate customer service calls, it’s not rude to ask why the representative requires the information they’re asking for. In a fake call, questions like that may fluster the scammer, so keep an ear tuned to their tone.
Overall, our best advice for handling suspicious emails is to delete them. If it’s truly important, the sender will contact you again. And if a thief somehow stole money from one of your payment apps, the customer service team should be able to walk you through the steps to recover it.
The transfer and handling of large sums of money would make anyone nervous. To give you peace of mind, consider partnering with a service that can help you recover should you ever fall for a scheme and compromise your PII. McAfee+ Ultimate helps you live your best life in private, and the service includes credit monitoring with all three credit bureaus, security freeze, and expert online support to help you navigate any scams you encounter.
Having McAfee+ can protect you from email phishing scams like this. Here are some of the top agencies to report this scam to, if it happens to you: Paypal Fraud Department, Federal Trade Commision , Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency USA.gov IC3
“Report it. Forward phishing emails to reportphishing@apwg.org (an address used by the Anti-Phishing Working Group, which includes ISPs, security vendors, financial institutions, and law enforcement agencies). Let the company or person that was impersonated know about the phishing scheme.” – FTC.gov
1ZDNET, “Watch out for this triple-pronged PayPal phishing and fraud scam.”
2Federal Communications Commission, “‘One Ring’ Phone Scam.”
The post A PayPal Email Scam Is Making the Rounds: Here’s How to Identify and Avoid It appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Happy National App Day! No, we don’t mean apps of the mozzarella stick and potato skin variety, but your mobile apps that let you order dinner, hail a taxi, stay connected to your friends, and entertain you for hours with silly videos. While they’re undoubtedly useful, mobile apps are also a weak spot in some people’s digital safety. Cybercriminals take every chance they get to trick people through all kinds of technology, and mobile apps are no exception.
To celebrate National App Day, here are a few tips to keep your mobile and your personally identifiable information (PII) safe.
Did you know that there are hundreds of apps on the Android and Apple app stores whose only aim is to steal your passwords? In 2022, Meta identified more than 400 fake apps disguised as various utilities that targeted users to weasel Facebook login and password combinations.1 Malicious apps also regularly masquerade as photo editors and wallpapers but their real purpose is to run malware in the background of the mobile device, such as this Squid Game app from 2021.
Little-known apps aren’t the only ones you have to be wary of either. The biggest companies are also falling to cybercrime. For instance, more details recently came to light about a breach at Uber that leaked the PII of 57 million users. Plus, the popular mobile payment service, Cash App had the personal details of 8.3 million current and former users leaked.2
To keep your cellphone free of malicious software and your PII and password secure, take these five mobile security tips with you into the new year.
The new year is as good a time as any to unload any unnecessary baggage, emotional, literal, or in this case, digital. Go through your phone and delete the apps you haven’t used in the last six months. Make sure to completely delete your account with that app and not just hide it from your homepage. The smaller your digital footprint, the less at risk your PII is of being compromised in a breach.
Before you download any new app, it’s a good idea to conduct some background research on it. How many detailed reviews does it have? Who is the app developer? A phony app usually reveals itself through its lack of reviews. Consider apps with less than 50 reviews fishy. Skim the reviews for specific details and typos. If it’s lacking in detail but brimming with typos and grammatical mistakes, it could signal a fake. This research should take about five minutes, so don’t worry; it shouldn’t be too much of an inconvenience, and that time will be well spent.
Just like it’s a good idea to keep on top of global news, set up news alerts for cybersecurity breaches. If a company falls to a cybercriminal, the alert will give you the valuable time you need to act quickly to either delete your account or change your password.
For every online account, it is essential to create a unique password or passphrase. That way, if you do get hacked through an app or get tricked by a fake one, you don’t have to worry about cybercriminals using that password to walk into your other accounts. Password managers are an excellent way to keep all your passwords secure and free up your brain space for things other than dozens of passwords.
When you sign up for a new app, you can expect to give it a username, a password, and maybe your first name; however, if it has optional fields for your full birthday or your address, consider leaving those blank. The less information the company has about you, the less that can end up in cybercriminals’ hands if the app is breached.
The first step to better cyber habits is arming yourself with the knowledge of the threats that are out there. The best advice here is to slow down, observe and think about your next move every time you download a new app. The signs of a fake are usually not difficult to spot. Then, once you’re confident in its legitimacy, limit the amount of PII you share with it. In this digital world we live in, consider everyone susceptible to a breach.
To give you peace of mind, supplement your great habits with a tool, like McAfee+ Ultimate, that will cover all your bases and be your partner to live your best private life online.
1Tech.co, “Data Breaches That Have Happened in 2022 So Far.”
2Termly, “98 Biggest Data Breaches, Hacks, and Exposures.”
The post 2022’s Top 5 App Security Tips appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Watch ThreatWise TV: Explorations in the spam folder
The spam folder: that dark and disregarded corner of every email account, full of too-good-to-be-true offers, unexpected shipments, and supposedly free giveaways.
You’re right to ignore this folder; few good things come from exploring it. But every once in a while one of these misleading, and sometimes malicious, emails manages to evade the filters that normally siphon them off, landing them in your inbox instead.
Fortunately, it’s easy enough to spot these emails if you know what to look for. We’ve investigated this folder once before, showcasing a variety of scams. With the holiday season in full swing, we thought this would be a good time to revisit how scammers are trying to trick unsuspecting users.
The holiday season is traditionally a time when this type of activity increases, and this year is no different. According to research published by credit reporting agency TransUnion, the average daily number of suspected digital fraud attempts was up 82 percent globally between Thanksgiving and Cyber Monday (Nov 24–Nov 28) compared to the rest of the year (Jan 1–Nov 23) and 127 percent higher for transactions originating in the US.
This level of activity makes it all the more important to be aware of these scams. With that in mind, let’s dive into the spam folder to get a picture of the types of campaigns currently circulating.
While much of the spam circulating is innocuous, many emails are phishing attempts, and some are indeed malicious. To explore these scams, we used a dedicated computer, segmented from the rest of the network, and leveraged Cisco Secure Malware Analytics to safely open the emails before clicking on links or opening attachments. The point being, we do not recommend doing this at home.
By far, the largest category of spam we saw were surveys scams. According to these emails, if you fill out a simple survey you’ll receive “exclusive offers” such as gift cards, smartphones, smart watches, power drills, or even pots and pans.

There are even some campaigns that specifically target the holiday shopping season.

Clicking the links in these emails takes the recipient to sites where they are asked to fill out a survey.

These pages often include fake testimonials that say how easy the survey is and what they did with their free gift.

The surveys are straightforward, comprising 10-20 simple questions that cover demographic information and shopping habits.

After the survey is completed, these sites offer the choice of a handful of rewards. All the recipient must do is pay for shipping. They are then brought to a page where they can fill out shipping and payment information, and the reward is supposedly shipped.

However, the attempts to make payment often appear to fail, or the recipient is informed that the prize is no longer available.

An unsuspecting user may simply give up at this point, disappointed that they won’t be getting their free gift. What they may not be aware of, is that they have just given their credit card details away in a phishing scam.
In their 2021 Internet Crime Report, the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) said that Non-Payment / Non-Delivery scams such as these led to more than $337 million in losses, up from $265 million in 2020. Credit card fraud amounted to $172 million in 2021 and has been climbing continuously at a conservative rate of 15-20 percent since 2019.
According to Cisco Umbrella, many of the sites asking for credit card details are known phishing sites, or worse, host malware.

Another topic that we covered the last time we explored these types of scams was package delivery spam. These continue to circulate today. There are a variety of shipping companies impersonated in these campaigns, and some generic ones as well.

Many of these campaigns claim that a package could not be delivered. If the recipient clicks on a link in an email, they’re brought to a web page that explains that there are outstanding delivery fees that need to be paid.

The recipient is further enticed by suggestions that the package contains a big-ticket item, such as an iPhone or iPad Pro. All the recipient is required to do is enter their credit card details to cover the shipping.

While no outright malicious activity was detected while examining these emails in Secure Malware Analytics, several suspicious behaviors were flagged. Chances are the bad actors behind these campaigns are phishing for credit card details.

Sometimes the simplest approaches can work just as well as the flashiest. This certainly holds true with spam campaigns, given the prominence of plain-text messages.

The topics covered in such emails run the gamut, including medical cures, 419 scams, romance and dating, pharmaceuticals, weight loss, and many of the scam types we’ve already covered. Many of these link to phishing sites, though some attempt to establish a dialog with the recipient, tricking them into sending the scammers money.
The IC3 report says that victims of confidence fraud and romance scams lost $956 million collectively, which is up from $600 million in 2020. Healthcare fraud, such as the miracle pills and prescriptions scams, resulted in $7 million in losses in 2021, but nearly $30 million in 2020. While these types of scams seem generic and easily spotted, they still work, and so it’s important to be aware and avoid them.
Many emails hitting the spam box attempt to trick users of various services into believing that there is a problem with their account. The problems cover all sorts of services, including streaming platforms, email providers, antivirus subscriptions, and even public records.

If the links are clicked, the recipient is presented with landing pages that mimic the respective services. Any details that are entered will likely be phished, leading to account takeover and/or access to personal records. However, some domains encountered in these cases may do more than just steal information, they could deliver malware too.

Another frequently encountered scam surrounds billing. Many of these appear to be unexpected bills for services the recipient never purchased.

These emails include attachments that are designed to look like official invoices. Interestingly, most of the attachments that we looked at this time were harmless. The goal is to get the recipient to call what appears to be a toll-free number.

While we haven’t called any of these numbers, the experience usually unfolds like a standard customer service call. In the end the “agents” simply claim the charges—which never existed in the first place—have been removed. Meanwhile the scammers steal any personal or financial information provided during the call.
While most billing scams we encountered played out as described above, a few did indeed contain malware.
In this example, the email appears to come from an internet service provider, informing us that our monthly bill is ready.

An invoice appears to be attached, stored within a .zip file. If the recipient opens it and double clicks the file within, a command prompt appears.

This may seem unusual to the recipient, especially since no invoice appears, but by this point it’s too late. The file contains a script that launches PowerShell and attempts to download a remote file.

While the remote file was no longer available at the time of analysis, there is a high likelihood it was malicious. But even though we were unable to determine its contents, Secure Malware Analytics flagged the script execution as malicious.

