Microsoft today issued security updates for more than 100 newly-discovered vulnerabilities in its Windows operating system and related software, including four flaws that are already being exploited. In addition, Apple recently released emergency updates to quash a pair of zero-day bugs in iOS.

Apple last week shipped emergency updates in iOS 17.0.3 and iPadOS 17.0.3 in response to active attacks. The patch fixes CVE-2023-42724, which attackers have been using in targeted attacks to elevate their access on a local device.
Apple said it also patched CVE-2023-5217, which is not listed as a zero-day bug. However, as Bleeping Computer pointed out, this flaw is caused by a weakness in the open-source “libvpx” video codec library, which was previously patched as a zero-day flaw by Google in the Chrome browser and by Microsoft in Edge, Teams, and Skype products. For anyone keeping count, this is the 17th zero-day flaw that Apple has patched so far this year.
Fortunately, the zero-days affecting Microsoft customers this month are somewhat less severe than usual, with the exception of CVE-2023-44487. This weakness is not specific to Windows but instead exists within the HTTP/2 protocol used by the World Wide Web: Attackers have figured out how to use a feature of HTTP/2 to massively increase the size of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and these monster attacks reportedly have been going on for several weeks now.
Amazon, Cloudflare and Google all released advisories today about how they’re addressing CVE-2023-44487 in their cloud environments. Google’s Damian Menscher wrote on Twitter/X that the exploit — dubbed a “rapid reset attack” — works by sending a request and then immediately cancelling it (a feature of HTTP/2). “This lets attackers skip waiting for responses, resulting in a more efficient attack,” Menscher explained.
Natalie Silva, lead security engineer at Immersive Labs, said this flaw’s impact to enterprise customers could be significant, and lead to prolonged downtime.
“It is crucial for organizations to apply the latest patches and updates from their web server vendors to mitigate this vulnerability and protect against such attacks,” Silva said. In this month’s Patch Tuesday release by Microsoft, they have released both an update to this vulnerability, as well as a temporary workaround should you not be able to patch immediately.”
Microsoft also patched zero-day bugs in Skype for Business (CVE-2023-41763) and Wordpad (CVE-2023-36563). The latter vulnerability could expose NTLM hashes, which are used for authentication in Windows environments.
“It may or may not be a coincidence that Microsoft announced last month that WordPad is no longer being updated, and will be removed in a future version of Windows, although no specific timeline has yet been given,” said Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7. “Unsurprisingly, Microsoft recommends Word as a replacement for WordPad.”
Other notable bugs addressed by Microsoft include CVE-2023-35349, a remote code execution weakness in the Message Queuing (MSMQ) service, a technology that allows applications across multiple servers or hosts to communicate with each other. This vulnerability has earned a CVSS severity score of 9.8 (10 is the worst possible). Happily, the MSMQ service is not enabled by default in Windows, although Immersive Labs notes that Microsoft Exchange Server can enable this service during installation.
Speaking of Exchange, Microsoft also patched CVE-2023-36778, a vulnerability in all current versions of Exchange Server that could allow attackers to run code of their choosing. Rapid7’s Barnett said successful exploitation requires that the attacker be on the same network as the Exchange Server host, and use valid credentials for an Exchange user in a PowerShell session.
For a more detailed breakdown on the updates released today, see the SANS Internet Storm Center roundup. If today’s updates cause any stability or usability issues in Windows, AskWoody.com will likely have the lowdown on that.
Please consider backing up your data and/or imaging your system before applying any updates. And feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience any difficulties as a result of these patches.
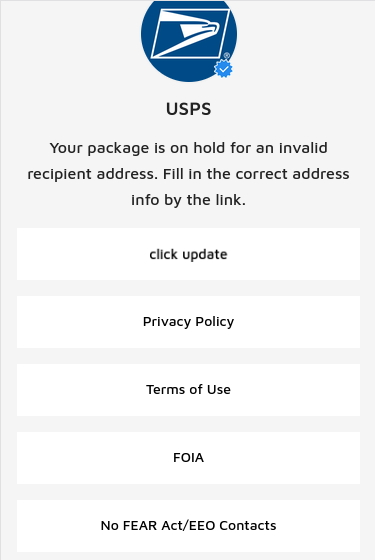
The fake USPS phishing page.
