The top-level domain for the United States — .US — is home to thousands of newly-registered domains tied to a malicious link shortening service that facilitates malware and phishing scams, new research suggests. The findings come close on the heels of a report that identified .US domains as among the most prevalent in phishing attacks over the past year.
Researchers at Infoblox say they’ve been tracking what appears to be a three-year-old link shortening service that is catering to phishers and malware purveyors. Infoblox found the domains involved are typically three to seven characters long, and hosted on bulletproof hosting providers that charge a premium to ignore any abuse or legal complaints. The short domains don’t host any content themselves, but are used to obfuscate the real address of landing pages that try to phish users or install malware.
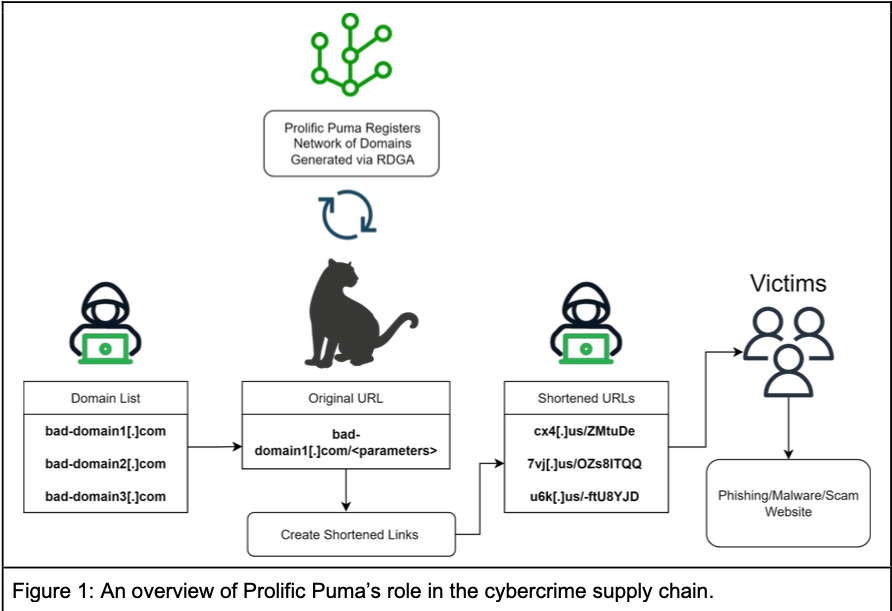
A graphic describing the operations of a malicious link shortening service that Infoblox has dubbed “Prolific Puma.”
Infoblox says it’s unclear how the phishing and malware landing pages tied to this service are being initially promoted, although they suspect it is mainly through scams targeting people on their phones via SMS. A new report says the company mapped the contours of this link shortening service thanks in part to pseudo-random patterns in the short domains, which all appear on the surface to be a meaningless jumble of letters and numbers.
“This came to our attention because we have systems that detect registrations that use domain name generation algorithms,” said Renee Burton, head of threat intelligence at Infoblox. “We have not found any legitimate content served through their shorteners.”
Infoblox determined that until May 2023, domains ending in .info accounted for the bulk of new registrations tied to the malicious link shortening service, which Infoblox has dubbed “Prolific Puma.” Since then, they found that whoever is responsible for running the service has used .US for approximately 55 percent of the total domains created, with several dozen new malicious .US domains registered daily.
.US is overseen by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), an executive branch agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce. But Uncle Sam has long outsourced the management of .US to various private companies, which have gradually allowed the United States’s top-level domain to devolve into a cesspool of phishing activity.
Or so concludes The Interisle Consulting Group, which gathers phishing data from multiple industry sources and publishes an annual report on the latest trends. As far back as 2018, Interisle found .US domains were the worst in the world for spam, botnet (attack infrastructure for DDOS etc.) and illicit or harmful content.
Interisle’s newest study examined six million phishing reports between May 1, 2022 and April 30, 2023, and identified approximately 30,000 .US phishing domains. Interisle found significant numbers of .US domains were registered to attack some of the United States’ most prominent companies, including Bank of America, Amazon, Apple, AT&T, Citi, Comcast, Microsoft, Meta, and Target. Others were used to impersonate or attack U.S. government agencies.
Under NTIA regulations, domain registrars processing .US domain registrations must take certain steps (PDF) to verify that those customers actually reside in the United States, or else own organizations based in the U.S. However, if one registers a .US domain through GoDaddy — the largest domain registrar and the current administrator of the .US contract — the way one “proves” their U.S. nexus is simply by choosing from one of three pre-selected affirmative responses.
In an age when most domain registrars are automatically redacting customer information from publicly accessible registration records to avoid running afoul of European privacy laws, .US has remained something of an outlier because its charter specifies that all registration records be made public. However, Infoblox said it found more than 2,000 malicious link shortener domains ending in .US registered since October 2023 through NameSilo that have somehow subverted the transparency requirements for the usTLD and converted to private registrations.
“Through our own experience with NameSilo, it is not possible to select private registration for domains in the usTLD through their interface,” Infoblox wrote. “And yet, it was done. Of the total domains with private records, over 99% were registered with NameSilo. At this time, we are not able to explain this behavior.”
NameSilo CEO Kristaps Ronka said the company actively responds to reports about abusive domains, but that it hasn’t seen any abuse reports related to Infoblox’s findings.
“We take down hundreds to thousands of domains, lots of them proactively to combat abuse,” Ronka said. “Our current abuse rate on abuseIQ for example is currently at 0%. AbuseIQ receives reports from countless sources and we are yet to see these ‘Puma’ abuse reports.”
Experts who track domains associated with malware and phishing say even phony information supplied at registration is useful in identifying potentially malicious or phishous domains before they can be used for abuse.
For example, when it was registered through NameSilo in July 2023, the domain 1ox[.]us — like thousands of others — listed its registrant as “Leila Puma” at a street address in Poland, and the email address blackpumaoct33@ukr.net. But according to DomainTools.com, on Oct. 1, 2023 those records were redacted and hidden by NameSilo.
Infoblox notes that the username portion of the email address appears to be a reference to the song October 33 by the Black Pumas, an Austin, Texas based psychedelic soul band. The Black Pumas aren’t exactly a household name, but they did recently have a popular Youtube video that featured a cover of the Kinks song “Strangers,” which included an emotional visual narrative about Ukrainians seeking refuge from the Russian invasion, titled “Ukraine Strangers.” Also, Leila Puma’s email address is at a Ukrainian email provider.
DomainTools shows that hundreds of other malicious domains tied to Prolific Puma previously were registered through NameCheap to a “Josef Bakhovsky” at a different street address in Poland. According to ancestry.com, the anglicized version of this surname — Bakovski — is the traditional name for someone from Bakowce, which is now known as Bakivtsi and is in Ukraine.
This possible Polish and/or Ukrainian connection may or may not tell us something about the “who” behind this link shortening service, but those details are useful for identifying and grouping these malicious short domains. However, even this meager visibility into .US registration data is now under threat.
The NTIA recently published a proposal that would allow registrars to redact all registrant data from WHOIS registration records for .US domains. A broad array of industry groups have filed comments opposing the proposed changes, saying they threaten to remove the last vestiges of accountability for a top-level domain that is already overrun with cybercrime activity.
Infoblox’s Burton says Prolific Puma is remarkable because they’ve been able to facilitate malicious activities for years while going largely unnoticed by the security industry.
