A new breach involving data from nine million AT&T customers is a fresh reminder that your mobile provider likely collects and shares a great deal of information about where you go and what you do with your mobile device — unless and until you affirmatively opt out of this data collection. Here’s a primer on why you might want to do that, and how.

Image: Shutterstock
Telecommunications giant AT&T disclosed this month that a breach at a marketing vendor exposed certain account information for nine million customers. AT&T said the data exposed did not include sensitive information, such as credit card or Social Security numbers, or account passwords, but was limited to “Customer Proprietary Network Information” (CPNI), such as the number of lines on an account.
Certain questions may be coming to mind right now, like “What the heck is CPNI?” And, ‘If it’s so ‘customer proprietary,’ why is AT&T sharing it with marketers?” Also maybe, “What can I do about it?” Read on for answers to all three questions.
AT&T’s disclosure said the information exposed included customer first name, wireless account number, wireless phone number and email address. In addition, a small percentage of customer records also exposed the rate plan name, past due amounts, monthly payment amounts and minutes used.
CPNI refers to customer-specific “metadata” about the account and account usage, and may include:
-Called phone numbers
-Time of calls
-Length of calls
-Cost and billing of calls
-Service features
-Premium services, such as directory call assistance
According to a succinct CPNI explainer at TechTarget, CPNI is private and protected information that cannot be used for advertising or marketing directly.
“An individual’s CPNI can be shared with other telecommunications providers for network operating reasons,” wrote TechTarget’s Gavin Wright. “So, when the individual first signs up for phone service, this information is automatically shared by the phone provider to partner companies.”
Is your mobile Internet usage covered by CPNI laws? That’s less clear, as the CPNI rules were established before mobile phones and wireless Internet access were common. TechTarget’s CPNI primer explains:
“Under current U.S. law, cellphone use is only protected as CPNI when it is being used as a telephone. During this time, the company is acting as a telecommunications provider requiring CPNI rules. Internet use, websites visited, search history or apps used are not protected CPNI because the company is acting as an information services provider not subject to these laws.”
Hence, the carriers can share and sell this data because they’re not explicitly prohibited from doing so. All three major carriers say they take steps to anonymize the customer data they share, but researchers have shown it is not terribly difficult to de-anonymize supposedly anonymous web-browsing data.
“Your phone, and consequently your mobile provider, know a lot about you,” wrote Jack Morse for Mashable. “The places you go, apps you use, and the websites you visit potentially reveal all kinds of private information — e.g. religious beliefs, health conditions, travel plans, income level, and specific tastes in pornography. This should bother you.”
Happily, all of the U.S. carriers are required to offer customers ways to opt out of having data about how they use their devices shared with marketers. Here’s a look at some of the carrier-specific practices and opt-out options.
AT&T’s policy says it shares device or “ad ID”, combined with demographics including age range, gender, and ZIP code information with third parties which explicitly include advertisers, programmers, and networks, social media networks, analytics firms, ad networks and other similar companies that are involved in creating and delivering advertisements.
AT&T said the data exposed on 9 million customers was several years old, and mostly related to device upgrade eligibility. This may sound like the data went to just one of its partners who experienced a breach, but in all likelihood it also went to hundreds of AT&T’s partners.
AT&T’s CPNI opt-out page says it shares CPNI data with several of its affiliates, including WarnerMedia, DirecTV and Cricket Wireless. Until recently, AT&T also shared CPNI data with Xandr, whose privacy policy in turn explains that it shares data with hundreds of other advertising firms. Microsoft bought Xandr from AT&T last year.
According to the Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC), T-Mobile seems to be the only company out of the big three to extend to all customers the rights conferred by the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
EPIC says T-Mobile customer data sold to third parties uses another unique identifier called mobile advertising IDs or “MAIDs.” T-Mobile claims that MAIDs don’t directly identify consumers, but under the CCPA MAIDs are considered “personal information” that can be connected to IP addresses, mobile apps installed or used with the device, any video or content viewing information, and device activity and attributes.
T-Mobile customers can opt out by logging into their account and navigating to the profile page, then to “Privacy and Notifications.” From there, toggle off the options for “Use my data for analytics and reporting” and “Use my data to make ads more relevant to me.”
Verizon’s privacy policy says it does not sell information that personally identities customers (e.g., name, telephone number or email address), but it does allow third-party advertising companies to collect information about activity on Verizon websites and in Verizon apps, through MAIDs, pixels, web beacons and social network plugins.
According to Wired.com’s tutorial, Verizon users can opt out by logging into their Verizon account through a web browser or the My Verizon mobile app. From there, select the Account tab, then click Account Settings and Privacy Settings on the web. For the mobile app, click the gear icon in the upper right corner and then Manage Privacy Settings.
On the privacy preferences page, web users can choose “Don’t use” under the Custom Experience section. On the My Verizon app, toggle any green sliders to the left.
EPIC notes that all three major carriers say resetting the consumer’s device ID and/or clearing cookies in the browser will similarly reset any opt-out preferences (i.e., the customer will need to opt out again), and that blocking cookies by default may also block the opt-out cookie from being set.
T-Mobile says its opt out is device-specific and/or browser-specific. “In most cases, your opt-out choice will apply only to the specific device or browser on which it was made. You may need to separately opt out from your other devices and browsers.”
Both AT&T and Verizon offer opt-in programs that gather and share far more information, including device location, the phone numbers you call, and which sites you visit using your mobile and/or home Internet connection. AT&T calls this their Enhanced Relevant Advertising Program; Verizon’s is called Custom Experience Plus.
In 2021, multiple media outlets reported that some Verizon customers were being automatically enrolled in Custom Experience Plus — even after those customers had already opted out of the same program under its previous name — “Verizon Selects.”
If none of the above opt out options work for you, at a minimum you should be able to opt out of CPNI sharing by calling your carrier, or by visiting one of their stores.
Why should you opt out of sharing CPNI data? For starters, some of the nation’s largest wireless carriers don’t have a great track record in terms of protecting the sensitive information that you give them solely for the purposes of becoming a customer — let alone the information they collect about your use of their services after that point.
In January 2023, T-Mobile disclosed that someone stole data on 37 million customer accounts, including customer name, billing address, email, phone number, date of birth, T-Mobile account number and plan details. In August 2021, T-Mobile acknowledged that hackers made off with the names, dates of birth, Social Security numbers and driver’s license/ID information on more than 40 million current, former or prospective customers who applied for credit with the company.
Last summer, a cybercriminal began selling the names, email addresses, phone numbers, SSNs and dates of birth on 23 million Americans. An exhaustive analysis of the data strongly suggested it all belonged to customers of one AT&T company or another. AT&T stopped short of saying the data wasn’t theirs, but said the records did not appear to have come from its systems and may be tied to a previous data incident at another company.
However frequently the carriers may alert consumers about CPNI breaches, it’s probably nowhere near often enough. Currently, the carriers are required to report a consumer CPNI breach only in cases “when a person, without authorization or exceeding authorization, has intentionally gained access to, used or disclosed CPNI.”
But that definition of breach was crafted eons ago, back when the primary way CPNI was exposed was through “pretexting,” such when the phone company’s employees are tricked into giving away protected customer data.
In January, regulators at the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) proposed amending the definition of “breach” to include things like inadvertent disclosure — such as when companies expose CPNI data on a poorly-secured server in the cloud. The FCC is accepting public comments on the matter until March 24, 2023.
While it’s true that the leak of CPNI data does not involve sensitive information like Social Security or credit card numbers, one thing AT&T’s breach notice doesn’t mention is that CPNI data — such as balances and payments made — can be abused by fraudsters to make scam emails and text messages more believable when they’re trying to impersonate AT&T and phish AT&T customers.
The other problem with letting companies share or sell your CPNI data is that the wireless carriers can change their privacy policies at any time, and you are assumed to be okay with those changes as long as you keep using their services.
For example, location data from your wireless device is most definitely CPNI, and yet until very recently all of the major carriers sold their customers’ real-time location data to third party data brokers without customer consent.
What was their punishment? In 2020, the FCC proposed fines totaling $208 million against all of the major carriers for selling their customers’ real-time location data. If that sounds like a lot of money, consider that all of the major wireless providers reported tens of billions of dollars in revenue last year (e.g., Verizon’s consumer revenue alone was more than $100 billion last year).
If the United States had federal privacy laws that were at all consumer-friendly and relevant to today’s digital economy, this kind of data collection and sharing would always be opt-in by default. In such a world, the enormously profitable wireless industry would likely be forced to offer clear financial incentives to customers who choose to share this information.
But until that day arrives, understand that the carriers can change their data collection and sharing policies when it suits them. And regardless of whether you actually read any notices about changes to their privacy policies, you will have agreed to those changes as long as you continue using their service.
The U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) this week arrested a New York man on suspicion of running BreachForums, a popular English-language cybercrime forum where some of the world biggest hacked databases routinely show up for sale. The forum’s administrator “Pompompurin” has been a thorn in the side of the FBI for years, and BreachForums is widely considered a reincarnation of RaidForums, a remarkably similar crime forum that the FBI infiltrated and dismantled in 2022.
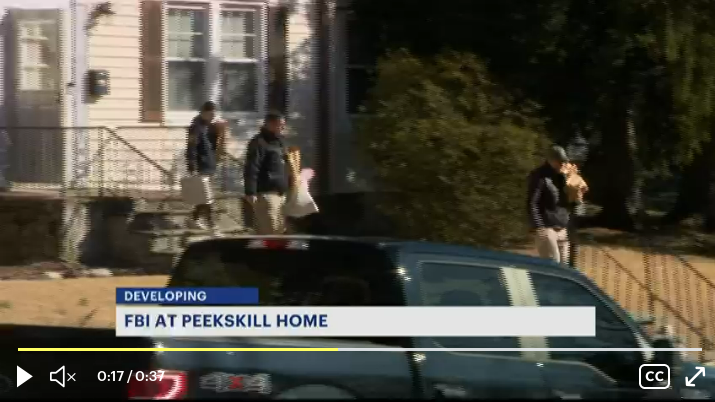
Federal agents carting items out of Fitzpatrick’s home on March 15. Image: News 12 Westchester.
In an affidavit filed with the District Court for the Southern District of New York, FBI Special Agent John Longmire said that at around 4:30 p.m. on March 15, 2023, he led a team of law enforcement agents that made a probable cause arrest of a Conor Brian Fitzpatrick in Peekskill, NY.
“When I arrested the defendant on March 15, 2023, he stated to me in substance and in part that: a) his name was Conor Brian Fitzpatrick; b) he used the alias ‘pompompurin/’ and c) he was the owner and administrator of ‘BreachForums’ the data breach website referenced in the Complaint,” Longmire wrote.
Pompompurin has been something of a nemesis to the FBI for several years. In November 2021, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that thousands of fake emails about a cybercrime investigation were blasted out from the FBI’s email systems and Internet addresses.
Pompompurin took credit for that stunt, and said he was able to send the FBI email blast by exploiting a flaw in an FBI portal designed to share information with state and local law enforcement authorities. The FBI later acknowledged that a software misconfiguration allowed someone to send the fake emails.
In December, 2022, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that hackers active on BreachForums had infiltrated the FBI’s InfraGard program, a vetted FBI program designed to build cyber and physical threat information sharing partnerships with experts in the private sector. The hackers impersonated the CEO of a major financial company, applied for InfraGard membership in the CEO’s name, and were granted admission to the community.
From there, the hackers plundered the InfraGard member database, and proceeded to sell contact information on more than 80,000 InfraGard members in an auction on BreachForums. The FBI responded by disabling the portal for some time, before ultimately forcing all InfraGard members to re-apply for membership.
More recently, BreachForums was the sales forum for data stolen from DC Health Link, a health insurance exchange based in Washington, D.C. that suffered a data breach this month. The sales thread initially said the data included the names, Social Security numbers, dates of birth, health plan and enrollee information and more on 170,000 individuals, although the official notice about the breach says 56,415 people were affected.
In April 2022, U.S. Justice Department seized the servers and domains for RaidForums, an extremely popular English-language cybercrime forum that sold access to more than 10 billion consumer records stolen in some of the world’s largest data breaches since 2015. As part of that operation, the feds also charged the alleged administrator, 21-year-old Diogo Santos Coelho of Portugal, with six criminal counts.
Coelho was arrested in the United Kingdom on Jan. 31, 2022. By that time, the new BreachForums had been live for just under a week, but with a familiar look.
BreachForums remains accessible online, and from reviewing the live chat stream on the site’s home page it appears the forum’s active users are only just becoming aware that their administrator — and the site’s database — is likely now in FBI hands:
“Wait if they arrested pom then doesn’t the FBI have all of our details we’ve registered with?” asked one worried BreachForums member.
“But we all have good VPNs I guess, right…right guys?” another denizen offered.
“Like pom would most likely do a plea bargain and cooperate with the feds as much as possible,” replied another.
Fitzpatrick could not be immediately reached for comment. The FBI declined to comment for this story.
There is only one page to the criminal complaint against Fitzpatrick (PDF), which charges him with one count of conspiracy to commit access device fraud. The affidavit on his arrest is available here (PDF).
Update: Corrected spelling of FBI agent’s last name.
Two U.S. men have been charged with hacking into a U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) online portal that taps into 16 different federal law enforcement databases. Both are alleged to be part of a larger criminal organization that specializes in using fake emergency data requests from compromised police and government email accounts to publicly threaten and extort their victims.

Prosecutors for the Eastern District of New York today unsealed criminal complaints against Sagar Steven Singh — a.k.a “Weep” — a 19-year-old from Pawtucket, Rhode Island; and Nicholas Ceraolo, 25, of Queens, NY, who allegedly went by the handles “Convict” and “Ominus.”
The Justice Department says Singh and Ceraolo belong to a group of cybercriminals known to its members as “ViLE,” who specialize in obtaining personal information about third-party victims, which they then use to harass, threaten or extort the victims, a practice known as “doxing.”
“ViLE is collaborative, and the members routinely share tactics and illicitly obtained information with each other,” prosecutors charged.
The government alleges the defendants and other members of ViLE use various methods to obtain victims’ personal information, including:
-tricking customer service employees;
-submitting fraudulent legal process to social media companies to elicit users’ registration information;
-co-opting and corrupting corporate insiders;
-searching public and private online databases;
-accessing a nonpublic United States government database without authorization
-unlawfully using official email accounts belonging to other countries.
The complaint says once they obtained a victim’s information, Singh and Ceraolo would post the information in an online forum. The government refers to this community only as “Forum-1,” saying that it is administered by the leader of ViLE (referenced in the complaint as “CC-1”).
“Victims are extorted into paying CC-1 to have their information removed from Forum-1,” prosecutors allege. “Singh also uses the threat of revealing personal information to extort victims into giving him access to their social media accounts, which Singh then resells.”
Sources tell KrebsOnSecurity in addition to being members of ViLE, both Weep and Ominous are or were staff members for Doxbin, a highly toxic online community that provides a forum for digging up personal information on people and posting it publicly. This is supported by the Doxbin administrator’s claimed responsibility for a high-profile intrusion at the DEA’s law enforcement data sharing portal last year.
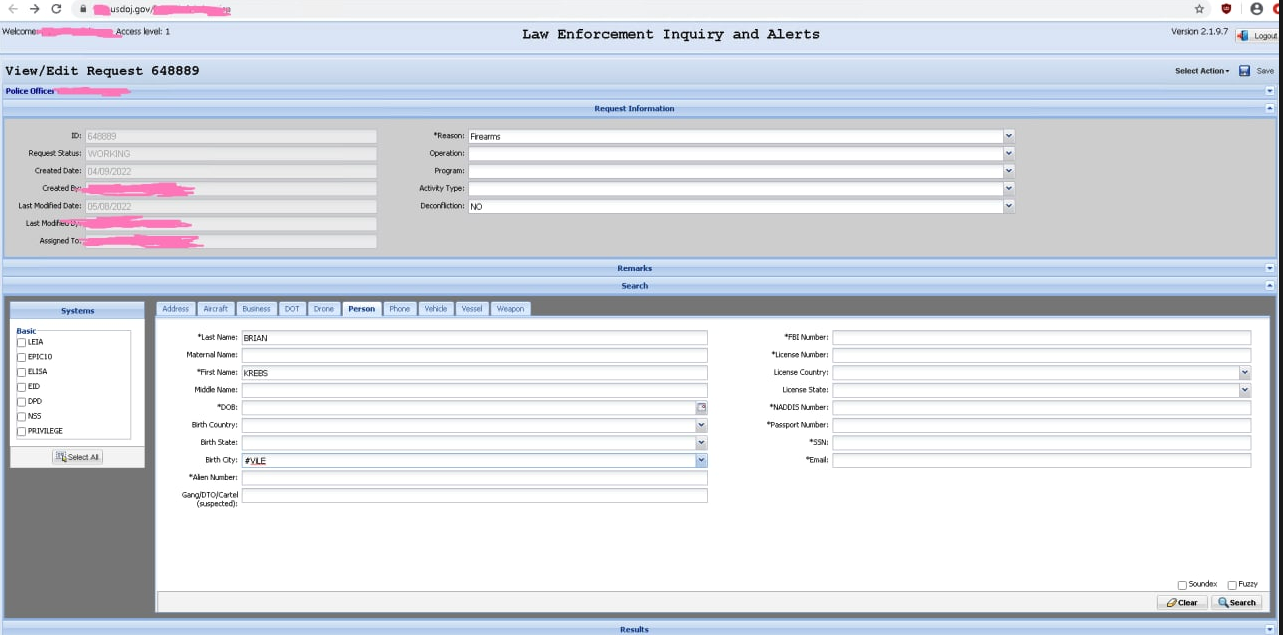
A screenshot of alleged access to the Drug Enforcement Agency’s intelligence sharing portal, shared by “KT,” the current administrator of the doxing and harassment community Doxbin.
The government alleges that on May 7, 2022, Singh used stolen credentials to log into a U.S. federal government portal without authorization. The complaint doesn’t specify which agency portal was hacked, but it does state that the portal included access to law enforcement databases that track narcotics seizures in the United States.
On May 12, 2022, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that hackers had gained access to a DEA portal that taps into 16 different federal law enforcement databases. As reported at the time, the inside scoop on how that hack went down came from KT, the current administrator of the Doxbin and the individual referenced in the government’s complaint as “CC-1.”
Indeed, a screenshot of the ViLE group website includes the group’s official roster, which lists KT at the top, followed by Weep and Ominus.

A screenshot of the website for the cybercriminal group “ViLE.” Image: USDOJ.
In March 2022, KrebsOnSecurity warned that multiple cybercrime groups were finding success with fraudulent Emergency Data Requests (EDRs), wherein the hackers use compromised police and government email accounts to file warrantless data requests with social media firms and mobile telephony providers, attesting that the information being requested can’t wait for a warrant because it relates to an urgent matter of life and death.
That story showed that the previous owner of the Doxbin also was part of a teenage hacking group that specialized in offering fake EDRs as a service on the dark web.
Prosecutors say they tied Singh to the government portal hack because he connected to it from an Internet address that he’d previously used to access a social media account registered in his name. When they raided Singh’s residence on Sept. 8, 2022 and seized his devices, investigators with Homeland Security found a cellular phone and laptop that allegedly “contained extensive evidence of access to the Portal.”
The complaint alleges that between February 2022 and May 2022, Ceraolo used an official email account belonging to a Bangladeshi police official to pose as a police officer in communication with U.S.-based social media platforms.
“In these communications, Ceraolo requested personal information about users of these platforms, under the false pretense that the users were committing crimes or in life-threatening danger,” the complaint states.
For example, on or about March 13, 2022, Ceraolo allegedly used the Bangladeshi police email account to falsely claim that the target of the EDR had sent bomb threats, distributed child pornography and threatened officials of the Bangladeshi government.
On or about May 9, 2022, the government says, Singh sent a friend screenshots of text messages between himself and someone he had doxed on the Doxbin and was trying to extort for their Instagram handle. The data included the victim’s Social Security number, driver’s license number, cellphone number, and home address.
“Look familiar?” Singh allegedly wrote to the victim. “You’re gonna comply to me if you don’t want anything negative to happen to your parents. . . I have every detail involving your parents . . . allowing me to do whatever I desire to them in malicious ways.”
Neither of the defendants could be immediately reached for comment. KT, the current administrator of Doxbin, declined a request for comment on the charges.
Ceraolo is a self-described security researcher who has been credited in many news stories over the years with discovering security vulnerabilities at AT&T, T-Mobile, Comcast and Cox Communications.
Ceraolo’s stated partner in most of these discoveries — a 30-year-old Connecticut man named Ryan “Phobia” Stevenson — was charged in 2019 with being part of a group that stole millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrencies via SIM-swapping, a crime that involves tricking a mobile provider into routing a target’s calls and text messages to another device.
In 2018, KrebsOnSecurity detailed how Stevenson earned bug bounty rewards and public recognition from top telecom companies for finding and reporting security holes in their websites, all the while secretly peddling those same vulnerabilities to cybercriminals.
According to the Justice Department, if convicted Ceraolo faces up to 20 years’ imprisonment for conspiracy to commit wire fraud; both Ceraolo and Singh face five years’ imprisonment for conspiracy to commit computer intrusions.
A copy of the complaint against Ceraolo and Singh is here (PDF).
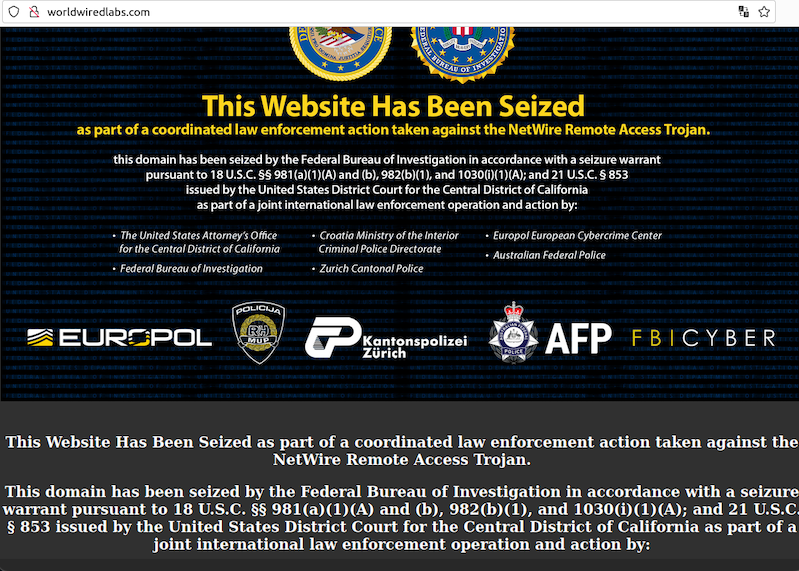
A Croatian national has been arrested for allegedly operating NetWire, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) marketed on cybercrime forums since 2012 as a stealthy way to spy on infected systems and siphon passwords. The arrest coincided with a seizure of the NetWire sales website by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). While the defendant in this case hasn’t yet been named publicly, the NetWire website has been leaking information about the likely true identity and location of its owner for the past 11 years.
Typically installed by booby-trapped Microsoft Office documents and distributed via email, NetWire is a multi-platform threat that is capable of targeting not only Microsoft Windows machines but also Android, Linux and Mac systems.
NetWire’s reliability and relatively low cost ($80-$140 depending on features) has made it an extremely popular RAT on the cybercrime forums for years, and NetWire infections consistently rank among the top 10 most active RATs in use.
NetWire has been sold openly on the same website since 2012: worldwiredlabs[.]com. That website now features a seizure notice from the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), which says the domain was taken as part of “a coordinated law enforcement action taken against the NetWire Remote Access Trojan.”
“As part of this week’s law enforcement action, authorities in Croatia on Tuesday arrested a Croatian national who allegedly was the administrator of the website,” reads a statement by the DOJ today. “This defendant will be prosecuted by Croatian authorities. Additionally, law enforcement in Switzerland on Tuesday seized the computer server hosting the NetWire RAT infrastructure.”
Neither the DOJ’s statement nor a press release on the operation published by Croatian authorities mentioned the name of the accused. But it’s fairly remarkable that it has taken so long for authorities in the United States and elsewhere to move against NetWire and its alleged proprietor, given that the RAT’s author apparently did very little to hide his real-life identity.
The WorldWiredLabs website first came online in February 2012 using a dedicated host with no other domains. The site’s true WHOIS registration records have always been hidden by privacy protection services, but there are plenty of clues in historical Domain Name System (DNS) records for WorldWiredLabs that point in the same direction.
In October 2012, the WorldWiredLabs domain moved to another dedicated server at the Internet address 198.91.90.7, which was home to just one other domain: printschoolmedia[.]org, also registered in 2012.
According to DomainTools.com, printschoolmedia[.]org was registered to a Mario Zanko in Zapresic, Croatia, and to the email address zankomario@gmail.com. DomainTools further shows this email address was used to register one other domain in 2012: wwlabshosting[.]com, also registered to Mario Zanko from Croatia.
A review of DNS records for both printschoolmedia[.]org and wwlabshosting[.]com shows that while these domains were online they both used the DNS name server ns1.worldwiredlabs[.]com. No other domains have been recorded using that same name server.