Recent weeks have seen a sizable uptick in the number of phishing scams targeting U.S. Postal Service (USPS) customers. Here’s a look at an extensive SMS phishing operation that tries to steal personal and financial data by spoofing the USPS, as well as postal services in at least a dozen other countries.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader who received an SMS purporting to have been sent by the USPS, saying there was a problem with a package destined for the reader’s address. Clicking the link in the text message brings one to the domain usps.informedtrck[.]com.
The landing page generated by the phishing link includes the USPS logo, and says “Your package is on hold for an invalid recipient address. Fill in the correct address info by the link.” Below that message is a “Click update” button that takes the visitor to a page that asks for more information.
The remaining buttons on the phishing page all link to the real USPS.com website. After collecting your address information, the fake USPS site goes on to request additional personal and financial data.
This phishing domain was recently registered and its WHOIS ownership records are basically nonexistent. However, we can find some compelling clues about the extent of this operation by loading the phishing page in Developer Tools, a set of debugging features built into Firefox, Chrome and Safari that allow one to closely inspect a webpage’s code and operations.
Check out the bottom portion of the screenshot below, and you’ll notice that this phishing site fails to load some external resources, including an image from a link called fly.linkcdn[.]to.
A search on this domain at the always-useful URLscan.io shows that fly.linkcdn[.]to is tied to a slew of USPS-themed phishing domains. Here are just a few of those domains (links defanged to prevent accidental clicking):
usps.receivepost[.]com
usps.informedtrck[.]com
usps.trckspost[.]com
postreceive[.]com
usps.trckpackages[.]com
usps.infortrck[.]com
usps.quicktpos[.]com
usps.postreceive].]com
usps.revepost[.]com
trackingusps.infortrck[.]com
usps.receivepost[.]com
usps.trckmybusi[.]com
postreceive[.]com
tackingpos[.]com
usps.trckstamp[.]com
usa-usps[.]shop
usps.infortrck[.]com