“This exposes how persistent the criminal economy can be at a supply chain level,” Burton said. “We’re always looking at the end malware or phishing page, but what we’re finding here is that there’s this middle layer of DNS threat actors persisting for years without notice.”
Infoblox’s full report on Prolific Puma is here.
Amir Golestan, the 40-year-old CEO of the Charleston, S.C. based technology company Micfo LLC, has been sentenced to five years in prison for wire fraud. Golestan’s sentencing comes nearly two years after he pleaded guilty to using an elaborate network of phony companies to secure more than 735,000 Internet Protocol (IP) addresses from the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN), the nonprofit which oversees IP addresses assigned to entities in the U.S., Canada, and parts of the Caribbean.

Amir Golestan, the former CEO of Micfo.
In 2018, ARIN sued Golestan and Micfo, alleging they had obtained hundreds of thousands of IP addresses under false pretenses. ARIN and Micfo settled that dispute in arbitration, with Micfo returning most of the addresses that it hadn’t already sold.
ARIN’s civil case caught the attention of federal prosecutors in South Carolina, who in May 2019 filed criminal wire fraud charges against Golestan, alleging he’d orchestrated a network of shell companies and fake identities to prevent ARIN from knowing the addresses were all going to the same buyer.
Prosecutors showed that each of those shell companies involved the production of notarized affidavits in the names of people who didn’t exist. As a result, the government was able to charge Golestan with 20 counts of wire fraud — one for each payment made by the phony companies that bought the IP addresses from ARIN.
Golestan initially sought to fight those charges. But on just the second day of his trial in November 2021, Golestan changed his mind and pleaded guilty to 20 counts of wire fraud in connection with the phantom companies he used to secure the IP addresses. Prosecutors estimated those addresses were valued at between $10 million and $14 million.
ARIN says the 5-year sentence handed down by the South Carolina judge “sends an important message of deterrence to other parties contemplating fraudulent schemes to obtain or transfer Internet resources.”
“Those who seek to defraud ARIN (or other Regional Internet Registries) are subject to costly and serious civil litigation, criminal charges, and, ultimately, a lengthy term of incarceration,” reads a statement from ARIN on Golestan’s sentencing.
By 2013, a number of Micfo’s customers had landed on the radar of Spamhaus, a group that many network operators rely upon to stem the tide of junk email. Shortly after Spamhaus started blocking Micfo’s IP address ranges, Micfo shifted gears and began reselling IP addresses mainly to companies marketing “virtual private networking” or VPN services that help customers hide their real IP addresses online.
Golestan did not respond to a request for comment. But in a 2020 interview with KrebsOnSecurity, Golestan claimed that Micfo was at one point responsible for brokering roughly 40 percent of the IP addresses used by the world’s largest VPN providers. Throughout that conversation, Golestan maintained his innocence, even as he explained that the creation of the phony companies was necessary to prevent entities like Spamhaus from interfering with his business going forward.
There are fewer than four billion so-called “Internet Protocol version 4” or IPv4 addresses available for use, but the vast majority of them have already been allocated. The global dearth of available IP addresses has turned them into a commodity wherein each IPv4 address can fetch between $15-$25 on the open market.
This has led to boom times for those engaged in the acquisition and sale of IP address blocks, but it has likewise emboldened those who specialize in absconding with and spamming from dormant IP address blocks without permission from the rightful owners.
The U.S Department of Justice says Golestan will serve 60 months in prison, followed by a 2-year term of court-ordered supervision. The Micfo CEO also was ordered to pay nearly $77,000 in restitution to ARIN for its work in assisting federal prosecutors.
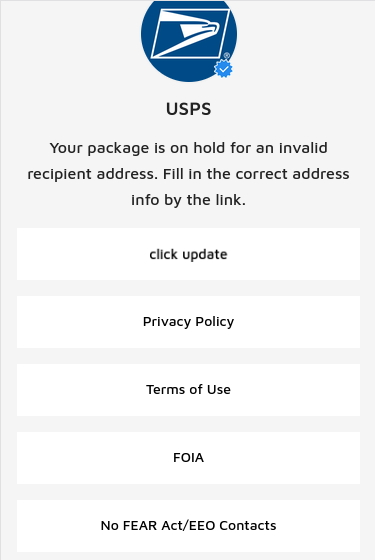
The fake USPS phishing page.
Recent weeks have seen a sizable uptick in the number of phishing scams targeting U.S. Postal Service (USPS) customers. Here’s a look at an extensive SMS phishing operation that tries to steal personal and financial data by spoofing the USPS, as well as postal services in at least a dozen other countries.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader who received an SMS purporting to have been sent by the USPS, saying there was a problem with a package destined for the reader’s address. Clicking the link in the text message brings one to the domain usps.informedtrck[.]com.
The landing page generated by the phishing link includes the USPS logo, and says “Your package is on hold for an invalid recipient address. Fill in the correct address info by the link.” Below that message is a “Click update” button that takes the visitor to a page that asks for more information.
The remaining buttons on the phishing page all link to the real USPS.com website. After collecting your address information, the fake USPS site goes on to request additional personal and financial data.
This phishing domain was recently registered and its WHOIS ownership records are basically nonexistent. However, we can find some compelling clues about the extent of this operation by loading the phishing page in Developer Tools, a set of debugging features built into Firefox, Chrome and Safari that allow one to closely inspect a webpage’s code and operations.
Check out the bottom portion of the screenshot below, and you’ll notice that this phishing site fails to load some external resources, including an image from a link called fly.linkcdn[.]to.
A search on this domain at the always-useful URLscan.io shows that fly.linkcdn[.]to is tied to a slew of USPS-themed phishing domains. Here are just a few of those domains (links defanged to prevent accidental clicking):
usps.receivepost[.]com
usps.informedtrck[.]com
usps.trckspost[.]com
postreceive[.]com
usps.trckpackages[.]com
usps.infortrck[.]com
usps.quicktpos[.]com
usps.postreceive].]com
usps.revepost[.]com
trackingusps.infortrck[.]com
usps.receivepost[.]com
usps.trckmybusi[.]com
postreceive[.]com
tackingpos[.]com
usps.trckstamp[.]com
usa-usps[.]shop
usps.infortrck[.]com
unlistedstampreceive[.]com
usps.stampreceive[.]com
usps.stamppos[.]com
usps.stampspos[.]com
usps.trckmypost[.]com
usps.trckintern[.]com
usps.tackingpos[.]com
usps.posinformed[.]com
As we can see in the screenshot below, the developer tools console for informedtrck[.]com complains that the site is unable to load a Google Analytics code — UA-80133954-3 — which apparently was rejected for pointing to an invalid domain.