The WorldWiredLabs website, in 2013. Source: Archive.org.
DNS records for worldwiredlabs[.]com also show the site forwarded incoming email to the address tommaloney@ruggedinbox.com. Constella Intelligence, a service that indexes information exposed by public database leaks, shows this email address was used to register an account at the clothing retailer romwe.com, using the password “123456xx.”
Running a reverse search on this password in Constella Intelligence shows there are more than 450 email addresses known to have used this credential, and two of those are zankomario@gmail.com and zankomario@yahoo.com.
A search on zankomario@gmail.com in Skype returns three results, including the account name “Netwire” and the username “Dugidox,” and another for a Mario Zanko (username zanko.mario).
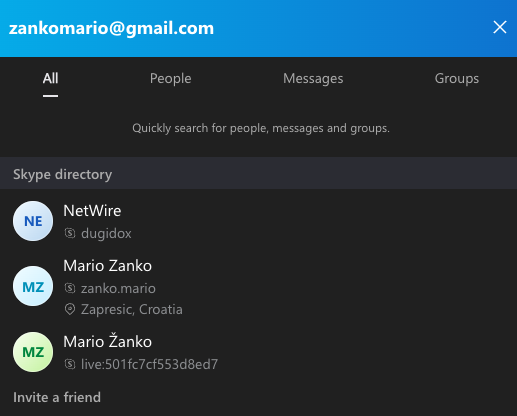 Dugidox corresponds to the hacker handle most frequently associated with NetWire sales and support discussion threads on multiple cybercrime forums over the years.
Dugidox corresponds to the hacker handle most frequently associated with NetWire sales and support discussion threads on multiple cybercrime forums over the years.
Constella ties dugidox@gmail.com to a number of website registrations, including the Dugidox handle on BlackHatWorld and HackForums, and to IP addresses in Croatia for both. Constella also shows the email address zankomario@gmail.com used the password “dugidox2407.”
In 2010, someone using the email address dugidox@gmail.com registered the domain dugidox[.]com. The WHOIS registration records for that domain list a “Senela Eanko” as the registrant, but the address used was the same street address in Zapresic that appears in the WHOIS records for printschoolmedia[.]org, which is registered in Mr. Zanco’s name.
Prior to the demise of Google+, the email address dugidox@gmail.com mapped to an account with the nickname “Netwire wwl.” The dugidox email also was tied to a Facebook account (mario.zanko3), which featured check-ins and photos from various places in Croatia.
That Facebook profile is no longer active, but back in January 2017, the administrator of WorldWiredLabs posted that he was considering adding certain Android mobile functionality to his service. Three days after that, the Mario.Zank3 profile posted a photo saying he was selected for an Android instruction course — with his dugidox email in the photo, naturally.
Incorporation records from the U.K.’s Companies House show that in 2017 Mr. Zanko became an officer in a company called Godbex Solutions LTD. A Youtube video invoking this corporate name describes Godbex as a “next generation platform” for exchanging gold and cryptocurrencies.
The U.K. Companies House records show Godbex was dissolved in 2020. It also says Mr. Zanko was born in July 1983, and lists his occupation as “electrical engineer.”
Mr. Zanko did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
A statement from the Croatian police about the NetWire takedown is here.
The domain name registrar Freenom, whose free domain names have long been a draw for spammers and phishers, has stopped allowing new domain name registrations. The move comes after the Dutch registrar was sued by Meta, which alleges the company ignores abuse complaints about phishing websites while monetizing traffic to those abusive domains.
Freenom is the domain name registry service provider for five so-called “country code top level domains” (ccTLDs), including .cf for the Central African Republic; .ga for Gabon; .gq for Equatorial Guinea; .ml for Mali; and .tk for Tokelau.
Freenom has always waived the registration fees for domains in these country-code domains, presumably as a way to encourage users to pay for related services, such as registering a .com or .net domain, for which Freenom does charge a fee.
On March 3, 2023, social media giant Meta sued Freenom in a Northern California court, alleging cybersquatting violations and trademark infringement. The lawsuit also seeks information about the identities of 20 different “John Does” — Freenom customers that Meta says have been particularly active in phishing attacks against Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp users.
The lawsuit points to a 2021 study (PDF) on the abuse of domains conducted by Interisle Consulting Group, which discovered that those ccTLDs operated by Freenom made up five of the Top Ten TLDs most abused by phishers.
“The five ccTLDs to which Freenom provides its services are the TLDs of choice for cybercriminals because Freenom provides free domain name registration services and shields its customers’ identity, even after being presented with evidence that the domain names are being used for illegal purposes,” the complaint charges. “Even after receiving notices of infringement or phishing by its customers, Freenom continues to license new infringing domain names to those same customers.”
Meta further alleges that “Freenom has repeatedly failed to take appropriate steps to investigate and respond appropriately to reports of abuse,” and that it monetizes the traffic from infringing domains by reselling them and by adding “parking pages” that redirect visitors to other commercial websites, websites with pornographic content, and websites used for malicious activity like phishing.
Freenom has not yet responded to requests for comment. But attempts to register a domain through the company’s website as of publication time generated an error message that reads:
“Because of technical issues the Freenom application for new registrations is temporarily out-of-order. Please accept our apologies for the inconvenience. We are working on a solution and hope to resume operations shortly. Thank you for your understanding.”
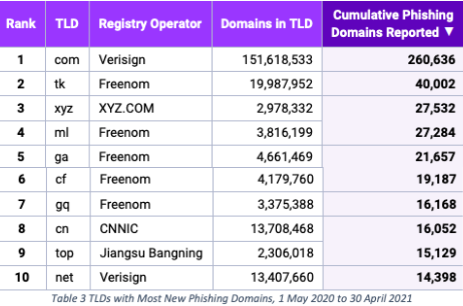
Image: Interisle Consulting Group, Phishing Landscape 2021, Sept. 2021.
Although Freenom is based in The Netherlands, some of its other sister companies named as defendants in the lawsuit are incorporated in the United States.
Meta initially filed this lawsuit in December 2022, but it asked the court to seal the case, which would have restricted public access to court documents in the dispute. That request was denied, and Meta amended and re-filed the lawsuit last week.
According to Meta, this isn’t just a case of another domain name registrar ignoring abuse complaints because it’s bad for business. The lawsuit alleges that the owners of Freenom “are part of a web of companies created to facilitate cybersquatting, all for the benefit of Freenom.”
“On information and belief, one or more of the ccTLD Service Providers, ID Shield, Yoursafe, Freedom Registry, Fintag, Cervesia, VTL, Joost Zuurbier Management Services B.V., and Doe Defendants were created to hide assets, ensure unlawful activity including cybersquatting and phishing goes undetected, and to further the goals of Freenom,” Meta charged.
It remains unclear why Freenom has stopped allowing domain registration. In June 2015, ICANN suspended Freenom’s ability to create new domain names or initiate inbound transfers of domain names for 90 days. According to Meta, the suspension was premised on ICANN’s determination that Freenom “has engaged in a pattern and practice of trafficking in or use of domain names identical or confusingly similar to a trademark or service mark of a third party in which the Registered Name Holder has no rights or legitimate interest.”
A spokesperson for ICANN said the organization has no insight as to why Freenom might have stopped registering domain names. But it said Freenom (d/b/a OpenTLD B.V.) also received formal enforcement notices from ICANN in 2017 and 2020 for violating different obligations.
A copy of the amended complaint against Freenom, et. al, is available here (PDF).
March 8, 6:11 p.m. ET: Updated story with response from ICANN. Corrected attribution of the domain abuse report.
The Biden administration today issued its vision for beefing up the nation’s collective cybersecurity posture, including calls for legislation establishing liability for software products and services that are sold with little regard for security. The White House’s new national cybersecurity strategy also envisions a more active role by cloud providers and the U.S. military in disrupting cybercriminal infrastructure, and it names China as the single biggest cyber threat to U.S. interests.

The strategy says the White House will work with Congress and the private sector to develop legislation that would prevent companies from disavowing responsibility for the security of their software products or services.
Coupled with this stick would be a carrot: An as-yet-undefined “safe harbor framework” that would lay out what these companies could do to demonstrate that they are making cybersecurity a central concern of their design and operations.
“Any such legislation should prevent manufacturers and software publishers with market power from fully disclaiming liability by contract, and establish higher standards of care for software in specific high-risk scenarios,” the strategy explains. “To begin to shape standards of care for secure software development, the Administration will drive the development of an adaptable safe harbor framework to shield from liability companies that securely develop and maintain their software products and services.”
Brian Fox, chief technology officer and founder of the software supply chain security firm Sonatype, called the software liability push a landmark moment for the industry.
“Market forces are leading to a race to the bottom in certain industries, while contract law allows software vendors of all kinds to shield themselves from liability,” Fox said. “Regulations for other industries went through a similar transformation, and we saw a positive result — there’s now an expectation of appropriate due care, and accountability for those who fail to comply. Establishing the concept of safe harbors allows the industry to mature incrementally, leveling up security best practices in order to retain a liability shield, versus calling for sweeping reform and unrealistic outcomes as previous regulatory attempts have.”
In 2012 (approximately three national cyber strategies ago), then director of the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Keith Alexander made headlines when he remarked that years of successful cyber espionage campaigns from Chinese state-sponsored hackers represented “the greatest transfer of wealth in history.”
The document released today says the People’s Republic of China (PRC) “now presents the broadest, most active, and most persistent threat to both government and private sector networks,” and says China is “the only country with both the intent to reshape the international order and, increasingly, the economic, diplomatic, military, and technological power to do so.”
Many of the U.S. government’s efforts to restrain China’s technology prowess involve ongoing initiatives like the CHIPS Act, a new law signed by President Biden last year that sets aside more than $50 billion to expand U.S.-based semiconductor manufacturing and research and to make the U.S. less dependent on foreign suppliers; the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative; and the National Strategy to Secure 5G.
As the maker of most consumer gizmos with a computer chip inside, China is also the source of an incredible number of low-cost Internet of Things (IoT) devices that are not only poorly secured, but are probably more accurately described as insecure by design.
The Biden administration said it would continue its previously announced plans to develop a system of labeling that could be applied to various IoT products and give consumers some idea of how secure the products may be. But it remains unclear how those labels might apply to products made by companies outside of the United States.
One could convincingly make the case that the world has witnessed yet another historic transfer of wealth and trade secrets over the past decade — in the form of ransomware and data ransom attacks by Russia-based cybercriminal syndicates, as well as Russian intelligence agency operations like the U.S. government-wide Solar Winds compromise.

On the ransomware front, the White House strategy seems to focus heavily on building the capability to disrupt the digital infrastructure used by adversaries that are threatening vital U.S. cyber interests. The document points to the 2021 takedown of the Emotet botnet — a cybercrime machine that was heavily used by multiple Russian ransomware groups — as a model for this activity, but says those disruptive operations need to happen faster and more often.
To that end, the Biden administration says it will expand the capacity of the National Cyber Investigative Joint Task Force (NCIJTF), the primary federal agency for coordinating cyber threat investigations across law enforcement agencies, the intelligence community, and the Department of Defense.
“To increase the volume and speed of these integrated disruption campaigns, the Federal Government must further develop technological and organizational platforms that enable continuous, coordinated operations,” the strategy observes. “The NCIJTF will expand its capacity to coordinate takedown and disruption campaigns with greater speed, scale, and frequency. Similarly, DoD and the Intelligence Community are committed to bringing to bear their full range of complementary authorities to disruption campaigns.”
The strategy anticipates the U.S. government working more closely with cloud and other Internet infrastructure providers to quickly identify malicious use of U.S.-based infrastructure, share reports of malicious use with the government, and make it easier for victims to report abuse of these systems.
“Given the interest of the cybersecurity community and digital infrastructure owners and operators in continuing this approach, we must sustain and expand upon this model so that collaborative disruption operations can be carried out on a continuous basis,” the strategy argues. “Threat specific collaboration should take the form of nimble, temporary cells, comprised of a small number of trusted operators, hosted and supported by a relevant hub. Using virtual collaboration platforms, members of the cell would share information bidirectionally and work rapidly to disrupt adversaries.”
But here, again, there is a carrot-and-stick approach: The administration said it is taking steps to implement Executive Order (EO) 13984 –issued by the Trump administration in January 2021 — which requires cloud providers to verify the identity of foreign persons using their services.
“All service providers must make reasonable attempts to secure the use of their infrastructure against abuse or other criminal behavior,” the strategy states. “The Administration will prioritize adoption and enforcement of a risk-based approach to cybersecurity across Infrastructure-as-a-Service providers that addresses known methods and indicators of malicious activity including through implementation of EO 13984.”
Ted Schlein, founding partner of the cybersecurity venture capital firm Ballistic Ventures, said how this gets implemented will determine whether it can be effective.
“Adversaries know the NSA, which is the elite portion of the nation’s cyber defense, cannot monitor U.S.-based infrastructure, so they just use U.S.-based cloud infrastructure to perpetrate their attacks,” Schlein said. “We have to fix this. I believe some of this section is a bit pollyannaish, as it assumes a bad actor with a desire to do a bad thing will self-identify themselves, as the major recommendation here is around KYC (‘know your customer’).”
One brief but interesting section of the strategy titled “Explore a Federal Cyber Insurance Backdrop” contemplates the government’s liability and response to a too-big-to-fail scenario or “catastrophic cyber incident.”
“We will explore how the government can stabilize insurance markets against catastrophic risk to drive better cybersecurity practices and to provide market certainty when catastrophic events do occur,” the strategy reads.
When the Bush administration released the first U.S. national cybersecurity strategy 20 years ago after the 9/11 attacks, the popular term for that same scenario was a “digital Pearl Harbor,” and there was a great deal of talk then about how the cyber insurance market would soon help companies shore up their cybersecurity practices.
In the wake of countless ransomware intrusions, many companies now hold cybersecurity insurance to help cover the considerable costs of responding to such intrusions. Leaving aside the question of whether insurance coverage has helped companies improve security, what happens if every one of these companies has to make a claim at the same time?
The notion of a Digital Pearl Harbor incident struck many experts at the time as a hyperbolic justification for expanding the government’s digital surveillance capabilities, and an overstatement of the capabilities of our adversaries. But back in 2003, most of the world’s companies didn’t host their entire business in the cloud.
Today, nobody questions the capabilities, goals and outcomes of dozens of nation-state level cyber adversaries. And these days, a catastrophic cyber incident could be little more than an extended, simultaneous outage at multiple cloud providers.
The full national cybersecurity strategy is available from the White House website (PDF).

Image: Shutterstock.com
Three different cybercriminal groups claimed access to internal networks at communications giant T-Mobile in more than 100 separate incidents throughout 2022, new data suggests. In each case, the goal of the attackers was the same: Phish T-Mobile employees for access to internal company tools, and then convert that access into a cybercrime service that could be hired to divert any T-Mobile user’s text messages and phone calls to another device.
The conclusions above are based on an extensive analysis of Telegram chat logs from three distinct cybercrime groups or actors that have been identified by security researchers as particularly active in and effective at “SIM-swapping,” which involves temporarily seizing control over a target’s mobile phone number.
Countless websites and online services use SMS text messages for both password resets and multi-factor authentication. This means that stealing someone’s phone number often can let cybercriminals hijack the target’s entire digital life in short order — including access to any financial, email and social media accounts tied to that phone number.
All three SIM-swapping entities that were tracked for this story remain active in 2023, and they all conduct business in open channels on the instant messaging platform Telegram. KrebsOnSecurity is not naming those channels or groups here because they will simply migrate to more private servers if exposed publicly, and for now those servers remain a useful source of intelligence about their activities.
Each advertises their claimed access to T-Mobile systems in a similar way. At a minimum, every SIM-swapping opportunity is announced with a brief “Tmobile up!” or “Tmo up!” message to channel participants. Other information in the announcements includes the price for a single SIM-swap request, and the handle of the person who takes the payment and information about the targeted subscriber.
The information required from the customer of the SIM-swapping service includes the target’s phone number, and the serial number tied to the new SIM card that will be used to receive text messages and phone calls from the hijacked phone number.
Initially, the goal of this project was to count how many times each entity claimed access to T-Mobile throughout 2022, by cataloging the various “Tmo up!” posts from each day and working backwards from Dec. 31, 2022.
But by the time we got to claims made in the middle of May 2022, completing the rest of the year’s timeline seemed unnecessary. The tally shows that in the last seven-and-a-half months of 2022, these groups collectively made SIM-swapping claims against T-Mobile on 104 separate days — often with multiple groups claiming access on the same days.
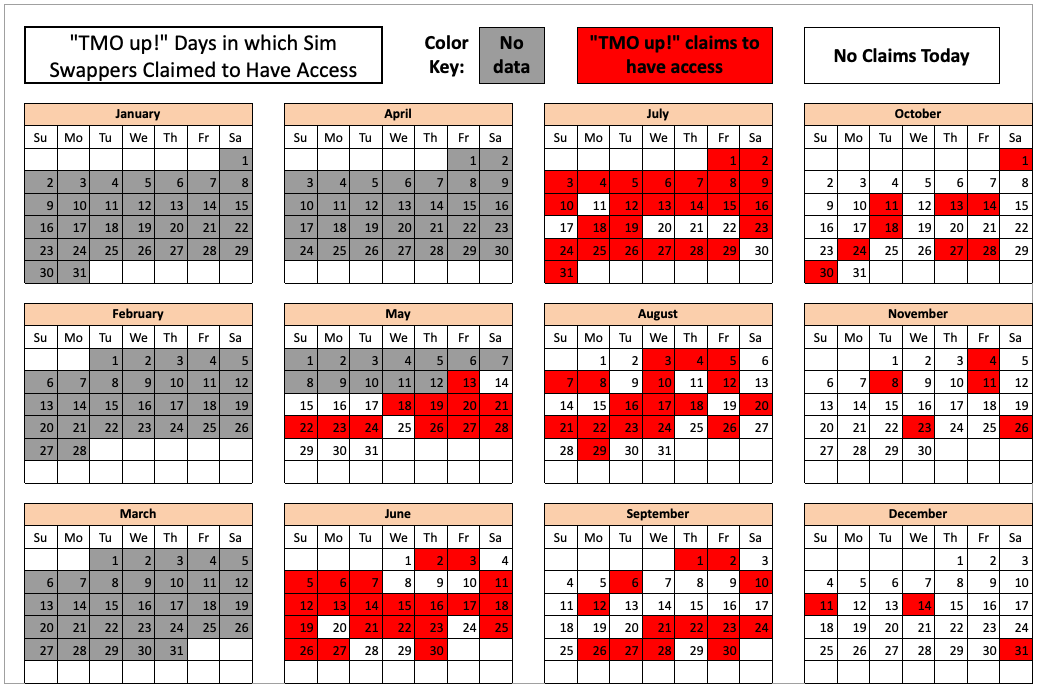
The 104 days in the latter half of 2022 in which different known SIM-swapping groups claimed access to T-Mobile employee tools.
KrebsOnSecurity shared a large amount of data gathered for this story with T-Mobile. The company declined to confirm or deny any of these claimed intrusions. But in a written statement, T-Mobile said this type of activity affects the entire wireless industry.
“And we are constantly working to fight against it,” the statement reads. “We have continued to drive enhancements that further protect against unauthorized access, including enhancing multi-factor authentication controls, hardening environments, limiting access to data, apps or services, and more. We are also focused on gathering threat intelligence data, like what you have shared, to help further strengthen these ongoing efforts.”
While it is true that each of these cybercriminal actors periodically offer SIM-swapping services for other mobile phone providers — including AT&T, Verizon and smaller carriers — those solicitations appear far less frequently in these group chats than T-Mobile swap offers. And when those offers do materialize, they are considerably more expensive.
The prices advertised for a SIM-swap against T-Mobile customers in the latter half of 2022 ranged between USD $1,000 and $1,500, while SIM-swaps offered against AT&T and Verizon customers often cost well more than twice that amount.
To be clear, KrebsOnSecurity is not aware of specific SIM-swapping incidents tied to any of these breach claims. However, the vast majority of advertisements for SIM-swapping claims against T-Mobile tracked in this story had two things in common that set them apart from random SIM-swapping ads on Telegram.
First, they included an offer to use a mutually trusted “middleman” or escrow provider for the transaction (to protect either party from getting scammed). More importantly, the cybercriminal handles that were posting ads for SIM-swapping opportunities from these groups generally did so on a daily or near-daily basis — often teasing their upcoming swap events in the hours before posting a “Tmo up!” message announcement.
In other words, if the crooks offering these SIM-swapping services were ripping off their customers or claiming to have access that they didn’t, this would be almost immediately obvious from the responses of the more seasoned and serious cybercriminals in the same chat channel.
There are plenty of people on Telegram claiming to have SIM-swap access at major telecommunications firms, but a great many such offers are simply four-figure scams, and any pretenders on this front are soon identified and banned (if not worse).
One of the groups that reliably posted “Tmo up!” messages to announce SIM-swap availability against T-Mobile customers also reliably posted “Tmo down!” follow-up messages announcing exactly when their claimed access to T-Mobile employee tools was discovered and revoked by the mobile giant.
A review of the timestamps associated with this group’s incessant “Tmo up” and “Tmo down” posts indicates that while their claimed access to employee tools usually lasted less than an hour, in some cases that access apparently went undiscovered for several hours or even days.
How could these SIM-swapping groups be gaining access to T-Mobile’s network as frequently as they claim? Peppered throughout the daily chit-chat on their Telegram channels are solicitations for people urgently needed to serve as “callers,” or those who can be hired to social engineer employees over the phone into navigating to a phishing website and entering their employee credentials.
Allison Nixon is chief research officer for the New York City-based cybersecurity firm Unit 221B. Nixon said these SIM-swapping groups will typically call employees on their mobile devices, pretend to be someone from the company’s IT department, and then try to get the person on the other end of the line to visit a phishing website that mimics the company’s employee login page.
Nixon argues that many people in the security community tend to discount the threat from voice phishing attacks as somehow “low tech” and “low probability” threats.
“I see it as not low-tech at all, because there are a lot of moving parts to phishing these days,” Nixon said. “You have the caller who has the employee on the line, and the person operating the phish kit who needs to spin it up and down fast enough so that it doesn’t get flagged by security companies. Then they have to get the employee on that phishing site and steal their credentials.”
In addition, she said, often there will be yet another co-conspirator whose job it is to use the stolen credentials and log into employee tools. That person may also need to figure out how to make their device pass “posture checks,” a form of device authentication that some companies use to verify that each login is coming only from employer-issued phones or laptops.
For aspiring criminals with little experience in scam calling, there are plenty of sample call transcripts available on these Telegram chat channels that walk one through how to impersonate an IT technician at the targeted company — and how to respond to pushback or skepticism from the employee. Here’s a snippet from one such tutorial that appeared recently in one of the SIM-swapping channels:
“Hello this is James calling from Metro IT department, how’s your day today?”
(yea im doing good, how r u)
i’m doing great, thank you for asking
i’m calling in regards to a ticket we got last week from you guys, saying you guys were having issues with the network connectivity which also interfered with [Microsoft] Edge, not letting you sign in or disconnecting you randomly. We haven’t received any updates to this ticket ever since it was created so that’s why I’m calling in just to see if there’s still an issue or not….”
The TMO UP data referenced above, combined with comments from the SIM-swappers themselves, indicate that while many of their claimed accesses to T-Mobile tools in the middle of 2022 lasted hours on end, both the frequency and duration of these events began to steadily decrease as the year wore on.

T-Mobile declined to discuss what it may have done to combat these apparent intrusions last year. However, one of the groups began to complain loudly in late October 2022 that T-Mobile must have been doing something that was causing their phished access to employee tools to die very soon after they obtained it.
One group even remarked that they suspected T-Mobile’s security team had begun monitoring their chats.
Indeed, the timestamps associated with one group’s TMO UP/TMO DOWN notices show that their claimed access was often limited to less than 15 minutes throughout November and December of 2022.
Whatever the reason, the calendar graphic above clearly shows that the frequency of claimed access to T-Mobile decreased significantly across all three SIM-swapping groups in the waning weeks of 2022.
T-Mobile US reported revenues of nearly $80 billion last year. It currently employs more than 71,000 people in the United States, any one of whom can be a target for these phishers.
T-Mobile declined to answer questions about what it may be doing to beef up employee authentication. But Nicholas Weaver, a researcher and lecturer at University of California, Berkeley’s International Computer Science Institute, said T-Mobile and all the major wireless providers should be requiring employees to use physical security keys for that second factor when logging into company resources.