unlistedstampreceive[.]com
usps.stampreceive[.]com
usps.stamppos[.]com
usps.stampspos[.]com
usps.trckmypost[.]com
usps.trckintern[.]com
usps.tackingpos[.]com
usps.posinformed[.]com
As we can see in the screenshot below, the developer tools console for informedtrck[.]com complains that the site is unable to load a Google Analytics code — UA-80133954-3 — which apparently was rejected for pointing to an invalid domain.
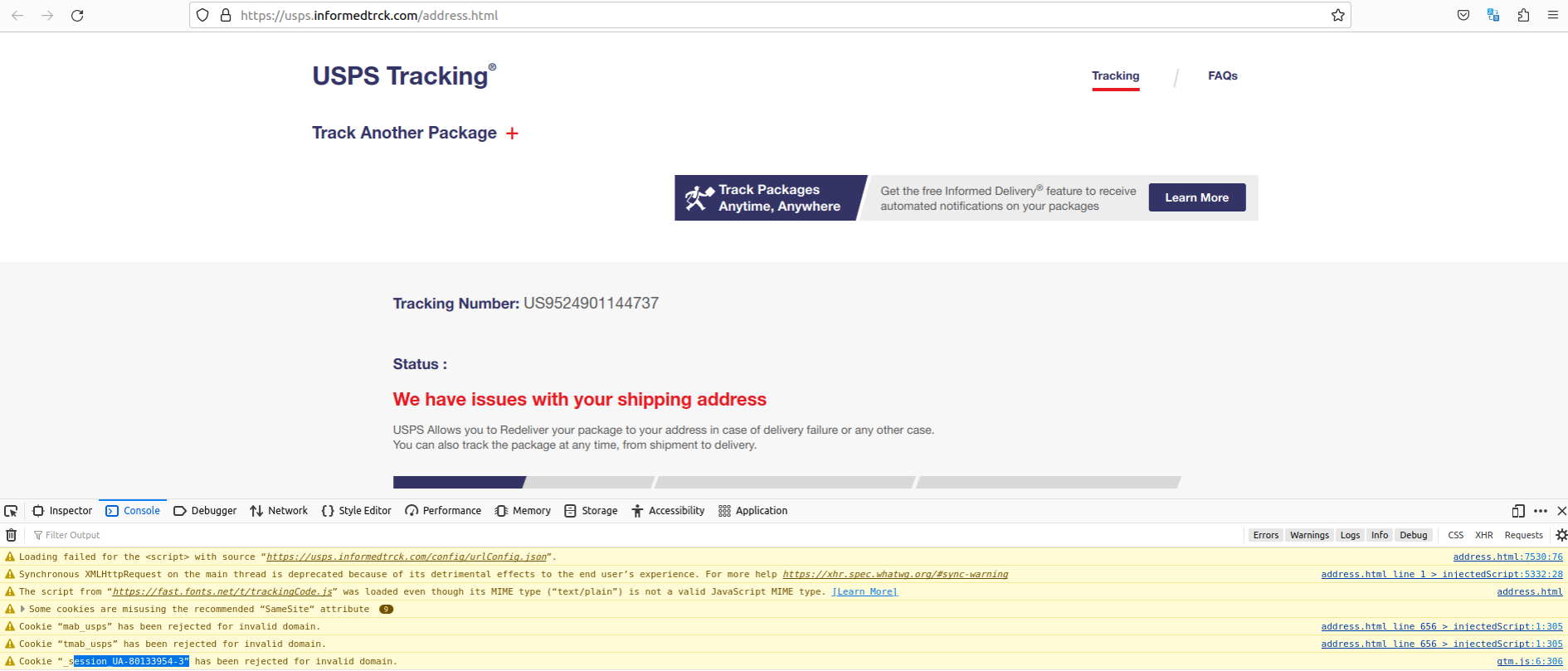
Notice the highlighted Google Analytics code exposed by a faulty Javascript element on the phishing website. Click to enlarge. That code actually belongs to the USPS.
The valid domain for that Google Analytics code is the official usps.com website. According to dnslytics.com, that same analytics code has shown up on at least six other nearly identical USPS phishing pages dating back nearly as many years, including onlineuspsexpress[.]com, which DomainTools.com says was registered way back in September 2018 to an individual in Nigeria.
A different domain with that same Google Analytics code that was registered in 2021 is peraltansepeda[.]com, which archive.org shows was running a similar set of phishing pages targeting USPS users. DomainTools.com indicates this website name was registered by phishers based in Indonesia.
DomainTools says the above-mentioned USPS phishing domain stamppos[.]com was registered in 2022 via Singapore-based Alibaba.com, but the registrant city and state listed for that domain says “Georgia, AL,” which is not a real location.
Alas, running a search for domains registered through Alibaba to anyone claiming to reside in Georgia, AL reveals nearly 300 recent postal phishing domains ending in “.top.” These domains are either administrative domains obscured by a password-protected login page, or are .top domains phishing customers of the USPS as well as postal services serving other countries.
Those other nations include the Australia Post, An Post (Ireland), Correos.es (Spain), the Costa Rican post, the Chilean Post, the Mexican Postal Service, Poste Italiane (Italy), PostNL (Netherlands), PostNord (Denmark, Norway and Sweden), and Posti (Finland). A complete list of these domains is available here (PDF).