Knowing about prevalent scams, especially during the holiday season, is a first step in guarding against them. Granted the bad actors who distribute these spam campaigns do everything they can to make their scams look legitimate.
Fortunately, there are several things that you can do to identify scams and defend against them:
But even the best of us can be fooled, and when overseeing a large operation it’s more a matter of when, rather than if, someone clicks on the wrong link. There are elements of the Cisco Secure portfolio that can help for when the inevitable happens.
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics is the malware analysis and malware threat intelligence engine behind all products across the Cisco Security Architecture. The system delivers enhanced, in-depth, advanced malware analysis and context-rich intelligence to help better understand and fight malware within your environments. Secure Malware Analytics is available as a standalone solution, as a component in other Cisco Security solutions, and through software-as-a-service (SaaS) in the cloud, on-premises, and hybrid delivery models.
Cisco Secure Email protects against fraudulent senders, malware, phishing links, and spam. Its advanced threat detection capabilities can uncover known, emerging, and targeted threats. In addition, it defends against phishing by using advance machine learning techniques, real time behavior analytics, relationship modeling, and telemetry that protects against identity deception–based threats.
Cisco Umbrella unifies multiple security functions in a single cloud service to secure internet access. By enforcing security at the DNS layer, Umbrella blocks requests to malware before a connection is even established—before they reach your network or endpoints. In addition, the secure web gateway logs and inspects all web traffic for greater transparency, control, and protection, while the cloud-delivered firewall helps to block unwanted traffic.
Cisco Secure Endpoint is a single-agent solution that provides comprehensive protection, detection, response, and user access coverage to defend against threats to your endpoints. The SecureX platform is built into Secure Endpoint, as are Extended Detection and Response (XDR) capabilities. With the introduction of Cisco Secure MDR for Endpoint, we have combined Secure Endpoint’s superior capabilities with security operations to create a comprehensive endpoint security solution that dramatically decreases the mean time to detect and respond to threats while offering the highest level of always-on endpoint protection.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels

This time of year, the air not only gets chillier but a bit cheerier for everyone … including online scammers. Holiday scams are a quick way to make a buck, and cybercriminals employ several holiday-themed schemes to weasel money and personally identifiable information (PII) from gift givers.
Here are three common holiday scams to watch out for this year, plus a few tips to help you stay safe online.
Gift cards are a standby present for the people on your list who are difficult to buy for or for people you don’t know too well but want to get them a small something. Whether the gift card is worth $5 or $500, an online scammer can steal the entire value through two techniques: a brute force attack or phishing. Known as gift card cracking, cybercriminals can take wild guesses at gift card codes and cash in the value for themselves by methodically guessing strings of numbers and letters and crossing their fingers for a match. Cybercriminals will also employ phishing emails, texts or social media direct messages to trick people into divulging gift card information.
To avoid gift card cracking, encourage gift receivers to redeem their gift card quickly to shorten the amount of time a scammer has to guess the code correctly. Or, you could opt for a paper gift certificate from a small business that doesn’t require online redeeming at all. To avoid gift card phishing scams, do not engage with any type of correspondence that claims they can double the value of your gift card or claims that there’s a problem with it. Be instantly on alert if anyone asks for the activation code. If the gift card-issuing business really needs to replace your purchase, they’ll issue you a new code. They’ll never ask for your existing one.
Are you a procrastinator? Watch out for last-minute shopping scams that are targeted at people who leave their gift buying until deep in December. As with anything else, if it’s too good to be true, it probably is. Shopping scams often take the form of phishing emails where criminals impersonate a well-known merchant or shipping company.
While sales often have a quick timeline, don’t let that short timeline pressure you into making an impulsive decision. Phishers rely on people’s excitement or inattention to trick them into giving up their credit card or banking information. Phishing emails, when you take the time to inspect them, are usually easy to spot. The logos are often blurry, there are often typos and grammar mistakes, and the tone of the message will seem “off.” Either it will sound very formal and impersonalized or it will sound very informal and seem pushy.
To protect your finances during the holiday season, consider putting a lock on your credit. This is easy to do with McAfee credit lock. You can still use your credit card and shop as you normally would. A credit lock is useful because, in case a criminal gets ahold of your PII, they won’t be able to open lines of credit in your name. This protects your credit score, which is essential to keep in good standing if you hope to buy a house or take out a loan anytime soon.
Just because a “company” has an ad on Facebook or Instagram doesn’t mean that it’s a legitimate establishment. Before buying from an online store you’ve never heard of, do some background research on it and read customer reviews to make sure that it’s real and will deliver you a quality product.
Take note of the online store’s URL before entering it. (You can preview the link by hovering over it with your cursor.) If the URL is a string of letters and numbers, it could be a malware site in disguise. One way to alert you to suspicious sites is McAfee Web Protection. Web Protection color codes links to identify potential malware and phishing sites and alert you to steer clear.
Your mind is already drawn in a bunch of different directions this holiday season (cooking, traveling, shopping, wrapping, tidying) so give yourself a respite from worrying about the safety of your identity and finances. McAfee+ Ultimate includes a VPN, Web Protection, credit lock, antivirus and more to cover all your bases to keep your devices and your PII safe.
The post ‘Tis the Season for Holiday Scams appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Even with the holidays in full swing, scammers won’t let up. In fact, it’s high time for some of their nastiest cons as people travel, donate to charities, and simply try to enjoy their time with friends and family.
Unfortunate as it is, scammers see this time of year as a tremendous opportunity to profit. While people focus giving to others, they focus on taking, propping up all manner of scams that use the holidays as a disguise. So as people move quickly about their day, perhaps with a touch of holiday stress in the mix, they hope to catch people off their guard with scams that wrap themselves in holiday trappings.
Yet once you know what to look for, they’re relatively easy to spot. The same scams roll out every year, sometimes changing in appearance yet remaining the same in substance. With a sharp eye, you can steer clear of them.
With Black Friday and Cyber Monday in the books, we can look forward to what’s next—a wave of post-holiday sales events that will likewise draw in millions of online shoppers. And just like those other big shopping days, bad actors will roll out a host of scams aimed at unsuspecting shoppers. Shopping scams take on several forms, which makes this a topic unto itself, one that we cover thoroughly in our Black Friday & Cyber Monday shopping scams blog. It’s worth a read if you haven’t done so already, as digs into the details of these scams and shows how you can avoid them.
However, the high-level advice for avoiding shopping scams is this: keep your eyes open. Deals that look too good to be true likely are, and shopping with retailers you haven’t heard of before requires a little bit of research to determine if their track record is clean. In the U.S., you can turn to the Better Business Bureau (BBB) for help with a listing of retailers you can search simply by typing in their names. You can also use https://whois.domaintools.com to look up the web address of the shopping site you want to research. There you can see its history and see when it was registered. A site that was registered only recently may be far less reputable than one that’s been registered for some time.
Plenty of new tech makes its way into our homes during the holiday season. And some of that tech can be a little challenging to set up. Be careful when you search for help online. Many scammers will establish phony tech support sites that aim to steal funds and credit card information. Go directly to the product manufacturer for help. Often, manufacturers will offer free support as part of the product warranty, so if you see a site advertising support for a fee, that could be a sign of a scam.
Likewise, scammers will reach out to you themselves. Whether through links from unsolicited emails, pop-up ads from risky sites, or by spammy phone calls, these scammers will pose as tech support from reputable brands. From there, they’ll falsely inform you that there’s something urgently wrong with your device and that you need to get it fixed right now—for a fee. Ignore these messages and don’t click on any links or attachments. Again, if you have concerns about your device, contact the manufacturer directly.
With the holidays comes travel, along with all the online booking and ticketing involved. Scammers will do their part to cash in here as well. Travel scams may include bogus emails that pose as reputable travel sites telling you something’s wrong with your booking. Clicking a link takes you to a similarly bogus site that asks for your credit card information to update the booking—which then passes it along to the scammer so they can rack up charges in your name. Other travel scams involve ads for cut-rate lodging, tours, airfare, and the like, all of which are served up on a phony website that only exists to steal credit card numbers and other personal information.
Some of these scams can look quite genuine, even though they’re not. They’ll use cleverly disguised web addresses that look legitimate, but aren’t, so don’t click any links. If you receive notice about an issue with your holiday travel, contact the company directly to follow up. Also, be wary of ads with unusually deep discounts or that promise availability in an otherwise busy season or time. These could be scams, so stick with reputable booking sites or with the websites maintained by hotels and travel providers themselves.
Donations to an organization or cause that’s close to someone’s heart make for a great holiday gift, just as they offer you a way to give back during the holiday season. And you guessed it, scammers will take advantage of this too. They’ll set up phony charities and apply tactics that pressure you into giving. As with so many scams out there, any time an email, text, direct message, or site urges you into immediate action—take pause. Research the charity. See how long they’ve been in operation, how they put their funds to work, and who truly benefits from them.
Likewise, note that there some charities pass along more money to their beneficiaries than others. As a general rule of thumb, most reputable organizations only keep 25% or less of their funds for operations, while some less-than-reputable organizations keep up to 95% of funds, leaving only 5% for advancing the cause they advocate. In the U.S., the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has a site full of resources so that you can make your donation truly count. Resources like Charity Watch and Charity Navigator, along with the BBB’s Wise Giving Alliance can also help you identify the best charities.
The holidays also mean a flight of big-time sporting events, and with the advent of online betting in many regions scammers want to cash in. This scam works quite like shopping scams, where bad actors will set up online betting sites that look legitimate. They’ll take your bet, but if you win, they won’t pay out. Per the U.S. Better Business Bureau (BBB), the scam plays out like this:
“You place a bet, and, at first, everything seems normal. But as soon as you try to cash out your winnings, you find you can’t withdraw a cent. Scammers will make up various excuses. For example, they may claim technical issues or insist on additional identity verification. In other cases, they may require you to deposit even more money before you can withdraw your winnings. Whatever you do, you’ll never be able to get your money off the site. And any personal information you shared is now in the hands of scam artists.”
You can avoid these sites rather easily. Stick with the online betting sites that are approved by your regional gambling commission. Even so, be sure to read the fine print on any promo offers that these sites advertise because even legitimate betting sites can freeze accounts and the funds associated with them based on their terms and conditions.
A complete suite of online protection software, such as McAfee+ Ultimate can offer layers of extra security. In addition to more private and secure time online with a VPN, identity monitoring, and password management, it includes web browser protection that can block malicious and suspicious links that could lead you down the road to malware or a phishing scam—which antivirus protection can’t do alone. Additionally, we offer $1M identity theft coverage and support from a recovery pro, just in case.
And because scammers use personal information such as email addresses and cell phone numbers to wage their attacks, other features like our Personal Data Cleanup service can scan high-risk data broker sites for your personal information and then help you remove it, which can help reduce spam, phishing attacks, and deny bad actors the information they need to commit identity theft.
That’s why they enjoy the holidays so much. With all our giving, travel, and charity in play, it’s prime time for their scams. Yet a little insight into their cons, along with some knowledge as to how they play out, you can avoid them.
Remember that they’re playing into the hustle and bustle of the season and that they’re counting on you to lower your guard more than you might during other times of the year. Keep an eye open for the signs, do a little research when it’s called for, and stick with reputable stores, charities, and online services. With a thoughtful pause and a second look, you can spare yourself the grief of a scam and fully enjoy your holidays.
The post Unwrapping Some of the Holiday Season’s Biggest Scams appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Do yourself a favor: Open a new browser tab and head to your search engine of choice. Type in your full name and home address. Then, see what pops up.
Are the results sparking an ember of unease in the back of your brain? Whether you’re a private person online or you’re comfortable sharing your daily life updates on social media, there are likely to be several personal details about you on sites that shouldn’t have that information. Some of these sites may be data brokerage websites.
Data brokerage sites are legal and are mostly used by annoying advertisers, though cybercriminals may also use them maliciously. The average person has their information for sale on 31 data brokerage sites, and 95% of people have their personal information on sale without their permission.
So how do you scrub the internet of your personal details to keep your identity secure? McAfee Personal Data Cleanup is a service that prevents your personal information from being collected and sold online. Here’s why you should consider taking a few easy steps now to give you peace of mind about the security of your personally identifiable information (PII).
Attack surface is a term usually applied to corporate security, but it’s a great visualization for everyday people going about their personal online errands and entertainment. An attack surface is the number of possible entry points a cybercriminal could weasel their way through to get at your valuable and private information. Entry points include your social media profiles, your online shopping accounts, and data brokerage sites. The fewer entry points you have, the harder it is for cybercriminals to find and exploit them.
While Social Security Numbers (SSNs) are generally revered as the piece of PII to guard most closely, a cybercriminal can still damage your identity with just your name and an address, email address, or phone number. For example, they can request new passwords or multifactor authentication one-time passcodes to break their way into online banking or shopping accounts. Security breaches are happening to huge companies all over the world. All it takes is for your SSN to be leaked in one of them, for a cybercriminal to piece together your digital clone and use it to harm your identity or credit.
Personal Data Cleanup minimizes your attack surface by removing as much PII as possible that’s floating around the internet, just waiting for someone to buy it.
When you’re aware of how many unauthorized vendors are selling your PII, it could be the wakeup call you need start adopting more cautious online habits. For instance, oversharing on social media leaks a lot of valuable details that a savvy criminal can then use to take educated guesses at your passwords or craft a social engineering plot catered just to you.
The present is as good a time as any to start protecting your identity for the future; however, getting started is often the most difficult step. It can seem overwhelming to reach out to every data brokerage site individually and request they remove your info. Personal Data Cleanup can be your partner not only in beginning the cleanup process but in monitoring your data security to keep your online presence as minimal as possible. The service scans the internet’s riskiest sites and then, before deleting your information from these sites, runs it by you to confirm. Then, it will continually monitor those same sites, as your information will likely reappear every two to four months.
Do not underestimate the tenacity of a cybercriminal. Even for people who have the attitude that their PII is bound to be somewhere online and that it’s no big deal, McAfee Personal Data Cleanup manages three key steps in the data removal process: scanning, removing, and monitoring. So, even if you’re not convinced that data brokerage sites are a threat, the process is too easy to put off any longer!
For those who are concerned about their online privacy, full-service Personal Data Cleanup is included in McAfee+ Ultimate, which is the complete package to let you live your online life in private. McAfee+ Ultimate also includes identity monitoring and identity theft resolution services, unlimited VPN, credit lock, and much more.
In 2021, more than 1.4 million identity theft complaints were filed to the Federal Trade Commission.1 Identity theft can occur to anyone, so take steps today, starting with data brokerage sites, to live a more secure and more private digital life.
1Federal Trade Commission, “New Data Shows FTC Received 2.8 Million Fraud Reports from Consumers in 2021”
The post McAfee Personal Data Cleanup: Your Partner in Living a More Private Online Life appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Have you ever been browsing online and clicked a link or search result that took you to a site that triggers a “your connection is not private” or “your connection is not secure” error code? If you’re not too interested in that particular result, you may simply move on to another result option. But if you’re tempted to visit the site anyway, you should be sure you understand what the warning means, what the risks are, and how to bypass the error if you need to.
A “your connection is not private” error means that your browser cannot determine with certainty that a website has safe encryption protocols in place to protect your device and data. You can bump into this error on any device connected to the internet — computer, smartphone, or tablet.
So, what exactly is going on when you see the “this connection is not private” error?
For starters, it’s important to know that seeing the error is just a warning, and it does not mean any of your private information is compromised. A “your connection is not private” error means the website you were trying to visit does not have an up-to-date SSL (secure sockets layer) security certificate.
Website owners must maintain the licensing regularly to ensure the site encryption capabilities are up to date. If the website’s SSL certificate is outdated, it means the site owners have not kept their encryption licensing current, but it doesn’t necessarily mean they are up to no good. Even major websites like LinkedIn have had momentary lapses that would throw the error. LinkedIn mistakenly let their subdomain SSL certificates lapse.
In late 2021, a significant provider of SSL certificates, Let’s Encrypt, went out of business. When their root domain officially lapsed, it created issues for many domain names and SSL certificates owned by legitimate companies. The privacy error created problems for unwitting businesses, as many of their website visitors were rightfully concerned about site security.
While it does not always mean a website is unsafe to browse, it should not be ignored. A secure internet connection is critical to protecting yourself online. Many nefarious websites are dangerous to visit, and this SSL certificate error will protect you from walking into them unaware.
SSL certification standards have helped make the web a safer place to transact. It helps ensure online activities like paying bills online, ordering products, connecting to online banking, or keeping your private email accounts safe and secure. Online security continues to improve with a new Transport Layer Security (TLS) standard, which promises to be the successor protocol to SSL.
So be careful whenever visiting sites that trigger the “connection is not private” error, as those sites can potentially make your personal data less secure and make your devices vulnerable to viruses and malware.
Note: The “your connection is not private” error is Google Chrome‘s phrasing. Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox users will instead see a “your connection is not secure” error as the warning message.
If you feel confident that a website or page is safe, despite the warning from your web browser, there are a few things you can do to troubleshoot the error.
Remember, you are taking your chances anytime you ignore an error. As we mentioned, you could leave yourself vulnerable to hackers after your passwords, personal information, and other risks.
Your data and private information are valuable to hackers, so they will continue to find new ways to try and procure it. Here are some ways to protect yourself and your data when browsing online.
As we continue to do more critical business online, we must also do our best to address the risks of the internet’s many conveniences.
A comprehensive cybersecurity tool like McAfee+ Ultimate can help protect you from online scams, identity theft, and phishing attempts, and ensure you always have a secure connection. McAfee helps keep your sensitive information out of the hands of hackers and can help you keep your digital data footprints lighter with personal data cleanup.
With McAfee’s experts on your side, you can enjoy everything the web offers with the confidence of total protection.
The post “This Connection Is Not Private” – What it Means and How to Protect Your Privacy appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It’s important to know that not all websites are safe to visit. In fact, some sites may contain malicious software (malware) that can harm your computer or steal your personal contact information or credit card numbers.
Phishing is another common type of web-based attack where scammers try to trick you into giving them your personal information, and you can be susceptible to this if you visit a suspicious site.
Identity theft is a serious problem, so it’s important to protect yourself when browsing the web. Online security threats can be a big issue for internet users, especially when visiting new websites or following site links.
So how can you tell if you’re visiting a safe website or an unsafe website? You can use a few different methods. This page discusses key things to look for in a website so you can stay safe online.
When you’re visiting a website, a few key indicators can help determine whether the site is safe. This section explores how to check the URL for two specific signs of a secure website.
“Https” in a website URL indicates that the website is safe to visit. The “s” stands for “secure,” and it means that the website uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption to protect your information. A verified SSL certificate tells your browser that the website is secure. This is especially important when shopping online or entering personal information into a website.
When you see “https” in a URL, the site is using a protocol that encrypts information before it’s sent from your computer to the website’s server. This helps prevent anyone from intercepting and reading your sensitive information as it’s transmitted.
The padlock icon near your browser’s URL field is another indicator that a webpage is safe to visit. This icon usually appears in the address bar and means the site uses SSL encryption. Security tools and icon and warning appearances depend on the web browser.
Let’s explore the cybersecurity tools on the three major web browsers:
Overall, the ”https” and the locked padlock icon are good signs that your personal data will be safe when you enter it on a website. But you can ensure a website’s security is up to par in other ways. This section will explore five in-depth methods for checking website safety.
McAfee WebAdvisor is a free toolbar that helps keep you safe online. It works with your existing antivirus software to provide an extra layer of protection against online threats. WebAdvisor also blocks unsafe websites and lets you know if a site is known for phishing or other malicious activity. In addition, it can help you avoid online scams and prevent you from accidentally downloading malware. Overall, McAfee WebAdvisor is a useful tool that can help you stay safe while browsing the web.
When you’re browsing the web, it’s important to be able to trust the websites you’re visiting. One way to determine if a website is trustworthy is to look for trust seals. Trust seals are logos or badges that indicate a website is safe and secure. They usually appear on the homepage or checkout page of a website.
There are many types of trust seals, but some of the most common include the Better Business Bureau (BBB) seal, VeriSign secure seal, and the McAfee secure seal. These seals indicate that a third-party organization has verified the website as safe and secure.
While trust seals can help determine whether a website is trustworthy, it’s important to remember that they are not foolproof. Website owners can create a fake trust seal, so it’s always important to do your own research to ensure a website is safe before entering personal information.
Another way to determine if a website is safe to visit is to check for a privacy policy. A privacy policy is a document that outlines how a website collects and uses personal information. It should also state how the site protects your data from being accessed or shared by scammers, hackers, or other unauthorized individuals.
If a website doesn’t have a privacy policy, that’s a red flag that you shouldn’t enter any personal information on the site. Even if a website does have a privacy policy, it’s important to read it carefully so you understand how the site uses your personal data.
It’s important to do some preliminary research before visiting a new website, especially if you’re shopping online or entering personal data like your address, credit card, or phone number. One way to determine if a website is safe and trustworthy is to check third-party reviews. Several websites provide reviews of other websites, so you should be able to find several reviews for any given site.
Trustpilot is one example of a website that provides reviews of other websites.
Look for common themes when reading reviews. If most of the reviews mention that a website is safe and easy to use, it’s likely that the site is indeed safe to visit. However, if a lot of negative reviews mention problems with viruses or malware, you might want to avoid the site.
You can also analyze the website design when deciding whether a website is safe to visit. Look for spelling errors, grammatical mistakes, and anything that appears off. If a website looks like it was made in a hurry or doesn’t seem to be well-designed, that’s usually a red flag that the site might not be safe.
Be especially careful of websites that have a lot of pop-ups. These sites are often spammy or contain malware. Don’t download anything from a website unless you’re absolutely sure it’s safe. These malicious websites rarely show up on the top of search engine results, so consider using a search engine to find what you’re looking for rather than a link that redirects you to an unknown website.
If you’re unsure whether a website is safe to visit, download McAfee WebAdvisor for free. McAfee WebAdvisor is a program that helps protect you from online threats, such as malware and viruses. It also blocks pop-ups and other intrusive ads so you can browse the web without worry. Plus, it’s completely free to download and use.
Download McAfee WebAdvisor now and stay safe while browsing the web.
The post How to Tell Whether a Website Is Safe or Unsafe appeared first on McAfee Blog.