A U2F device made by Yubikey.
“These breaches should not happen,” Weaver said. “Because T-Mobile should have long ago issued all employees security keys and switched to security keys for the second factor. And because security keys provably block this style of attack.”
The most commonly used security keys are inexpensive USB-based devices. A security key implements a form of multi-factor authentication known as Universal 2nd Factor (U2F), which allows the user to complete the login process simply by inserting the USB key and pressing a button on the device. The key works without the need for any special software drivers.
The allure of U2F devices for multi-factor authentication is that even if an employee who has enrolled a security key for authentication tries to log in at an impostor site, the company’s systems simply refuse to request the security key if the user isn’t on their employer’s legitimate website, and the login attempt fails. Thus, the second factor cannot be phished, either over the phone or Internet.
Nixon said one confounding aspect of SIM-swapping is that these criminal groups tend to recruit teenagers to do their dirty work.
“A huge reason this problem has been allowed to spiral out of control is because children play such a prominent role in this form of breach,” Nixon said.
Nixon said SIM-swapping groups often advertise low-level jobs on places like Roblox and Minecraft, online games that are extremely popular with young adolescent males.
“Statistically speaking, that kind of recruiting is going to produce a lot of people who are underage,” she said. “They recruit children because they’re naive, you can get more out of them, and they have legal protections that other people over 18 don’t have.”
For example, she said, even when underage SIM-swappers are arrested, the offenders tend to go right back to committing the same crimes as soon as they’re released.
In January 2023, T-Mobile disclosed that a “bad actor” stole records on roughly 37 million current customers, including their name, billing address, email, phone number, date of birth, and T-Mobile account number.
In August 2021, T-Mobile acknowledged that hackers made off with the names, dates of birth, Social Security numbers and driver’s license/ID information on more than 40 million current, former or prospective customers who applied for credit with the company. That breach came to light after a hacker began selling the records on a cybercrime forum.
In the shadow of such mega-breaches, any damage from the continuous attacks by these SIM-swapping groups can seem insignificant by comparison. But Nixon says it’s a mistake to dismiss SIM-swapping as a low volume problem.
“Logistically, you may only be able to get a few dozen or a hundred SIM-swaps in a day, but you can pick any customer you want across their entire customer base,” she said. “Just because a targeted account takeover is low volume doesn’t mean it’s low risk. These guys have crews that go and identify people who are high net worth individuals and who have a lot to lose.”
Nixon said another aspect of SIM-swapping that causes cybersecurity defenders to dismiss the threat from these groups is the perception that they are full of low-skilled “script kiddies,” a derisive term used to describe novice hackers who rely mainly on point-and-click hacking tools.
“They underestimate these actors and say this person isn’t technically sophisticated,” she said. “But if you’re rolling around in millions worth of stolen crypto currency, you can buy that sophistication. I know for a fact some of these compromises were at the hands of these ‘script kiddies,’ but they’re not ripping off other people’s scripts so much as hiring people to make scripts for them. And they don’t care what gets the job done, as long as they get to steal the money.”
A security firm has discovered that a six-year-old crafty botnet known as Mylobot appears to be powering a residential proxy service called BHProxies, which offers paying customers the ability to route their web traffic anonymously through compromised computers. Here’s a closer look at Mylobot, and a deep dive into who may be responsible for operating the BHProxies service.
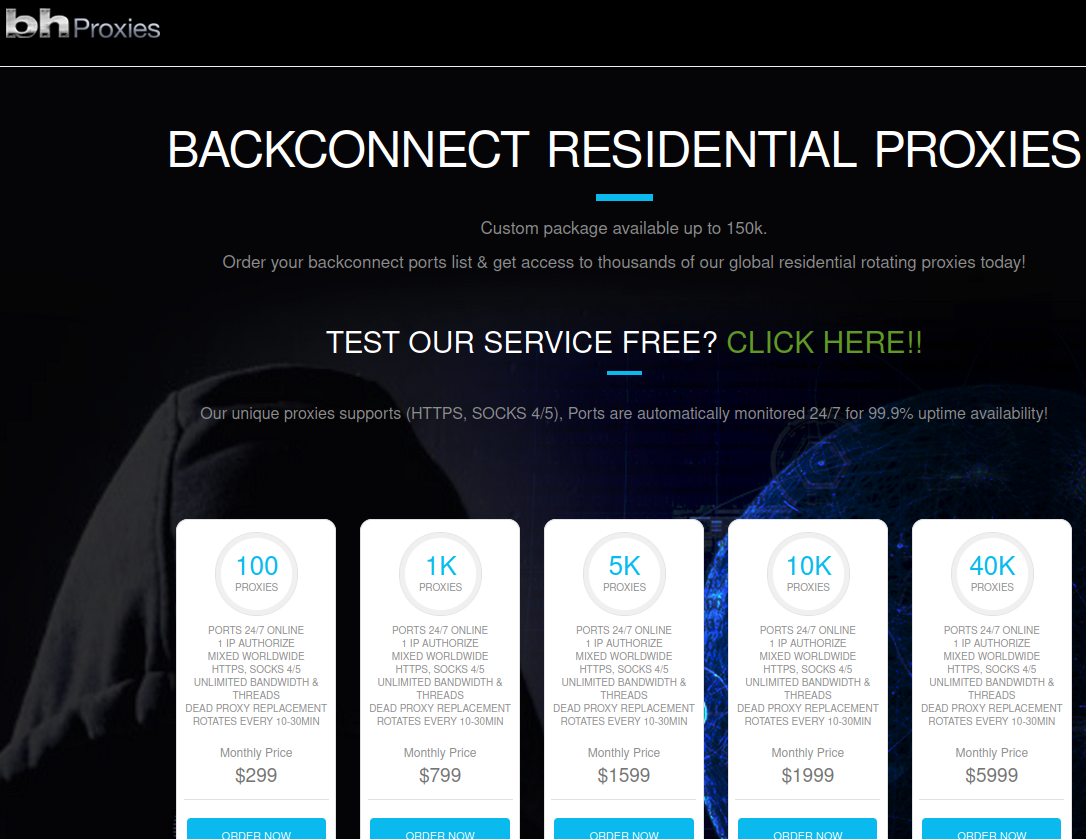
The BHProxies website.
First identified in 2017 by the security firm Deep Instinct, Mylobot employs a number of fairly sophisticated methods to remain undetected on infected hosts, such as running exclusively in the computer’s temporary memory, and waiting 14 days before attempting to contact the botnet’s command and control servers.
Last year, researchers at Minerva Labs spotted the botnet being used to blast out sextortion scams. But according to a new report from BitSight, the Mylobot botnet’s main functionality has always been about transforming the infected system into a proxy.
The Mylobot malware includes more than 1,000 hard-coded and encrypted domain names, any one of which can be registered and used as control networks for the infected hosts. BitSight researchers found significant overlap in the Internet addresses used by those domains and a domain called BHproxies[.]com.
BHProxies sells access to “residential proxy” networks, which allow someone to rent a residential IP address to use as a relay for their Internet communications, providing anonymity and the advantage of being perceived as a residential user surfing the web. The service is currently advertising access to more than 150,000 devices globally.
“At this point, we cannot prove that BHProxies is linked to Mylobot, but we have a strong suspicion,” wrote BitSight’s Stanislas Arnoud.
To test their hypothesis, BitSight obtained 50 proxies from BHProxies. The researchers were able to use 48 of those 50 proxies to browse to a website they controlled — allowing them to record the true IP addresses of each proxy device.
“Among these 48 recovered residential proxies IP addresses, 28 (58.3%) of those were already present in our sinkhole systems, associated with the Mylobot malware family,” Arnoud continued. “This number is probably higher, but we don’t have a full visibility of the botnet. This gave us clear evidence that Mylobot infected computers are used by the BHProxies service.”
BitSight said it is currently seeing more than 50,000 unique Mylobot infected systems every day, and that India appears to be the most targeted country, followed by the United States, Indonesia and Iran.
“We believe we are only seeing part of the full botnet, which may lead to more than 150,000 infected computers as advertised by BHProxies’ operators,” Arnoud wrote.
The website BHProxies[.]com has been advertised for nearly a decade on the forum Black Hat World by the user BHProxies. BHProxies has authored 129 posts on Black Hat World since 2012, and their last post on the forum was in December 2022.
BHProxies initially was fairly active on Black Hat World between May and November 2012, after which it suddenly ceased all activity. The account didn’t resume posting on the forum until April 2014.
According to cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, the user BHProxies also used the handle “hassan_isabad_subar” and marketed various software tools, including “Subar’s free email creator” and “Subar’s free proxy scraper.”
Intel 471’s data shows that hassan_isabad_subar registered on the forum using the email address jesus.fn.christ@gmail.com. In a June 2012 private message exchange with a website developer on Black Hat World, hassan_isabad_subar confided that they were working at the time to develop two websites, including the now-defunct customscrabblejewelry.com.
DomainTools.com reports that customscrabblejewelry.com was registered in 2012 to a Teresa Shotliff in Chesterland, Ohio. A search on jesus.fn.christ@gmail.com at Constella Intelligence, a company that tracks compromised databases, shows this email address is tied to an account at the fundraising platform omaze.com, for a Brian Shotliff from Chesterland, Ohio.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Shotliff said he sold his BHProxies account to another Black Hat World forum user from Egypt back in 2014. Shotliff shared an April 2014 password reset email from Black Hat World, which shows he forwarded the plaintext password to the email address legendboy2050@yahoo.com. He also shared a PayPal receipt and snippets of Facebook Messenger logs showing conversations in March 2014 with legendboy2050@yahoo.com.
Constella Intelligence confirmed that legendboy2050@yahoo.com was indeed another email address tied to the hassan_isabad_subar/BHProxies identity on Black Hat World. Constella also connects legendboy2050 to Facebook and Instagram accounts for one Abdala Tawfik from Cairo. This user’s Facebook page says Tawfik also uses the name Abdalla Khafagy.
Tawfik’s Instagram account says he is a former operations manager at the social media network TikTok, as well as a former director at Crypto.com.
Abdalla Khafagy’s LinkedIn profile says he was “global director of community” at Crypto.com for about a year ending in January 2022. Before that, the resume says he was operations manager of TikTok’s Middle East and North Africa region for approximately seven months ending in April 2020.
Khafagy’s LinkedIn profile says he is currently founder of LewkLabs, a Dubai-based “blockchain-powered, SocialFi content monetization platform” that last year reported funding of $3.26 million from private investors.
The only experience listed for Khafagy prior to the TikTok job is labeled “Marketing” at “Confidential,” from February 2014 to October 2019.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Khafagy told KrebsOnSecurity that he had a Black Hat World account at some point, but that he didn’t recall ever having used an account by the name BHProxies or hassan_isabad_subar. Khafagy said he couldn’t remember the name of the account he had on the forum.
“I had an account that was simply hacked from me shortly after and I never bothered about it because it wasn’t mine in the first place,” he explained.
Khafagy declined to elaborate on the five-year stint in his resume marked “Confidential.” When asked directly whether he had ever been associated with the BHProxies service, Mr. Khafagy said no.
That Confidential job listing is interesting because its start date lines up with the creation of BHproxies[.]com. Archive.org indexed its first copy of BHProxies[.]com on Mar. 5, 2014, but historic DNS records show BHproxies[.]com first came online Feb. 25, 2014.
Shortly after that conversation with Mr. Khafagy, Mr. Shotliff shared a Facebook/Meta message he received that indicated Mr. Khafagy wanted him to support the claim that the BHProxies account had somehow gone missing.
“Hey mate, it’s been a long time. Hope you are doing well. Someone from Krebs on Security reached out to me about the account I got from you on BHW,” Khafagy’s Meta account wrote. “Didn’t we try to retrieve this account? I remember mentioning to you that it got stolen and I was never able to retrieve it.”
Mr. Shotliff said Khafagy’s sudden message this week was the first time he’d heard that claim.
“He bought the account,” Shotliff said. “He might have lost the account or had it stolen, but it’s not something I remember.”
If you liked this story, you may also enjoy these other investigations into botnet-based proxy services:
A Deep Dive Into the Residential Proxy Service ‘911’
911 Proxy Service Implodes After Disclosing Breach
Meet the Administrators of the RSOCKS Proxy Botnet
The Link Between AWM Proxy & the Glupteba Botnet
15-Year-Old Malware Proxy Network VIP72 Goes Dark
Who’s Behind the TDSS Botnet?
Millions of Americans receiving food assistance benefits just earned a new right that they can’t yet enforce: The right to be reimbursed if funds on their Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) cards are stolen by card skimming devices secretly installed at cash machines and grocery store checkout lanes.

On December 29, 2022, President Biden signed into law the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023, which — for the first time ever — includes provisions for the replacement of stolen EBT benefits. This is a big deal because in 2022, organized crime groups began massively targeting EBT accounts — often emptying affected accounts at ATMs immediately after the states disperse funds each month.
EBT cards can be used along with a personal identification number (PIN) to pay for goods at participating stores, and to withdraw cash from an ATM. However, EBT cards differ from debit cards issued to most Americans in two important ways. First, most states do not equip EBT cards with smart chip technology, which can make the cards more difficult and expensive for skimming thieves to clone.
More critically, EBT participants traditionally have had little hope of recovering food assistance funds when their cards were copied by card-skimming devices and used for fraud. That’s because while the EBT programs are operated by individually by the states, those programs are funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), which until late last year was barred from reimbursing states for stolen EBT funds.
The protections passed in the 2023 Appropriations Act allow states to use federal funds to replace stolen EBT benefits, and they permit states to seek reimbursement for any skimmed EBT funds they may have replaced from their own coffers (dating back to Oct. 1, 2022).
But first, all 50 states must each submit a plan for how they are going to protect and replace food benefits stolen via card skimming. Guidance for the states in drafting those plans was issued by the USDA on Jan. 31 (PDF), and states that don’t get them done before Feb. 27, 2023 risk losing the ability to be reimbursed for EBT fraud losses.
Deborah Harris is a staff attorney at The Massachusetts Law Reform Institute (MLRI), a nonprofit legal assistance organization that has closely tracked the EBT skimming epidemic. In November 2022, the MLRI filed a class-action lawsuit against Massachusetts on behalf of thousands of low-income families who were collectively robbed of more than $1 million in food assistance benefits by card skimming devices secretly installed at cash machines and grocery store checkout lanes across the state.
Harris said she’s pleased that the USDA guidelines were issued so promptly, and that the guidance for states was not overly prescriptive. For example, some security experts have suggested that adding contactless capability to EBT cards could help participants avoid skimming devices altogether. But Harris said contactless cards do not require a PIN, which is the only thing that stops EBT cards from being drained at the ATM when a participant’s card is lost or stolen.
Then again, nothing in the guidance even mentions chip-based cards, or any other advice for improving the physical security of EBT cards. Rather, it suggests states should seek to develop the capability to perform basic fraud detection and alerting on suspicious transactions, such as when an EBT card that is normally used only in one geographic area suddenly is used to withdraw cash at an ATM halfway across the country.
“Besides having the states move fast to approve their plans, we’d also like to see a focused effort to move states from magstripe-only cards to chip, and also assisting states to develop the algorithms that will enable them to identify likely incidents of stolen benefits,” Harris said.
Harris said Massachusetts has begun using algorithms to look for these suspicious transaction patterns throughout its EBT network, and now has the ability to alert households and verify transactions. But she said most states do not have this capability.
“We have heard that other states aren’t currently able to do that,” Harris said. “But encouraging states to more affirmatively identify instances of likely theft and assisting with the claims and verification process is critical. Most households can’t do that on their own, and in Massachusetts it’s very hard for a person to get a copy of their transaction history. Some states can do that through third-party apps, but something so basic should not be on the burden of EBT households.”
Some states aren’t waiting for direction from the federal government to beef up EBT card security. Like Maryland, which identified more than 1,400 households hit by EBT skimming attacks last year — a tenfold increase over 2021.
Advocates for EBT beneficiaries in Maryland are backing Senate Bill 401 (PDF), which would require the use of chip technology and ongoing monitoring for suspicious activity (a hearing on SB401 is scheduled in the Maryland Senate Finance Commission for Thursday, Feb. 23, at 1 p.m.).
Michelle Salomon Madaio is a director at the Homeless Persons Representation Project, a legal assistance organization based in Silver Spring, Md. Madaio said the bill would require the state Department of Human Services to replace skimmed benefits, not only after the bill goes into effect but also retroactively from January 2020 to the present.
Madaio said the bill also would require the state to monitor for patterns of suspicious activity on EBT cards, and to develop a mechanism to contact potentially affected households.
“For most of the skimming victims we’ve worked with, the fraudulent transactions would be pretty easy to spot because they mostly happened in the middle of the night or out of state, or both,” Madaio said. “To make matters worse, a lot of families whose benefits were scammed then incurred late fees on many other things as a result.”
It is not difficult to see why organized crime groups have pounced on EBT cards as easy money. In most traditional payment card transactions, there are usually several parties that have a financial interest in minimizing fraud and fraud losses, including the bank that issued the card, the card network (Visa, MasterCard, Discover, etc.), and the merchant.
But that infrastructure simply does not exist within state EBT programs, and it certainly isn’t a thing at the inter-state level. What that means is that the vast majority of EBT cards have zero fraud controls, which is exactly what continues to make them so appealing to thieves.
For now, the only fraud controls available to most EBT cardholders include being especially paranoid about where they use their cards, and frequently changing their PINs.
According to USDA guidance issued prior to the passage of the appropriations act, EBT cardholders should consider changing their card PIN at least once a month.
“By changing PINs frequently, at least monthly, and doing so before benefit issuance dates, households can minimize their risk of stolen benefits from a previously skimmed EBT card,” the USDA advised.
KrebsOnSecurity will likely have a decent amount of screen time in an upcoming Hulu documentary series about the 2015 megabreach at marital infidelity site Ashley Madison. While I can’t predict what the producers will do with the video interviews we shot, it’s fair to say the series will explore compelling new clues as to who may have been responsible for the attack.