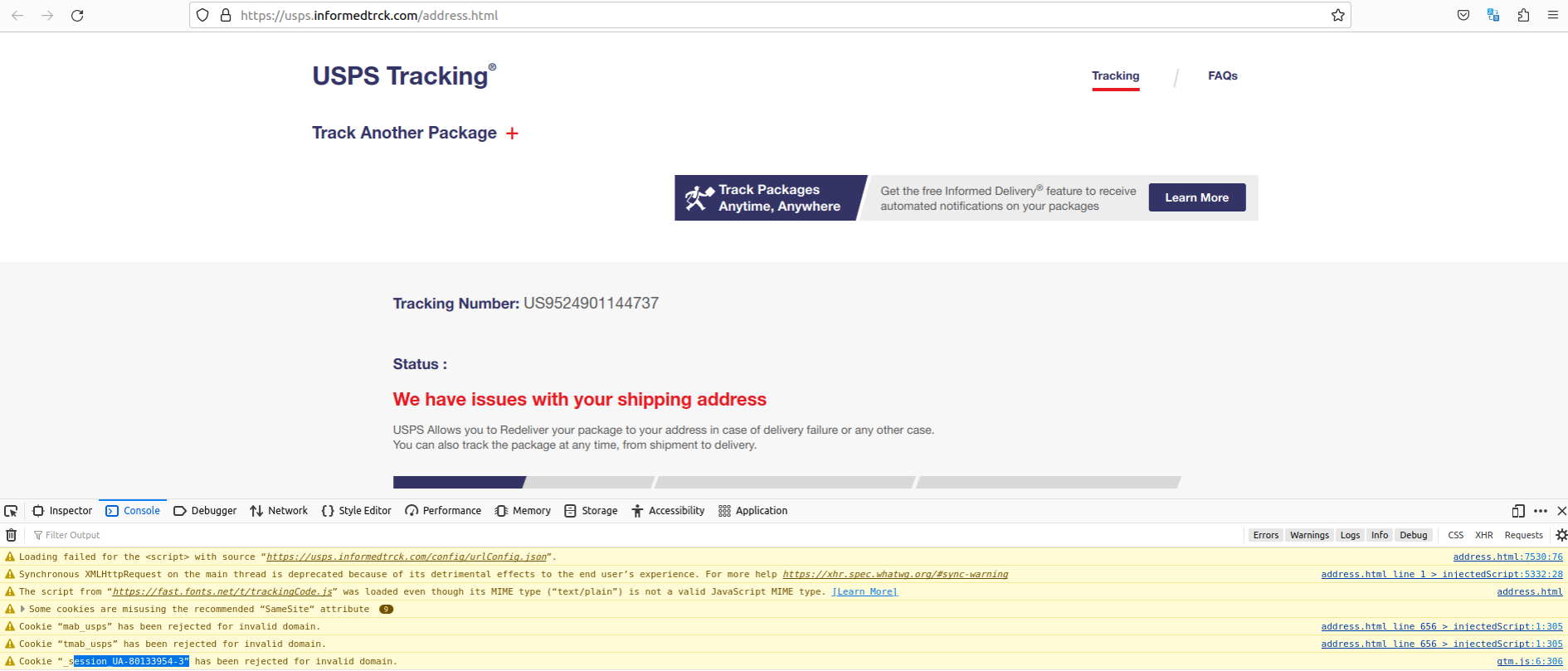
Notice the highlighted Google Analytics code exposed by a faulty Javascript element on the phishing website. Click to enlarge. That code actually belongs to the USPS.
The valid domain for that Google Analytics code is the official usps.com website. According to dnslytics.com, that same analytics code has shown up on at least six other nearly identical USPS phishing pages dating back nearly as many years, including onlineuspsexpress[.]com, which DomainTools.com says was registered way back in September 2018 to an individual in Nigeria.
A different domain with that same Google Analytics code that was registered in 2021 is peraltansepeda[.]com, which archive.org shows was running a similar set of phishing pages targeting USPS users. DomainTools.com indicates this website name was registered by phishers based in Indonesia.
DomainTools says the above-mentioned USPS phishing domain stamppos[.]com was registered in 2022 via Singapore-based Alibaba.com, but the registrant city and state listed for that domain says “Georgia, AL,” which is not a real location.
Alas, running a search for domains registered through Alibaba to anyone claiming to reside in Georgia, AL reveals nearly 300 recent postal phishing domains ending in “.top.” These domains are either administrative domains obscured by a password-protected login page, or are .top domains phishing customers of the USPS as well as postal services serving other countries.
Those other nations include the Australia Post, An Post (Ireland), Correos.es (Spain), the Costa Rican post, the Chilean Post, the Mexican Postal Service, Poste Italiane (Italy), PostNL (Netherlands), PostNord (Denmark, Norway and Sweden), and Posti (Finland). A complete list of these domains is available here (PDF).
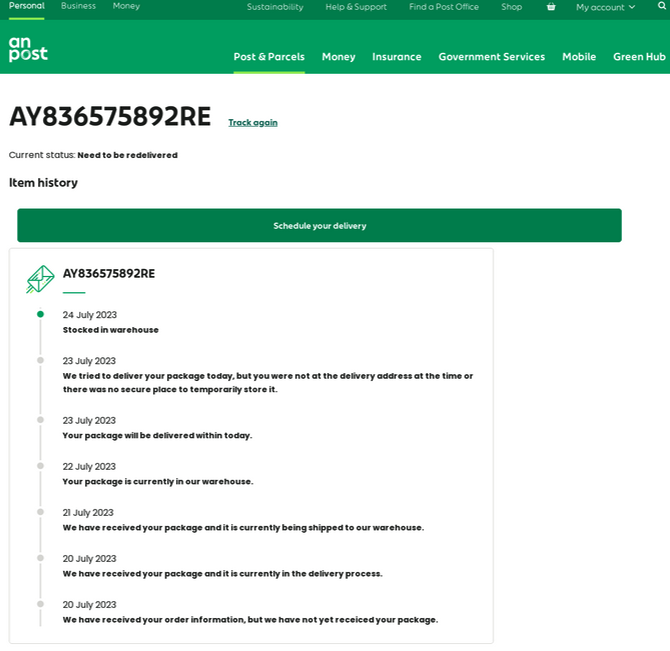
A phishing page targeting An Post, the state-owned provider of postal services in Ireland.
The Georgia, AL domains at Alibaba also encompass several that spoof sites claiming to collect outstanding road toll fees and fines on behalf of the governments of Australia, New Zealand and Singapore.
An anonymous reader wrote in to say they submitted fake information to the above-mentioned phishing site usps.receivepost[.]com via the malware sandbox any.run. A video recording of that analysis shows that the site sends any submitted data via an automated bot on the Telegram instant messaging service.
The traffic analysis just below the any.run video shows that any data collected by the phishing site is being sent to the Telegram user @chenlun, who offers to sell customized source code for phishing pages. From a review of @chenlun’s other Telegram channels, it appears this account is being massively spammed at the moment — possibly thanks to public attention brought by this story.
Meanwhile, researchers at DomainTools recently published a report on an apparently unrelated but equally sprawling SMS-based phishing campaign targeting USPS customers that appears to be the work of cybercriminals based in Iran.
Phishers tend to cast a wide net and often spoof entities that are broadly used by the local population, and few brands are going to have more household reach than domestic mail services. In June, the United Parcel Service (UPS) disclosed that fraudsters were abusing an online shipment tracking tool in Canada to send highly targeted SMS phishing messages that spoofed the UPS and other brands.
With the holiday shopping season nearly upon us, now is a great time to remind family and friends about the best advice to sidestep phishing scams: Avoid clicking on links or attachments that arrive unbidden in emails, text messages and other mediums. Most phishing scams invoke a temporal element that warns of negative consequences should you fail to respond or act quickly.
If you’re unsure whether the message is legitimate, take a deep breath and visit the site or service in question manually — ideally, using a browser bookmark so as to avoid potential typosquatting sites.
Update: Added information about the Telegram bot and any.run analysis.
In November 2022, the password manager service LastPass disclosed a breach in which hackers stole password vaults containing both encrypted and plaintext data for more than 25 million users. Since then, a steady trickle of six-figure cryptocurrency heists targeting security-conscious people throughout the tech industry has led some security experts to conclude that crooks likely have succeeded at cracking open some of the stolen LastPass vaults.