What color jersey will you be sporting this November and December? The World Cup is on its way to television screens around the world, and scores of fans are dreaming of cheering on their team at stadiums throughout Qatar. Meanwhile, cybercriminals are dreaming of stealing the personally identifiable information (PII) of fans seeking last-minute vacation and ticket deals.
Don’t let the threat of phishers and online scammers dampen your team spirit this World Cup tournament. Here are three common schemes cybercriminals will likely employ and a few tips to help you dribble around their clumsy offense and protect your identity, financial information, and digital privacy.
Phishers will be out in full force attempting to capitalize on World Cup fever. People wrapped up in the excitement may jump on offers that any other time of the year they would treat with skepticism. For example, in years past, fake contests and travel deals inundated email inboxes across the world. Some companies do indeed run legitimate giveaways, and cybercriminals slip in their phishing attempts among them.
If you receive an email or text saying that you’re the winner of a ticket giveaway, think back: Did you even enter a contest? If not, treat any “winner” notification with skepticism. It’s very rare for a company to automatically enter people into a drawing. Usually, companies want you to act – subscribe to a newsletter or engage with a social media post, for example – in exchange for your entry into their contest. Also, beware of emails that urge you to respond within a few hours to “claim your prize.” While it’s true that real contest winners must reply promptly, organized companies will likely give you at least a day if not longer to acknowledge receipt.
Traveling is rarely an inexpensive endeavor. Flights, hotels, rental cars, dining costs, and tourist attraction admission fees add up quickly. In the case of this year’s host country, Qatar, there’s an additional cost for American travelers: visas.
If you see package travel deals to the World Cup that seem too good to pass up … pass them up. Fake ads for ultra-cheap flights, hotels, and tickets may appear not only in your email inbox but also on your social media feed. Just because it’s an ad doesn’t mean it comes from a legitimate company. Legitimate travel companies will likely have professional-looking websites with clear graphics and clean website copy. Search for the name of the organization online and see what other people have to say about the company. If no search results appear or the website looks sloppy, proceed with caution or do not approach at all.
Regarding visas, be wary of anyone offering to help you apply for a visa. There are plenty of government-run websites that’ll walk you through the process, which isn’t difficult as long as you leave enough time for processing. Do not send your physical passport to anyone who is not a confirmed government official.
Even fans who’ve given up on watching World Cup matches in person aren’t out of the path of scams. Sites claiming to have crystal clear streams of every game could be malware spreaders in disguise. Malware and ransomware targeting home computers often lurk on sketchy sites. All it takes is a click on one bad link to let a cybercriminal or a virus into your device.
Your safest route to good-quality live game streams is through the official sites of your local broadcasting company or the official World Cup site. You may have to pay a fee, but in the grand scheme of things, that fee could be a lot less expensive than replacing or repairing an infected device.
Here’s an excellent rule to follow with any electronic correspondence: Never send anyone your passwords, routing and account number, passport information, or Social Security Number. A legitimate organization will never ask for your password, and it’s best to communicate any sensitive financial or identifiable information over the phone, not email or text as they can easily fall into the wrong hands. Also, do not wire large sums of money to someone you just met online.
Don’t let scams ruin your enjoyment of this year’s World Cup! With these tips, you should be able to avoid the most common schemes but to boost your confidence in your online presence, consider signing up for McAfee+. Think of McAfee+ as the ultimate goalkeeper who’ll block any cybercriminals looking to score on you. With identity monitoring, credit lock, unlimited VPN and antivirus, and more, you can surf safely and with peace of mind.
The post Watch Out for These 3 World Cup Scams appeared first on McAfee Blog.








Monkey in the middle, the beloved playground staple, extends beyond schoolyards into corporate networks, home desktops, and personal mobile devices in a not-so-fun way. Known as a monkey-in-the-middle or man-in-the-middle attack (MiTM), it’s a type of cybercrime that can happen to anyone.
Here’s everything you need to know about mobile MiTM schemes specifically, how to identify when your mobile device is experiencing one, and how to protect your personally identifiable information (PII) and your device from cybercriminals.
A man-in-the-middle attack, or MiTM attack, is a scheme where a cybercriminal intercepts someone’s online activity and impersonates a trusted person or organization. From there, the criminal may ask personal questions or attempt to get financial information; however, since the mobile device owner thinks they’re communicating with someone with good intentions, they give up these details freely.
MiTM is an umbrella term that includes several cybercrime tactics, such as:
Cybercriminals gain access to mobile devices to carry out MiTM mobile attacks through three main methods: Wi-Fi eavesdropping, malware, or phishing.
The most common giveaway of a MiTM attack is a spotty internet connection. If a cybercriminal has a hold on your device, they may disconnect you from the internet so they can take your place in sessions or steal your username and password combination.
If your device is overheating or the battery life is much shorter than normal, it could indicate that it is running malware in the background.
If you can identify the signs of a MiTM attack, that’s a great first step in protecting your device. Awareness of your digital surroundings is another way to keep your device and PII safe. Steer clear of websites that look sloppy, and do not stream or download content from unofficial sites. Malware is often hidden in links on dubious sites.
To safeguard your Wi-Fi connection, protect your home router with a strong password or passphrase. When connecting to public Wi-Fi, confirm with the hotel or café’s staff their official Wi-Fi network name. Then, make sure to connect to a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your online activity, which makes it impossible for someone to digitally eavesdrop.
Finally, a comprehensive antivirus software can clean up your device of malicious programs it might have contracted.
McAfee+ Ultimate includes unlimited VPN and antivirus, plus a whole lot more to keep all your devices safe. It also includes web protection that alerts you to suspicious websites, identity monitoring, and daily credit reports to help you browse safely and keep on top of any threats to your identity or credit.
A cybercriminal’s prize for winning a mobile scheme of monkey in the middle is your personal information. With preparation and excellent digital protection tools on your team, you can make sure you emerge victorious and safe.
The post Everything You Need to Know to Avoid a Man-in-the-Middle Mobile Attack appeared first on McAfee Blog.









Organizations embrace the public cloud for the agility, scalability, and reliability it offers when running applications. But just as organizations need these capabilities to ensure their applications operate where needed and as needed, they also require their security does the same. Organizations may introduce multiple individual firewalls into their AWS infrastructure to produce this outcome. In theory, this may be a good decision, but in practice—this could lead to asymmetric routing issues. Complex SNAT configuration can mitigate asymmetric routing issues, but this isn’t practical for sustaining public cloud operations. Organizations are looking out for their long-term cloud strategies by ruling out SNAT and are calling for a more reliable and scalable solution for connecting their applications and security for always-on protection.
To solve these challenges, Cisco created stateful firewall clustering with Secure Firewall in AWS.
Firewall clustering for Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual provides a highly resilient and reliable architecture for securing your AWS cloud environment. This capability lets you group multiple Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual appliances together as a single logical device, known as a “cluster.”
A cluster provides all the conveniences of a single device (management and integration into a network) while taking advantage of the increased throughput and redundancy you would expect from deploying multiple devices individually. Cisco uses Cluster Control Link (CCL) for forwarding asymmetric traffic across devices in the cluster. Clusters can go up to 16 members, and we use VxLAN for CCL.
In this case, clustering has the following roles:

The above diagram explains traffic flow between the client and the server with the insertion of the firewall cluster in the network. Below defines the roles of clustering and how packet flow interacts at each step.
Owner: The Owner is the node in the cluster that initially receives the connection.
Backup Owner: The node that stores TCP/UDP state information received from the Owner so that the connection can be seamlessly transferred to a new owner in case of failure.
Director: The Director is the node in the cluster that handles owner lookup requests from the Forwarder(s).
Forwarder: The Forwarder is a node in the cluster that redirects packets to the Owner.
Fragment Owner: For fragmented packets, cluster nodes that receive a fragment determine a Fragment Owner using a hash of the fragment source IP address, destination IP address, and the packet ID. All fragments are then redirected to the Fragment Owner over Cluster Control Link.
Cisco brought support for AWS Gateway Load Balancer (Figure 2). This feature enables organizations to scale their firewall presence as needed to meet demand (see details here).

Building off the previous figure, organizations can take advantage of the AWS Gateway Load Balancer with Secure Firewall’s clustering capability to evenly distribute traffic at the Secure Firewall cluster. This enables organizations to maximize the benefits of clustering capabilities including increased throughput and redundancy. Figure 3 shows how positioning a Secure Firewall cluster behind the AWS Gateway Load Balancer creates a resilient architecture. Let’s take a closer look at what is going on in the diagram.

Figure 3 shows an Internet user looking to access a workload. Before the user can access the workload, the user’s traffic is routed to Firewall Node 2 for inspection. The traffic flow for this example includes:
User -> IGW -> GWLBe -> GWLB -> Secure Firewall (2) -> GLWB -> GWLBe -> Workload
In the event of failure, the AWS Gateway Load Balancer cuts off existing connections to the failed node, making the above solution non-stateful.
Recently, AWS announced a new feature for their load balancers known as Target Failover for Existing Flows. This feature enables forwarding of existing connections to another target in the event of failure.
Cisco is an early adaptor of this feature and has combined Target Failover for Existing Flows with Secure Firewall clustering capabilities to create the industry’s first stateful cluster in AWS.