The new docuseries produced by ABC News Studios and Wall to Wall Media is tentatively titled, “The Ashley Madison Affair,” and is slated for release on Hulu in late Spring 2023. Wall to Wall Media is part of the Warner Bros. International Television Production group.
“Featuring exclusive footage and untold firsthand interviews from those involved, the series will explore infidelity, morality, cyber-shaming and blackmail and tell the story of ordinary people with big secrets and a mystery that remains unsolved to this day,” reads a Jan. 12, 2023 scoop from The Wrap.
There are several other studios pursuing documentaries on the Ashley Madison breach, and it’s not hard to see why. On July 19, 2015, a hacker group calling itself The Impact Team leaked Ashley Madison internal company data, and announced it would leak all user data in a month unless Ashley Madison voluntarily shut down before then.
A month later, The Impact Team published more than 60 gigabytes of data, including user names, home addresses, search history, and credit card transaction records. The leak led to the public shaming and extortion of many Ashley Madison users, and to at least two suicides. It’s impossible to say how many users lost their jobs or marriages as a result of the breach.
I’m aware that there are multiple studios working on Ashley Madison documentaries because I broke the story of the breach in 2015, and all of those production houses approached me with essentially the same pitch: It would be a shame if your voice wasn’t included in our project.
What stood out about the inquiry from Wall to Wall was that their researchers had already gathered piles of clues about the breach that I’d never seen before.
I’d assumed that participating in their documentary would involve sitting for a few interviews about known historical facts related to the breach. But when Wall to Wall shared what they’d found, I was hooked, and spent several weeks investigating those leads further.
The result was a collaborative research effort revealing key aspects of the breach that have somehow escaped public notice over the years.
I won’t go into detail on what we discovered until the Hulu series is ready for release. Also, I am not privy to what they will produce with the interviews I gave. I can’t say that what we found untangles everything about the breach that was previously unknown, but it sure explains a lot.
Most people who operate DDoS-for-hire businesses attempt to hide their true identities and location. Proprietors of these so-called “booter” or “stresser” services — designed to knock websites and users offline — have long operated in a legally murky area of cybercrime law. But until recently, their biggest concern wasn’t avoiding capture or shutdown by the feds: It was minimizing harassment from unhappy customers or victims, and insulating themselves against incessant attacks from competing DDoS-for-hire services.
And then there are booter store operators like John Dobbs, a 32-year-old computer science graduate student living in Honolulu, Hawaii. For at least a decade until late last year, Dobbs openly operated IPStresser[.]com, a popular and powerful attack-for-hire service that he registered with the state of Hawaii using his real name and address. Likewise, the domain was registered in Dobbs’s name and hometown in Pennsylvania.
Dobbs, in an undated photo from his Github profile. Image: john-dobbs.github.io
The only work experience Dobbs listed on his resume was as a freelance developer from 2013 to the present day. Dobbs’s resume doesn’t name his booter service, but in it he brags about maintaining websites with half a million page views daily, and “designing server deployments for performance, high-availability and security.”
In December 2022, the U.S. Department of Justice seized Dobbs’s IPStresser website and charged him with one count of aiding and abetting computer intrusions. Prosecutors say his service attracted more than two million registered users, and was responsible for launching a staggering 30 million distinct DDoS attacks.
The government seized four-dozen booter domains, and criminally charged Dobbs and five other U.S. men for allegedly operating stresser services. This was the Justice Department’s second such mass takedown targeting DDoS-for-hire services and their accused operators. In 2018, the feds seized 15 stresser sites, and levied cybercrime charges against three men for their operation of booter services.
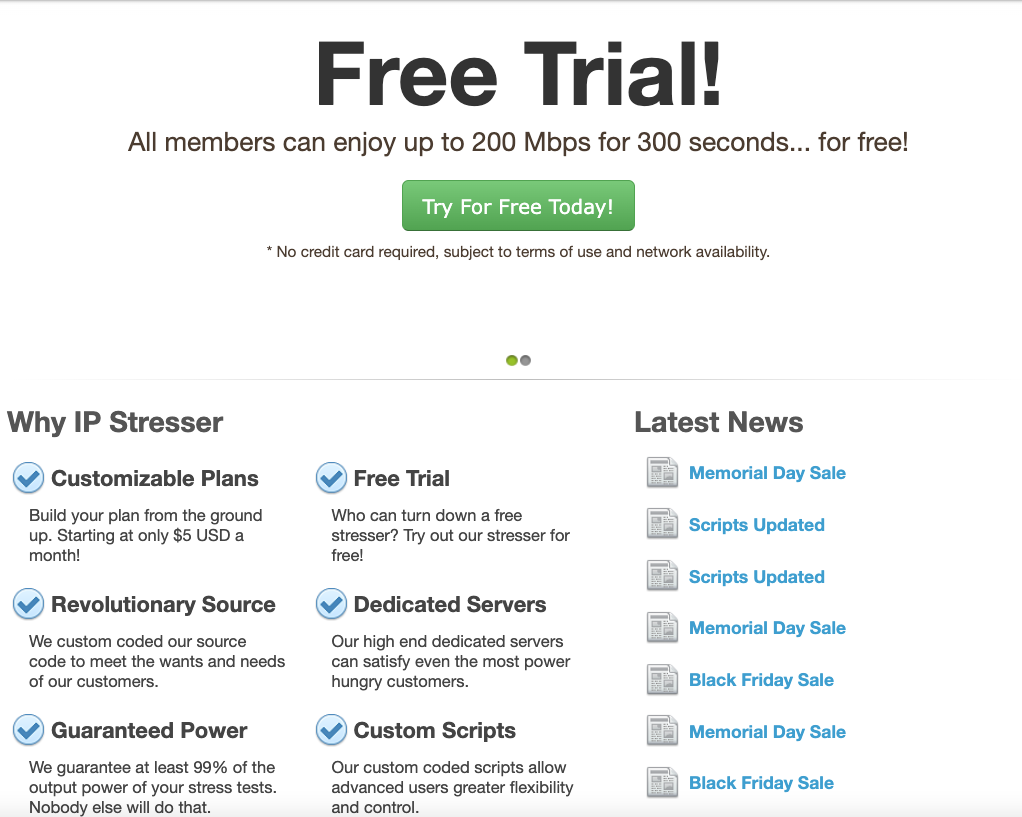
Dobbs’s booter service, IPStresser, in June 2020. Image: archive.org.
Many accused stresser site operators have pleaded guilty over the years after being hit with federal criminal charges. But the government’s core claim — that operating a booter site is a violation of U.S. computer crime laws — wasn’t properly tested in the courts until September 2021.
That was when a jury handed down a guilty verdict against Matthew Gatrel, a then 32-year-old St. Charles, Ill. man charged in the government’s first 2018 mass booter bust-up. Despite admitting to FBI agents that he ran two booter services (and turning over plenty of incriminating evidence in the process), Gatrel opted to take his case to trial, defended the entire time by court-appointed attorneys.
Prosecutors said Gatrel’s booter services — downthem[.]org and ampnode[.]com — helped some 2,000 paying customers launch debilitating digital assaults on more than 20,000 targets, including many government, banking, university and gaming websites.
Gatrel was convicted on all three charges of violating the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, including conspiracy to commit unauthorized impairment of a protected computer, conspiracy to commit wire fraud, and unauthorized impairment of a protected computer. He was sentenced to two years in prison.
Now, it appears Dobbs is also planning to take his chances with a jury. On Jan. 4, Dobbs entered a plea of not guilty. Neither Dobbs nor his court-appointed attorney responded to requests for comment.
But as it happens, Dobbs himself provided some perspective on his thinking in an email exchange with KrebsOnSecurity back in 2020. I’d reached out to Dobbs because it was obvious he didn’t mind if people knew he operated one of the world’s most popular DDoS-for-hire sites, and I was genuinely curious why he was so unafraid of getting raided by the feds.
“Yes, I am the owner of the domain you listed, however you are not authorized to post an article containing said domain name, my name or this email address without my prior written permission,” Dobbs replied to my initial outreach on March 10, 2020 using his email address from the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
A few hours later, I received more strident instructions from Dobbs, this time via his official email address at ipstresser[.]com.
“I will state again for absolute clarity, you are not authorized to post an article containing ipstresser.com, my name, my GitHub profile and/or my hawaii.edu email address,” Dobbs wrote, as if taking dictation from a lawyer who doesn’t understand how the media works.
When pressed for particulars on his business, Dobbs replied that the number of IPStresser customers was “privileged information,” and said he didn’t even advertise the service. When asked whether he was concerned that many of his competitors were by then serving jail time for operating similar booter services, Dobbs maintained that the way he’d set up the business insulated him from any liability.
“I have been aware of the recent law enforcement actions against other operators of stress testing services,” Dobbs explained. “I cannot speak to the actions of these other services, but we take proactive measures to prevent misuse of our service and we work with law enforcement agencies regarding any reported abuse of our service.”
What were those proactive measures? In a 2015 interview with ZDNet France, Dobbs asserted that he was immune from liability because his clients all had to submit a digital signature attesting that they wouldn’t use the site for illegal purposes.
“Our terms of use are a legal document that protects us, among other things, from certain legal consequences,” Dobbs told ZDNet. “Most other sites are satisfied with a simple checkbox, but we ask for a digital signature in order to imply real consent from our customers.”
Dobbs told KrebsOnSecurity his service didn’t generate much of a profit, but rather that he was motivated by “filling a legitimate need.”
“My reason for offering the service is to provide the ability to test network security measures before someone with malicious intent attacks said network and causes downtime,” he said. “Sure, some people see only the negatives, but there is a long list of companies I have worked with over the years who would say my service is a godsend and has helped them prevent tens of thousands of dollars in downtime resulting from a malicious attack.”
“I do not believe that providing such a service is illegal, assuming proper due diligence to prevent malicious use of the service, as is the case for IPstresser[.]com,” Dobbs continued. “Someone using such a service to conduct unauthorized testing is illegal in many countries, however, the legal liability is that of the user, not of the service provider.”
Dobbs’s profile on GitHub includes more of his ideas about his work, including a curious piece on “software engineering ethics.” In his January 2020 treatise “My Software Engineering Journey,” Dobbs laments that nothing in his formal education prepared him for the reality that a great deal of his work would be so tedious and repetitive (this tracks closely with a 2020 piece here called Career Choice Tip: Cybercrime is Mostly Boring).
“One area of software engineering that I think should be covered more in university classes is maintenance,” Dobbs wrote. “Projects are often worked on for at most a few months, and students do not experience the maintenance aspect of software engineering until they reach the workplace. Let’s face it, ongoing maintenance of a project is boring; there is nothing like the euphoria of completing a project you have been working on for months and releasing it to the world, but I would say that half of my professional career has been related to maintenance.”
Allison Nixon is chief research officer at the New York-based cybersecurity firm Unit 221B. Nixon is part of a small group of researchers who have been closely tracking the DDoS-for-hire industry for years, and she said Dobbs’s claim that what he’s doing is legal makes sense given that it took years for the government to recognize the size of the problem.
“These guys are arguing that their services are legal because for a long time nothing happened to them,” Nixon said. “It’s difficult to argue something is illegal if no one has ever been arrested for it before.”
Nixon says the government’s fight against the booter services — and by extension other types of cybercrimes — is hampered by a legal system that often takes years to cycle through cybercrime cases.
“With cybercrime, the cycle between the crime and investigation and arrest can often take a year or more, and that’s for a really fast case,” Nixon said. “If someone robbed a store, we’d expect a police response within a few minutes. If someone robs a bank’s website, there might be some indication of police activity within a year.”
Nixon praised the 2022 and 2018 booter takedown operations as “huge steps forward,” but added that “there need to be more of them, and faster.”
“This time lag is part of the reason it’s so difficult to shut down the pipeline of new talent going into cybercrime,” she said. “They think what they’re doing is legal because nothing has happened, and because of the amount of time it takes to shut these things down. And it’s really a big problem, where we see a lot of people becoming criminals on the basis that what they’re doing isn’t really illegal because the cops won’t do anything.”
In December 2020, Dobbs filed an application with the state of Hawaii to withdraw IP Stresser Inc. from its roster of active companies. But according to prosecutors, Dobbs would continue to operate his DDoS-for-hire site until at least November 2022.
Two months after our 2020 email interview, Dobbs would earn his second bachelor’s degree (in computer science; his resume says he earned a bachelor’s in civil engineering from Drexel University in 2013). The federal charges against Dobbs came just as he was preparing to enter his final semester toward a master’s degree in computer science at the University of Hawaii.
Nixon says she has a message for anyone involved in operating a DDoS-for-hire service.
“Unless you are verifying that the target owns the infrastructure you’re targeting, there is no legal way to operate a DDoS-for-hire service,” she said. “There is no Terms of Service you could put on the site that would somehow make it legal.”
And her message to the customers of those booter services? It’s a compelling one to ponder, particularly now that investigators in the United States, U.K. and elsewhere have started going after booter service customers.
“When a booter service claims they don’t share logs, they’re lying because logs are legal leverage for when the booter service operator gets arrested,” Nixon said. “And when they do, you’re going to be the first people they throw under the bus.”
Identity thieves have been exploiting a glaring security weakness in the website of Experian, one of the big three consumer credit reporting bureaus. Normally, Experian requires that those seeking a copy of their credit report successfully answer several multiple choice questions about their financial history. But until the end of 2022, Experian’s website allowed anyone to bypass these questions and go straight to the consumer’s report. All that was needed was the person’s name, address, birthday and Social Security number.
The vulnerability in Experian’s website was exploitable after one applied to see their credit file via annualcreditreport.com.
In December, KrebsOnSecurity heard from Jenya Kushnir, a security researcher living in Ukraine who said he discovered the method being used by identity thieves after spending time on Telegram chat channels dedicated to the cashing out of compromised identities.
“I want to try and help to put a stop to it and make it more difficult for [ID thieves] to access, since [Experian is] not doing shit and regular people struggle,” Kushnir wrote in an email to KrebsOnSecurity explaining his motivations for reaching out. “If somehow I can make small change and help to improve this, inside myself I can feel that I did something that actually matters and helped others.”
Kushnir said the crooks learned they could trick Experian into giving them access to anyone’s credit report, just by editing the address displayed in the browser URL bar at a specific point in Experian’s identity verification process.
Following Kushnir’s instructions, I sought a copy of my credit report from Experian via annualcreditreport.com — a website that is required to provide all Americans with a free copy of their credit report from each of the three major reporting bureaus, once per year.
Annualcreditreport.com begins by asking for your name, address, SSN and birthday. After I supplied that and told Annualcreditreport.com I wanted my report from Experian, I was taken to Experian.com to complete the identity verification process.
Normally at this point, Experian’s website would present four or five multiple-guess questions, such as “Which of the following addresses have you lived at?”
Kushnir told me that when the questions page loads, you simply change the last part of the URL from “/acr/oow/” to “/acr/report,” and the site would display the consumer’s full credit report.
But when I tried to get my report from Experian via annualcreditreport.com, Experian’s website said it didn’t have enough information to validate my identity. It wouldn’t even show me the four multiple-guess questions. Experian said I had three options for a free credit report at this point: Mail a request along with identity documents, call a phone number for Experian, or upload proof of identity via the website.
But that didn’t stop Experian from showing me my full credit report after I changed the Experian URL as Kushnir had instructed — modifying the error page’s trailing URL from “/acr/OcwError” to simply “/acr/report”.
Experian’s website then immediately displayed my entire credit file.
Even though Experian said it couldn’t tell that I was actually me, it still coughed up my report. And thank goodness it did. The report contains so many errors that it’s probably going to take a good deal of effort on my part to straighten out.
Now I know why Experian has NEVER let me view my own file via their website. For example, there were four phone numbers on my Experian credit file: Only one of them was mine, and that one hasn’t been mine for ages.
I was so dumbfounded by Experian’s incompetence that I asked a close friend and trusted security source to try the method on her identity file at Experian. Sure enough, when she got to the part where Experian asked questions, changing the last part of the URL in her address bar to “/report” bypassed the questions and immediately displayed her full credit report. Her report also was replete with errors.
KrebsOnSecurity shared Kushnir’s findings with Experian on Dec. 23, 2022. On Dec. 27, 2022, Experian’s PR team acknowledged receipt of my Dec. 23 notification, but the company has so far ignored multiple requests for comment or clarification.
By the time Experian confirmed receipt of my report, the “exploit” Kushnir said he learned from the identity thieves on Telegram had been patched and no longer worked. But it remains unclear how long Experian’s website was making it so easy to access anyone’s credit report.
In response to information shared by KrebsOnSecurity, Senator Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) said he was disappointed — but not at all surprised — to hear about yet another cybersecurity lapse at Experian.
“The credit bureaus are poorly regulated, act as if they are above the law and have thumbed their noses at Congressional oversight,” Wyden said in a written statement. “Just last year, Experian ignored repeated briefing requests from my office after you revealed another cybersecurity lapse the company.”
Sen. Wyden’s quote above references a story published here in July 2022, which broke the news that identity thieves were hijacking consumer accounts at Experian.com just by signing up as them at Experian once more, supplying the target’s static, personal information (name, DoB/SSN, address) but a different email address.
From interviews with multiple victims who contacted KrebsOnSecurity after that story, it emerged that Experian’s own customer support representatives were actually telling consumers who got locked out of their Experian accounts to recreate their accounts using their personal information and a new email address. This was Experian’s advice even for people who’d just explained that this method was what identity thieves had used to lock them in out in the first place.
Clearly, Experian found it simpler to respond this way, rather than acknowledging the problem and addressing the root causes (lazy authentication and abhorrent account recovery practices). It’s also worth mentioning that reports of hijacked Experian.com accounts persisted into late 2022. That screw-up has since prompted a class action lawsuit against Experian.
Sen. Wyden said the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) need to do much more to protect Americans from screw-ups by the credit bureaus.
“If they don’t believe they have the authority to do so, they should endorse legislation like my Mind Your Own Business Act, which gives the FTC power to set tough mandatory cybersecurity standards for companies like Experian,” Wyden said.
Sadly, none of this is terribly shocking behavior for Experian, which has shown itself a completely negligent custodian of obscene amounts of highly sensitive consumer information.
In April 2021, KrebsOnSecurity revealed how identity thieves were exploiting lax authentication on Experian’s PIN retrieval page to unfreeze consumer credit files. In those cases, Experian failed to send any notice via email when a freeze PIN was retrieved, nor did it require the PIN to be sent to an email address already associated with the consumer’s account.
A few days after that April 2021 story, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that an Experian API was exposing the credit scores of most Americans.
It’s bad enough that we can’t really opt out of companies like Experian making $2.6 billion each quarter collecting and selling gobs of our personal and financial information. But there has to be some meaningful accountability when these monopolistic companies engage in negligent and reckless behavior with the very same consumer data that feeds their quarterly profits. Or when security and privacy shortcuts are found to be intentional, like for cost-saving reasons.
And as we saw with Equifax’s consolidated class-action settlement in response to letting state-sponsored hackers from China steal data on nearly 150 million Americans back in 2017, class-actions and more laughable “free credit monitoring” services from the very same companies that created the problem aren’t going to cut it.
It is easy to adopt a defeatist attitude with the credit bureaus, who often foul things up royally even for consumers who are quite diligent about watching their consumer credit files and disputing any inaccuracies.
But there are some concrete steps that everyone can take which will dramatically lower the risk that identity thieves will ruin your financial future. And happily, most of these steps have the side benefit of costing the credit bureaus money, or at least causing the data they collect about you to become less valuable over time.
The first step is awareness. Find out what these companies are saying about you behind your back. Keep in mind that — fair or not — your credit score as collectively determined by these bureaus can affect whether you get that loan, apartment, or job. In that context, even small, unintentional errors that are unrelated to identity theft can have outsized consequences for consumers down the road.
Each bureau is required to provide a free copy of your credit report every year. The easiest way to get yours is through annualcreditreport.com.
Some consumers report that this site never works for them, and that each bureau will insist they don’t have enough information to provide a report. I am definitely in this camp. Thankfully, a financial institution that I already have a relationship with offers the ability to view your credit file through them. Your mileage on this front may vary, and you may end up having to send copies of your identity documents through the mail or website.
When you get your report, look for anything that isn’t yours, and then document and file a dispute with the corresponding credit bureau. And after you’ve reviewed your report, set a calendar reminder to recur every four months, reminding you it’s time to get another free copy of your credit file.
If you haven’t already done so, consider making 2023 the year that you freeze your credit files at the three major reporting bureaus, including Experian, Equifax and TransUnion. It is now free to people in all 50 U.S. states to place a security freeze on their credit files. It is also free to do this for your partner and/or your dependents.
Freezing your credit means no one who doesn’t already have a financial relationship with you can view your credit file, making it unlikely that potential creditors will grant new lines of credit in your name to identity thieves. Freezing your credit file also means Experian and its brethren can no longer sell peeks at your credit history to others.
Anytime you wish to apply for new credit or a new job, or open an account at a utility or communications provider, you can quickly thaw a freeze on your credit file, and set it to freeze automatically again after a specified length of time.
Please don’t confuse a credit freeze (a.k.a. “security freeze”) with the alternative that the bureaus will likely steer you towards when you ask for a freeze: “Credit lock” services.
The bureaus pitch these credit lock services as a way for consumers to easily toggle their credit file availability with push of a button on a mobile app, but they do little to prevent the bureaus from continuing to sell your information to others.
My advice: Ignore the lock services, and just freeze your credit files already.
One final note. Frequent readers here will have noticed that I’ve criticized these so-called “knowledge-based authentication” or KBA questions that Experian’s website failed to ask as part of its consumer verification process.
KrebsOnSecurity has long assailed KBA as weak authentication because the questions and answers are drawn largely from consumer records that are public and easily accessible to organized identity theft groups.
That said, given that these KBA questions appear to be the ONLY thing standing between me and my Experian credit report, it seems like maybe they should at least take care to ensure that those questions actually get asked.
Millions of people likely just received an email or snail mail notice saying they’re eligible to claim a class action payment in connection with the 2017 megabreach at consumer credit bureau Equifax. Given the high volume of reader inquiries about this, it seemed worth pointing out that while this particular offer is legit (if paltry), scammers are likely to soon capitalize on public attention to the settlement money.

One reader’s copy of their Equifax Breach Settlement letter. They received a check for $6.97.
In 2017, Equifax disclosed a massive, extended data breach that led to the theft of Social Security Numbers, dates of birth, addresses and other personal information on nearly 150 million people. Following a public breach response perhaps best described as a giant dumpster fire, the big-three consumer credit reporting bureau was quickly hit with nearly two dozen class-action lawsuits.
In exchange for resolving all outstanding class action claims against it, Equifax in 2019 agreed to a settlement that includes up to $425 million to help people affected by the breach.
Affected consumers were eligible to apply for at least three years of credit monitoring via all three major bureaus simultaneously, including Equifax, Experian and TransUnion. Or, if you didn’t want to take advantage of the credit monitoring offers, you could opt for a cash payment of up to $125.
The settlement also offered reimbursement for the time you may have spent remedying identity theft or misuse of your personal information caused by the breach, or purchasing credit monitoring or credit reports. This was capped at 20 total hours at $25 per hour ($500), with total cash reimbursement payments not to exceed $20,000 per consumer.
Those who did file a claim probably started receiving emails or other communications earlier this year from the Equifax Breach Settlement Fund, which has been messaging class participants about methods of collecting their payments.
How much each recipient receives appears to vary quite a bit, but probably most people will have earned a payment on the smaller end of that $125 scale — like less than $10. Those who received higher amounts likely spent more time documenting actual losses and/or explaining how the breach affected them personally.
So far this week, KrebsOnSecurity has received at least 20 messages from readers seeking more information about these notices. Some readers shared copies of letters they got in the mail along with a paper check from the Equifax Breach Settlement Fund (see screenshot above).
Others said they got emails from the Equifax Breach Settlement domain that looked like an animated greeting card offering instructions on how to redeem a virtual prepaid card.
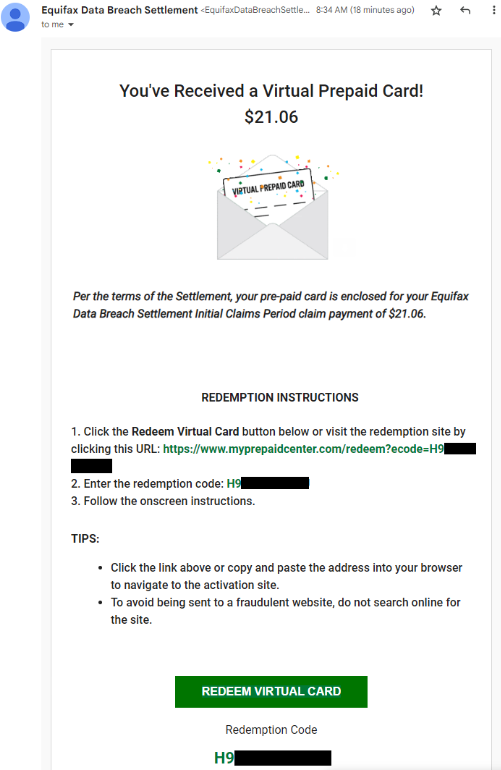
If you received one of these settlement emails and are wary about clicking the included links (good for you, by the way), copy the redemption code and paste it into the search box at myprepaidcenter.com/redeem. Successfully completing the card application requires accepting a prepaid MasterCard agreement (PDF).
The website for the settlement — equifaxbreachsettlement.com — also includes a lookup tool that lets visitors check whether they were affected by the breach; it requires your last name and the last six digits of your Social Security Number.
But be aware that phishers and other scammers are likely to take advantage of increased public awareness of the payouts to snooker people. Tim Helming, security evangelist at DomainTools.com, today flagged several new domains that mimic the name of the real Equifax Breach Settlement website and do not appear to be defensively registered by Equifax, including equifaxbreechsettlement[.]com, equifaxbreachsettlementbreach[.]com, and equifaxsettlements[.]co.
In February 2020, the U.S. Justice Department indicted four Chinese officers of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) for perpetrating the 2017 Equifax hack. DOJ officials said the four men were responsible for carrying out the largest theft of sensitive personal information by state-sponsored hackers ever recorded.
Equifax surpassed Wall Street’s expectations in its most recent quarterly earnings: The company reported revenues of $1.24 billion for the quarter ending September 2022.
Of course, most of those earnings come from Equifax’s continued legal ability to buy and sell eye-popping amounts of financial and personal data on U.S. consumers. As one of the three major credit bureaus, Equifax collects and packages information about your credit, salary, and employment history. It tracks how many credit cards you have, how much money you owe, and how you pay your bills. Each company creates a credit report about you, and then sells this report to businesses who are deciding whether to give you credit.
Americans currently have no legal right to opt out of this data collection and trade. But you can and also should freeze your credit, which by the way can make your credit profile less profitable for companies like Equifax — because they make money every time some potential creditor wants a peek inside your financial life. Also, it’s probably a good idea to freeze the credit of your children and/or dependents as well. It’s free on both counts.

Photo: BrandonKleinPhoto / Shutterstock.com
Two U.S. men have been charged with hacking into the Ring home security cameras of a dozen random people and then “swatting” them — falsely reporting a violent incident at the target’s address to trick local police into responding with force. Prosecutors say the duo used the compromised Ring devices to stream live video footage on social media of police raiding their targets’ homes, and to taunt authorities when they arrived.
Prosecutors in Los Angeles allege 20-year-old James Thomas Andrew McCarty, a.k.a. “Aspertaine,” of Charlotte, N.C., and Kya Christian Nelson, a.k.a. “ChumLul,” 22, of Racine, Wisc., conspired to hack into Yahoo email accounts belonging to victims in the United States. From there, the two allegedly would check how many of those Yahoo accounts were associated with Ring accounts, and then target people who used the same password for both accounts.
An indictment unsealed this week says that in the span of just one week in November 2020, McCarty and Nelson identified and swatted at least a dozen different victims across the country.
“The defendants then allegedly accessed without authorization the victims’ Ring devices and transmitted the audio and video from those devices on social media during the police response,” reads a statement from Martin Estrada, the U.S. Attorney for the Central District of California. “They also allegedly verbally taunted responding police officers and victims through the Ring devices during several of the incidents.”

James Thomas Andrew McCarty.
The indictment charges that McCarty continued his swatting spree in 2021 from his hometown in Kayenta, Ariz., where he called in bomb threats or phony hostage situations on more than two dozen occasions.
The Telegram and Discord aliases allegedly used by McCarty — “Aspertaine” and “Couch,” among others — correspond to an identity that was active in certain channels dedicated to SIM-swapping, a crime that involves stealing wireless phone numbers and hijacking the online financial and social media accounts tied to those numbers.
Aspertaine bragged on Discord that he’d amassed more than $330,000 in virtual currency. On Telegram, the Aspertaine/Couch alias frequented several popular SIM-swapping channels, where they initially were active as a “holder” — a SIM-swapping group member who agrees to hold SIM cards used in the heist after an account takeover is completed. Aspertaine later claimed more direct involvement in individual SIM-swapping attacks.
In September, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news about a wide-ranging federal investigation into “violence-as-a-service” offerings on Telegram and other social media networks, wherein people can settle scores by hiring total strangers to carry out physical attacks such as brickings, shootings, and firebombings at a target’s address.
The story observed that SIM swappers were especially enamored of these “IRL” or “In Real Life” violence services, which they frequently used to target one another in response to disagreements over how stolen money should be divided amongst themselves. And a number of Aspertaine’s peers on these SIM-swapping channels claimed they’d been ripped off after Aspertaine took more than a fair share from them.
In August, a member of a popular SIM-swapping group on Telegram who was slighted by Aspertaine put out the word that he was looking for some physical violence to be visited on McCarty’s address in North Carolina. “Anyone live near here and wants to [do] a job for me,” the job ad with McCarty’s home address read. “Jobs range from $1k-$50k. Payment in BTC [bitcoin].” It’s unclear if anyone responded to that job offer.
Ring, Inc., which is owned by Amazon, said it learned bad actors used stolen customer email credentials obtained from external (non-Ring) services to access other accounts, and took immediate steps to help those customers secure their Ring accounts.
“We also supported the FBI in identifying the individuals responsible,” the company said in a written statement. “We take the security of our customers extremely seriously — that’s why we made two-step verification mandatory, conduct regular scans for Ring passwords compromised in non-Ring breaches, and continually invest in new security protections to harden our systems. We are committed to continuing to protect our customers and vigorously going after those who seek to harm them.”
KrebsOnSecurity recently published The Wages of Password ReUse: Your Money or Your Life, which noted that when normal computer users fall into the nasty habit of recycling passwords, the result is most often some type of financial loss. Whereas, when cybercriminals reuse passwords, it often costs them their freedom.
But perhaps that story should be updated, because it’s now clear that password reuse can also put you in mortal danger. Swatting attacks are dangerous, expensive hoaxes that sometimes end in tragedy.
In June 2021, an 18-year-old serial swatter from Tennessee was sentenced to five years in prison for his role in a fraudulent swatting attack that led to the death of a 60-year-old man.
In 2019, prosecutors handed down a 20-year sentence to Tyler Barriss, a then 26-year-old serial swatter from California who admitted making a phony emergency call to police in late 2017 that led to the shooting death of an innocent Kansas man.
McCarty was arrested last week, and charged with conspiracy to intentionally access computers without authorization. Prosecutors said Nelson is currently incarcerated in Kentucky in connection with unrelated investigation.
If convicted on the conspiracy charge, both defendants would face a statutory maximum penalty of five years in federal prison. The charge of intentionally accessing without authorization a computer carries a maximum possible sentence of five years. A conviction on the additional charge against Nelson — aggravated identity theft — carries a mandatory two-year consecutive sentence.
Update, 11:48 a.m., Dec. 20: Added statement from Ring. Modified description of a “holder” in the SIM-swapping parlance.
ConnectWise, which offers a self-hosted, remote desktop software application that is widely used by Managed Service Providers (MSPs), is warning about an unusually sophisticated phishing attack that can let attackers take remote control over user systems when recipients click the included link. The warning comes just weeks after the company quietly patched a vulnerability that makes it easier for phishers to launch these attacks.