Taylor Monahan is lead product manager of MetaMask, a popular software cryptocurrency wallet used to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. Since late December 2022, Monahan and other researchers have identified a highly reliable set of clues that they say connect recent thefts targeting more than 150 people. Collectively, these individuals have been robbed of more than $35 million worth of crypto.
Monahan said virtually all of the victims she has assisted were longtime cryptocurrency investors, and security-minded individuals. Importantly, none appeared to have suffered the sorts of attacks that typically preface a high-dollar crypto heist, such as the compromise of one’s email and/or mobile phone accounts.
“The victim profile remains the most striking thing,” Monahan wrote. “They truly all are reasonably secure. They are also deeply integrated into this ecosystem, [including] employees of reputable crypto orgs, VCs [venture capitalists], people who built DeFi protocols, deploy contracts, run full nodes.”
Monahan has been documenting the crypto thefts via Twitter/X since March 2023, frequently expressing frustration in the search for a common cause among the victims. Then on Aug. 28, Monahan said she’d concluded that the common thread among nearly every victim was that they’d previously used LastPass to store their “seed phrase,” the private key needed to unlock access to their cryptocurrency investments.
MetaMask owner Taylor Monahan on Twitter. Image: twitter.com/tayvano_
Armed with your secret seed phrase, anyone can instantly access all of the cryptocurrency holdings tied to that cryptographic key, and move the funds to anywhere they like.
Which is why the best practice for many cybersecurity enthusiasts has long been to store their seed phrases either in some type of encrypted container — such as a password manager — or else inside an offline, special-purpose hardware encryption device, such as a Trezor or Ledger wallet.
“The seed phrase is literally the money,” said Nick Bax, director of analytics at Unciphered, a cryptocurrency wallet recovery company. “If you have my seed phrase, you can copy and paste that into your wallet, and then you can see all my accounts. And you can transfer my funds.”
Bax said he closely reviewed the massive trove of cryptocurrency theft data that Taylor Monahan and others have collected and linked together.
“It’s one of the broadest and most complex cryptocurrency investigations I’ve ever seen,” Bax said. “I ran my own analysis on top of their data and reached the same conclusion that Taylor reported. The threat actor moved stolen funds from multiple victims to the same blockchain addresses, making it possible to strongly link those victims.”
Bax, Monahan and others interviewed for this story say they’ve identified a unique signature that links the theft of more than $35 million in crypto from more than 150 confirmed victims, with roughly two to five high-dollar heists happening each month since December 2022.
KrebsOnSecurity has reviewed this signature but is not publishing it at the request of Monahan and other researchers, who say doing so could cause the attackers to alter their operations in ways that make their criminal activity more difficult to track.
But the researchers have published findings about the dramatic similarities in the ways that victim funds were stolen and laundered through specific cryptocurrency exchanges. They also learned the attackers frequently grouped together victims by sending their cryptocurrencies to the same destination crypto wallet.
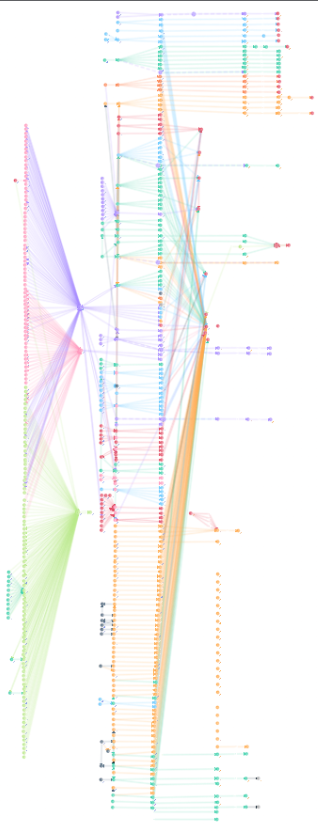
A graphic published by @tayvano_ on Twitter depicting the movement of stolen cryptocurrencies from victims who used LastPass to store their crypto seed phrases.
By identifying points of overlap in these destination addresses, the researchers were then able to track down and interview new victims. For example, the researchers said their methodology identified a recent multi-million dollar crypto heist victim as an employee at Chainalysis, a blockchain analysis firm that works closely with law enforcement agencies to help track down cybercriminals and money launderers.
Chainalysis confirmed that the employee had suffered a high-dollar cryptocurrency heist late last month, but otherwise declined to comment for this story.
Bax said the only obvious commonality between the victims who agreed to be interviewed was that they had stored the seed phrases for their cryptocurrency wallets in LastPass.
“On top of the overlapping indicators of compromise, there are more circumstantial behavioral patterns and tradecraft which are also consistent between different thefts and support the conclusion,” Bax told KrebsOnSecuirty. “I’m confident enough that this is a real problem that I’ve been urging my friends and family who use LastPass to change all of their passwords and migrate any crypto that may have been exposed, despite knowing full well how tedious that is.”
LastPass declined to answer questions about the research highlighted in this story, citing an ongoing law enforcement investigation and pending litigation against the company in response to its 2022 data breach.
“Last year’s incident remains the subject of an ongoing investigation by law enforcement and is also the subject of pending litigation,” LastPass said in a written statement provided to KrebsOnSecurity. “Since last year’s attack on LastPass, we have remained in contact with law enforcement and continue to do so.”
Their statement continues:
“We have shared various technical information, Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), and threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) with our law enforcement contacts as well as our internal and external threat intelligence and forensic partners in an effort to try and help identify the parties responsible. In the meantime, we encourage any security researchers to share any useful information they believe they may have with our Threat Intelligence team by contacting securitydisclosure@lastpass.com.”
On August 25, 2022, LastPass CEO Karim Toubba wrote to users that the company had detected unusual activity in its software development environment, and that the intruders stole some source code and proprietary LastPass technical information. On Sept. 15, 2022, LastPass said an investigation into the August breach determined the attacker did not access any customer data or password vaults.
But on Nov. 30, 2022, LastPass notified customers about another, far more serious security incident that the company said leveraged data stolen in the August breach. LastPass disclosed that criminal hackers had compromised encrypted copies of some password vaults, as well as other personal information.
In February 2023, LastPass disclosed that the intrusion involved a highly complex, targeted attack against a DevOps engineer who was one of only four LastPass employees with access to the corporate vault.
“This was accomplished by targeting the DevOps engineer’s home computer and exploiting a vulnerable third-party media software package, which enabled remote code execution capability and allowed the threat actor to implant keylogger malware,” LastPass officials wrote. “The threat actor was able to capture the employee’s master password as it was entered, after the employee authenticated with MFA, and gain access to the DevOps engineer’s LastPass corporate vault.”
Dan Goodin at Ars Technica reported and then confirmed that the attackers exploited a known vulnerability in a Plex media server that the employee was running on his home network, and succeeded in installing malicious software that stole passwords and other authentication credentials. The vulnerability exploited by the intruders was patched back in 2020, but the employee never updated his Plex software.
As it happens, Plex announced its own data breach one day before LastPass disclosed its initial August intrusion. On August 24, 2022, Plex’s security team urged users to reset their passwords, saying an intruder had accessed customer emails, usernames and encrypted passwords.
A basic functionality of LastPass is that it will pick and remember lengthy, complex passwords for each of your websites or online services. To automatically populate the appropriate credentials at any website going forward, you simply authenticate to LastPass using your master password.