Figure 4 shows a firewall failure event and how the AWS Gateway Load Balancer uses the Target Failover for Existing Flows feature to switch the traffic flow from Firewall Node 2 to Firewall Node 3. The traffic flow for this example includes:
User -> IGW -> GWLBe -> GWLB -> Secure Firewall (3) -> GLWB -> GWLBe -> Workload
Organizations need reliable and scalable security to protect always-on applications in their AWS cloud environment. With stateful firewall clustering capabilities from Cisco, organizations can protect their applications while maintaining cloud benefits such as agility, scalability, and reliability.
Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual is available in the AWS marketplace, providing features like firewalling, application visibility & control, IPS, URL filtering, and malware defense. Cisco offers flexible options for firewall licensing, such as pay-as-you-go (PAYG) and bring-your-own-license (BYOL). To learn more about how Cisco Secure Firewall clustering capabilities can help protect your AWS applications, see our additional resources, check out our 30-day free trial, or speak to your Cisco sales representative.
Cisco Secure Firewall Clustering in the Cloud
Introducing AWS Gateway Load Balancer Target Failover for Existing Flows
Secure Firewall for Public Cloud webpage
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels
The word is out! Cisco Secure Endpoint’s effectiveness is off the charts in protecting your enterprise environment.
This is not just a baseless opinion; however, the facts are rooted in actual test results from the annual AV-Comparative EPR Test Report published in October 2022. Not only did Secure Endpoint knock it out of the park in enterprise protection; but Cisco Secure Endpoint obtained the lowest total cost of ownership (TCO) per agent at $587 over 5 years. No one else was remotely close in this area. More to come on that later.
If you are not familiar with the “AV-Comparatives Endpoint Prevention and Response Test is the most comprehensive test of EPR products ever performed. The 10 products in the test were subjected to 50 separate targeted attack scenarios, which used a variety of different techniques.”
These results are from an industry-respected third-party organization that assesses antivirus software and has just confirmed what we know and believe here at Cisco, which is our Secure Endpoint product is the industry’s best of the best.
Look for yourself at where we landed. That’s right, Cisco Secure Endpoint smashed this test, we are almost off the quadrant as one of the “Strategic Leaders”.

We ended up here for a combination of reasons, with the top being our efficacy in protecting our customers’ environments in this real-world test that emulates multi-stage attacks similar to MITRE’s ATT&CK evaluations which are conducted as part of this process (click here for an overview of MITRE ATT&CK techniques). Out of all the 50 scenarios tested, Secure Endpoint was the only product that STOPPED 100% of targeted threats toward enterprise users, which prevented further infiltration into the organization.
In addition, this test not only assesses the efficacy of endpoint security products but also analyzes their cost-effectiveness. Following up on my earlier remarks about achieving the lowest cost of ownership, the graph below displays how we stacked up against other industry players in this space including several well-known vendors that chose not to display their names due to poor results.

These results provide a meaningful proof point that Cisco Secure Endpoint is perfectly positioned to secure the enterprise as well as secure the future of hybrid workers.
Enriched with built-in Extended Detection and Response (XDR) capabilities, Cisco Secure Endpoint has allowed our customers to maintain resiliency when faced with outside threats.
As we embark on securing “what’s next” by staying ahead of unforeseen cyber threats of tomorrow, Cisco Secure Endpoint integration with the complete Cisco Secure Solutions portfolio allows you to move forward with the peace of mind that if it’s connected, we can and will protect it.
Now that you have seen how effective Secure Endpoint is with live real-world testing, try it for yourself with one of our live instant demos. Click here to access instructions on how to download and install your demo account for a test drive.
Click here to see what analysts, customers, and third-party testing organizations have to say about Cisco Secure Endpoint Security efficacy, easy implementation and overall low total cost of ownership for their organization —and stay ahead of threats.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels

What you paid for your home, who lives there with you, your age, your children, your driving record, education, occupation, estimated income, purchasing habits, and any political affiliations you may have—all pretty personal information, right? Well, there’s a good chance that anyone can find it online. All it takes is your name and address.
Thankfully, there’s something you can do about it.
But first, go ahead and give it a try. Type your name and address in a search bar and see what comes up. If you’re like most people, your search results turned up dozens of sites with your information on them. Some sites offer bits of it for free. Other sites offer far more detailed information, for a price.
Who’s behind all this? Data brokers. All part of a global data economy estimated at $200 billion U.S. dollars a year fueled by thousands of data points on billions of people scraped from public records, social media, third-party sources, and sometimes other data broker sites as well.
The result? A chillingly accurate picture of you.
So accurate, that reporters and law enforcement will often use profiles from data broker sites to dig up a person’s background. And so could scammers and thieves.
Ever wonder how you end up with all those spam calls and texts? Look no further than the data brokers. They help scammers compile the calling and texting lists they use. Yet spammy calls and texts are just part of the problem with these sites. They can give thieves the tools they need to steal your identity.
How? Visualize your identity as a jigsaw puzzle. Every bit of personal information makes up a piece, and if you cobble enough pieces together, a scammer or thief could have enough information to steal your identity. And data brokers compile all those pieces in one place and offer up them up in droves.
If you’re wondering if this activity is legal or at least regulated in some way, it largely isn’t. For example, the U.S. has no federal laws that require data brokers to remove personal information from their sites if requested to do so. On the state level, Nevada, Vermont, and California have legislation in place aimed at protecting consumers from having their data disclosed on these sites. Other legislation is being considered, yet as of this writing there’s very little on the books right now.
With next to no oversight, data brokers continue to collect personal information, which may or may not be accurate. It may be out of date or flat out wrong. Likewise, as it is with any large data store, data brokers are subject to hacks and attacks, which may lead to breaches that release detailed personal information onto the dark web and into the hands of bad actors.
Put plainly, data brokers collect, buy, and sell high volumes of personal information, often in ways that leave no trace that it’s happening to you—or that the information is correct in any way.
All this can feel like it’s out of your control. And maybe the search you did on yourself made you a little uneasy. (Understandable!) Yet you have plenty of ways you can curb this activity and even remove your information from some of the riskiest data broker sites as well.
It starts by finding out which sites have information on you, followed by filing requests to have it removed. Yet with dozens and dozens of these sites proliferating online, this can be a time-consuming process. Not to mention a frustrating one. We created McAfee+ so people can not only be safe but feel safe online, particularly in a time when there’s so much concern about identity theft and invasion of our online privacy. McAfee+ contains a comprehensive set of tools, such as Personal Data Cleanup which are designed to help protect your online privacy.
Personal Data Cleanup scans some of the riskiest data broker sites and shows you which ones are selling your personal info. It also provides guidance on how you can remove your data from those sites and can even manage the removal for you depending on your plan.
And because getting your info removed once isn’t a guarantee that a data broker won’t collect and post it again, Personal Data Cleanup can continually monitor those sites. So should your info get posted again, you can request its removal again as well.
The other way you can thwart data brokers involves cleaning up your tracks when you go online, essentially leaving a smaller amount of data in your wake that they can collect and resell.
Searching for your name and address can turn up some surprises and introduce you to the world of data brokers, the dozens and dozens of companies that collect, buy, and sell your personal information. While data brokers sell this information to companies for advertising and marketing purposes, they will also sell that information to hackers, scammers, and thieves. Simply put, they don’t discriminate when selling your personal info. That puts more than just your privacy at risk, it can put your identity at risk as well. By selling your personal information, it can give bad actors the info they need to commit identity fraud and theft.
While cleaning up personal information from these sites is often a difficult and time-consuming task, tools like our Personal Data Cleanup can now dig out the sites where your personal info is posted and can help you remove it. Moreover, you now have several tricks and tactics you can use to reduce the amount of personal data these sites can collect. In all, you now have far more control over what data brokers can collect, buy, and sell than you had before. And now is most certainly a time to take that control given all the time we spend online and the many ways we rely on it to help us work, play, and simply get things done.
The post How much of your personal info is available online? A simple search could show you plenty. appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Going beyond the hype, passwordless authentication is now a reality. Cisco Duo’s passwordless authentication is now generally available across all Duo Editions.
“Cisco Duo simplifies the passwordless journey for organizations that want to implement phishing-resistant authentication and adopt a zero trust security strategy.”
—Jack Poller, Senior Analyst, ESG
We received tremendous participation and feedback during our public preview, and we are now excited to bring this capability to our customers and prospects.
“Over the last few years, we have increased our password complexities and required 2FA wherever possible. With this approach, employees had more password lock outs, password fatigue, and forgetting their longer passwords due to password rotations. With Duo Passwordless, we are excited to introduce this feature to our employees to keep our password complexities in place and leverage different Biometric options whether that is using their mobile device, Windows Hello, or a provided FIDO security key.
The Duo Push for passwordless authentication feature is simple and easy and introduces a more pleasant experience overall. Using Duo’s device insight and application policies, we are able to leverage and verify the security of the mobile devices before the device is allowed to be used. To top it off, Duo is connected to our SIEM and our InfoSec team is able to review detailed logs and setup alerts to be able to keep everything secure.”
—Vice President of IT, Banking and Financial Services Customer
As with any new technology, getting to a completely passwordless state will be a journey for many organizations. We see customers typically starting their passwordless journey with web-based applications that support modern authentication. To that effect, Duo’s passwordless authentication is enabled through Duo Single Sign-On (SSO) for federated applications. Customers can choose to integrate their existing SAML Identity provider such as Microsoft (ADFS, Azure), Okta or Ping Identity; or choose to use Duo SSO (Available across all Duo editions).
“Password management is a challenging proposition for many enterprises, especially in light of BYOD and ever increasing sophistication of phishing schemes. Cisco aims to simplify the process with its Duo passwordless authentication that offers out-of-box integrations with popular single sign-on solutions.”
—Will Townsend, Vice President & Principal Analyst, Networking & Security, Moor Insights & Strategy
Duo offers a flexible choice of passwordless authentication options to meet the needs of businesses and their use cases. This includes:
No matter which authentication option you choose, it is secure and inherently multi-factor authentication. We are eliminating the need for the weak knowledge factor (something you know – passwords) which are shared during authentication and can be easily compromised. Instead, we are relying on stronger factors, which are the inherence factor (something you are – biometrics) and possession factor (something you have – a registered device). A user completes this authentication in a single gesture without having to remember a complex string of characters. This significantly improves the user experience and mitigates the risk of stolen credentials and man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks.
FIDO2 authentication is regarded as phishing-resistant authentication because it:
Using Duo with FIDO2 authenticators enables organizations to enforce phishing-resistant MFA in their environment. It also complies with the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) guidance issued earlier this year in a memo titled “Moving the U.S. Government Towards Zero Trust Cybersecurity Principles”. The memo specifically requires agencies to use phishing-resistant authentication method.
We understand that getting the IT infrastructure ready to support FIDO2 can be expensive and is typically a long-term project for organizations. In addition, deploying and managing 3rd party security keys creates IT overhead that some organizations are not able to undertake immediately.
Alternatively, using Duo Push for passwordless authentication is an easy, cost effective to get started on a passwordless journey for many organizations, without compromising on security.
We have incorporated security into the login workflow to bind the browser session and the device being used. So, organizations get the same benefits of eliminating use of stolen credentials and mitigation of phishing attacks. To learn more about passwordless authentication with Duo Push, check out our post: Available Now! Passwordless Authentication Is Just a Tap Away.
In addition to going passwordless, many organizations are looking to implement zero trust access in their IT environment. This environment typically is a mix of modern and legacy applications, meaning passwordless cannot be universally adopted. At least not until all applications can support modern authentication.
Additionally, organizations need to support a broad range of use cases to allow access from both managed and unmanaged (personal or 3rd party contractor) devices. And IT security teams need visibility into these devices and the ability to enforce compliance to meet the organization’s security policies such as ensuring that the operating system (OS) and web browser versions are up to date. The importance of verifying device posture at the time of authentication is emphasized in the guidance provided by OMB’s zero trust memorandum – “authorization systems should work to incorporate at least one device-level signal alongside identity information about the authenticated user.”
Duo can help organizations adopt a zero trust security model by enforcing strong user authentication across the board either through passwordless authentication where applicable or thought password + MFA where necessary, while providing a consistent user experience. Further, with capabilities such as device trust and granular adaptive policies, and with our vision for Continuous Trusted Access, organizations get a trusted security partner they can rely on for implementing zero trust access in their environment.
To learn more, check out the eBook – Passwordless: The Future of Authentication, which outlines a 5-step path to get started. And watch the passwordless product demo in this on-demand webinar .
Many of our customers have already begun their passwordless journey. If you are looking to get started as well, sign-up for a free trial and reach out to our amazing representatives.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels

On Black Friday and Cyber Monday, the deals roll out. So do some of the worst Black Friday and Cyber Monday scams.
Hackers, scammers, and thieves look to cash in this time of year by blending in with the holiday rush, spinning up their own fake shipping notices, phony deals, and even bogus charities that look legitimate at first glance, yet are anything but. Instead, they may be loaded with malware, point you to phishing sites that steal your personal info, or they may simply rip you off.
Classically, many online scams play on emotions by creating a sense of urgency or even fear. And for the holidays, you can throw stress into that mix as well—the stress of time, money, or even the pressure of finding that hard-to-get gift that seems to be out of stock everywhere. The bad actors out there will tailor their attacks around these feelings, hoping that they’ll catch you with your guard down during this busy time of year.
So while knowing how to spot a great gift at a great price is solid skill to have this time of year, so is the ability to spot a scam. Let’s look at some of the worst ones out there, along with what you can do to steer clear of them.
Come this time of year, keeping tabs on all the packages you have in transit can get tricky. You may have an armload of them enroute at any given time, and scammers will look to slip into this mix with phony order confirmations sent to your mailbox or your phone by text. Packed with either an email attachment or a link to a bogus website, they’ll try to get you to download malware or visit a site that attempts to steal your identity.
These messages can look quite legit, so the best way to keep track of your orders is on the sites where you purchased them. Go directly to those sites rather than clicking on any links or attachments you get.
This scam plays out much like the fake order scam, yet in this case the crooks will send a phony package tracking notification, again either as a link or as an attachment. For starters, legitimate retailers won’t send tracking numbers in an attached file. If you see anything like that, it’s surely a scam designed to inject malware onto your device. In the case of a link, the scammers aim to send you to a site that will steal your personal info, just like in the case above.
Once again, the best way to track your packages is to go to the source. Visit the online store where you made your purchase, open your current orders, and get your package tracking information from there.
A classic scammer move is to “typosquat” phony email addresses and URLs that look awfully close to legitimate addresses of legitimate companies and retailers. So close that you may overlook them. They often appear in phishing emails and instead of leading you to a great deal, these can in fact link you to scam sites that can then lift your login credentials, payment info, or even funds should you try to place an order through them.
You can avoid these sites by going to the retailer’s site directly. Be skeptical of any links you receive by email, text, or direct message—it’s best to go to the site yourself by manually typing in the legitimate address yourself and look for the deal there.
At the heart of holiday shopping is scarcity. And scarcity is something scammers love. There’s always some super-popular holiday item that’s tough to find, and scammers will spin up phony websites and offers around those items to lure you in. They may use the typosquatting technique mentioned above to pose as a legitimate retailer, or they may set up a site with their own branding to look legitimate on their own (or at least try). Either way, these scams can hurt you in a couple of ways—one, you’ll pay for the goods and never receive them; and two, the scammers will now have your payment info and address, which they can use to commit further fraud.
If the pricing, availability, or delivery time all look too good to be true for the item in question, it may be a scam designed to harvest your personal info and accounts. Use caution here before you click. If you’re unsure about a product or retailer, read reviews from trusted websites to help see if it’s legitimate. (The Better Business Bureau is a great place to start—more on that in moment.)
In the season of giving, donating to charities in your name or in the name of others makes for a popular holiday gesture. Scammers know this too and will set up phony charities to cash in. Some indications that a phony charity has reached you include an urgent pitch that asks you to “act now.” A proper charity will certainly make their case for a donation, yet they won’t pressure you into it. Moreover, phony charities will outright ask for payment in the form of gift cards, wire transfers (like Western Union), money orders, or even cryptocurrency—because once those funds are sent, they’re nearly impossible to reclaim when you find out you’ve been scammed.
There are plenty of ways to make donations to legitimate charities, and the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has a site full of resources so that you can make your donation truly count.
Some of it takes an eagle eye that can spot these scams as they pop up in your inbox, texts, social media feed, and so on. Yet you have further ways you can keep safe while shopping on Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and any time.
This is a great one to start with. Directly typing in the correct address for online stores and retailers is a prime way to avoid scammers online. In the case of retailers that you don’t know much about, the U.S. Better Business Bureau (BBB) asks shoppers to do their research and make sure that retailer has a good reputation. The BBB makes that easier with a listing of retailers you can search simply by typing in their name.
Secure websites begin their address with “https,” not just “http.” That extra “s” in stands for “secure,” which means that it uses a secure protocol for transmitting sensitive info like passwords, credit card numbers, and the like over the internet. It often appears as a little padlock icon in the address bar of your browser, so double-check for that. If you don’t see that it’s secure, it’s best to avoid making purchases on that website.
In the U.S., the Fair Credit Billing Act offers the public protection against fraudulent charges on credit cards, where citizens can dispute charges over $50 for goods and services that were never delivered or otherwise billed incorrectly. Note that many credit card companies have their own policies that improve upon the Fair Credit Billing Act as well. However, debit cards aren’t afforded the same protection under the Act. Avoid using a debit card while shopping online and use your credit card instead.
Two-factor authentication is an extra layer of defense on top of your username and password. It adds in the use of a special one-time-use code to access your account, usually sent to you via email or to your phone by text or a phone call. In all, it combines something you know, like your password, with something you have, like your smartphone. Together, that makes it tougher for a crook to hack your account. If any of your accounts support two-factor authentication, the few extra seconds it takes to set up is more than worth the big boost in protection you’ll get.
Public Wi-Fi in coffee shops and other public locations can expose your private surfing to prying eyes because those networks are open to all. Using a virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your browsing, shopping, and other internet traffic, thus making it secure from attempts at intercepting your data on public Wi-Fi, such as your passwords and credit card numbers.
What’s more, a VPN masks your whereabouts and your IP address, plus uses encryption that helps keep your activities private. As a result, companies and data brokers can potentially learn far less about you, your shopping, your travels, your habits, and any other information that they could possibly collect and otherwise profit from.
Yes, it’s true. Your information gets collected, bought, and solid online. In fact, personal information fuels a global data trading economy estimated at $200 billion U.S. dollars a year. Run by data brokers that keep hundreds and even thousands of data points on billions of people, these sites gather, analyze, buy, and sell this information to other companies as well as to advertisers. Likewise, these data brokers may sell this information to bad actors, such as hackers, spammers, and identity thieves who would twist this information for their own purposes.
Getting your info removed from these sites can seem like a daunting task. (Where do I start, and just how many of these sites are out there?) Our Personal Data Cleanup can help by regularly scanning these high-risk data broker sites for info like your home address, date of birth, and names of relatives. It identifies which sites are selling your data, and depending on your plan, automatically requests removal.
Another place where personal information is bought and sold, stored, and exchanged is the dark web. The problem is that it’s particularly difficult for you to determine what, if any, of your info is on the dark web, stashed away in places where hackers and thieves can get their hands on it. Identity monitoring can help. McAfee’s identity monitoring helps you keep your personal info safe by alerting you if your data is found on the dark web, an average of 10 months before our competitors.
Monitored info can range anywhere from bank account and credit card numbers to your email addresses and government ID number, depending on your location. If your information gets spotted, you’ll get an alert, along with steps you can take to minimize or even prevent damage if the information hasn’t already been put to illegal use.
Identity protection through McAfee takes identity monitoring a step further by offering, depending on your location and plan, identity theft coverage for financial losses and expenses due to identity theft, in addition to hands-on help from a recovery professional to help restore your identity—all in addition to the identity monitoring called out above, again depending on your location and plan.
Keeping an eye on your bills and statements as they come in can help you spot unusual activity on your accounts. A credit monitoring service can do that one better by keeping daily tabs on your credit report. While you can do this manually, there are limitations. First, it involves logging into each bureau and doing some digging of your own. Second, there are limitations as to how many free credit reports you can pull each year. A service does that for you and without impacting your credit score.
Depending on your location and plan, McAfee’s credit monitoring allows you to look after your credit score and the accounts within it to see fluctuations and help you identify unusual activity, all in one place, checking daily for signs of identity theft.
A complete suite of online protection software like McAfee+ can offer layers of extra security while you shop. In addition to the VPN, identity, credit monitoring, and other features mentioned above, it includes web browser protection that can block malicious and suspicious links that could lead you down the road to malware or a phishing scam—along with a password manager that can create strong, unique passwords and store them securely as well. Taken together, McAfee+ offers all-in-one online protection for your identity, privacy, and security that can keep you far safer when you shop online—and as you spend your time online in general.
Even if you take the proper precautions the unexpected can happen. Whether it’s a scam, an identity crime, or flat-out theft, there are steps you can take right away to help minimize the damage.
The first bit of advice is to take a deep breath and get right to work on recovery. From there, you can take the following steps:
Whether you spot a curious charge on your bank statement, discover potentially a fraudulent account when you check credit report, or when you get an alert from your monitoring service, let the bank or organization involved know you suspect fraud or theft. With a visit to their website, you can track down the appropriate number to call and get the investigation process started.
Some businesses will require you to file a local police report and acquire a case number to complete your claim. Beyond that, filing a report is a good idea in itself. Identity theft is still theft and reporting it provides an official record of the incident. Should your case of identity theft lead to someone impersonating you or committing a crime in your name, filing a police report right away can help clear your name down the road. Be sure to save any evidence you have, like statements or documents that are associated with the theft. They can help clean up your record as well.
In the U.S., the identity theft website from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is a fantastic resource should you find yourself in need. In addition to keeping records of the theft, the FTC can provide you with a step-by-step recovery plan—and even walk you through the process if you create an account with them. Additionally, reporting theft to the FTC can prove helpful if debtors come knocking to collect on any bogus charges in your name. With a copy of your report, you can ask debtors to stop.
An instance of identity fraud or theft, suspected or otherwise, is a good time to review your options for a credit freeze or lock. As mentioned earlier, see what the credit bureaus in your region offer, along with the terms and conditions of each. With the right decision, a freeze or lock can help minimize and prevent further harm.
Strongly consider using a monitoring service like the one we described earlier to help you continue to keep tabs on your identity. The unfortunate fact of identity theft and fraud is that it can mark the start of a long, drawn-out affair. One instance of theft can possibly lead to another, so even what may appear to be an isolated bad charge on your credit card calls for keeping an eye on your identity all around. Many of the tools you would use up to this point still apply, such as checking up on your credit reports, maintaining fraud alerts as needed, and reviewing your accounts closely—along with utilizing an identity monitoring service.
A recovery service can help you clean up your credit in the wake of fraud or theft, all by working on your behalf. Given the time, money, and stress that can come along with setting your financial record straight, leaning on the expertise of a professional can provide you with much-needed relief on several counts.
Just as it’s always been, hackers, scammers, and thieves want to ruin a good thing. In this case, it’s your spirit of giving and sharing in the holiday season. Yet with this list of top scams and ways you can avoid them, you can keep bad actors like them at bay. Remember, they’re counting on you to be in a hurry this time of year, and maybe a bit stressed and a little disorganized to boot. Take your time while shopping out there and keep an eye out for their tricks. That extra moment can save you far more time and money than you may think.
The post The Worst Black Friday and Cyber Monday Scams – And How to Avoid Them appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Just a few years ago when the topic of supporting offsite workers arose, some of the key conversation topics were related to purchase, logistics, deployment, maintenance and similar issues. The discussions back then were more like “special cases” vs. today’s environment where supporting workers offsite (now known as the hybrid workforce) has become a critical mainstream topic.