A phishing attack targeting MSP customers using ConnectWise.
ConnectWise Control is extremely popular among MSPs that manage, protect and service large numbers of computers remotely for client organizations. Their product provides a dynamic software client and hosted server that connects two or more computers together, and provides temporary or persistent remote access to those client systems.
When a support technician wants to use it to remotely administer a computer, the ConnectWise website generates an executable file that is digitally signed by ConnectWise and downloadable by the client via a hyperlink.
When the remote user in need of assistance clicks the link, their computer is then directly connected to the computer of the remote administrator, who can then control the client’s computer as if they were seated in front of it.
While modern Microsoft Windows operating systems by default will ask users whether they want to run a downloaded executable file, many systems set up for remote administration by MSPs disable that user account control feature for this particular application.
In October, security researcher Ken Pyle alerted ConnectWise that their client executable file gets generated based on client-controlled parameters. Meaning, an attacker could craft a ConnectWise Control client download link that would bounce or proxy the remote connection from the MSP’s servers to a server that the attacker controls.
This is dangerous because many organizations that rely on MSPs to manage their computers often set up their networks so that only remote assistance connections coming from their MSP’s networks are allowed.
Using a free ConnectWise trial account, Pyle showed the company how easy it was to create a client executable that is cryptographically signed by ConnectWise and can bypass those network restrictions by bouncing the connection through an attacker’s ConnectWise Control server.
“You as the attacker have full control over the link’s parameters, and that link gets injected into an executable file that is downloaded by the client through an unauthenticated Web interface,” said Pyle, a partner and exploit developer at the security firm Cybir. “I can send this link to a victim, they will click this link, and their workstation will connect back to my instance via a link on your site.”
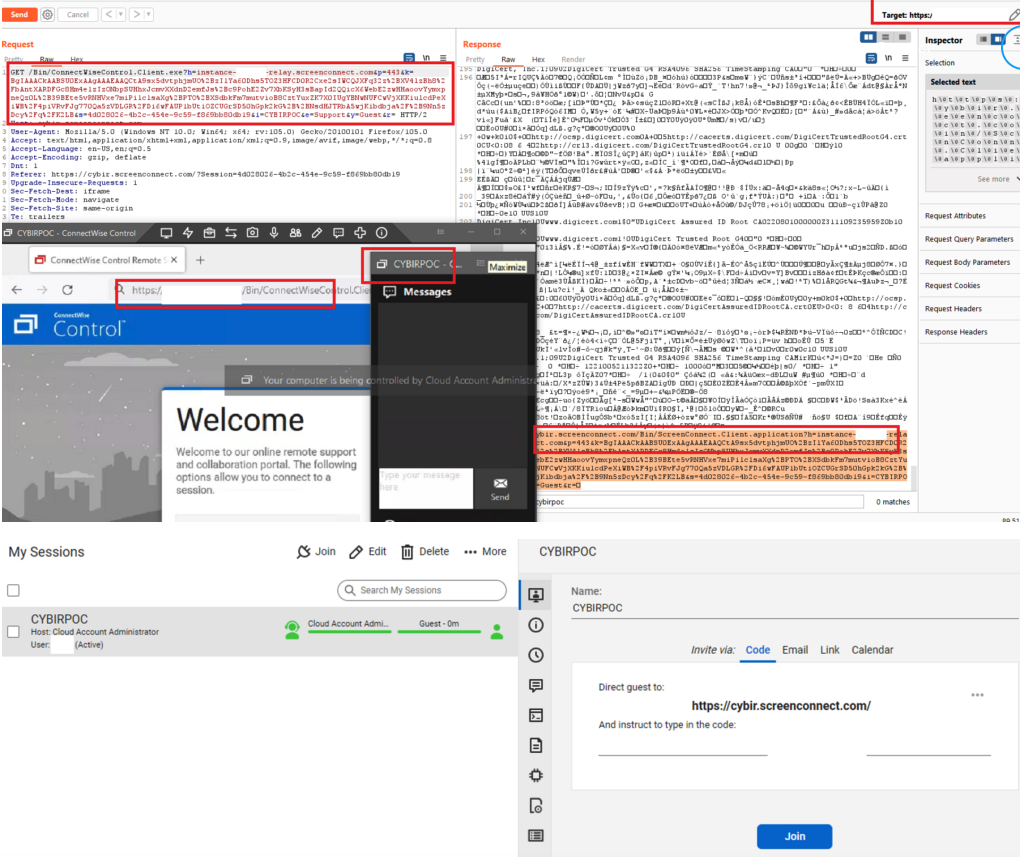
A composite of screenshots researcher Ken Pyle put together to illustrate the ScreenConnect vulnerability.
On Nov. 29, roughly the same time Pyle published a blog post about his findings, ConnectWise issued an advisory warning users to be on guard against a new round email phishing attempts that mimic legitimate email alerts the company sends when it detects unusual activity on a customer account.
“We are aware of a phishing campaign that mimics ConnectWise Control New Login Alert emails and has the potential to lead to unauthorized access to legitimate Control instances,” the company said.
ConnectWise said it released software updates last month that included new protections against the misdirection vulnerability that Pyle reported. But the company said there is no reason to believe the phishers they warned about are exploiting any of the issues reported by Pyle.
“Our team quickly triaged the report and determined the risk to partners to be minimal,” said Patrick Beggs, ConnectWise’s chief information security officer. “Nevertheless, the mitigation was simple and presented no risk to partner experience, so we put it into the then-stable 22.8 build and the then-canary 22.9 build, which were released as part of our normal release processes. Due to the low severity of the issue, we didn’t (and don’t plan to) issue a security advisory or alert, since we reserve those notifications for serious security issues.”
Beggs said the phishing attacks that sparked their advisory stemmed from an instance that was not hosted by ConnectWise.
“So we can confirm they are unrelated,” he said. “Unfortunately, phishing attacks happen far too regularly across a variety of industries and products. The timing of our advisory and Mr. Pyle’s blog were coincidental. That said, we’re all for raising more awareness of the seriousness of phishing attacks and the general importance of staying alert and aware of potentially dangerous content.”
The ConnectWise advisory warned users that before clicking any link that appears to come from their service, users should validate the content includes “domains owned by trusted sources,” and “links to go to places you recognize.”
But Pyle said this advice is not terribly useful for customers targeted in his attack scenario because the phishers can send emails directly from ConnectWise, and the short link that gets presented to the user is a wildcard domain that ends in ConnectWise Control’s own domain name — screenconnect.com. What’s more, examining the exceedingly long link generated by ConnectWise’s systems offers few insights to the average user.
“It’s signed by ConnectWise and comes from them, and if you sign up for a free trial instance, you can email people invites directly from them,” Pyle said.
ConnectWise’s warnings come amid breach reports from another major provider of remote support technologies: GoTo disclosed on Nov. 30 that it is investigating a security incident involving “unusual activity within our development environment and third-party cloud storage services. The third-party cloud storage service is currently shared by both GoTo and its affiliate, the password manager service LastPass.
In its own advisory on the incident, LastPass said they believe the intruders leveraged information stolen during a previous intrusion in August 2022 to gain access to “certain elements of our customers’ information.” However, LastPass maintains that its “customer passwords remain safely encrypted due to LastPass’s Zero Knowledge architecture.”
In short, that architecture means if you lose or forget your all-important master LastPass password — the one needed to unlock access to all of your other passwords stored with them — LastPass can’t help you with that, because they don’t store it. But that same architecture theoretically means that hackers who might break into LastPass’s networks can’t access that information either.
Update, 7:25 p.m. ET: Included statement from ConnectWise CISO.
A recent scoop by Reuters revealed that mobile apps for the U.S. Army and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) were integrating software that sends visitor data to a Russian company called Pushwoosh, which claims to be based in the United States. But that story omitted an important historical detail about Pushwoosh: In 2013, one of its developers admitted to authoring the Pincer Trojan, malware designed to surreptitiously intercept and forward text messages from Android mobile devices.
Pushwoosh says it is a U.S. based company that provides code for software developers to profile smartphone app users based on their online activity, allowing them to send tailor-made notifications. But a recent investigation by Reuters raised questions about the company’s real location and truthfulness.
The Army told Reuters it removed an app containing Pushwoosh in March, citing “security concerns.” The Army app was used by soldiers at one of the nation’s main combat training bases.
Reuters said the CDC likewise recently removed Pushwoosh code from its app over security concerns, after reporters informed the agency Pushwoosh was not based in the Washington D.C. area — as the company had represented — but was instead operated from Novosibirsk, Russia.
Pushwoosh’s software also was found in apps for “a wide array of international companies, influential nonprofits and government agencies from global consumer goods company Unilever and the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) to the politically powerful U.S. gun lobby, the National Rifle Association (NRA), and Britain’s Labour Party.”
The company’s founder Max Konev told Reuters Pushwoosh “has no connection with the Russian government of any kind” and that it stores its data in the United States and Germany.
But Reuters found that while Pushwoosh’s social media and U.S. regulatory filings present it as a U.S. company based variously in California, Maryland and Washington, D.C., the company’s employees are located in Novosibirsk, Russia.
Reuters also learned that the company’s address in California does not exist, and that two LinkedIn accounts for Pushwoosh employees in Washington, D.C. were fake.
“Pushwoosh never mentioned it was Russian-based in eight annual filings in the U.S. state of Delaware, where it is registered, an omission which could violate state law,” Reuters reported.
Pushwoosh admitted the LinkedIn profiles were fake, but said they were created by a marketing firm to drum up business for the company — not misrepresent its location.
Pushwoosh told Reuters it used addresses in the Washington, D.C. area to “receive business correspondence” during the coronavirus pandemic. A review of the Pushwoosh founder’s online presence via Constella Intelligence shows his Pushwoosh email address was tied to a phone number in Washington, D.C. that was also connected to email addresses and account profiles for over a dozen other Pushwoosh employees.
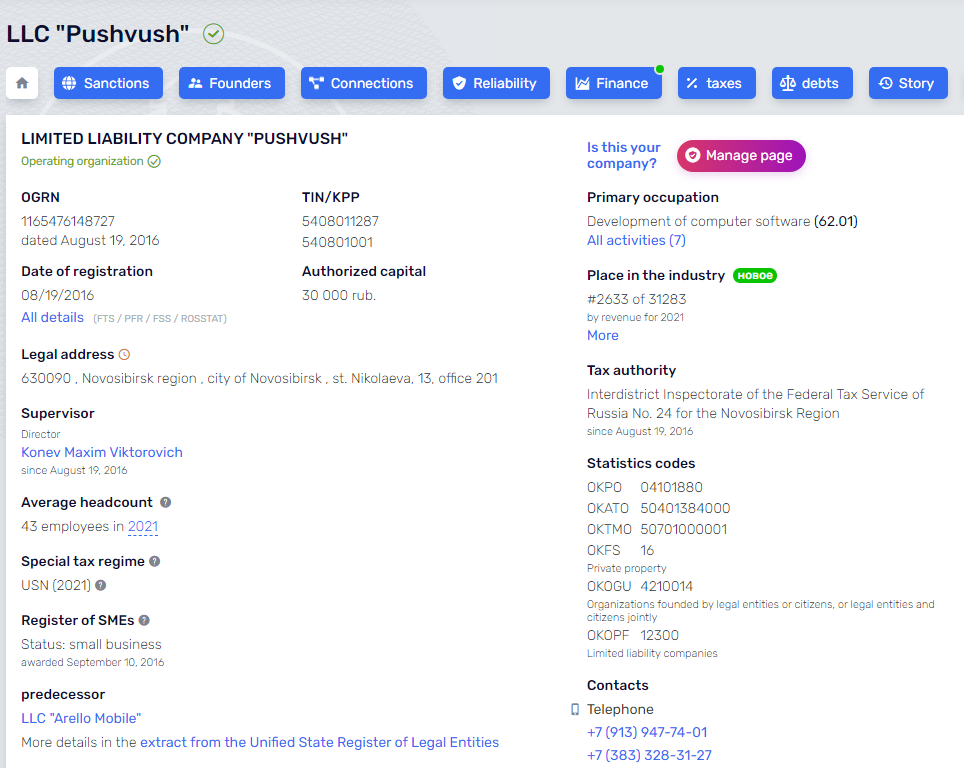
Pushwoosh was incorporated in Novosibirsk, Russia in 2016.
The dust-up over Pushwoosh came in part from data gathered by Zach Edwards, a security researcher who until recently worked for the Internet Safety Labs, a nonprofit organization that funds research into online threats.
Edwards said Pushwoosh began as Arello-Mobile, and for several years the two co-branded — appearing side by side at various technology expos. Around 2016, he said, the two companies both started using the Pushwoosh name.
A search on Pushwoosh’s code base shows that one of the company’s longtime developers is a 41-year-old from Novosibirsk named Yuri Shmakov. In 2013, KrebsOnSecurity interviewed Shmakov for the story, “Who Wrote the Pincer Android Trojan?” wherein Shmakov acknowledged writing the malware as a freelance project.
Shmakov told me that, based on the client’s specifications, he suspected it might ultimately be put to nefarious uses. Even so, he completed the job and signed his work by including his nickname in the app’s code.
“I was working on this app for some months, and I was hoping that it would be really helpful,” Shmakov wrote. “[The] idea of this app is that you can set it up as a spam filter…block some calls and SMS remotely, from a Web service. I hoped that this will be [some kind of] blacklist, with logging about blocked [messages/calls]. But of course, I understood that client [did] not really want this.”
Shmakov did not respond to requests for comment. His LinkedIn profile says he stopped working for Arello Mobile in 2016, and that he currently is employed full-time as the Android team leader at an online betting company.
In a blog post responding to the Reuters story, Pushwoosh said it is a privately held company incorporated under the state laws of Delaware, USA, and that Pushwoosh Inc. was never owned by any company registered in the Russian Federation.
“Pushwoosh Inc. used to outsource development parts of the product to the Russian company in Novosibirsk, mentioned in the article,” the company said. “However, in February 2022, Pushwoosh Inc. terminated the contract.”
However, Edwards noted that dozens of developer subdomains on Pushwoosh’s main domain still point to JSC Avantel, an Internet provider based in Novosibirsk, Russia.
Edwards said the U.S. Army’s app had a custom Pushwoosh configuration that did not appear on any other customer implementation.
“It had an extremely custom setup that existed nowhere else,” Edwards said. “Originally, it was an in-app Web browser, where it integrated a Pushwoosh javascript so that any time a user clicked on links, data went out to Pushwoosh and they could push back whatever they wanted through the in-app browser.”
An Army Times article published the day after the Reuters story ran said at least 1,000 people downloaded the app, which “delivered updates for troops at the National Training Center on Fort Irwin, Calif., a critical waypoint for deploying units to test their battlefield prowess before heading overseas.”
In April 2022, roughly 4,500 Army personnel converged on the National Training Center for a war games exercise on how to use lessons learned from Russia’s war against Ukraine to prepare for future fights against a major adversary such as Russia or China.
Edwards said despite Pushwoosh’s many prevarications, the company’s software doesn’t appear to have done anything untoward to its customers or users.
“Nothing they did has been seen to be malicious,” he said. “Other than completely lying about where they are, where their data is being hosted, and where they have infrastructure.”
Edwards also found Pushwoosh’s technology embedded in nearly two dozen mobile apps that were sold to cities and towns across Illinois as a way to help citizens access general information about their local communities and officials.
 The Illinois apps that bundled Pushwoosh’s technology were produced by a company called Government 311, which is owned by Bill McCarty, the current director of the Springfield Office of Budget and Management. A 2014 story in The State Journal-Register said Gov 311’s pricing was based on population, and that the app would cost around $2,500 per year for a city with approximately 25,000 people.
The Illinois apps that bundled Pushwoosh’s technology were produced by a company called Government 311, which is owned by Bill McCarty, the current director of the Springfield Office of Budget and Management. A 2014 story in The State Journal-Register said Gov 311’s pricing was based on population, and that the app would cost around $2,500 per year for a city with approximately 25,000 people.
McCarty told KrebsOnSecurity that his company stopped using Pushwoosh “years ago,” and that it now relies on its own technology to provide push notifications through its 311 apps.
But Edwards found some of the 311 apps still try to phone home to Pushwoosh, such as the 311 app for Riverton, Ill.
“Riverton ceased being a client several years ago, which [is] probably why their app was never updated to change out Pushwoosh,” McCarty explained. “We are in the process of updating all client apps and a website refresh. As part of that, old unused apps like Riverton 311 will be deleted.”
Edwards said it’s far from clear how many other state and local government apps and Web sites rely on technology that sends user data to U.S. adversaries overseas. In July, Congress introduced an amended version of the Intelligence Authorization Act for 2023, which included a new section focusing on data drawn from online ad auctions that could be used to geolocate individuals or gain other information about them.
Business Insider reports that if this section makes it into the final version — which the Senate also has to pass — the Office for the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) will have 60 days after the Act becomes law to produce a risk assessment. The assessment will look into “the counterintelligence risks of, and the exposure of intelligence community personnel to, tracking by foreign adversaries through advertising technology data,” the Act states.
Edwards says he’s hoping those changes pass, because what he found with Pushwoosh is likely just a drop in a bucket.
“I’m hoping that Congress acts on that,” he said. “If they were to put a requirement that there’s an annual audit of risks from foreign ad tech, that would at least force people to identify and document those connections.”
A nonprofit organization is suing the state of Massachusetts on behalf of thousands of low-income families who were collectively robbed of more than a $1 million in food assistance benefits by card skimming devices secretly installed at cash machines and grocery store checkout lanes across the state. Federal law bars states from replacing these benefits using federal funds, and a recent rash of skimming incidents nationwide has disproportionately affected those receiving food assistance via state-issued prepaid debit cards.

The Massachusetts SNAP benefits card looks more like a library card than a payment card.
On Nov. 4, The Massachusetts Law Reform Institute (MLRI) filed a class action lawsuit on behalf of low-income families whose Supplemental Nutrition and Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits were stolen from their accounts. The SNAP program serves over a million people in Massachusetts, and 41 million people nationally.
“Over the past few months, thieves have stolen over a million SNAP dollars from thousands of Massachusetts families – putting their nutrition and economic stability at risk,” the MLRI said in a statement on the lawsuit. “The criminals attach a skimming device on a POS (point of sale) terminal to capture the household’s account information and PIN. The criminals then use that information to make a fake card and steal the SNAP benefits.”
In announcing the lawsuit, the MRLI linked to a story KrebsOnSecurity published last month that examined how skimming thieves increasingly are targeting SNAP payment card holders nationwide. The story looked at how the vast majority of SNAP benefit cards issued by the states do not include the latest chip technology that makes it more difficult and expensive for thieves to clone them.
The story also highlighted how SNAP cardholders usually have little recourse to recover any stolen funds — even in unlikely cases where the victim has gathered mountains of proof to show state and federal officials that the fraudulent withdrawals were not theirs.
Deborah Harris is a staff attorney at the MLRI. Harris said the goal of the lawsuit is to force Massachusetts to reimburse SNAP skimming victims using state funds, and to convince The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) — which funds the program that states draw from — to change its policies and allow states to replace stolen benefits with federal funds.
“Ultimately we think it’s the USDA that needs to step up and tell states they have a duty to restore the stolen benefits, and that USDA will cover the cost at least until there is better security in place, such as chip cards,” Harris told KrebsOnSecurity.
“The losses we’re talking about are relatively small in the scheme of total SNAP expenditures which are billions,” she said. “But if you are a family that can’t pay for food because you suddenly don’t have money in your account, it’s devastating for the family.”
The USDA has not said it will help states restore the stolen funds. But on Oct. 31, 2022, the agency released guidance (PDF) whose primary instructions were included in an appendix titled, Card Security Options Available to Households. Notably, the USDA did not mention the idea of shifting to chip-based SNAP benefits cards.

The recently issued USDA guidance.
“The guidance generally continues to make households responsible for preventing the theft of their benefits as well as for suffering the loss when benefits are stolen through no fault of the household,” Harris said. “Many of the recommendations are not practical for households who don’t have a smartphone to receive text messages and aren’t able to change their PIN after each transaction and keep track of the new PIN.”
Harris said three of the four recommendations are not currently available in Massachusetts, and they are very likely not currently available in other states. For example, she said, Massachusetts households do not have the option of freezing or locking their cards between transactions. Nor do they receive alerts about transactions. And they most certainly don’t have any way to block out-of-state transactions.
“Perhaps these are options that [card] processors and states could provide, but they are not available now as far as we know,” Harris said. “Most likely they would take time to implement.”
The Center for Law and Social Policy (CLASP) recently published Five Ways State Agencies Can Support EBT Users at Risk of Skimming. CLASP says while it is true states can’t use federal funds to replace benefits unless the loss was due to a “system error,” states could use their own funds.
“Doing so will ensure families don’t have to go without food, gas money, or their rent for the month,” CLASP wrote.
That would help address the symptoms of card skimming, but not a root cause. Hardly anyone is suggesting the obvious, which is to equip SNAP benefit cards with the same security technology afforded to practically everyone else participating in the U.S. banking system.
There are several reasons most state-issued SNAP benefit cards do not include chips. For starters, nobody says they have to. Also, it’s a fair bit more expensive to produce chip cards versus plain old magnetic stripe cards, and many state assistance programs are chronically under-funded. Finally, there is no vocal (or at least well-heeled) constituency advocating for change.
A copy of the class action complaint filed by the MLRI is available here.
Responding to a recent surge in AI-generated bot accounts, LinkedIn is rolling out new features that it hopes will help users make more informed decisions about with whom they choose to connect. Many LinkedIn profiles now display a creation date, and the company is expanding its domain validation offering, which allows users to publicly confirm that they can reply to emails at the domain of their stated current employer.
LinkedIn’s new “About This Profile” section — which is visible by clicking the “More” button at the top of a profile — includes the year the account was created, the last time the profile information was updated, and an indication of how and whether an account has been verified.
LinkedIn also said it is adding a warning to some LinkedIn messages that include high-risk content, or that try to entice the user into taking the conversation to another platform (like WeChat).
“We may warn you about messages that ask you to take the conversation to another platform because that can be a sign of a scam,” the company said in a blog post. “These warnings will also give you the choice to report the content without letting the sender know.”
In late September 2022, KrebsOnSecurity warned about the proliferation of fake LinkedIn profiles for Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at some of the world’s largest corporations. A follow-up story on Oct. 5 showed how the phony profile problem has affected virtually all executive roles at corporations, and how these fake profiles are creating an identity crisis for the businesses networking site and the companies that rely on it to hire and screen prospective employees.
Reporting here last month also tracked a massive drop in profiles claiming to work at several major technology companies, as LinkedIn apparently took action against hundreds of thousands of inauthentic accounts that falsely claimed roles at these companies.
For example, on October 10, 2022, there were 576,562 LinkedIn accounts that listed their current employer as Apple Inc. The next day, half of those profiles no longer existed. At around the same time, the number of LinkedIn profiles claiming current roles at Amazon fell from roughly 1.25 million to 838,601 in just one day, a 33 percent drop.
For whatever reason, the majority of the phony LinkedIn profiles reviewed by this author were young women with profile photos that appear to have been generated by artificial intelligence (AI) tools.
“We’re seeing rapid advances in AI-based synthetic image generation technology and we’ve created a deep learning model to better catch profiles made with this technology,” LinkedIn’s Oscar Rodriguez wrote. “AI-based image generators can create an unlimited number of unique, high-quality profile photos that do not correspond to real people.”
It remains unclear who or what is behind the recent proliferation of fake executive profiles on LinkedIn, but likely they are from a combination of scams. Cybersecurity firm Mandiant (recently acquired by Google) told Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean government have been copying resumes and profiles from leading job listing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency firms.
Identity thieves have been known to masquerade on LinkedIn as job recruiters, collecting personal and financial information from people who fall for employment scams.
Also, fake profiles also may be tied to so-called “pig butchering” scams, wherein people are lured by flirtatious strangers online into investing in cryptocurrency trading platforms that eventually seize any funds when victims try to cash out.
A 25-year-old Finnish man has been charged with extorting a once popular and now-bankrupt online psychotherapy company and its patients. Finnish authorities rarely name suspects in an investigation, but they were willing to make an exception for Julius “Zeekill” Kivimaki, a notorious hacker who — at the tender age of 17 — had been convicted of more than 50,000 cybercrimes, including data breaches, payment fraud, operating botnets, and calling in bomb threats.
In late October 2022, Kivimaki was charged (and arrested in absentia, according to the Finns) with attempting to extort money from the Vastaamo Psychotherapy Center. On October 21, 2020, Vastaamo became the target of blackmail when a tormentor identified as “ransom_man” demanded payment of 40 bitcoins (~450,000 euros at the time) in return for a promise not to publish highly sensitive therapy session notes Vastaamo had exposed online.
In a series of posts over the ensuing days on a Finnish-language dark net discussion board, ransom_man said Vastaamo appeared unwilling to negotiate a payment, and that he would start publishing 100 patient profiles every 24 hours “to provide further incentive for the company to continue communicating with us.”
“We’re not asking for much, approximately 450,000 euros which is less than 10 euros per patient and only a small fraction of the around 20 million yearly revenues of this company,” ransom_man wrote.
When Vastaamo declined to pay, ransom_man shifted to extorting individual patients. According to Finnish police, some 22,000 victims reported extortion attempts targeting them personally, targeted emails that threatened to publish their therapy notes online unless paid a 500 euro ransom.

The extortion message targeted Vastaamo patients.
On Oct. 23, 2020, ransom_man uploaded to the dark web a large compressed file that included all of the stolen Vastaamo patient records. But investigators found the file also contained an entire copy of ransom_man’s home folder, a likely mistake that exposed a number of clues that they say point to Kivimaki.
Ransom_man quickly deleted the large file (accompanied by a “whoops” notation), but not before it had been downloaded a number of times. The entire archive has since been made into a searchable website on the Dark Web.
Among those who grabbed a copy of the database was Antti Kurittu, a team lead at Nixu Corporation and a former criminal investigator. In 2013, Kurittu worked on investigation involving Kivimaki’s use of the Zbot botnet, among other activities Kivimaki engaged in as a member of the hacker group Hack the Planet.
“It was a huge opsec [operational security] fail, because they had a lot of stuff in there — including the user’s private SSH folder, and a lot of known hosts that we could take a very good look at,” Kurittu told KrebsOnSecurity, declining to discuss specifics of the evidence investigators seized. “There were also other projects and databases.”
Kurittu said he and others he and others who were familiar with illegal activities attributed to Kivimäki couldn’t shake suspicion that the infamous cybercriminal was also behind the Vastaamo extortion.
“I couldn’t find anything that would link that data directly to one individual, but there were enough indicators in there that put the name in my head and I couldn’t shake it,” Kurittu said. “When they named him as the prime suspect I was not surprised.”
A handful of individually extorted victims paid a ransom, but when news broke that the entire Vastaamo database had been leaked online, the extortion threats no longer held their sting. However, someone would soon set up a site on the dark web where anyone could search this sensitive data.
Kivimaki stopped using his middle name Julius in favor of his given first name Aleksanteri when he moved abroad several years ago. A Twitter account by that name was verified by Kivimaki’s attorney as his, and through that account he denied being involved in the Vastaamo extortion.
“I believe [the Finnish authorities] brought this to the public in order to influence the decision-making of my old case from my teenage years, which was just processed in the Court of Appeal, both cases are investigated by the same persons,” Kivimaki tweeted on Oct. 28.
Kivimaki is appealing a 2020 district court decision sentencing him to “one year of conditional imprisonment for two counts of fraud committed as a young person, and one of gross fraud, interference with telecommunications as a young person, aggravated data breach as a young person and incitement to fraud as a young person,” according to the Finnish tabloid Ilta-Sanomat.
“Now in the Court of Appeal, the prosecutor is demanding a harsher punishment for the man, i.e. unconditional imprisonment,” reads the Ilta-Sanomat story. “The prosecutor notes in his complaint that the young man has been committing cybercrimes from Espoo since he was 15 years old, and the actions have had to be painstakingly investigated through international legal aid.”
As described in this Wired story last year, Vastaamo filled an urgent demand for psychological counseling, and it won accolades from Finnish health authorities and others for its services.
“Vastaamo was a private company, but it seemed to operate in the same spirit of tech-enabled ease and accessibility: You booked a therapist with a few clicks, wait times were tolerable, and Finland’s Social Insurance Institution reimbursed a big chunk of the session fee (provided you had a diagnosed mental disorder),” William Ralston wrote for Wired. “The company was run by Ville Tapio, a 39-year-old coder and entrepreneur with sharp eyebrows, slicked-back brown hair, and a heavy jawline. He’d cofounded the company with his parents. They pitched Vastaamo as a humble family-run enterprise committed to improving the mental health of all Finns.”
But for all the good it brought, the healthcare records management system that Vastaamo used relied on little more than a MySQL database that was left dangerously exposed to the web for 16 months, guarded by nothing more than an administrator account with a blank password.
The Finnish daily Iltalehti said Tapio was relieved of his duties as CEO of Vastaamo in October 2020, and that in September, prosecutors brought charges against Tapio for a data protection offense in connection with Vastaamo’s information leak.
“According to Vastaamo, the data breach in Vastaamo’s customer databases took place in November 2018,” Iltalehti reported last month. “According to Vastaamo, Tapio concealed information about the data breach for more than a year and a half.”
A 26-year-old Ukrainian man is awaiting extradition from The Netherlands to the United States on charges that he acted as a core developer for Raccoon, a popular “malware-as-a-service” offering that helped paying customers steal passwords and financial data from millions of cybercrime victims. KrebsOnSecurity has learned that the defendant was busted in March 2022, after fleeing mandatory military service in Ukraine in the weeks following the Russian invasion.