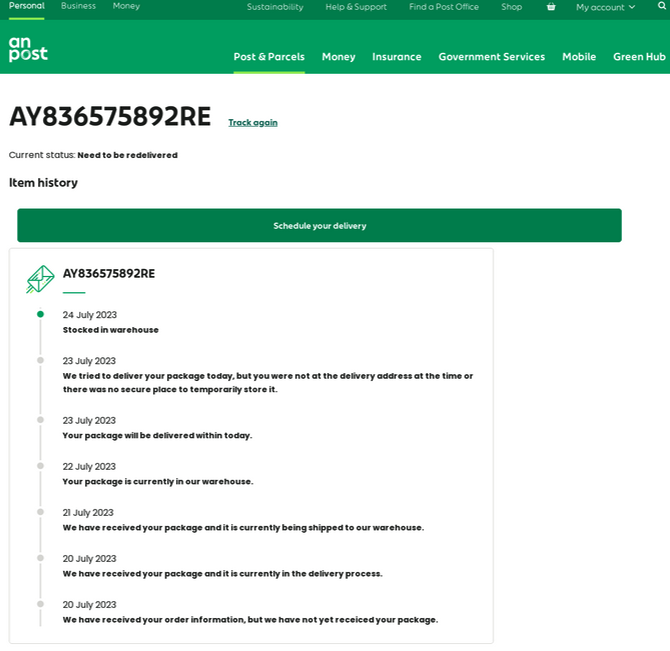
A phishing page targeting An Post, the state-owned provider of postal services in Ireland.
The Georgia, AL domains at Alibaba also encompass several that spoof sites claiming to collect outstanding road toll fees and fines on behalf of the governments of Australia, New Zealand and Singapore.
An anonymous reader wrote in to say they submitted fake information to the above-mentioned phishing site usps.receivepost[.]com via the malware sandbox any.run. A video recording of that analysis shows that the site sends any submitted data via an automated bot on the Telegram instant messaging service.
The traffic analysis just below the any.run video shows that any data collected by the phishing site is being sent to the Telegram user @chenlun, who offers to sell customized source code for phishing pages. From a review of @chenlun’s other Telegram channels, it appears this account is being massively spammed at the moment — possibly thanks to public attention brought by this story.
Meanwhile, researchers at DomainTools recently published a report on an apparently unrelated but equally sprawling SMS-based phishing campaign targeting USPS customers that appears to be the work of cybercriminals based in Iran.
Phishers tend to cast a wide net and often spoof entities that are broadly used by the local population, and few brands are going to have more household reach than domestic mail services. In June, the United Parcel Service (UPS) disclosed that fraudsters were abusing an online shipment tracking tool in Canada to send highly targeted SMS phishing messages that spoofed the UPS and other brands.
With the holiday shopping season nearly upon us, now is a great time to remind family and friends about the best advice to sidestep phishing scams: Avoid clicking on links or attachments that arrive unbidden in emails, text messages and other mediums. Most phishing scams invoke a temporal element that warns of negative consequences should you fail to respond or act quickly.
If you’re unsure whether the message is legitimate, take a deep breath and visit the site or service in question manually — ideally, using a browser bookmark so as to avoid potential typosquatting sites.
Update: Added information about the Telegram bot and any.run analysis.
Many organizations — including quite a few Fortune 500 firms — have exposed web links that allow anyone to initiate a Zoom video conference meeting as a valid employee. These company-specific Zoom links, which include a permanent user ID number and an embedded passcode, can work indefinitely and expose an organization’s employees, customers or partners to phishing and other social engineering attacks.

Image: @Pressmaster on Shutterstock.
At issue is the Zoom Personal Meeting ID (PMI), which is a permanent identification number linked to your Zoom account and serves as your personal meeting room available around the clock. The PMI portion forms part of each new meeting URL created by that account, such as:
zoom.us/j/5551112222
Zoom has an option to include an encrypted passcode within a meeting invite link, which simplifies the process for attendees by eliminating the need to manually enter the passcode. Following the previous example, such a link might look something like this:
zoom.us/j/5551112222/pwd=jdjsklskldklsdksdklsdkll
Using your PMI to set up new meetings is convenient, but of course convenience often comes at the expense of security. Because the PMI remains the same for all meetings, anyone with your PMI link can join any ongoing meeting unless you have locked the meeting or activated Zoom’s Waiting Room feature.