Now with the bulk of many organization’s workers off-premise, the topic of security and the ability of a security vendor to help support an organization’s hybrid workers has risen to the top of the selection criteria. In a soon to be released Cisco endpoint survey, it’s not surprising that the ability of a security vendor to make supporting the hybrid workforce easier and more efficient was the key motivating factor when organizations choose security solutions.

Today, when prospects and existing customers look at Cisco’s ability to support hybrid workers with our advanced security solution set and open platform, it’s quite clear that we can deliver on that promise. But, yes, good tools make it easier and more efficient, but the reality is that running a SOC or any security group, large or small, still takes a lot of work. Most organizations not only rely on advanced security tools but utilize a set of best practices to provide clarity of roles, efficiency of operation, and for the more prepared, have tested these best practices to prove to themselves that they are prepared for what’s next.
Knowing that not all organizations have this degree of security maturity and preparedness, we gathered a couple of subject matter experts together to discuss 5 areas of time-tested best practices that, besides the advanced tools offered by Cisco and others, can help your SOC (or small security team) yield actionable insights and guide you faster, and with more confidence, toward the outcomes you want.
In this webinar you will hear practical advice from Cisco technical marketing and a representative from our award winning Talos Threat Intelligence group, the same group who have created and are maintaining breach defense in partnership with Fortune 500 Security Operating Centers (SOC) around the globe.

You can expect to hear our 5 Best Practices recommendations on the following topics;
Check out our webinar to find out how you can become more security resilient and be better prepared for what’s next.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels
Today we’re examining some of the revelations in the Q3 Cisco Talos Incident Response Trends Report. This document is an anonymized look at of all the engagements that the Cisco Talos Incident Response team have been involved in over the previous three months. It also features threat intelligence from our team of researchers and analysts.
To start, take a watch of this episode of ThreatWise TV which explores how these trends have evolved since the previous quarter. Our guests also talk about incidents and cyber-attacks that they themselves have consulted on recently, including a particularly interesting insider threat case.
Ransomware returned as the top threat this quarter, after commodity trojans narrowly surpassed ransomware last quarter. Ransomware made up nearly 18 percent of all threats observed, up from 15 percent last quarter. Cisco Talos Incident Response (CTIR) observed high-profile families, such as Vice Society and Hive, as well as the newer family Blast Basta, which first emerged in April of this year.
Also noteworthy is the fact that CTIR saw an equal number in ransomware and pre- ransomware engagements this quarter, totalling nearly 40 percent of threats observed. Pre-ransomware is when we have observed a ransomware attack is about to happen, but the encryption of files has not yet taken place.
Pre-ransomware comprised 18 percent of threats this quarter, up from less than 5 percent previously. While it’s difficult to determine an adversary’s motivations if encryption does not take place, several behavioral characteristics bolster Talos’ confidence that ransomware may likely be the final objective. In these engagements adversaries were observed deploying frameworks such as Cobalt Strike and Mimikatz, alongside numerous enumeration and discovery techniques.
Commodity malware, such as the Qakbot banking trojan, was observed in multiple engagements this quarter. In one engagement, several compromised endpoints were seen communicating with IP addresses associated with Qakbot C2 traffic. This activity coincides with a general resurgence of Qakbot and its delivery of emerging ransomware families and offensive security frameworks that we have not previously observed Qakbot deploy. This comes at a time where competing email-based botnets like Emotet and Trickbot have suffered continued setbacks from law enforcement and tech companies.
Other threats this quarter include infostealers like Redline Stealer and Raccoon Stealer. Redline Stealer was observed across three engagements this quarter, two of which involved ransomware. The malware operators behind Raccoon introduced new functionality to the malware at the end of June, which likely contributed to its increased presence in engagements this quarter.
As infostealers have continued to rank highly in CTIR engagements, let’s explore them in a bit more detail.
Throughout the incidents discussed over the last few quarters, and CTIR engagements in general, information stealing plays a big part of the attackers’ TTPs.
From a high level, infostealers can be used to gain access a variety of sensitive information, such as contact information, financial details, and even intellectual property. The adversaries involved often proceed to exfiltrate this information and may then attempt to sell it in dark web forums, threaten to release it if a ransom isn’t paid, among other things.
While these instances can and do crop up in CTIR engagements, many of the infostealers seen in this space are used for accessing and collecting user credentials. Once an attacker has gained an initial foothold on a system, there are many places within an operating system that they can look for and collect credentials through the practice of credential dumping.
These stolen credentials may be offered up for sale on the dark web, alongside the stolen information mentioned above, but they can also prove to be a key weapon in an attacker’s arsenal. Their usefulness lies in one simple concept—why force your way into a system when you can just log in?
There are several advantages for bad actors that use this approach. Probably the most oblivious of these is that using pre-existing credentials is far more likely to go unnoticed than other more flagrant tactics an attacker can use. If part of the goal of an attack is to remain under the radar, activities carried out by “known users” are less likely to trigger security alerts when compared to tactics such as exploiting vulnerabilities or downloading malware binaries.
Adversaries tend to seek credentials with higher privileges, allowing them further control over the systems they compromise, with those including administrative access being the crown jewels.
User credentials can not only provide an attacker with means to elevate privileges and establish persistence on a system, but also to move laterally through a network. Some credentials, especially those with administrative privileges, can offer access to multiple systems throughout a network. By obtaining them, many more options become available to further an attack.
There are several threats involved in information stealing that appear repeatedly in CTIR engagements over the last few quarters.
Perhaps the most notorious is Mimikatz—a tool used to pull credentials from operating systems. Mimikatz is not malware per-se and can be useful for penetration testing and red team activities. But bad actors leverage it as well, and over the last few quarters CTIR has observed it being used in ransomware-as-a-service attacks, as well as pre-ransomware incidents.
CTIR has also observed Redline Stealer being utilized by adversaries in CTIR engagements across quarters. This infostealer has grown in popularity as a supplementary tool used alongside other malware. On more than one occasion, CTIR has identified stolen credentials on the dark web that claimed to have been obtained via Redline Stealer.
Other information stealers seen across the last few quarters include the Vidar information stealer, Raccoon Stealer, and SolarMaker, all of which have been used to further an adversary’s attacks.
Over the last several months, Talos has seen an increasing number of engagements involving insider threats. In one engagement this quarter, passwords were reset through a management console of a perimeter firewall that a disgruntled employee had access to.
The organization’s team changed all associated passwords but overlooked one administrative account. On the following day, someone logged in using that account, deleted all other accounts and firewall rules, and created one local account, likely to provide persistence.
You’ll hear Alexis Merritt, Incident Response Consultant for Cisco Talos, talk about this more in the ThreatWise TV episode.
To help protect against this threat when an individual leaves an organization, steps like disabling accounts and ensuring that connections to the enterprise remotely through VPN has been removed can be very valuable. Implementing a mechanism to wipe systems, especially for remote employees, is important as well.
For more on this topic, Cisco Secure recently put together a white paper on the Insider Threat Maturity FrameWork.
In several incidents over the last few quarters that involved information stealers, multi-factor authentication (MFA) was not properly implemented by the organizations impacted, providing adversaries an opportunity to infiltrate the networks. MFA tools like Cisco Secure Access by Duo can prevent attackers from successfully gaining access.
And finally, Cisco Advisory CISO Wolfgang Goerlich has created this storytelling video, to help people think about incident response in a new way:
Join the Cisco Talos Incident Response team for a live debrief of the Q3 report on 27th October.
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels
The concept of zero trust is not a new one, and some may even argue that the term is overused. In reality, however, its criticality is growing with each passing day. Why? Because many of today’s attacks begin with the user. According to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report, 82% of breaches involve the human element — whether it’s stolen credentials, phishing, misuse or error.
Additionally, today’s businesses are hyper-connected, meaning that — in addition to your employees — customers, partners and suppliers are all part of your ecosystem. Couple that with hybrid work, IoT, the move to the cloud, and more emboldened attackers, and organizational risk increases exponentially.
Adopting a zero trust model can dramatically reduce this risk by eliminating implicit trust. It has become so crucial, in fact, that several governments including the U.S., UK and Australia have released mandates and guidance for how organizations should deploy zero trust to improve national security.
However, because zero trust is more of a concept than a technology, and so many vendors use the term, organizations struggle with the best way to implement it. At Cisco, we believe you should take a holistic approach to zero trust, starting with what you have and adding on as you identify gaps in your defenses. And while layers of protection are necessary for powerful security, so is ease of use.
Zero trust plays a major role in building security resilience, or the ability to withstand unpredictable threats or changes and emerge stronger. Through zero trust, the identity and security posture of users, devices and applications are continuously checked and verified to prevent network intrusions — and to also limit impact if an unauthorized entity does gain access.
Organizations with high zero trust maturity are twice as likely to achieve business resilience.
– Cisco’s Guide to Zero Trust Maturity
Eliminating trust, however, doesn’t really conjure up images of user-friendly technology. No matter how necessary they are for the business, employees are unlikely to embrace security measures that make their jobs more cumbersome and time-consuming. Instead, they want fast, consistent access to any application no matter where they are or which device they are using.
That’s why Cisco is taking a different approach to zero trust — one that removes friction for the user. For example, with Cisco Secure Access by Duo, organizations can provide those connecting to their network with several quick, easy authentication options. This way, they can put in place multi-factor authentication (MFA) that frustrates attackers, not users.
Cisco Secure Access by Duo is a key pillar of zero trust security, providing industry-leading features for secure access, authentication and device monitoring. Duo is customizable, straightforward to use, and simple to set up. It enables the use of modern authentication methods including biometrics, passwordless and single sign-on (SSO) to help organizations advance zero trust without sacrificing user experience. Duo also provides the flexibility organizations need to enable secure remote access with or without a VPN connection.
During Cisco’s own roll-out of Duo to over 100,000 people, less than 1% of users contacted the help desk for assistance. On an annual basis, Duo is saving Cisco $3.4 million in employee productivity and $500,000 in IT help desk support costs. Furthermore, 86,000 potential compromises are averted by Duo each month.
La-Z-Boy, one of the world’s leading residential furniture producers, also wanted to defend its employees against cybersecurity breaches through MFA and zero trust. It needed a data security solution that worked agnostically, could grow with the company, and that was easy to roll out and implement.
“When COVID first hit and people were sent home to work remotely, we started seeing more hacking activity…” said Craig Vincent, director of IT infrastructure and operations at La-Z-Boy. “We were looking for opportunities to secure our environment with a second factor…. We knew that even post-pandemic we would need a hybrid solution.”
“It was very quick and easy to see where Duo fit into our environment quite well, and worked with any application or legacy app, while deploying quickly.” – Craig Vincent, Director of IT Infrastructure and Operations, La-Z-Boy
Today, Duo helps La-Z-Boy maintain a zero trust framework, stay compliant, and get clear visibility into what is connecting to its network and VPN. Zero trust helps La-Z-Boy secure its organization against threats such as phishing, stolen credentials and out-of-date devices that may be vulnerable to known exploits and malware.
As mentioned, zero trust is a framework, not a single product or technology. For zero trust to be truly effective, it must do four things:
Many technology companies may offer a single component of zero trust, or one aspect of protection, but Cisco’s robust networking and security expertise enables us to provide a holistic zero trust solution. Not only can we support all the steps above, but we can do so across your whole IT ecosystem.
Modern organizations are operating multi-environment ecosystems that include a mix of on-premises and cloud technologies from various vendors. Zero trust solutions should be able to protect across all this infrastructure, no matter which providers are in use. Protections should also extend from the network and cloud to users, devices, applications and data. With Cisco’s extensive security portfolio, operating on multiple clouds and platforms, zero trust controls can be embedded at every layer.
Depending on where you are in your security journey, embedding zero trust at every layer of your infrastructure may sound like a lofty endeavor. That’s why we meet customers where they are on their path to zero trust. Whether your first priority is to meet regulatory requirements, secure hybrid work, protect the cloud, or something else, we have the expertise to help you get started. We provide clear guidance and technologies for zero trust security mapped to established frameworks from organizations like CISA and NIST.
Much of our Cisco Secure portfolio can be used to build a successful zero trust framework, but some examples of what we offer include:
All of our technologies and services are backed by the unparalleled intelligence of Cisco Talos — so you always have up-to-date protection as you build your zero trust architecture. Additionally, our open, integrated security platform — Cisco SecureX — makes it simple to expand and scale your security controls, knowing they will work with your other technologies for more unified defenses.
As Italy’s leading insurance company, Sara Assicurazioni requires complete visibility into its extended network, including a multi-cloud architecture and hybrid workforce. The company has adopted a comprehensive zero trust strategy through Cisco Secure.
“Our decentralized users, endpoints, and cloud-based servers and workloads contribute to a large attack surface,” says Paolo Perrucci, director of information and communications technology architectures and operations at Sara Assicurazioni. “With Cisco, we have the right level of visibility on this surface.”
“The main reason we chose Cisco is that only Cisco can offer a global security solution rather than covering one specific point…. Thanks to Cisco Secure, I’m quite confident that our security posture is now many times better because we are leveraging more scalable, state-of-the-art security solutions.” – Luigi Vassallo, COO & CTO, Sara Assicurazioni
To learn more, explore our zero trust page and sign up for one of our free zero trust workshops.
Watch video: How Cisco implemented zero trust in just five months
We’d love to hear what you think. Ask a Question, Comment Below, and Stay Connected with Cisco Secure on social!
Cisco Secure Social Channels