Ukrainian national Mark Sokolovsky, seen here in a Porsche Cayenne on Mar. 18 fleeing mandatory military service in Ukraine. This image was taken by Polish border authorities as Sokolovsky’s vehicle entered Germany. Image: KrebsOnSecurity.com.
The U.S. Attorney for the Western District of Texas unsealed an indictment last week that named Ukrainian national Mark Sokolovsky as the core developer for the Raccoon Infostealer business, which was marketed on several Russian-language cybercrime forums beginning in 2019.
Raccoon was essentially a Web-based control panel, where — for $200 a month — customers could get the latest version of the Raccoon Infostealer malware, and interact with infected systems in real time. Security experts say the passwords and other data stolen by Raccoon malware were often resold to groups engaged in deploying ransomware.
Working with investigators in Italy and The Netherlands, U.S. authorities seized a copy of the server used by Raccoon to help customers manage their botnets. According to the U.S. Justice Department, FBI agents have identified more than 50 million unique credentials and forms of identification (email addresses, bank accounts, cryptocurrency addresses, credit card numbers, etc.) stolen with the help of Raccoon.
The Raccoon v. 1 web panel, where customers could search by infected IP, and stolen cookies, wallets, domains and passwords.
The unsealed indictment (PDF) doesn’t delve much into how investigators tied Sokolovsky to Raccoon, but two sources close to the investigation shared more information about that process on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to discuss the case publicly.
According to those sources, U.S. authorities zeroed in on an operational security mistake that the Raccoon developer made early on in his posts to the crime forums, connecting a Gmail account for a cybercrime forum identity used by the Raccoon developer (“Photix”) to an Apple iCloud account belonging to Sokolovsky. For example, the indictment includes a photo that investigators subpoenaed from Sokolovsky’s iCloud account that shows him posing with several stacks of bundled cash.

A selfie pulled from Mark Sokolovsky’s iCloud account. Image: USDOJ.
When Russia invaded Ukraine in late February 2022, Sokolovsky was living in Kharkiv, a city in northeast Ukraine that would soon come under heavy artillery bombardment from Russian forces. Authorities monitoring Sokolovsky’s iCloud account had spent weeks watching him shuttle between Kharkiv and the Ukrainian capital Kyiv, but on Mar. 18, 2022, his phone suddenly showed up in Poland.
Investigators learned from Polish border guards that Sokolovsky had fled Ukraine in a Porsche Cayenne along with a young blond woman, leaving his mother and other family behind. The image at the top of this post was shared with U.S. investigators by Polish border security officials, and it shows Sokolovsky leaving Poland for Germany on Mar. 18.
At the time, all able-bodied men of military age were required to report for service to help repel the Russian invasion, and it would have been illegal for Sokolovsky to leave Ukraine without permission. But both sources said investigators believe Sokolovsky bribed border guards to let them pass.
Authorities soon tracked Sokolovsky’s phone through Germany and eventually to The Netherlands, with his female companion helpfully documenting every step of the trip on her Instagram account. Here is a picture she posted of the two embracing upon their arrival in Amsterdam’s Dam Square:

Authorities in The Netherlands arrested Sokolovsky on Mar. 20, and quickly seized control over the Raccoon Infostealer infrastructure. Meanwhile, on March 25 the accounts that had previously advertised the Raccoon Stealer malware on cybercrime forums announced the service was closing down. The parting message to customers said nothing of an arrest, and instead insinuated that the core members in charge of the malware-as-a-service project had perished in the Russian invasion.
“Unfortunately, due to the ‘special operation,’ we will have to close our Raccoon Stealer project,” the team announced Mar. 25. “Our team members who were responsible for critical components of the product are no longer with us. Thank you for this experience and time, for every day, unfortunately everything, sooner or later, the end of the WORLD comes to everyone.”
Sokolovsky’s extradition to the United States has been granted, but he is appealing that decision. He faces one count of conspiracy to commit computer fraud; one count of conspiracy to commit wire fraud; one count of conspiracy to commit money laundering, and one count of aggravated identity theft.
Sources tell KrebsOnSecurity that Sokolovsky has been consulting with Houston, Tx.-based attorney F. Andino Reynal, the same lawyer who represented Alex Jones in the recent defamation lawsuit against Jones and his conspiracy theory website Infowars. Reynal was responsible for what Jones himself referred to as the “Perry Mason” moment of the trial, wherein the plaintiff’s lawyer revealed that Reynal had inadvertently given them an entire digital copy of Jones’s cell phone. Mr. Reynal did not respond to requests for comment.
If convicted, Sokolovsky faces a maximum penalty of 20 years in prison for the wire fraud and money laundering offenses, five years for the conspiracy to commit computer fraud charge, and a mandatory consecutive two-year term for the aggravated identity theft offense.
The Justice Department has set up a website — raccoon.ic3.gov — that allows visitors to check whether their email address shows up in the data collected by the Raccoon Stealer service.
On October 10, 2022, there were 576,562 LinkedIn accounts that listed their current employer as Apple Inc. The next day, half of those profiles no longer existed. A similarly dramatic drop in the number of LinkedIn profiles claiming employment at Amazon comes as LinkedIn is struggling to combat a significant uptick in the creation of fake employee accounts that pair AI-generated profile photos with text lifted from legitimate users.
Jay Pinho is a developer who is working on a product that tracks company data, including hiring. Pinho has been using LinkedIn to monitor daily employee headcounts at several dozen large organizations, and last week he noticed that two of them had far fewer people claiming to work for them than they did just 24 hours previously.
Pinho’s screenshot below shows the daily count of employees as displayed on Amazon’s LinkedIn homepage. Pinho said his scraper shows that the number of LinkedIn profiles claiming current roles at Amazon fell from roughly 1.25 million to 838,601 in just one day, a 33 percent drop:
The number of LinkedIn profiles claiming current positions at Amazon fell 33 percent overnight. Image: twitter.com/jaypinho
As stated above, the number of LinkedIn profiles that claimed to work at Apple fell by approximately 50 percent on Oct. 10, according to Pinho’s analysis:
Image: twitter.com/jaypinho
Neither Amazon or Apple responded to requests for comment. LinkedIn declined to answer questions about the account purges, saying only that the company is constantly working to keep the platform free of fake accounts. In June, LinkedIn acknowledged it was seeing a rise in fraudulent activity happening on the platform.
KrebsOnSecurity hired Menlo Park, Calif.-based SignalHire to check Pinho’s numbers. SignalHire keeps track of active and former profiles on LinkedIn, and during the Oct 9-11 timeframe SignalHire said it saw somewhat smaller but still unprecedented drops in active profiles tied to Amazon and Apple.
“The drop in the percentage of 7-10 percent [of all profiles], as it happened [during] this time, is not something that happened before,” SignalHire’s Anastacia Brown told KrebsOnSecurity.
Brown said the normal daily variation in profile numbers for these companies is plus or minus one percent.
“That’s definitely the first huge drop that happened throughout the time we’ve collected the profiles,” she said.
In late September 2022, KrebsOnSecurity warned about the proliferation of fake LinkedIn profiles for Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at some of the world’s largest corporations. A follow-up story on Oct. 5 showed how the phony profile problem has affected virtually all executive roles at corporations, and how these fake profiles are creating an identity crisis for the businesses networking site and the companies that rely on it to hire and screen prospective employees.
A day after that second story ran, KrebsOnSecurity heard from a recruiter who noticed the number of LinkedIn profiles that claimed virtually any role in network security had dropped seven percent overnight. LinkedIn declined to comment about that earlier account purge, saying only that, “We’re constantly working at taking down fake accounts.”
A “swarm” of LinkedIn AI-generated bot accounts flagged by a LinkedIn group administrator recently.
It’s unclear whether LinkedIn is responsible for this latest account purge, or if individually affected companies are starting to take action on their own. The timing, however, argues for the former, as the account purges for Apple and Amazon employees tracked by Pinho appeared to happen within the same 24 hour period.
It’s also unclear who or what is behind the recent proliferation of fake executive profiles on LinkedIn. Cybersecurity firm Mandiant (recently acquired by Google) told Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean government have been copying resumes and profiles from leading job listing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency firms.
On this point, Pinho said he noticed an account purge in early September that targeted fake profiles tied to jobs at cryptocurrency exchange Binance. Up until Sept. 3, there were 7,846 profiles claiming current executive roles at Binance. The next day, that number stood at 6,102, a 23 percent drop (by some accounts that 6,102 head count is still wildly inflated).
Fake profiles also may be tied to so-called “pig butchering” scams, wherein people are lured by flirtatious strangers online into investing in cryptocurrency trading platforms that eventually seize any funds when victims try to cash out.
In addition, identity thieves have been known to masquerade on LinkedIn as job recruiters, collecting personal and financial information from people who fall for employment scams.
Nicholas Weaver, a researcher for the International Computer Science Institute at University of California, Berkeley, suggested another explanation for the recent glut of phony LinkedIn profiles: Someone may be setting up a mass network of accounts in order to more fully scrape profile information from the entire platform.
“Even with just a standard LinkedIn account, there’s a pretty good amount of profile information just in the default two-hop networks,” Weaver said. “We don’t know the purpose of these bots, but we know creating bots isn’t free and creating hundreds of thousands of bots would require a lot of resources.”
In response to last week’s story about the explosion of phony accounts on LinkedIn, the company said it was exploring new ways to protect members, such as expanding email domain verification. Under such a scheme, LinkedIn users would be able to publicly attest that their profile is accurate by verifying that they can respond to email at the domain associated with their current employer.
LinkedIn claims that its security systems detect and block approximately 96 percent of fake accounts. And despite the recent purges, LinkedIn may be telling the truth, Weaver said.
“There’s no way you can test for that,” he said. “Because technically, it may be that there were actually 100 million bots trying to sign up at LinkedIn as employees at Amazon.”
Weaver said the apparent mass account purge at LinkedIn underscores the size of the bot problem, and could present a “real and material change” for LinkedIn.
“It may mean the statistics they’ve been reporting about usage and active accounts are off by quite a bit,” Weaver said.
Microsoft today released updates to fix at least 85 security holes in its Windows operating systems and related software, including a new zero-day vulnerability in all supported versions of Windows that is being actively exploited. However, noticeably absent from this month’s Patch Tuesday are any updates to address a pair of zero-day flaws being exploited this past month in Microsoft Exchange Server.

The new zero-day flaw– CVE-2022-41033 — is an “elevation of privilege” bug in the Windows COM+ event service, which provides system notifications when users logon or logoff. Microsoft says the flaw is being actively exploited, and that it was reported by an anonymous individual.
“Despite its relatively low score in comparison to other vulnerabilities patched today, this one should be at the top of everyone’s list to quickly patch,” said Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs. “This specific vulnerability is a local privilege escalation, which means that an attacker would already need to have code execution on a host to use this exploit. Privilege escalation vulnerabilities are a common occurrence in almost every security compromise. Attackers will seek to gain SYSTEM or domain-level access in order to disable security tools, grab credentials with tools like Mimkatz and move laterally across the network.
Indeed, Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, notes that almost half of the security flaws Microsoft patched this week are elevation of privilege bugs.
Some privilege escalation bugs can be particularly scary. One example is CVE-2022-37968, which affects organizations running Kubernetes clusters on Azure and earned a CVSS score of 10.0 — the most severe score possible.
Microsoft says that to exploit this vulnerability an attacker would need to know the randomly generated DNS endpoint for an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. But that may not be such a tall order, says Breen, who notes that a number of free and commercial DNS discovery services now make it easy to find this information on potential targets.
Late last month, Microsoft acknowledged that attackers were exploiting two previously unknown vulnerabilities in Exchange Server. Paired together, the two flaws are known as “ProxyNotShell” and they can be chained to allow remote code execution on Exchange Server systems.
Microsoft said it was expediting work on official patches for the Exchange bugs, and it urged affected customers to enable certain settings to mitigate the threat from the attacks. However, those mitigation steps were soon shown to be ineffective, and Microsoft has been adjusting them on a daily basis nearly each day since then.
The lack of Exchange patches leaves a lot of Microsoft customers exposed. Security firm Rapid7 said that as of early September 2022 the company observed more than 190,000 potentially vulnerable instances of Exchange Server exposed to the Internet.
“While Microsoft confirmed the zero-days and issued guidance faster than they have in the past, there are still no patches nearly two weeks out from initial disclosure,” said Caitlin Condon, senior manager of vulnerability research at Rapid7. “Despite high hopes that today’s Patch Tuesday release would contain fixes for the vulnerabilities, Exchange Server is conspicuously missing from the initial list of October 2022 security updates. Microsoft’s recommended rule for blocking known attack patterns has been bypassed multiple times, emphasizing the necessity of a true fix.”
Adobe also released security updates to fix 29 vulnerabilities across a variety of products, including Acrobat and Reader, ColdFusion, Commerce and Magento. Adobe said it is not aware of active attacks against any of these flaws.
For a closer look at the patches released by Microsoft today and indexed by severity and other metrics, check out the always-useful Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. And it’s not a bad idea to hold off updating for a few days until Microsoft works out any kinks in the updates: AskWoody.com usually has the lowdown on any patches that may be causing problems for Windows users.
As always, please consider backing up your system or at least your important documents and data before applying system updates. And if you run into any problems with these updates, please drop a note about it here in the comments.

When U.S. consumers have their online bank accounts hijacked and plundered by hackers, U.S. financial institutions are legally obligated to reverse any unauthorized transactions as long as the victim reports the fraud in a timely manner. But new data released this week suggests that for some of the nation’s largest banks, reimbursing account takeover victims has become more the exception than the rule.
The findings came in a report released by Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.), who in April 2022 opened an investigation into fraud tied to Zelle, the “peer-to-peer” digital payment service used by many financial institutions that allows customers to quickly send cash to friends and family.
Zelle is run by Early Warning Services LLC (EWS), a private financial services company which is jointly owned by Bank of America, Capital One, JPMorgan Chase, PNC Bank, Truist, U.S. Bank, and Wells Fargo. Zelle is enabled by default for customers at over 1,000 different financial institutions, even if a great many customers still don’t know it’s there.
Sen. Warren said several of the EWS owner banks — including Capital One, JPMorgan and Wells Fargo — failed to provide all of the requested data. But Warren did get the requested information from PNC, Truist and U.S. Bank.
“Overall, the three banks that provided complete data sets reported 35,848 cases of scams, involving over $25.9 million of payments in 2021 and the first half of 2022,” the report summarized. “In the vast majority of these cases, the banks did not repay the customers that reported being scammed. Overall these three banks reported repaying customers in only 3,473 cases (representing nearly 10% of scam claims) and repaid only $2.9 million.”
Importantly, the report distinguishes between cases that involve straight up bank account takeovers and unauthorized transfers (fraud), and those losses that stem from “fraudulently induced payments,” where the victim is tricked into authorizing the transfer of funds to scammers (scams).
A common example of the latter is the Zelle Fraud Scam, which uses an ever-shifting set of come-ons to trick people into transferring money to fraudsters. The Zelle Fraud Scam often employs text messages and phone calls spoofed to look like they came from your bank, and the scam usually relates to fooling the customer into thinking they’re sending money to themselves when they’re really sending it to the crooks.
Here’s the rub: When a customer issues a payment order to their bank, the bank is obligated to honor that order so long as it passes a two-stage test. The first question asks, Did the request actually come from an authorized owner or signer on the account? In the case of Zelle scams, the answer is yes.
Trace Fooshee, a strategic advisor in the anti money laundering practice at Aite-Novarica, said the second stage requires banks to give the customer’s transfer order a kind of “sniff test” using “commercially reasonable” fraud controls that generally are not designed to detect patterns involving social engineering.
Fooshee said the legal phrase “commercially reasonable” is the primary reason why no bank has much — if anything — in the way of controlling for scam detection.
“In order for them to deploy something that would detect a good chunk of fraud on something so hard to detect they would generate egregiously high rates of false positives which would also make consumers (and, then, regulators) very unhappy,” Fooshee said. “This would tank the business case for the service as a whole rendering it something that the bank can claim to NOT be commercially reasonable.”
Sen. Warren’s report makes clear that banks generally do not pay consumers back if they are fraudulently induced into making Zelle payments.
“In simple terms, Zelle indicated that it would provide redress for users in cases of unauthorized transfers in which a user’s account is accessed by a bad actor and used to transfer a payment,” the report continued. “However, EWS’ response also indicated that neither Zelle nor its parent bank owners would reimburse users fraudulently induced by a bad actor into making a payment on the platform.”
Still, the data suggest banks did repay at least some of the funds stolen from scam victims about 10 percent of the time. Fooshee said he’s surprised that number is so high.
“That banks are paying victims of authorized payment fraud scams anything at all is noteworthy,” he said. “That’s money that they’re paying for out of pocket almost entirely for goodwill. You could argue that repaying all victims is a sound strategy especially in the climate we’re in but to say that it should be what all banks do remains an opinion until Congress changes the law.”
However, when it comes to reimbursing victims of fraud and account takeovers, the report suggests banks are stiffing their customers whenever they can get away with it. “Overall, the four banks that provided complete data sets indicated that they reimbursed only 47% of the dollar amount of fraud claims they received,” the report notes.
How did the banks behave individually? From the report:
-In 2021 and the first six months of 2022, PNC Bank indicated that its customers reported 10,683 cases of unauthorized payments totaling over $10.6 million, of which only 1,495 cases totaling $1.46 were refunded to consumers. PNC Bank left 86% of its customers that reported cases of fraud without recourse for fraudulent activity that occurred on Zelle.
-Over this same time period, U.S. Bank customers reported a total of 28,642 cases of unauthorized transactions totaling over $16.2 million, while only refunding 8,242 cases totaling less than $4.7 million.
-In the period between January 2021 and September 2022, Bank of America customers reported 81,797 cases of unauthorized transactions, totaling $125 million. Bank of America refunded only $56.1 million in fraud claims – less than 45% of the overall dollar value of claims made in that time.
–Truist indicated that the bank had a much better record of reimbursing defrauded customers over this same time period. During 2021 and the first half of 2022, Truist customers filed 24,752 unauthorized transaction claims amounting to $24.4 million. Truist reimbursed 20,349 of those claims, totaling $20.8 million – 82% of Truist claims were reimbursed over this period. Overall, however, the four banks that provided complete data sets indicated that they reimbursed only 47% of the dollar amount of fraud claims they received.
Fooshee said there has long been a great deal of inconsistency in how banks reimburse unauthorized fraud claims — even after the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CPFB) came out with guidance on what qualifies as an unauthorized fraud claim.
“Many banks reported that they were still not living up to those standards,” he said. “As a result, I imagine that the CFPB will come down hard on those with fines and we’ll see a correction.”
Fooshee said many banks have recently adjusted their reimbursement policies to bring them more into line with the CFPB’s guidance from last year.
“So this is heading in the right direction but not with sufficient vigor and speed to satisfy critics,” he said.
Seth Ruden is a payments fraud expert who serves as director of global advisory for digital identity company BioCatch. Ruden said Zelle has recently made “significant changes to its fraud program oversight because of consumer influence.”
“It is clear to me that despite sensational headlines, progress has been made to improve outcomes,” Ruden said. “Presently, losses in the network on a volume-adjusted basis are lower than those typical of credit cards.”
But he said any failure to reimburse victims of fraud and account takeovers only adds to pressure on Congress to do more to help victims of those scammed into authorizing Zelle payments.
“The bottom line is that regulations have not kept up with the speed of payment technology in the United States, and we’re not alone,” Ruden said. “For the first time in the UK, authorized payment scam losses have outpaced credit card losses and a regulatory response is now on the table. Banks have the choice right now to take action and increase controls or await regulators to impose a new regulatory environment.”
Sen. Warren’s report is available here (PDF).
There are, of course, some versions of the Zelle fraud scam that may be confusing financial institutions as to what constitutes “authorized” payment instructions. For example, the variant I wrote about earlier this year began with a text message that spoofed the target’s bank and warned of a pending suspicious transfer.
Those who responded at all received a call from a number spoofed to make it look like the victim’s bank calling, and were asked to validate their identities by reading back a one-time password sent via SMS. In reality, the thieves had simply asked the bank’s website to reset the victim’s password, and that one-time code sent via text by the bank’s site was the only thing the crooks needed to reset the target’s password and drain the account using Zelle.
None of the above discussion involves the risks affecting businesses that bank online. Businesses in the United States do not enjoy the same fraud liability protection afforded to consumers, and if a banking trojan or clever phishing site results in a business account getting drained, most banks will not reimburse that loss.
This is why I have always and will continue to urge small business owners to conduct their online banking affairs only from a dedicated, access restricted and security-hardened device — and preferably a non-Windows machine.
For consumers, the same old advice remains the best: Watch your bank statements like a hawk, and immediately report and contest any charges that appear fraudulent or unauthorized.
A recent proliferation of phony executive profiles on LinkedIn is creating something of an identity crisis for the business networking site, and for companies that rely on it to hire and screen prospective employees. The fabricated LinkedIn identities — which pair AI-generated profile photos with text lifted from legitimate accounts — are creating major headaches for corporate HR departments and for those managing invite-only LinkedIn groups.

Some of the fake profiles flagged by the co-administrator of a popular sustainability group on LinkedIn.
Last week, KrebsOnSecurity examined a flood of inauthentic LinkedIn profiles all claiming Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at various Fortune 500 companies, including Biogen, Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Hewlett Packard.
Since then, the response from LinkedIn users and readers has made clear that these phony profiles are showing up en masse for virtually all executive roles — but particularly for jobs and industries that are adjacent to recent global events and news trends.
Hamish Taylor runs the Sustainability Professionals group on LinkedIn, which has more than 300,000 members. Together with the group’s co-owner, Taylor said they’ve blocked more than 12,700 suspected fake profiles so far this year, including dozens of recent accounts that Taylor describes as “cynical attempts to exploit Humanitarian Relief and Crisis Relief experts.”
“We receive over 500 fake profile requests to join on a weekly basis,” Taylor said. “It’s hit like hell since about January of this year. Prior to that we did not get the swarms of fakes that we now experience.”

The opening slide for a plea by Taylor’s group to LinkedIn.
Taylor recently posted an entry on LinkedIn titled, “The Fake ID Crisis on LinkedIn,” which lampooned the “60 Least Wanted ‘Crisis Relief Experts’ — fake profiles that claimed to be experts in disaster recovery efforts in the wake of recent hurricanes. The images above and below show just one such swarm of profiles the group flagged as inauthentic. Virtually all of these profiles were removed from LinkedIn after KrebsOnSecurity tweeted about them last week.

Another “swarm” of LinkedIn bot accounts flagged by Taylor’s group.
Mark Miller is the owner of the DevOps group on LinkedIn, and says he deals with fake profiles on a daily basis — often hundreds per day. What Taylor called “swarms” of fake accounts Miller described instead as “waves” of incoming requests from phony accounts.
“When a bot tries to infiltrate the group, it does so in waves,” Miller said. “We’ll see 20-30 requests come in with the same type of information in the profiles.”
After screenshotting the waves of suspected fake profile requests, Miller started sending the images to LinkedIn’s abuse teams, which told him they would review his request but that he may never be notified of any action taken.
Some of the bot profiles identified by Mark Miller that were seeking access to his DevOps LinkedIn group. Miller said these profiles are all listed in the order they appeared.
Miller said that after months of complaining and sharing fake profile information with LinkedIn, the social media network appeared to do something which caused the volume of group membership requests from phony accounts to drop precipitously.
“I wrote our LinkedIn rep and said we were considering closing the group down the bots were so bad,” Miller said. “I said, ‘You guys should be doing something on the backend to block this.”
Jason Lathrop is vice president of technology and operations at ISOutsource, a Seattle-based consulting firm with roughly 100 employees. Like Miller, Lathrop’s experience in fighting bot profiles on LinkedIn suggests the social networking giant will eventually respond to complaints about inauthentic accounts. That is, if affected users complain loudly enough (posting about it publicly on LinkedIn seems to help).
Lathrop said that about two months ago his employer noticed waves of new followers, and identified more than 3,000 followers that all shared various elements, such as profile photos or text descriptions.
“Then I noticed that they all claim to work for us at some random title within the organization,” Lathrop said in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity. “When we complained to LinkedIn, they’d tell us these profiles didn’t violate their community guidelines. But like heck they don’t! These people don’t exist, and they’re claiming they work for us!”
Lathrop said that after his company’s third complaint, a LinkedIn representative responded by asking ISOutsource to send a spreadsheet listing every legitimate employee in the company, and their corresponding profile links.
Not long after that, the phony profiles that were not on the company’s list were deleted from LinkedIn. Lathrop said he’s still not sure how they’re going to handle getting new employees allowed into their company on LinkedIn going forward.
It remains unclear why LinkedIn has been flooded with so many fake profiles lately, or how the phony profile photos are sourced. Random testing of the profile photos shows they resemble but do not match other photos posted online. Several readers pointed out one likely source — the website thispersondoesnotexist.com, which makes using artificial intelligence to create unique headshots a point-and-click exercise.
Cybersecurity firm Mandiant (recently acquired by Google) told Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean government have been copying resumes and profiles from leading job listing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency firms.
Fake profiles also may be tied to so-called “pig butchering” scams, wherein people are lured by flirtatious strangers online into investing in cryptocurrency trading platforms that eventually seize any funds when victims try to cash out.
In addition, identity thieves have been known to masquerade on LinkedIn as job recruiters, collecting personal and financial information from people who fall for employment scams.
But the Sustainability Group administrator Taylor said the bots he’s tracked strangely don’t respond to messages, nor do they appear to try to post content.
“Clearly they are not monitored,” Taylor assessed. “Or they’re just created and then left to fester.”
This experience was shared by the DevOp group admin Miller, who said he’s also tried baiting the phony profiles with messages referencing their fakeness. Miller says he’s worried someone is creating a massive social network of bots for some future attack in which the automated accounts may be used to amplify false information online, or at least muddle the truth.
“It’s almost like someone is setting up a huge bot network so that when there’s a big message that needs to go out they can just mass post with all these fake profiles,” Miller said.
In last week’s story on this topic, I suggested LinkedIn could take one simple step that would make it far easier for people to make informed decisions about whether to trust a given profile: Add a “created on” date for every profile. Twitter does this, and it’s enormously helpful for filtering out a great deal of noise and unwanted communications.
Many of our readers on Twitter said LinkedIn needs to give employers more tools — perhaps some kind of application programming interface (API) — that would allow them to quickly remove profiles that falsely claim to be employed at their organizations.
Another reader suggested LinkedIn also could experiment with offering something akin to Twitter’s verified mark to users who chose to validate that they can respond to email at the domain associated with their stated current employer.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, LinkedIn said it was considering the domain verification idea.
“This is an ongoing challenge and we’re constantly improving our systems to stop fakes before they come online,” LinkedIn said in a written statement. “We do stop the vast majority of fraudulent activity we detect in our community – around 96% of fake accounts and around 99.1% of spam and scams. We’re also exploring new ways to protect our members such as expanding email domain verification. Our community is all about authentic people having meaningful conversations and to always increase the legitimacy and quality of our community.”
In a story published Wednesday, Bloomberg noted that LinkedIn has largely so far avoided the scandals about bots that have plagued networks like Facebook and Twitter. But that shine is starting to come off, as more users are forced to waste more of their time fighting off inauthentic accounts.
“What’s clear is that LinkedIn’s cachet as being the social network for serious professionals makes it the perfect platform for lulling members into a false sense of security,” Bloomberg’s Tim Cuplan wrote. “Exacerbating the security risk is the vast amount of data that LinkedIn collates and publishes, and which underpins its whole business model but which lacks any robust verification mechanisms.”
Microsoft Corp. is investigating reports that attackers are exploiting two previously unknown vulnerabilities in Exchange Server, a technology many organizations rely on to send and receive email. Microsoft says it is expediting work on software patches to plug the security holes. In the meantime, it is urging a subset of Exchange customers to enable a setting that could help mitigate ongoing attacks.