LastPass has always emphasized that if you lose this master password, that’s too bad because they don’t store it and their encryption is so strong that even they can’t help you recover it.
But experts say all bets are off when cybercrooks can get their hands on the encrypted vault data itself — as opposed to having to interact with LastPass via its website. These so-called “offline” attacks allow the bad guys to conduct unlimited and unfettered “brute force” password cracking attempts against the encrypted data using powerful computers that can each try millions of password guesses per second.
“It does leave things vulnerable to brute force when the vaults are stolen en masse, especially if info about the vault HOLDER is available,” said Nicholas Weaver, a researcher at University of California, Berkeley’s International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) and lecturer at UC Davis. “So you just crunch and crunch and crunch with GPUs, with a priority list of vaults you target.”
How hard would it be for well-resourced criminals to crack the master passwords securing LastPass user vaults? Perhaps the best answer to this question comes from Wladimir Palant, a security researcher and the original developer behind the Adblock Plus browser plugin.
In a December 2022 blog post, Palant explained that the crackability of a LastPass master password depends largely on two things: The complexity of the master password, and the default settings for LastPass users, which appear to have varied quite a bit based on when those users began patronizing the service.
LastPass says that since 2018 it has required a twelve-character minimum for master passwords, which the company said “greatly minimizes the ability for successful brute force password guessing.”
But Palant said while LastPass indeed improved its master password defaults in 2018, it did not force all existing customers who had master passwords of lesser lengths to pick new credentials that would satisfy the 12-character minimum.
“If you are a LastPass customer, chances are that you are completely unaware of this requirement,” Palant wrote. “That’s because LastPass didn’t ask existing customers to change their master password. I had my test account since 2018, and even today I can log in with my eight-character password without any warnings or prompts to change it.”
Palant believes LastPass also failed to upgrade many older, original customers to more secure encryption protections that were offered to newer customers over the years. One important setting in LastPass is the number of “iterations,” or how many times your master password is run through the company’s encryption routines. The more iterations, the longer it takes an offline attacker to crack your master password.
Palant noted last year that for many older LastPass users, the initial default setting for iterations was anywhere from “1” to “500.” By 2013, new LastPass customers were given 5,000 iterations by default. In February 2018, LastPass changed the default to 100,100 iterations. And very recently, it upped that again to 600,000.
Palant said the 2018 change was in response to a security bug report he filed about some users having dangerously low iterations in their LastPass settings.
“Worse yet, for reasons that are beyond me, LastPass didn’t complete this migration,” Palant wrote. “My test account is still at 5,000 iterations, as are the accounts of many other users who checked their LastPass settings. LastPass would know how many users are affected, but they aren’t telling that. In fact, it’s painfully obvious that LastPass never bothered updating users’ security settings. Not when they changed the default from 1 to 500 iterations. Not when they changed it from 500 to 5,000. Only my persistence made them consider it for their latest change. And they still failed implementing it consistently.”
A chart on Palant’s blog post offers an idea of how increasing password iterations dramatically increases the costs and time needed by the attackers to crack someone’s master password. Palant said it would take a single GPU about a year to crack a password of average complexity with 500 iterations, and about 10 years to crack the same password run through 5,000 iterations.
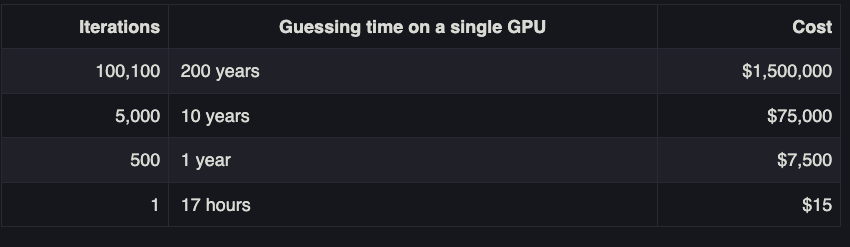
Image: palant.info
However, these numbers radically come down when a determined adversary also has other large-scale computational assets at their disposal, such as a bitcoin mining operation that can coordinate the password-cracking activity across multiple powerful systems simultaneously.
Weaver said a password or passphrase with average complexity — such as “Correct Horse Battery Staple” is only secure against online attacks, and that its roughly 40 bits of randomness or “entropy” means a graphics card can blow through it in no time.
“An Nvidia 3090 can do roughly 4 million [password guesses] per second with 1000 iterations, but that would go down to 8 thousand per second with 500,000 iterations, which is why iteration count matters so much,” Weaver said. “So a combination of ‘not THAT strong of a password’ and ‘old vault’ and ‘low iteration count’ would make it theoretically crackable but real work, but the work is worth it given the targets.”
Reached by KrebsOnSecurity, Palant said he never received a response from LastPass about why the company apparently failed to migrate some number of customers to more secure account settings.
“I know exactly as much as everyone else,” Palant wrote in reply. “LastPass published some additional information in March. This finally answered the questions about the timeline of their breach – meaning which users are affected. It also made obvious that business customers are very much at risk here, Federated Login Services being highly compromised in this breach (LastPass downplaying as usual of course).”
Palant said upon logging into his LastPass account a few days ago, he found his master password was still set at 5,000 iterations.
KrebsOnSecurity interviewed one of the victims tracked down by Monahan, a software engineer and startup founder who recently was robbed of approximately $3.4 million worth of different cryptocurrencies. The victim agreed to tell his story in exchange for anonymity because he is still trying to claw back his losses. We’ll refer to him here as “Connor” (not his real name).
Connor said he began using LastPass roughly a decade ago, and that he also stored the seed phrase for his primary cryptocurrency wallet inside of LastPass. Connor chose to protect his LastPass password vault with an eight character master password that included numbers and symbols (~50 bits of entropy).
“I thought at the time that the bigger risk was losing a piece of paper with my seed phrase on it,” Connor said. “I had it in a bank security deposit box before that, but then I started thinking, ‘Hey, the bank might close or burn down and I could lose my seed phrase.'”
Those seed phrases sat in his LastPass vault for years. Then, early on the morning of Sunday, Aug. 27, 2023, Connor was awoken by a service he’d set up to monitor his cryptocurrency addresses for any unusual activity: Someone was draining funds from his accounts, and fast.
Like other victims interviewed for this story, Connor didn’t suffer the usual indignities that typically presage a cryptocurrency robbery, such as account takeovers of his email inbox or mobile phone number.
Connor said he doesn’t know the number of iterations his master password was given originally, or what it was set at when the LastPass user vault data was stolen last year. But he said he recently logged into his LastPass account and the system forced him to upgrade to the new 600,000 iterations setting.
“Because I set up my LastPass account so early, I’m pretty sure I had whatever weak settings or iterations it originally had,” he said.
Connor said he’s kicking himself because he recently started the process of migrating his cryptocurrency to a new wallet protected by a new seed phrase. But he never finished that migration process. And then he got hacked.
“I’d set up a brand new wallet with new keys,” he said. “I had that ready to go two months ago, but have been procrastinating moving things to the new wallet.”
Connor has been exceedingly lucky in regaining access to some of his stolen millions in cryptocurrency. The Internet is swimming with con artists masquerading as legitimate cryptocurrency recovery experts. To make matters worse, because time is so critical in these crypto heists, many victims turn to the first quasi-believable expert who offers help.
Instead, several friends steered Connor to Flashbots.net, a cryptocurrency recovery firm that employs several custom techniques to help clients claw back stolen funds — particularly those on the Ethereum blockchain.