Automobile manufacturer Toyota recently announced a data breach that may have exposed the emails of up to 300,000 customers for a period of nearly five years.
Toyota says the breach is the result of a subcontractor posting source code for Toyota’s “T-Connect” app on the software development platform GitHub in December 2017. This code included an access key to the data server that hosted the e-mail addresses and customer management numbers of T-Connect users. The publicly available source code was found on September 15th, 2022, at which time Toyota changed the access key.
Toyota customers affected by this data breach include T-Connect users who registered their email on the Toyota T-Connect site since July 2017.
According to Toyota’s announcement and apology no other personal information such as customer names, phone numbers, and credit cards were affected. (Note that this announcement was published in Japanese—you can use your browser to translate.)
The company further could not confirm whether this information was in fact accessed. However, the company could not deny the possibility that it was at some point during that five-year period.
Toyota said that it will individually send an apology and notification to the registered email address of any customer whose information may have been leaked.
Any time a data breach occurs, it means that your personal information could end up in the hands of a bad actor. Different pieces of personal information can be more useful to them than others. Some are directly useful, such as a Social Security Number or credit card information because they uniquely identify you. Others are indirectly helpful, like device IDs, browsing history, geolocation information, and internet protocol addresses. On their own, such information will not uniquely identify you. Yet with enough indirect information, and in the right combination, a bad actor could use them to piece together your identity.
In light of this, there are a few steps you can take to protect yourself in the aftermath of a data breach, which involves a combination of preventative steps and some monitoring on your part.
Given that email addresses may have been compromised, Toyota specifically warned its customers about the possibility of phishing attacks and other unsolicited emails that may contain malware or links to malicious sites. While it’s always wise to keep a skeptical eye open for unsolicited messages that ask you for information or that contain attachments you weren’t expecting, it’s particularly important after breaches. If you receive such emails, delete them, and don’t click on any links or attachments.
Also note that bad actors may launch phishing attacks where they pose as Toyota, all with the aim to steal personal information. Such emails can clearly look like a scam, such as when they include typos, grammatical errors, or sloppy graphics. Others can look far more sophisticated, almost like a legitimate email. Learning how to tell the two apart can take a little skill, and you can check out this quick read so you can spot and protect yourself from phishing scams.
A complete suite of online protection software can offer layers of extra security. In addition to more private and secure time online with a VPN, identity monitoring, and password management, it includes web browser protection that can block malicious and suspicious links that could lead you down the road to malware or a phishing scam—which antivirus protection can’t do alone. Additionally, we offer $1M identity theft coverage and support from a recovery pro, just in case.
As far as passwords go, strong and unique passwords are best, which means never reusing your passwords across different sites and platforms. Using a password manager will help you keep on top of it all, while also storing your passwords securely. Moreover, changing your passwords regularly may make a stolen password worthless because it’s out of date.
Because so many accounts use an email address as the username, and because email addresses were exposed in the Toyota leak, updating your passwords across your accounts can provide an extra level of protection.
While a strong and unique password is a good first line of defense, enabling two-factor authentication across your accounts will help your cause by providing an added layer of security. It’s increasingly common to see nowadays, where banks and all manner of online services will only allow access to your accounts after you’ve provided a one-time passcode sent to your email or smartphone. If your accounts support two-factor authentication, enable it.
An identity monitoring service can monitor everything from email addresses to IDs and phone numbers for signs of breaches so you can take action to secure your accounts before they’re used for identity theft. Personal information harvested from data breaches can end up on dark web marketplaces where it’s bought by other bad actors so they can launch their own attacks. McAfee’s monitors the dark web for your personal info and provides early alerts if your data is found on there, an average of 10 months ahead of similar services. We also provide guidance to help you act if your information is found.
As mentioned earlier, information stolen in a data breach may indirectly identify you. Yet when pieced together with other information, it can then directly identify you. Cad actors can complete this identity picture puzzle with information provided by data brokers that buy and sell personal information online. However, you can take some control over this. Our Personal Data Cleanup service scans high-risk data broker sites for your personal information and then helps you remove it—which denies bad actors the information they may need to commit identity theft.
If your personal information gets caught up in a data leak or breach, take the steps to protect yourself. Should that information get into the hands of bad actors, it could lead to follow-on attacks such as phishing attempts, account hacks, and, in extreme cases, identity crime.
Further, as in the case of Toyota, it can take months or even years for companies to discover leaks and breaches. From there, it can take yet longer before a company announces the leak or breach. Together, that leaves bad actors with plenty of opportunity to commit all kinds of identity crime in the meantime.
Because of this, taking preventative steps to secure and monitor your identity can help protect you from harm—even if your information wasn’t involved in an attack. With data leaks and breaches of all sizes now commonplace, a proactive stance offers far better protection than reactionary measures taken after the fact.
The post Toyota Data Breach Exposes Customer Data – What You Can Do to Protect Yourself appeared first on McAfee Blog.