In customer guidance released Thursday, Microsoft said it is investigating two reported zero-day flaws affecting Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, 2016, and 2019. CVE-2022-41040, is a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability that can enable an authenticated attacker to remotely trigger the second zero-day vulnerability — CVE-2022-41082 — which allows remote code execution (RCE) when PowerShell is accessible to the attacker.
Microsoft said Exchange Online has detections and mitigation in place to protect customers. Customers using on-premises Microsoft Exchange servers are urged to review the mitigations suggested in the security advisory, which Microsoft says should block the known attack patterns.
Vietnamese security firm GTSC on Thursday published a writeup on the two Exchange zero-day flaws, saying it first observed the attacks in early August being used to drop “webshells.” These web-based backdoors offer attackers an easy-to-use, password-protected hacking tool that can be accessed over the Internet from any browser.
“We detected webshells, mostly obfuscated, being dropped to Exchange servers,” GTSC wrote. “Using the user-agent, we detected that the attacker uses Antsword, an active Chinese-based opensource cross-platform website administration tool that supports webshell management. We suspect that these come from a Chinese attack group because the webshell codepage is 936, which is a Microsoft character encoding for simplified Chinese.”
GTSC’s advisory includes details about post-compromise activity and related malware, as well as steps it took to help customers respond to active compromises of their Exchange Server environment. But the company said it would withhold more technical details of the vulnerabilities for now.
In March 2021, hundreds of thousands of organizations worldwide had their email stolen and multiple backdoor webshells installed, all thanks to four zero-day vulnerabilities in Exchange Server.
Granted, the zero-day flaws that powered that debacle were far more critical than the two detailed this week, and there are no signs yet that exploit code has been publicly released (that will likely change soon). But part of what made last year’s Exchange Server mass hack so pervasive was that vulnerable organizations had little or no advance notice on what to look for before their Exchange Server environments were completely owned by multiple attackers.
Microsoft is quick to point out that these zero-day flaws require an attacker to have a valid username and password for an Exchange user, but this may not be such a tall order for the hackers behind these latest exploits against Exchange Server.
Steven Adair is president of Volexity, the Virginia-based cybersecurity firm that was among the first to sound the alarm about the Exchange zero-days targeted in the 2021 mass hack. Adair said GTSC’s writeup includes an Internet address used by the attackers that Volexity has tied with high confidence to a China-based hacking group that has recently been observed phishing Exchange users for their credentials.
In February 2022, Volexity warned that this same Chinese hacking group was behind the mass exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability in the Zimbra Collaboration Suite, which is a competitor to Microsoft Exchange that many enterprises use to manage email and other forms of messaging.
If your organization runs Exchange Server, please consider reviewing the Microsoft mitigations and the GTSC post-mortem on their investigations.
Someone has recently created a large number of fake LinkedIn profiles for Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at some of the world’s largest corporations. It’s not clear who’s behind this network of fake CISOs or what their intentions may be. But the fabricated LinkedIn identities are confusing search engine results for CISO roles at major companies, and they are being indexed as gospel by various downstream data-scraping sources.
If one searches LinkedIn for the CISO of the energy giant Chevron, one might find the profile for a Victor Sites, who says he’s from Westerville, Ohio and is a graduate of Texas A&M University.
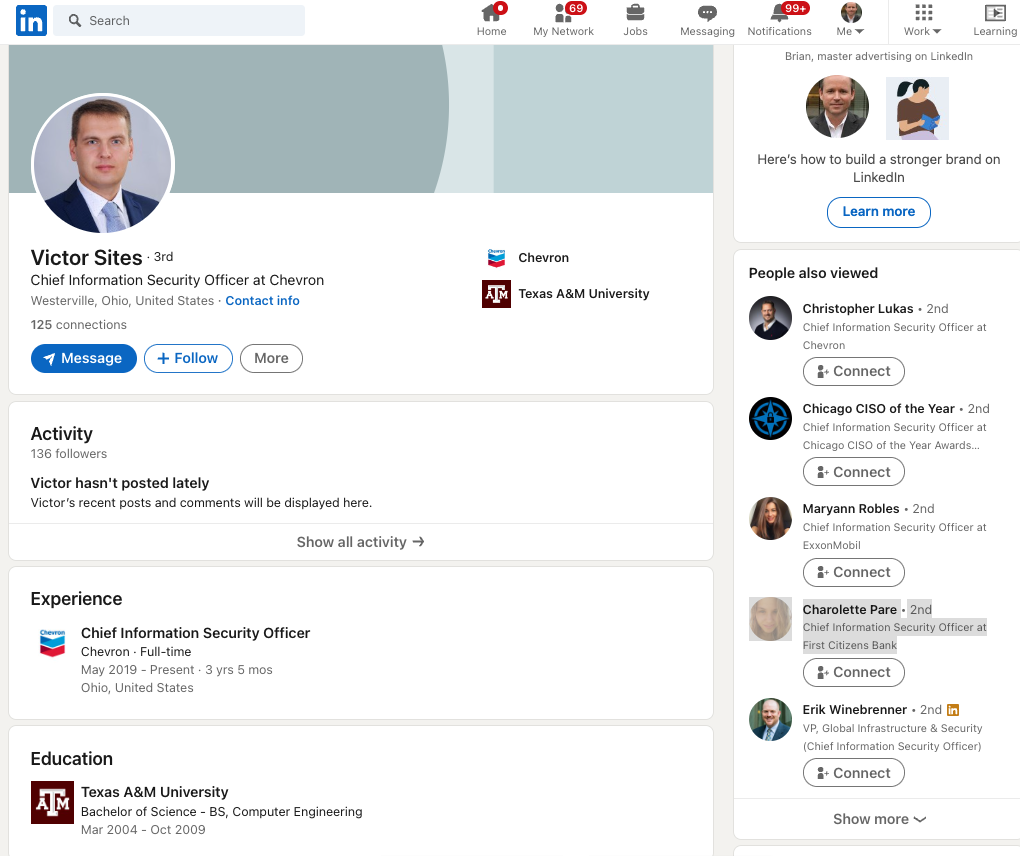
The LinkedIn profile for Victor Sites, who is most certainly NOT the CISO of Chevron.
Of course, Sites is not the real CISO of Chevron. That role is currently occupied by Christopher Lukas of Danville, Calif. If you were confused at this point, you might ask Google who it thinks is the current Chief Information Security Officer of Chevron. When KrebsOnSecurity did that earlier this morning, the fake CISO profile was the very first search result returned (followed by the LinkedIn profile for the real Chevron CISO).
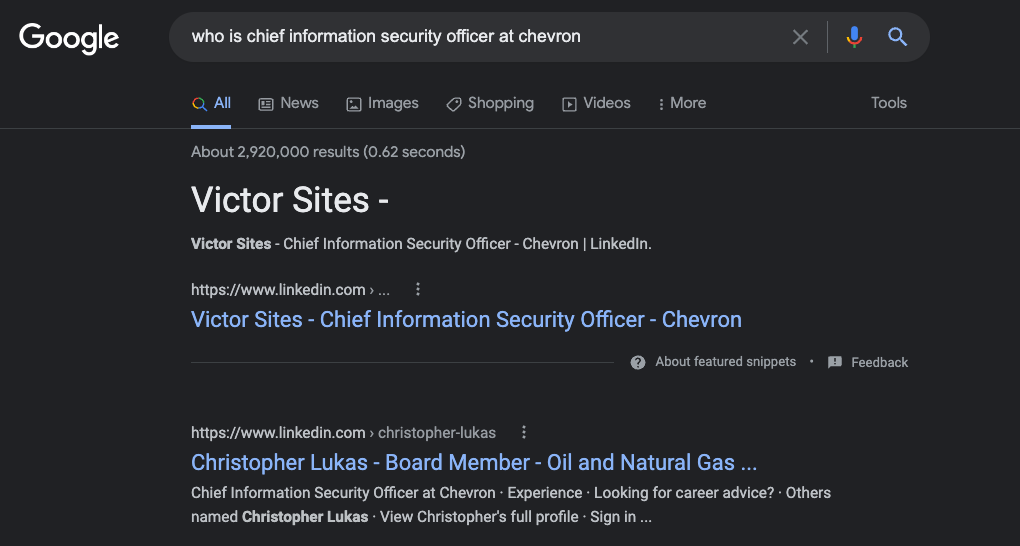
Helpfully, LinkedIn seems to be able to detect something in common about all these fake CISO profiles, because it suggested I view a number of them in the “People Also Viewed” column seen in the image above. There are two fake CISO profiles suggested there, including one for a Maryann Robles, who claims to be the CISO of another energy giant — ExxonMobil.
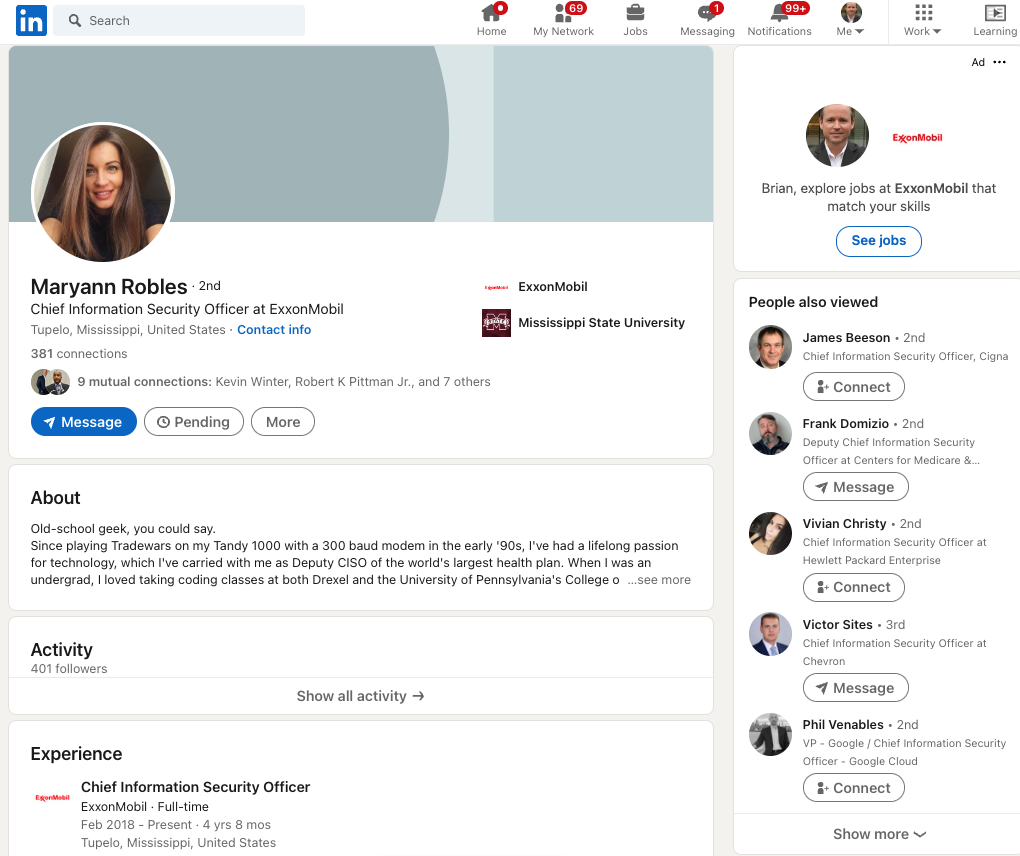
Maryann’s profile says she’s from Tupelo, Miss., and includes this detail about how she became a self-described “old-school geek.”
“Since playing Tradewars on my Tandy 1000 with a 300 baud modem in the early ’90s, I’ve had a lifelong passion for technology, which I’ve carried with me as Deputy CISO of the world’s largest health plan,” her profile reads.
However, this description appears to have been lifted from the profile for the real CISO at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services in Baltimore, Md.
Interestingly, Maryann’s LinkedIn profile was accepted as truth by Cybercrime Magazine’s CISO 500 listing, which claims to maintain a list of the current CISOs at America’s largest companies:
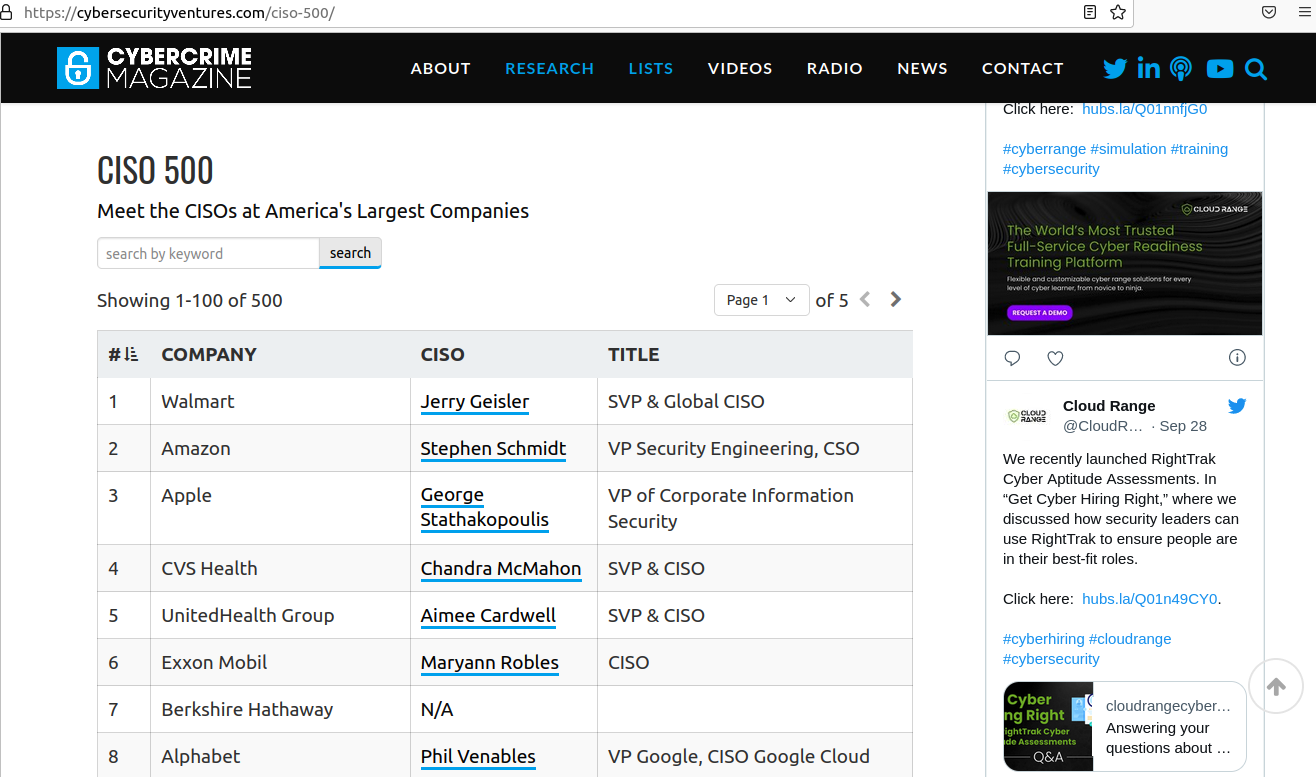
The fake CISO for ExxOnMobil was indexed in Cybercrime Magazine’s CISO 500.
Rich Mason, the former CISO at Fortune 500 firm Honeywell, began warning his colleagues on LinkedIn about the phony profiles earlier this week.
“It’s interesting the downstream sources that repeat LinkedIn bogus content as truth,” Mason said. “This is dangerous, Apollo.io, Signalhire, and Cybersecurity Ventures.”
Google wasn’t fooled by the phony LinkedIn profile for Jennie Biller, who claims to be CISO at biotechnology giant Biogen (the real Biogen CISO is Russell Koste). But Biller’s profile is worth mentioning because it shows how some of these phony profiles appear to be quite hastily assembled. Case in point: Biller’s name and profile photo suggest she is female, however the “About” description of her accomplishments uses male pronouns. Also, it might help that Jennie only has 18 connections on LinkedIn.
Again, we don’t know much about who or what is behind these profiles, but in August the security firm Mandiant (recently acquired by Google) told Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean government have been copying resumes and profiles from leading job listing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency firms.
None of the profiles listed here responded to requests for comment (or to become a connection).
In a statement provided to KrebsOnSecurity, LinkedIn said its teams were actively working to take these fake accounts down.
“We do have strong human and automated systems in place, and we’re continually improving, as fake account activity becomes more sophisticated,” the statement reads. “In our transparency report we share how our teams plus automated systems are stopping the vast majority of fraudulent activity we detect in our community – around 96% of fake accounts and around 99.1% of spam and scam.”
LinkedIn could take one simple step that would make it far easier for people to make informed decisions about whether to trust a given profile: Add a “created on” date for every profile. Twitter does this, and it’s enormously helpful for filtering out a great deal of noise and unwanted communications.
The former CISO Mason said LinkedIn also could experiment with offering something akin to Twitter’s verified mark to users who chose to validate that they can respond to email at the domain associated with their stated current employer.
“If I saw that a LinkedIn profile had been domain-validated, then my confidence in that profile would go way up,” Mason said, noting that many of the fake profiles had hundreds of followers, including dozens of real CISOs. Maryann’s profile grew by a hundred connections in just the past few days, he said.
“If we have CISOs that are falling for this, what hopes do the masses have?” Mason said.
Mason said LinkedIn also needs a more streamlined process for allowing employers to remove phony employee accounts. He recently tried to get a phony profile removed from LinkedIn for someone who falsely claimed to have worked for his company.
“I shot a note to LinkedIn and said please remove this, and they said, well, we have to contact that person and arbitrate this,” he said. “They gave the guy two weeks and he didn’t respond, so they took it down. But that doesn’t scale, and there needs to be a mechanism where an employer can contact LinkedIn and have these fake profiles taken down in less than two weeks.”
Three men in the United Kingdom were arrested this month for attempting to assault a local man and steal his virtual currencies. The incident is the latest example of how certain cybercriminal communities are increasingly turning to physical violence to settle scores and disputes.

Shortly after 11 p.m. on September 6, a resident in the Spalding Common area in the district of Lincolnshire, U.K. phoned police to say three men were acting suspiciously, and had jumped a nearby fence.
“The three men made off in a VW Golf and were shortly stopped nearby,” reads a statement by the Lincolnshire Police. “The car was searched by officers who found an imitation firearm, taser, a baseball bat and police uniform in the boot.”
Thomas Green, 23, Rayhan Miah, 23, and Leonardo Sapiano, 24 were all charged with possession of the weapons, and “with intent to cause loss to another to make an unwarranted demand of Crypto Currency from a person.”
KrebsOnSecurity has learned that the defendants were in Spalding Common to pay a surprise visit to a 19-year-old hacker known by the handles “Discoli,” “Disco Dog,” and “Chinese.” In December 2020, Discoli took credit for hacking and leaking the user database for OGUsers, a forum overrun with people looking to buy, sell and trade access to compromised social media accounts.
Reached via Telegram, Discoli confirmed that police believe the trio was trying to force their way into his home in Spalding Common, and that one of them was wearing a police uniform when they approached his residence.
“They were obvious about being fake police, so much so that one of our neighbours called,” Discoli said in an instant message chat. “That call led to the arrests. Their intent was for robbery/blackmail of crypto, I just happened to not be home at the time.”
The Lincolnshire Police declined to comment for this story, citing an ongoing investigation.
Discoli said he didn’t know any of the men charged, but believes they were hired by one of his enemies. And he said his would-be assailants didn’t just target him specifically.
“They had a list of people they wanted to hit consecutively as far as I know,” he said.
The foiled robbery is the latest drama tied to members of certain criminal hacking communities who are targeting one another with physical violence, by making a standing offer to pay thousands of dollars to anyone in the target’s region who agrees to carry out the assaults.
Last month, a 21-year-old New Jersey man was arrested and charged with stalking in connection with a federal investigation into groups of cybercriminals who are settling scores by hiring people to carry out physical attacks on their rivals.
Prosecutors say Patrick McGovern-Allen recently participated in several of these schemes — including firing a handgun into a Pennsylvania home and torching a residence in another part of the state with a Molotov Cocktail.
McGovern-Allen and the three U.K. defendants are part of an online community that is at the forefront of a dangerous escalation in coercion and intimidation tactics increasingly used by competing cybercriminal groups to steal cryptocurrency from one another and to keep their rivals in check.
The Telegram chat channels where these young men transact have hundreds to thousands of members each, and some of the more interesting solicitations on these communities are job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
A number of these classified ads are in service of performing “brickings,” where someone is hired to visit a specific address and toss a brick through the target’s window. Indeed, prior to McGovern-Allen’s arrest, his alleged Telegram persona bragged that he’d carried out several brickings for hire.
Many of the individuals involved in paying others to commit these physical attacks are also frequent participants in Telegram chat channels focused singularly on SIM swapping, a crime in which identity thieves hijack a target’s mobile phone number and use that to wrest control over the victim’s various online accounts and identities.
Unsurprisingly, the vast majority of people currently being targeted for brickings and other real-life physical assaults via Telegram tend to be other cybercriminals involved in SIM swapping crimes (or individuals on the periphery of that scene).
The United Kingdom is home to a number of young men accused of stealing millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrencies via SIM swapping. Joseph James O’Connor, a.k.a. “Plugwalk Joe”, was arrested in Spain in July 2021 under an FBI warrant on 10 counts of offenses related to unauthorized computer access and cyber bullying. U.S. investigators say O’Connor also played a central role in the 2020 intrusion at Twitter, wherein Twitter accounts for top celebrities and public figures were forced to tweet out links to cryptocurrency scams. O’Connor is currently fighting extradition to the United States.
Robert Lewis Barr, a 25-year-old Scottish man who allegedly stole more than $8 million worth of crypto, was arrested on an FBI warrant last year and is also fighting his extradition. U.S. investigators say Barr SIM swapped a U.S. bitcoin broker in 2017, and that he spent much of the stolen funds throwing lavish parties at rented luxury apartments in central Glasgow.
In many ways, these violence-as-a-service incidents are a natural extension of “swatting,” wherein fake bomb threats, hostage situations and other violent scenarios are phoned in to police as part of a scheme to trick them into visiting potentially deadly force on a target’s address. According to prosecutors, both Barr and O’Connor have a history of swatting their enemies and their SIM swapping victims.
This month’s Patch Tuesday offers a little something for everyone, including security updates for a zero-day flaw in Microsoft Windows that is under active attack, and another Windows weakness experts say could be used to power a fast-spreading computer worm. Also, Apple has also quashed a pair of zero-day bugs affecting certain macOS and iOS users, and released iOS 16, which offers a new privacy and security feature called “Lockdown Mode.” And Adobe axed 63 vulnerabilities in a range of products.
Microsoft today released software patches to plug at least 64 security holes in Windows and related products. Worst in terms of outright scariness is CVE-2022-37969, which is a “privilege escalation” weakness in the Windows Common Log File System Driver that allows attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges on a vulnerable host. Microsoft says this flaw is already being exploited in the wild.
Kevin Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, said any vulnerability that is actively targeted by attackers in the wild must be put to the top of any patching list.
“Not to be fooled by its relatively low CVSS score of 7.8, privilege escalation vulnerabilities are often highly sought after by cyber attackers,” Breen said. “Once an attacker has managed to gain a foothold on a victim’s system, one of their first actions will be to gain a higher level of permissions, allowing the attacker to disable security applications and any device monitoring. There is no known workaround to date, so patching is the only effective mitigation.”
Satnam Narang at Tenable said CVE-2022-24521 — a similar vulnerability in the same Windows log file component — was patched earlier this year as part of Microsoft’s April Patch Tuesday release and was also exploited in the wild.
“CVE-2022-37969 was disclosed by several groups, though it’s unclear if CVE-2022-37969 is a patch-bypass for CVE-2022-24521 at this point,” Narang said.
Another vulnerability Microsoft patched this month — CVE-2022-35803 — also seems to be related to the same Windows log file component. While there are no indications CVE-2022-35803 is being actively exploited, Microsoft suggests that exploitation of this flaw is more likely than not.
Trend Micro’s Dustin Childs called attention to CVE-2022-34718, a remote code execution flaw in the Windows TCP/IP service that could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute code with elevated privileges on affected systems without user interaction.
“That officially puts it into the ‘wormable’ category and earns it a CVSS rating of 9.8,” Childs said. “However, only systems with IPv6 enabled and IPSec configured are vulnerable. While good news for some, if you’re using IPv6 (as many are), you’re probably running IPSec as well. Definitely test and deploy this update quickly.”
Cisco Talos warns about four critical vulnerabilities fixed this month — CVE-2022-34721 and CVE-2022-34722 — which have severity scores of 9.8, though they are “less likely” to be exploited, according to Microsoft.
“These are remote code execution vulnerabilities in the Windows Internet Key Exchange protocol that could be triggered if an attacker sends a specially crafted IP packet,” wrote Jon Munshaw and Asheer Malhotra. “Two other critical vulnerabilities, CVE-2022-35805 and CVE-2022-34700 exist in on-premises instances of Microsoft Dynamics 365. An authenticated attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities to run a specially crafted trusted solution package and execute arbitrary SQL commands. The attacker could escalate their privileges further and execute commands as the database owner.”
 Not to be outdone, Apple fixed at least two zero-day vulnerabilities when it released updates for iOS, iPadOS, macOS and Safari. CVE-2022-32984 is a problem in the deepest recesses of the operating system (the kernel). Apple pushed an emergency update for a related zero-day last month in CVE-2022-32983, which could be used to foist malware on iPhones, iPads and Macs that visited a booby-trapped website.
Not to be outdone, Apple fixed at least two zero-day vulnerabilities when it released updates for iOS, iPadOS, macOS and Safari. CVE-2022-32984 is a problem in the deepest recesses of the operating system (the kernel). Apple pushed an emergency update for a related zero-day last month in CVE-2022-32983, which could be used to foist malware on iPhones, iPads and Macs that visited a booby-trapped website.
Also listed under active attack is CVE-2022-32817, which has been fixed on macOS 12.6 (Monterey), macOS 11.7 (Big Sur), iOS 15.7 and iPadOS 15.7, and iOS 16. The same vulnerability was fixed in Apple Watch in July 2022, and credits Xinru Chi of Japanese cybersecurity firm Pangu Lab.
“Interestingly, this CVE is also listed in the advisory for iOS 16, but it is not called out as being under active exploit for that flavor of the OS,” Trend Micro’s Childs noted. “Apple does state in its iOS 16 advisory that ‘Additional CVE entries to be added soon.’ It’s possible other bugs could also impact this version of the OS. Either way, it’s time to update your Apple devices.”
Apple’s iOS 16 includes two new security and privacy features — Lockdown Mode and Safety Check. Wired.com describes Safety Check as a feature for users who are at risk for, or currently experiencing, domestic abuse.
“The tool centralizes a number of controls in one place to make it easier for users to manage and revoke access to their location data and reset privacy-related permissions,” wrote Lily Hay Newman.
“Lockdown Mode, on the other hand, is meant for users who potentially face targeted spyware attacks and aggressive state-backed hacking. The feature comprehensively restricts any nonessential iOS features so there are as few potential points of entry to a device as possible. As more governments and repressive entities around the world have begun purchasing powerful commodity spyware to target individuals of particular importance or interest, iOS’s general security defenses haven’t been able to keep pace with these specialized threats.”
To turn on Lockdown Mode in iOS 16, go to Settings, then Privacy and Security, then Lockdown Mode. Safety Check is located in the same area.
Finally, Adobe released seven patches addressing 63 security holes in Adobe Experience Manager, Bridge, InDesign, Photoshop, InCopy, Animate, and Illustrator. More on those updates is here.
Don’t forget to back up your data and/or system before applying any security updates. If you experience glitches or problems installing any of these patches this month, please consider leaving a comment about it below; there’s a decent chance other readers have experienced the same and may chime in here with useful tips.
Communities like Craigslist, OfferUp, Facebook Marketplace and others are great for finding low- or no-cost stuff that one can pick up directly from a nearby seller, and for getting rid of useful things that don’t deserve to end up in a landfill. But when dealing with strangers from the Internet, there is always a risk that the person you’ve agreed to meet has other intentions.
Nearly all U.S. states now have designated safe trading stations — mostly at local police departments — which ensure that all transactions are handled in plain view of both the authorities and security cameras.