Including an encrypted passcode in the Zoom link definitely makes it easier for attendees to join, but it might open your meetings to unwanted intruders if not handled responsibly. Particularly if that Zoom link is somehow indexed by Google or some other search engine, which happens to be the case for thousands of organizations.
Armed with one of these links, an attacker can create meetings and invite others using the identity of the authorized employee. And many companies using Zoom have made it easy to find recently created meeting links that include encrypted passcodes, because they have dedicated subdomains at Zoom.us.
Using the same method, KrebsOnSecurity also found working Zoom meeting links for The National Football League (NFL), LinkedIn, Oracle, Humana, Disney, Warner Bros, and Uber. And that was from just a few minutes of searching. And to illustrate the persistence of some of these Zoom links, Archive.org says several of the links were first created as far back as 2020 and 2021.
KrebsOnSecurity received a tip about the Zoom exposures from Charan Akiri, a researcher and security engineer at Reddit. In April 2023, this site featured research by Akiri showing that many public Salesforce websites were leaking private data, including banks and healthcare organizations (Akiri said Salesforce also had these open Zoom meeting links before he notified them).
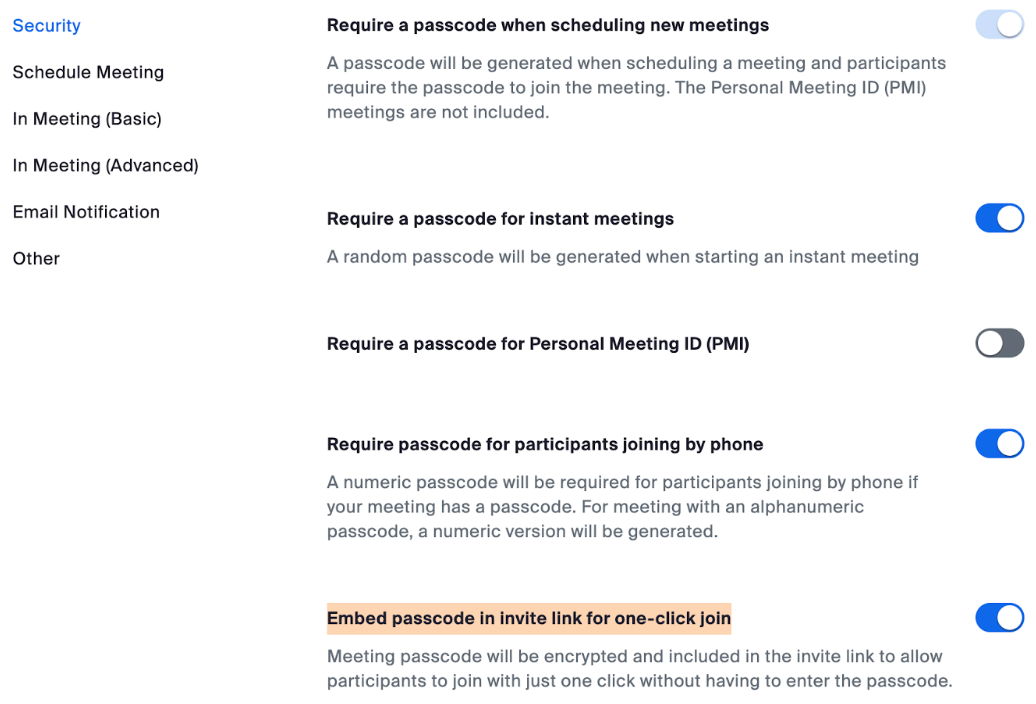
The Zoom links that exposed working meeting rooms all had enabled the highlighted option.
Akiri said the misuse of PMI links, particularly those with passcodes embedded, can give unauthorized individuals access to meetings.
“These one-click links, which are not subject to expiration or password requirement, can be exploited by attackers for impersonation,” Akiri said. “Attackers exploiting these vulnerabilities can impersonate companies, initiating meetings unknowingly to users. They can contact other employees or customers while posing as the company, gaining unauthorized access to confidential information, potentially for financial gain, recruitment, or fraudulent advertising campaigns.”