According to Connor, Flashbots helped rescue approximately $1.5 million worth of the $3.4 million in cryptocurrency value that was suddenly swept out of his account roughly a week ago. Lucky for him, Connor had some of his assets tied up in a type of digital loan that allowed him to borrow against his various cryptocurrency assets.
Without giving away too many details about how they clawed back the funds, here’s a high level summary: When the crooks who stole Connor’s seed phrase sought to extract value from these loans, they were borrowing the maximum amount of credit that he hadn’t already used. But Connor said that left open an avenue for some of that value to be recaptured, basically by repaying the loan in many small, rapid chunks.
According to MetaMask’s Monahan, users who stored any important passwords with LastPass — particularly those related to cryptocurrency accounts — should change those credentials immediately, and migrate any crypto holdings to new offline hardware wallets.
“Really the ONLY thing you need to read is this,” Monahan pleaded to her 70,000 followers on Twitter/X: “PLEASE DON’T KEEP ALL YOUR ASSETS IN A SINGLE KEY OR SECRET PHRASE FOR YEARS. THE END. Split up your assets. Get a hw [hardware] wallet. Migrate. Now.”
If you also had passwords tied to banking or retirement accounts, or even just important email accounts — now would be a good time to change those credentials as well.
I’ve never been comfortable recommending password managers, because I’ve never seriously used them myself. Something about putting all your eggs in one basket. Heck, I’m so old-fashioned that most of my important passwords are written down and tucked away in safe places.
But I recognize this antiquated approach to password management is not for everyone. Connor says he now uses 1Password, a competing password manager that recently earned the best overall marks from Wired and The New York Times.
1Password says that three things are needed to decrypt your information: The encrypted data itself, your account password, and your Secret Key. Only you know your account password, and your Secret Key is generated locally during setup.
“The two are combined on-device to encrypt your vault data and are never sent to 1Password,” explains a 1Password blog post ‘What If 1Password Gets Hacked?‘ “Only the encrypted vault data lives on our servers, so neither 1Password nor an attacker who somehow manages to guess or steal your account password would be able to access your vaults – or what’s inside them.
Weaver said that Secret Key adds an extra level of randomness to all user master passwords that LastPass didn’t have.
“With LastPass, the idea is the user’s password vault is encrypted with a cryptographic hash (H) of the user’s passphrase,” Weaver said. “The problem is a hash of the user’s passphrase is remarkably weak on older LastPass vaults with master passwords that do not have many iterations. 1Password uses H(random-key||password) to generate the password, and it is why you have the QR code business when adding a new device.”
Weaver said LastPass deserves blame for not having upgraded iteration counts for all users a long time ago, and called the latest forced upgrades “a stunning indictment of the negligence on the part of LastPass.”
“That they never even notified all those with iteration counts of less than 100,000 — who are really vulnerable to brute force even with 8-character random passwords or ‘correct horse battery staple’ type passphrases — is outright negligence,” Weaver said. “I would personally advocate that nobody ever uses LastPass again: Not because they were hacked. Not because they had an architecture (unlike 1Password) that makes such hacking a problem. But because of their consistent refusal to address how they screwed up and take proactive efforts to protect their customers.”
Bax and Monahan both acknowledged that their research alone can probably never conclusively tie dozens of high-dollar crypto heists over the past year to the LastPass breach. But Bax says at this point he doesn’t see any other possible explanation.
“Some might say it’s dangerous to assert a strong connection here, but I’d say it’s dangerous to assert there isn’t one,” he said. “I was arguing with my fiance about this last night. She’s waiting for LastPass to tell her to change everything. Meanwhile, I’m telling her to do it now.”

Domain names ending in “.US” — the top-level domain for the United States — are among the most prevalent in phishing scams, new research shows. This is noteworthy because .US is overseen by the U.S. government, which is frequently the target of phishing domains ending in .US. Also, .US domains are only supposed to be available to U.S. citizens and to those who can demonstrate that they have a physical presence in the United States.
.US is the “country code top-level domain” or ccTLD of the United States. Most countries have their own ccTLDs: .MX for Mexico, for example, or .CA for Canada. But few other major countries in the world have anywhere near as many phishing domains each year as .US.
That’s according to The Interisle Consulting Group, which gathers phishing data from multiple industry sources and publishes an annual report on the latest trends. Interisle’s newest study examined six million phishing reports between May 1, 2022 and April 30, 2023, and found 30,000 .US phishing domains.
.US is overseen by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), an executive branch agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce. However, NTIA currently contracts out the management of the .US domain to GoDaddy, by far the world’s largest domain registrar.
Under NTIA regulations, the administrator of the .US registry must take certain steps to verify that their customers actually reside in the United States, or own organizations based in the U.S. But Interisle found that whatever GoDaddy was doing to manage that vetting process wasn’t working.
“The .US ‘nexus’ requirement theoretically limits registrations to parties with a national connection, but .US had very high numbers of phishing domains,” Interisle wrote. “This indicates a possible problem with the administration or application of the nexus requirements.”
Dean Marks is emeritus executive director for a group called the Coalition for Online Accountability, which has been critical of the NTIA’s stewardship of .US. Marks says virtually all European Union member state ccTLDs that enforce nexus restrictions also have massively lower levels of abuse due to their policies and oversight.
“Even very large ccTLDs, like .de for Germany — which has a far larger market share of domain name registrations than .US — have very low levels of abuse, including phishing and malware,” Marks told KrebsOnSecurity. “In my view, this situation with .US should not be acceptable to the U.S. government overall, nor to the US public.”
Marks said there are very few phishing domains ever registered in other ccTLDs that also restrict registrations to their citizens, such as .HU (Hungary), .NZ (New Zealand), and .FI (Finland), where a connection to the country, a proof of identity, or evidence of incorporation are required.
“Or .LK (Sri Lanka), where the acceptable use policy includes a ‘lock and suspend’ if domains are reported for suspicious activity,” Marks said. “These ccTLDs make a strong case for validating domain registrants in the interest of public safety.”
Sadly, .US has been a cesspool of phishing activity for many years. As far back as 2018, Interisle found .US domains were the worst in the world for spam, botnet (attack infrastructure for DDOS etc.) and illicit or harmful content. Back then, .US was being operated by a different contractor.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, GoDaddy said all .US registrants must certify that they meet the NTIA’s nexus requirements. But this appears to be little more than an affirmative response that is already pre-selected for all new registrants.
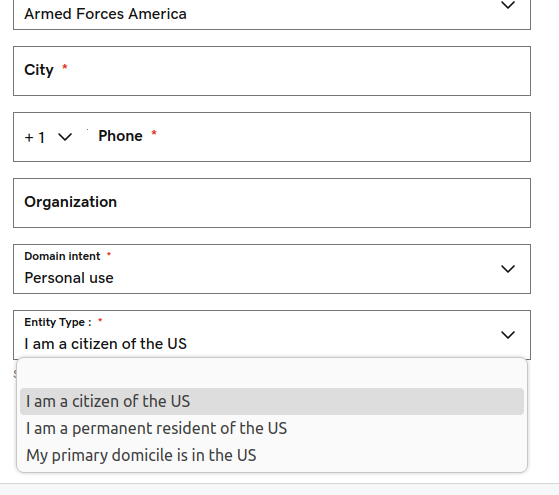
Attempting to register a .US domain through GoDaddy, for example, leads to a U.S. Registration Information page that auto-populates the nexus attestation field with the response, “I am a citizen of the US.” Other options include, “I am a permanent resident of the US,” and “My primary domicile is in the US.” It currently costs just $4.99 to obtain a .US domain through GoDaddy.