These safe trading places exist because sometimes in-person transactions from the Internet don’t end well for one or more parties involved. The website Craigslistkillers has catalogued news links for at least 132 murders linked to Craigslist transactions since 2015. Many of these killings involved high-priced items like automobiles and consumer electronics, where the prospective buyer apparently intended all along to kill the owner and steal the item offered for sale. Others were motivated simply by a desire to hurt people.
This is not to say that using Craigslist is uniquely risky or dangerous; I’m sure the vast majority of transactions generated by the site end amicably and without physical violence. And that probably holds true for all of Craigslist’s competitors.
Still, the risk of a deal going badly when one meets total strangers from the Internet is not zero, and so it’s only sensible to take a few simple precautions. For example, choosing to transact at a designated safe place such as a police station dramatically reduces the likelihood that anyone wishing you harm would even show up.
I recently stumbled upon one of these designated exchange places by accident, hence my interest in learning more about them. The one I encountered was at a Virginia county sheriff’s office, and it has two parking spots reserved with a sign that reads, “Internet Purchase & Exchange Location: This Area is Under 24 Hour Video Surveillance” [image above].
According to the list maintained at Safetradestations.com, there are four other such designated locations in Northern Virginia. And it appears most states now have them in at least some major cities. Safeexchangepoint.com also has a searchable index of safe trading locations in the United States and Canada.
Granted, not everyone is going to live close to one of these designated trading stations. Or maybe what you want to buy, sell or trade you’d rather not have recorded in front of police cameras. Either way, here are a few tips on staying safe while transacting in real life with strangers from the Internet (compliments of the aforementioned safe trading websites).
The safest exchange points are easily accessible and in a well-lit, public place where transactions are visible to others nearby. Try to arrange a meeting time that is during daylight hours, and consider bringing a friend along — especially when dealing with high-value items like laptops and smart phones.
Safeexchangepoint.com also advises that police or merchants that host their own exchange locations generally won’t get involved in the details of your transaction unless specified otherwise, and that many police departments (but not all) are willing to check the serial number of an item for sale to make sure it’s not known to be stolen property.
Of course, it’s not always practical or possible to haul that old sofa to the local police department, or a used car that isn’t working. In those situations, safetradestations.com has some decent suggestions:
A 21-year-old New Jersey man has been arrested and charged with stalking in connection with a federal investigation into groups of cybercriminals who are settling scores by hiring people to carry out physical attacks on their rivals. Prosecutors say the defendant recently participated in several of these schemes — including firing a handgun into a Pennsylvania home and torching a residence in another part of the state with a Molotov Cocktail.
Patrick McGovern-Allen of Egg Harbor Township, N.J. was arrested on Aug. 12 on a warrant from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation. An FBI complaint alleges McGovern-Allen was part of a group of co-conspirators who are at the forefront of a dangerous escalation in coercion and intimidation tactics increasingly used by competing cybercriminal groups.
Prosecutors say that around 2 a.m. on Jan 2, 2022, McGovern-Allen and an unidentified co-conspirator fired multiple handgun rounds into a residence in West Chester, Pa. Fortunately, none of the residents inside the home at the time were injured. But prosecutors say the assailants actually recorded video of the attack as “proof” that the shooting had been carried out.
A copy of that video was obtained by KrebsOnSecurity. According to investigators, McGovern-Allen was one of the shooters, who yelled “Justin Active was here” as they haphazardly fired at least eight rounds into the lower story of the West Chester residence.
On Dec. 18, 2021, police in Abington Township, Pa., responded to reports of a house fire from homeowners who said it sounded like something was thrown at their residence just prior to the fire.
Weeks later, on the day of the shooting in West Chester, a detective with the Westtown East Goshen Police Department contacted the Abington police and shared another video that was circulating on several online message boards that appeared to show two individuals setting fire to the Abington Township residence. The criminal complaint said the two police officers agreed the same suspect was present in both videos.
A copy of that video also was obtained by KrebsOnSecurity, and it shows at least two individuals smashing a window, then lighting a rag-soaked Mad Dog 20/20 grape wine bottle and hurling it at the side of the home [Update: My apologies for the file download link, but YouTube just deleted both of the videos included in this story — for allegedly violating their community standards].
“The Molotov cocktail caused the immediate surrounding area to ignite, including the siding of the house, grass, and the wooden chair,” the government’s complaint against McGovern-Allen states. “The two suspects then fled on foot toward the street and begin yelling something when the video stops.”
The government mentions the victims only by their initials — “K.M.” in the shooting and “A.R.” in the firebombing — but said both had been the target of previous harassment by rival cybercriminal groups that included swatting attacks, wherein the perpetrators spoof a distress call to the police about a hostage situation, suicide or bomb threat with the goal of sending a heavily-armed police response to a targeted address.
A number of previous swatting incidents have turned deadly. But these more “hands-on” and first person attacks are becoming increasingly common within certain cybercriminal communities, particularly those engaged in SIM swapping, a crime in which identity thieves hijack a target’s mobile phone number and use that to wrest control over the victim’s various online accounts and identities.
The complaint mentions a handle and user ID allegedly used by McGovern-Allen’s online persona “Tongue” on the Discord chat service, (user: “Tongue#0001”).
“In the chats, [Tongue] tells other Discord users that he was the person who shot K.M.’s house and that he was willing to commit firebombings using Molotov Cocktails,” the complaint alleges. “For example, in one Discord chat from March 2022, [the defendant] states ‘if you need anything done for $ lmk [“let me know”]/I did a shooting/Molotov/but I can also do things for ur entertainment.”
KrebsOnsecurity reviewed hundreds of chat records tied to this Tongue alias, and it appears both attacks were motivated by a desire to get back at a rival cybercriminal by attacking the female friends of that rival.
Recall that the shooters in the West Chester, Pa. incident shouted “Justin Active was here.” Justin Active is the nickname of an individual who is just as active in the same cybercriminal channels, but who has vehemently denied knowledge of or participation in the shooting. Justin Active said on Telegram that the person targeted in the shooting was his ex-girlfriend, and that the firebombing targeted another friend of his.
Justin Active has claimed for months that McGovern-Allen was responsible for both attacks, saying they were intended as an intimidation tactic against him. “DO THE PATRICK MCGOVERN ALLEN RAID DANCE!,” Justin Active’s alias “Nutcase68” shouted on Telegram on Aug. 12, the same day McGovern-Allen was arrested by authorities.
Justin Active’s version of events seems to be supported by a reference in the criminal complaint to an April 2, 2022 chat in which Tongue explained the reason for the shooting.
“The video/is [K]’s house/getting shit/shot/justin active/ was her current bf/ the reason it happened,” Tongue explained. “So that’s why Justin active was there.”
The Telegram chat channels that Justin Active and Tongue both frequented have hundreds to thousands of members each, and some of the more interesting solicitations on these communities are job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
A number of these classified ads are in service of performing “brickings,” where someone is hired to visit a specific address and toss a brick through the target’s window.
“If you live near Edmonton Canada dm me need someone bricked,” reads on Telegram message on May 31, 2022.
“If you live near [address redacted] Lakewood, CA, dm [redacted] Paying 3k to slash the tires,” reads another help wanted ad in the same channel on Feb. 24, 2022. “If you live near here and can brick them, dm [address omitted] Richland, WA,” reads another from that same day.

McGovern-Allen was in the news not long ago. According to a Sept. 2020 story from The Press of Atlantic City, a then 19-year-old Patrick McGovern Allen was injured after driving into a building and forcing residents from their home.
“Police found a 2007 Lexus, driven by Patrick McGovern-Allen, 19, that had lost control and left the road, crashing into the eastern end of the 1600 building,” the story recounted. “The car was driven through the steps that provide access to the second-floor apartments, destroying them, and also caused damage to the outer wall.”
A search on the Inmate Locator of the U.S. Bureau of Prisons website shows that McGovern-Allen remains in federal custody at a detention facility in Philadelphia. He’s currently represented by a public defender who has not responded to requests for comment.
A copy of the criminal complaint against McGovern-Allen is available here (PDF).
Many of the individuals involved in paying others to commit these physical attacks are also frequent participants in several Telegram channels focused singularly on SIM swapping activity. As a result, the vast majority of the people being targeted for brickings and other real-life physical assaults tend to be other cybercriminals involved in SIM swapping crimes (or individuals on the periphery of that scene).
There are dozens of SIM swappers who are now teenage or 20-something millionaires, by virtue of having stolen vast sums of cryptocurrencies from SIM swapping victims. And now many of these same individuals are finding that communities like Telegram can be leveraged to hire physical harassment and intimidation of their rivals and competitors.
The primary barrier to hiring someone to brick a home or slash some tires seems to be the costs involved: A number of solicitations for these services advertised payment of $3,000 or more upon proof of successful completion, which usually involves recording the attack and hiring a getaway driver in the town where the crime is to take place (calling a cab or hailing an Uber from the scene of a bricking isn’t the brightest idea).
My fear is these violence-as-a-service offerings will at some point migrate outside of the SIM swapping communities. This is precisely what happened with swatting, which for years was a crime perpetrated almost exclusively against online gamers and people streaming their games online. These days, swatting attacks are commonly used by SIM swapping groups as a way to harass and extort regular Internet users into giving up prized social media account names that can be resold for thousands of dollars.
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is urging states and localities to beef up security around proprietary devices that connect to the Emergency Alert System — a national public warning system used to deliver important emergency information, such as severe weather and AMBER alerts. The DHS warning came in advance of a workshop to be held this weekend at the DEFCON security conference in Las Vegas, where a security researcher is slated to demonstrate multiple weaknesses in the nationwide alert system.

A Digital Alert Systems EAS encoder/decoder that Pyle said he acquired off eBay in 2019. It had the username and password for the system printed on the machine.
The DHS warning was prompted by security researcher Ken Pyle, a partner at security firm Cybir. Pyle said he started acquiring old EAS equipment off of eBay in 2019, and that he quickly identified a number of serious security vulnerabilities in a device that is broadly used by states and localities to encode and decode EAS alert signals.
“I found all kinds of problems back then, and reported it to the DHS, FBI and the manufacturer,” Pyle said in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity. “But nothing ever happened. I decided I wasn’t going to tell anyone about it yet because I wanted to give people time to fix it.”
Pyle said he took up the research again in earnest after an angry mob stormed the U.S. Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021.
“I was sitting there thinking, ‘Holy shit, someone could start a civil war with this thing,”’ Pyle recalled. “I went back to see if this was still a problem, and it turns out it’s still a very big problem. So I decided that unless someone actually makes this public and talks about it, clearly nothing is going to be done about it.”
The EAS encoder/decoder devices Pyle acquired were made by Lyndonville, NY-based Digital Alert Systems (formerly Monroe Electronics, Inc.), which issued a security advisory this month saying it released patches in 2019 to fix the flaws reported by Pyle, but that some customers are still running outdated versions of the device’s firmware. That may be because the patches were included in version 4 of the firmware for the EAS devices, and many older models apparently do not support the new software.
“The vulnerabilities identified present a potentially serious risk, and we believe both were addressed in software updates issued beginning Oct 2019,” EAS said in a written statement. “We also provided attribution for the researcher’s responsible disclosure, allowing us to rectify the matters before making any public statements. We are aware that some users have not taken corrective actions and updated their software and should immediately take action to update the latest software version to ensure they are not at risk. Anything lower than version 4.1 should be updated immediately. On July 20, 2022, the researcher referred to other potential issues, and we trust the researcher will provide more detail. We will evaluate and work to issue any necessary mitigations as quickly as possible.”
But Pyle said a great many EAS stakeholders are still ignoring basic advice from the manufacturer, such as changing default passwords and placing the devices behind a firewall, not directly exposing them to the Internet, and restricting access only to trusted hosts and networks.

Pyle, in a selfie that is heavily redacted because the EAS device behind him had its user credentials printed on the lid.
Pyle said the biggest threat to the security of the EAS is that an attacker would only need to compromise a single EAS station to send out alerts locally that can be picked up by other EAS systems and retransmitted across the nation.
“The process for alerts is automated in most cases, hence, obtaining access to a device will allow you to pivot around,” he said. “There’s no centralized control of the EAS because these devices are designed such that someone locally can issue an alert, but there’s no central control over whether I am the one person who can send or whatever. If you are a local operator, you can send out nationwide alerts. That’s how easy it is to do this.”
One of the Digital Alert Systems devices Pyle sourced from an electronics recycler earlier this year was non-functioning, but whoever discarded it neglected to wipe the hard drive embedded in the machine. Pyle soon discovered the device contained the private cryptographic keys and other credentials needed to send alerts through Comcast, the nation’s third-largest cable company.
“I can issue and create my own alert here, which has all the valid checks or whatever for being a real alert station,” Pyle said in an interview earlier this month. “I can create a message that will start propagating through the EAS.”
Comcast told KrebsOnSecurity that “a third-party device used to deliver EAS alerts was lost in transit by a trusted shipping provider between two Comcast locations and subsequently obtained by a cybersecurity researcher.
“We’ve conducted a thorough investigation of this matter and have determined that no customer data, and no sensitive Comcast data, were compromised,” Comcast spokesperson David McGuire said.
The company said it also confirmed that the information included on the device can no longer be used to send false messages to Comcast customers or used to compromise devices within Comcast’s network, including EAS devices.
“We are taking steps to further ensure secure transfer of such devices going forward,” McGuire said. “Separately, we have conducted a thorough audit of all EAS devices on our network and confirmed that they are updated with currently available patches and are therefore not vulnerable to recently reported security issues. We’re grateful for the responsible disclosure and to the security research community for continuing to engage and share information with our teams to make our products and technologies ever more secure. Mr. Pyle informed us promptly of his research and worked with us as we took steps to validate his findings and ensure the security of our systems.”
The user interface for an EAS device.
Unauthorized EAS broadcast alerts have happened enough that there is a chronicle of EAS compromises over at fandom.com. Thankfully, most of these incidents have involved fairly obvious hoaxes.
According to the EAS wiki, in February 2013, hackers broke into the EAS networks in Great Falls, Mt. and Marquette, Mich. to broadcast an alert that zombies had risen from their graves in several counties. In Feb. 2017, an EAS station in Indiana also was hacked, with the intruders playing the same “zombies and dead bodies” audio from the 2013 incidents.
“On February 20 and February 21, 2020, Wave Broadband’s EASyCAP equipment was hacked due to the equipment’s default password not being changed,” the Wiki states. “Four alerts were broadcasted, two of which consisted of a Radiological Hazard Warning and a Required Monthly Test playing parts of the Hip Hop song Hot by artist Young Thug.”
In January 2018, Hawaii sent out an alert to cell phones, televisions and radios, warning everyone in the state that a missile was headed their way. It took 38 minutes for Hawaii to let people know the alert was a misfire, and that a draft alert was inadvertently sent. The news video clip below about the 2018 event in Hawaii does a good job of walking through how the EAS works.

Image: Shutterstock.
A cybersecurity firm says it has intercepted a large, unique stolen data set containing the names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, Social Security Numbers and dates of birth on nearly 23 million Americans. The firm’s analysis of the data suggests it corresponds to current and former customers of AT&T. The telecommunications giant stopped short of saying the data wasn’t theirs, but it maintains the records do not appear to have come from its systems and may be tied to a previous data incident at another company.
Milwaukee-based cybersecurity consultancy Hold Security said it intercepted a 1.6 gigabyte compressed file on a popular dark web file-sharing site. The largest item in the archive is a 3.6 gigabyte file called “dbfull,” and it contains 28.5 million records, including 22.8 million unique email addresses and 23 million unique SSNs. There are no passwords in the database.
Hold Security founder Alex Holden said a number of patterns in the data suggest it relates to AT&T customers. For starters, email addresses ending in “att.net” accounted for 13.7 percent of all addresses in the database, with addresses from SBCGLobal.net and Bellsouth.net — both AT&T companies — making up another seven percent. In contrast, Gmail users made up more than 30 percent of the data set, with Yahoo addresses accounting for 24 percent. More than 10,000 entries in the database list “none@att.com” in the email field.
Hold Security found these email domains account for 87% of all domains in the data set. Nearly 21% belonged to AT&T customers.
Holden’s team also examined the number of email records that included an alias in the username portion of the email, and found 293 email addresses with plus addressing. Of those, 232 included an alias that indicated the customer had signed up at some AT&T property; 190 of the aliased email addresses were “+att@”; 42 were “+uverse@,” an oddly specific reference to an AT&T entity that included broadband Internet. In September 2016, AT&T rebranded U-verse as AT&T Internet.
According to its website, AT&T Internet is offered in 21 states, including Alabama, Arkansas, California, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Missouri, Nevada, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Texas and Wisconsin. Nearly all of the records in the database that contain a state designation corresponded to those 21 states; all other states made up just 1.64 percent of the records, Hold Security found.
Image: Hold Security.
The vast majority of records in this database belong to consumers, but almost 13,000 of the entries are for corporate entities. Holden said 387 of those corporate names started with “ATT,” with various entries like “ATT PVT XLOW” appearing 81 times. And most of the addresses for these entities are AT&T corporate offices.
How old is this data? One clue may be in the dates of birth exposed in this database. There are very few records in this file with dates of birth after 2000.
“Based on these statistics, we see that the last significant number of subscribers born in March of 2000,” Holden told KrebsOnSecurity, noting that AT&T requires new account holders to be 18 years of age or older. “Therefore, it makes sense that the dataset was likely created close to March of 2018.”
There was also this anomaly: Holden said one of his analysts is an AT&T customer with a 13-letter last name, and that her AT&T bill has always had the same unique misspelling of her surname (they added yet another letter). He said the analyst’s name is identically misspelled in this database.
KrebsOnSecurity shared the large data set with AT&T, as well as Hold Security’s analysis of it. AT&T ultimately declined to say whether all of the people in the database are or were at some point AT&T customers. The company said the data appears to be several years old, and that “it’s not immediately possible to determine the percentage that may be customers.”
“This information does not appear to have come from our systems,” AT&T said in a written statement. “It may be tied to a previous data incident at another company. It is unfortunate that data can continue to surface over several years on the dark web. However, customers often receive notices after such incidents, and advice for ID theft is consistent and can be found online.”
The company declined to elaborate on what they meant by “a previous data incident at another company.”
But it seems likely that this database is related to one that went up for sale on a hacker forum on August 19, 2021. That auction ran with the title “AT&T Database +70M (SSN/DOB),” and was offered by ShinyHunters, a well-known threat actor with a long history of compromising websites and developer repositories to steal credentials or API keys.
Image: BleepingComputer
ShinyHunters established the starting price for the auction at $200,000, but set the “flash” or “buy it now” price at $1 million. The auction also included a small sampling of the stolen information, but that sample is no longer available. The hacker forum where the ShinyHunters sales thread existed was seized by the FBI in April, and its alleged administrator arrested.
But cached copies of the auction, as recorded by cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, show ShinyHunters received bids of up to $230,000 for the entire database before they suspended the sale.
“This thread has been deleted several times,” ShinyHunters wrote in their auction discussion on Sept. 6, 2021. “Therefore, the auction is suspended. AT&T will be available on WHM as soon as they accept new vendors.”
The WHM initialism was a reference to the White House Market, a dark web marketplace that shut down in October 2021.
“In many cases, when a database is not sold, ShinyHunters will release it for free on hacker forums,” wrote BleepingComputer’s Lawrence Abrams, who broke the news of the auction last year and confronted AT&T about the hackers’ claims.
AT&T gave Abrams a similar statement, saying the data didn’t come from their systems.
“When asked whether the data may have come from a third-party partner, AT&T chose not to speculate,” Abrams wrote. “‘Given this information did not come from us, we can’t speculate on where it came from or whether it is valid,'” AT&T told BleepingComputer.
Asked to respond to AT&T’s denial, ShinyHunters told BleepingComputer at the time, “I don’t care if they don’t admit. I’m just selling.”
On June 1, 2022, a 21-year-old Frenchman was arrested in Morocco for allegedly being a member of ShinyHunters. Databreaches.net reports the defendant was arrested on an Interpol “Red Notice” at the request of a U.S. federal prosecutor from Washington state.
Databreaches.net suggests the warrant could be tied to a ShinyHunters theft in May 2020, when the group announced they had exfiltrated 500 GB of Microsoft’s source code from Microsoft’s private GitHub repositories.
“Researchers assess that Shiny Hunters gained access to roughly 1,200 private repositories around March 28, 2020, which have since been secured,” reads a May 2020 alert posted by the New Jersey Cybersecurity & Communications Integration Cell, a component within the New Jersey Office of Homeland Security and Preparedness.
“Though the breach was largely dismissed as insignificant, some images of the directory listing appear to contain source code for Azure, Office, and some Windows runtimes, and concerns have been raised regarding access to private API keys or passwords that may have been mistakenly included in some private repositories,” the alert continues. “Additionally, Shiny Hunters is flooding dark web marketplaces with breached databases.”
Last month, T-Mobile agreed to pay $350 million to settle a consolidated class action lawsuit over a breach in 2021 that affected 40 million current and former customers. The breach came to light on Aug. 16, 2021, when someone starting selling tens of millions of SSN/DOB records from T-Mobile on the same hacker forum where the ShinyHunters would post their auction for the claimed AT&T database just three days later.
T-Mobile has not disclosed many details about the “how” of last year’s breach, but it said the intruder(s) “leveraged their knowledge of technical systems, along with specialized tools and capabilities, to gain access to our testing environments and then used brute force attacks and other methods to make their way into other IT servers that included customer data.”
A sales thread tied to the stolen T-Mobile customer data.