Akiri said he built a simple program to crawl the web for working Zoom meeting links from different organizations, and so far it has identified thousands of organizations with these perfectly functional zombie Zoom links.
According to Akiri, here are several tips for using Zoom links more safely:
Don’t Use Personal Meeting ID for Public Meetings: Your Personal Meeting ID (PMI) is the default meeting that launches when you start an ad hoc meeting. Your PMI doesn’t change unless you change it yourself, which makes it very useful if people need a way to reach you. But for public meetings, you should always schedule new meetings with randomly generated meeting IDs. That way, only invited attendees will know how to join your meeting. You can also turn off your PMI when starting an instant meeting in your profile settings.
Require a Passcode to Join: You can take meeting security even further by requiring a passcode to join your meetings. This feature can be applied to both your Personal Meeting ID, so only those with the passcode will be able to reach you, and to newly scheduled meetings. To learn all the ways to add a passcode for your meetings, see this support article.
Only Allow Registered or Domain Verified Users: Zoom can also give you peace of mind by letting you know exactly who will be attending your meeting. When scheduling a meeting, you can require attendees to register with their email, name, and custom questions. You can even customize your registration page with a banner and logo. By default, Zoom also restricts participants to those who are logged into Zoom, and you can even restrict it to Zoom users whose email address uses a certain domain.
Further reading: How to Keep Uninvited Guests Out of Your Zoom Meeting
Update 12:33 p.m.: The list of affected organizations was updated, because several companies listed apparently only exposed links that let anyone connect to existing, always-on meeting rooms — not initiate and completely control a Zoom meeting. The real danger with the zombie links described above is that anyone can find and use them to create new meetings and invite others.
The victim shaming site operated by the Snatch ransomware group is leaking data about its true online location and internal operations, as well as the Internet addresses of its visitors, KrebsOnSecurity has found. The leaked data suggest that Snatch is one of several ransomware groups using paid ads on Google.com to trick people into installing malware disguised as popular free software, such as Microsoft Teams, Adobe Reader, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Discord.