GoDaddy said it also conducts a scan of selected registration request information, and conducts “spot checks” on registrant information.
“We conduct regular reviews, per policy, of registration data within the Registry database to determine Nexus compliance with ongoing communications to registrars and registrants,” the company said in a written statement.
GoDaddy says it “is committed to supporting a safer online environment and proactively addressing this issue by assessing it against our own anti-abuse mitigation system.”
“We stand against DNS abuse in any form and maintain multiple systems and protocols to protect all the TLDs we operate,” the statement continued. “We will continue to work with registrars, cybersecurity firms and other stakeholders to make progress with this complex challenge.”
Interisle found significant numbers of .US domains were registered to attack some of the United States’ most prominent companies, including Bank of America, Amazon, Apple, AT&T, Citi, Comcast, Microsoft, Meta, and Target.
“Ironically, at least 109 of the .US domains in our data were used to attack the United States government, specifically the United States Postal Service and its customers,” Interisle wrote. “.US domains were also used to attack foreign government operations: six .US domains were used to attack Australian government services, six attacked Great’s Britain’s Royal Mail, one attacked Canada Post, and one attacked the Denmark Tax Authority.”
The NTIA recently published a proposal that would allow GoDaddy to redact registrant data from WHOIS registration records. The current charter for .US specifies that all .US registration records be public.
Interisle argues that without more stringent efforts to verify a United States nexus for new .US domain registrants, the NTIA’s proposal will make it even more difficult to identify phishers and verify registrants’ identities and nexus qualifications.
In a written statement, the NTIA said DNS abuse is a priority issue for the agency, and that NTIA supports “evidence-based policymaking.”
“We look forward to reviewing the report and will engage with our contractor for the .US domain on steps that we can take not only to address phishing, but the other forms of DNS abuse as well,” the statement reads.
Interisle sources its phishing data from several places, including the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), OpenPhish, PhishTank, and Spamhaus. For more phishing facts, see Interisle’s 2023 Phishing Landscape report (PDF).’
Update, Sept. 5, 1:44 p.m. ET: Updated story with statement provided today by the NTIA.






In large metropolitan areas, tourists are often easy to spot because they’re far more inclined than locals to gaze upward at the surrounding skyscrapers. Security experts say this same tourist dynamic is a dead giveaway in virtually all computer intrusions that lead to devastating attacks like data theft and ransomware, and that more organizations should set simple virtual tripwires that sound the alarm when authorized users and devices are spotted exhibiting this behavior.

In a blog post published last month, Cisco Talos said it was seeing a worrisome “increase in the rate of high-sophistication attacks on network infrastructure.” Cisco’s warning comes amid a flurry of successful data ransom and state-sponsored cyber espionage attacks targeting some of the most well-defended networks on the planet.
But despite their increasing complexity, a great many initial intrusions that lead to data theft could be nipped in the bud if more organizations started looking for the telltale signs of newly-arrived cybercriminals behaving like network tourists, Cisco says.
“One of the most important things to talk about here is that in each of the cases we’ve seen, the threat actors are taking the type of ‘first steps’ that someone who wants to understand (and control) your environment would take,” Cisco’s Hazel Burton wrote. “Examples we have observed include threat actors performing a ‘show config,’ ‘show interface,’ ‘show route,’ ‘show arp table’ and a ‘show CDP neighbor.’ All these actions give the attackers a picture of a router’s perspective of the network, and an understanding of what foothold they have.”
Cisco’s alert concerned espionage attacks from China and Russia that abused vulnerabilities in aging, end-of-life network routers. But at a very important level, it doesn’t matter how or why the attackers got that initial foothold on your network.
It might be zero-day vulnerabilities in your network firewall or file-transfer appliance. Your more immediate and primary concern has to be: How quickly can you detect and detach that initial foothold?
The same tourist behavior that Cisco described attackers exhibiting vis-a-vis older routers is also incredibly common early on in ransomware and data ransom attacks — which often unfurl in secret over days or weeks as attackers methodically identify and compromise a victim’s key network assets.
These virtual hostage situations usually begin with the intruders purchasing access to the target’s network from dark web brokers who resell access to stolen credentials and compromised computers. As a result, when those stolen resources first get used by would-be data thieves, almost invariably the attackers will run a series of basic commands asking the local system to confirm exactly who and where they are on the victim’s network.
This fundamental reality about modern cyberattacks — that cybercriminals almost always orient themselves by “looking up” who and where they are upon entering a foreign network for the first time — forms the business model of an innovative security company called Thinkst, which gives away easy-to-use tripwires or “canaries” that can fire off an alert whenever all sorts of suspicious activity is witnessed.
“Many people have pointed out that there are a handful of commands that are overwhelmingly run by attackers on compromised hosts (and seldom ever by regular users/usage),” the Thinkst website explains. “Reliably alerting when a user on your code-sign server runs whoami.exe can mean the difference between catching a compromise in week-1 (before the attackers dig in) and learning about the attack on CNN.”
These canaries — or “canary tokens” — are meant to be embedded inside regular files, acting much like a web beacon or web bug that tracks when someone opens an email.
The Canary Tokens website from Thinkst Canary lists nearly two-dozen free customizable canaries.
“Imagine doing that, but for file reads, database queries, process executions or patterns in log files,” the Canary Tokens documentation explains. “Canarytokens does all this and more, letting you implant traps in your production systems rather than setting up separate honeypots.”
Thinkst operates alongside a burgeoning industry offering so-called “deception” or “honeypot” services — those designed to confuse, disrupt and entangle network intruders. But in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity, Thinkst founder and CEO Haroon Meer said most deception techniques involve some degree of hubris.
“Meaning, you’ll have deception teams in your network playing spy versus spy with people trying to break in, and it becomes this whole counterintelligence thing,” Meer said. “Nobody really has time for that. Instead, we are saying literally the opposite: That you’ve probably got all these [security improvement] projects that are going to take forever. But while you’re doing all that, just drop these 10 canaries, because everything else is going to take a long time to do.”
The idea here is to lay traps in sensitive areas of your network or web applications where few authorized users should ever trod. Importantly, the canary tokens themselves are useless to an attacker. For example, that AWS canary token sure looks like the digital keys to your cloud, but the token itself offers no access. It’s just a lure for the bad guys, and you get an alert when and if it is ever touched.
One nice thing about canary tokens is that Thinkst gives them away for free. Head over to canarytokens.org, and choose from a drop-down menu of available tokens, including:
-a web bug / URL token, designed to alert when a particular URL is visited;
-a DNS token, which alerts when a hostname is requested;
-an AWS token, which alerts when a specific Amazon Web Services key is used;
-a “custom exe” token, to alert when a specific Windows executable file or DLL is run;
-a “sensitive command” token, to alert when a suspicious Windows command is run.
-a Microsoft Excel/Word token, which alerts when a specific Excel or Word file is accessed.
Much like a “wet paint” sign often encourages people to touch a freshly painted surface anyway, attackers often can’t help themselves when they enter a foreign network and stumble upon what appear to be key digital assets, Meer says.
“If an attacker lands on your server and finds a key to your cloud environment, it’s really hard for them not to try it once,” Meer said. “Also, when these sorts of actors do land in a network, they have to orient themselves, and while doing that they are going to trip canaries.”
Meer says canary tokens are as likely to trip up attackers as they are “red teams,” security experts hired or employed by companies seeking to continuously probe their own computer systems and networks for security weaknesses.
“The concept and use of canary tokens has made me very hesitant to use credentials gained during an engagement, versus finding alternative means to an end goal,” wrote Shubham Shah, a penetration tester and co-founder of the security firm Assetnote. “If the aim is to increase the time taken for attackers, canary tokens work well.”
Thinkst makes money by selling Canary Tools, which are honeypots that emulate full blown systems like Windows servers or IBM mainframes. They deploy in minutes and include a personalized, private Canarytoken server.
“If you’ve got a sophisticated defense team, you can start putting these things in really interesting places,” Meer said. “Everyone says their stuff is simple, but we obsess over it. It’s really got to be so simple that people can’t mess it up. And if it works, it’s the best bang for your security buck you’re going to get.”
Further reading:
Dark Reading: Credential Canaries Create Minefield for Attackers
NCC Group: Extending a Thinkst Canary to Become an Interactive Honeypot
Cruise Automation’s experience deploying canary tokens
You’ve probably never heard of “16Shop,” but there’s a good chance someone using it has tried to phish you.
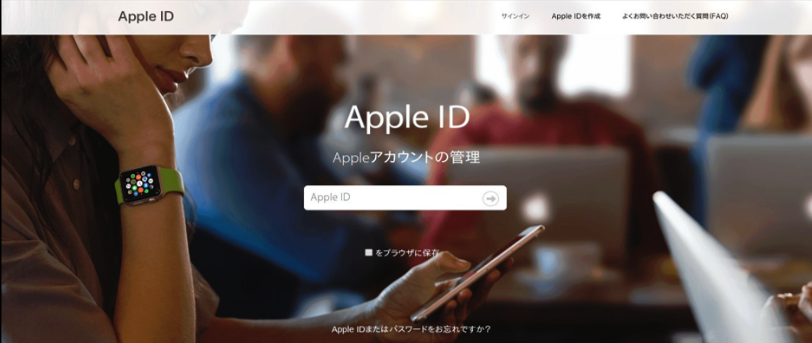
A 16Shop phishing page spoofing Apple and targeting Japanese users. Image: Akamai.com.
The international police organization INTERPOL said last week it had shuttered the notorious 16Shop, a popular phishing-as-a-service platform launched in 2017 that made it simple for even complete novices to conduct complex and convincing phishing scams. INTERPOL said authorities in Indonesia arrested the 21-year-old proprietor and one of his alleged facilitators, and that a third suspect was apprehended in Japan.
The INTERPOL statement says the platform sold hacking tools to compromise more than 70,000 users in 43 countries. Given how long 16Shop has been around and how many paying customers it enjoyed over the years, that number is almost certainly highly conservative.
Also, the sale of “hacking tools” doesn’t quite capture what 16Shop was all about: It was a fully automated phishing platform that gave its thousands of customers a series of brand-specific phishing kits to use, and provided the domain names needed to host the phishing pages and receive any stolen credentials.
Security experts investigating 16Shop found the service used an application programming interface (API) to manage its users, an innovation that allowed its proprietors to shut off access to customers who failed to pay a monthly fee, or for those attempting to copy or pirate the phishing kit.
16Shop also localized phishing pages in multiple languages, and the service would display relevant phishing content depending on the victim’s geolocation.

Various 16Shop lures for Apple users in different languages. Image: Akamai.
For example, in 2019 McAfee found that for targets in Japan, the 16Shop kit would also collect Web ID and Card Password, while US victims will be asked for their Social Security Number.
“Depending on location, 16Shop will also collect ID numbers (including Civil ID, National ID, and Citizen ID), passport numbers, social insurance numbers, sort codes, and credit limits,” McAfee wrote.
In addition, 16Shop employed various tricks to help its users’ phishing pages stay off the radar of security firms, including a local “blacklist” of Internet addresses tied to security companies, and a feature that allowed users to block entire Internet address ranges from accessing phishing pages.
The INTERPOL announcement does not name any of the suspects arrested in connection with the 16Shop investigation. However, a number of security firms — including Akamai, McAfee and ZeroFox, previously connected the service to a young Indonesian man named Riswanda Noor Saputra, who sold 16Shop under the hacker handle “Devilscream.”
According to the Indonesian security blog Cyberthreat.id, Saputra admitted being the administrator of 16Shop, but told the publication he handed the project off to others by early 2020.
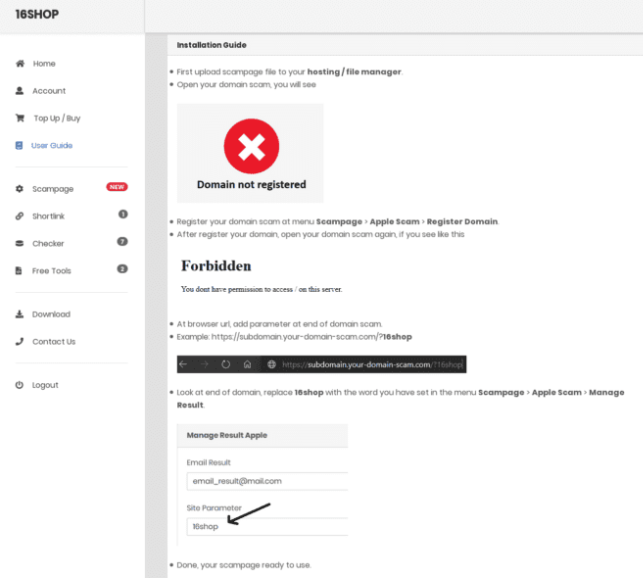
16Shop documentation instructing operators on how to deploy the kit. Image: ZeroFox.
Nevertheless, Cyberthreat reported that Devilscream was arrested by Indonesian police in late 2021 as part of a collaboration between INTERPOL and the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). Still, researchers who tracked 16Shop since its inception say Devilscream was not the original proprietor of the phishing platform, and he may not be the last.
It is not uncommon for cybercriminals to accidentally infect their own machines with password-stealing malware, and that is exactly what seems to have happened with one of the more recent administrators of 16Shop.
Constella Intelligence, a data breach and threat actor research platform, now allows users to cross-reference popular cybercrime websites and denizens of these forums with inadvertent malware infections by information-stealing trojans. A search in Constella on 16Shop’s domain name shows that in mid-2022, a key administrator of the phishing service infected their Microsoft Windows desktop computer with the Redline information stealer trojan — apparently by downloading a cracked (and secretly backdoored) copy of Adobe Photoshop.
Redline infections steal gobs of data from the victim machine, including a list of recent downloads, stored passwords and authentication cookies, as well as browser bookmarks and auto-fill data. Those records indicate the 16Shop admin used the nicknames “Rudi” and “Rizki/Rizky,” and maintained several Facebook profiles under these monikers.
It appears this user’s full name (or at least part of it) is Rizky Mauluna Sidik, and they are from Bandung in West Java, Indonesia. One of this user’s Facebook pages says Rizky is the chief executive officer and founder of an entity called BandungXploiter, whose Facebook page indicates it is a group focused mainly on hacking and defacing websites.
A LinkedIn profile for Rizky says he is a backend Web developer in Bandung who earned a bachelor’s degree in information technology in 2020. Mr. Rizky did not respond to requests for comment.