First spotted in 2018, the Snatch ransomware group has published data stolen from hundreds of organizations that refused to pay a ransom demand. Snatch publishes its stolen data at a website on the open Internet, and that content is mirrored on the Snatch team’s darknet site, which is only reachable using the global anonymity network Tor.
KrebsOnSecurity has learned that Snatch’s darknet site exposes its “server status” page, which includes information about the true Internet addresses of users accessing the website.
Refreshing this page every few seconds shows that the Snatch darknet site generates a decent amount of traffic, often attracting thousands of visitors each day. But by far the most frequent repeat visitors are coming from Internet addresses in Russia that either currently host Snatch’s clear web domain names or recently did.
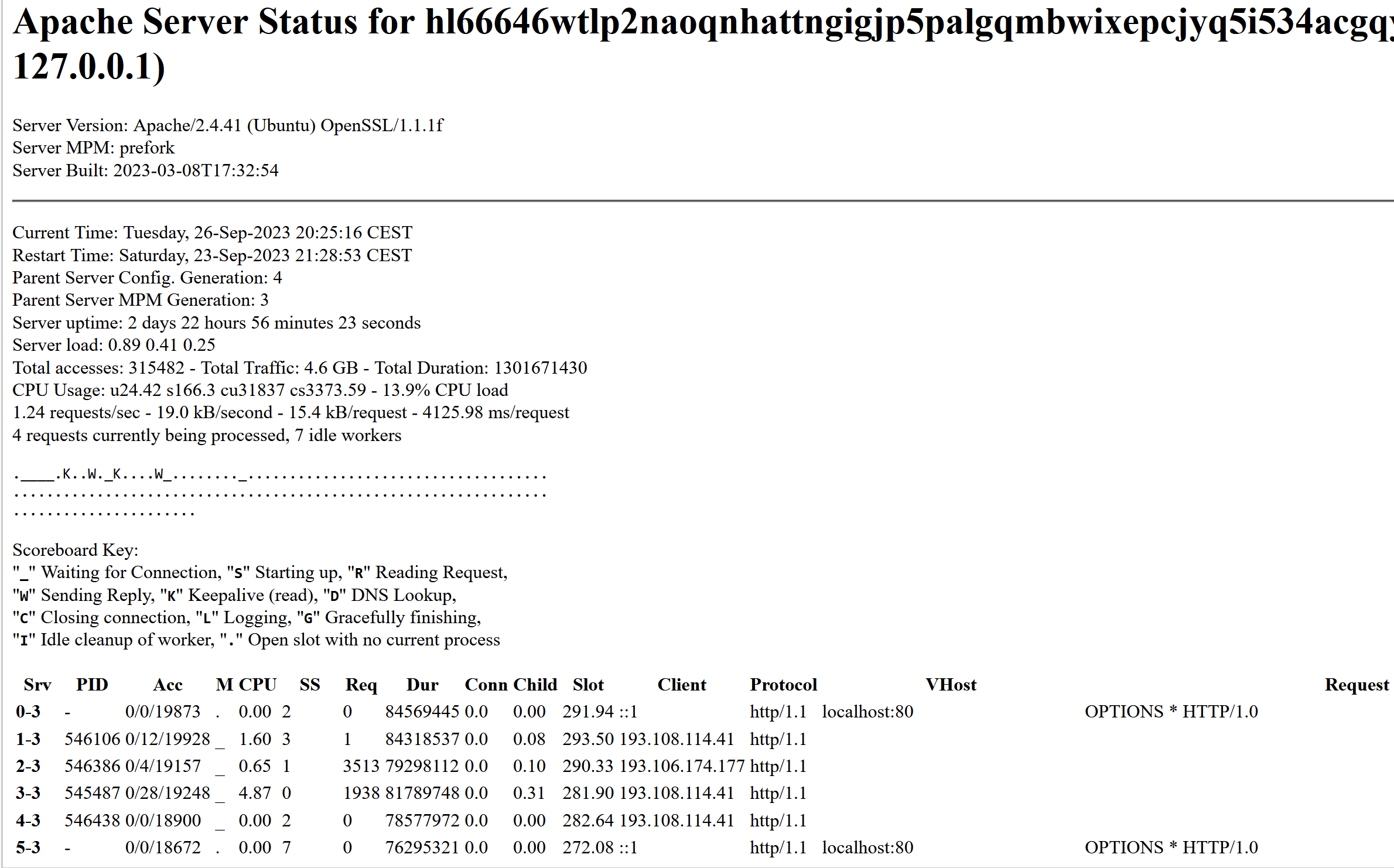
The Snatch ransomware gang’s victim shaming site on the darknet is leaking data about its visitors. This “server status” page says that Snatch’s website is on Central European Summer Time (CEST) and is powered by OpenSSL/1.1.1f, which is no longer supported by security updates.
Probably the most active Internet address accessing Snatch’s darknet site is 193.108.114[.]41, which is a server in Yekaterinburg, Russia that hosts several Snatch domains, including snatchteam[.]top, sntech2ch[.]top, dwhyj2[.]top and sn76930193ch[.]top. It could well be that this Internet address is showing up frequently because Snatch’s clear-web site features a toggle button at the top that lets visitors switch over to accessing the site via Tor.
Another Internet address that showed up frequently in the Snatch server status page was 194.168.175[.]226, currently assigned to Matrix Telekom in Russia. According to DomainTools.com, this address also hosts or else recently hosted the usual coterie of Snatch domains, as well as quite a few domains phishing known brands such as Amazon and Cashapp.
The Moscow Internet address 80.66.64[.]15 accessed the Snatch darknet site all day long, and that address also housed the appropriate Snatch clear-web domains. More interestingly, that address is home to multiple recent domains that appear confusingly similar to known software companies, including libreoff1ce[.]com and www-discord[.]com.
This is interesting because the phishing domains associated with the Snatch ransomware gang were all registered to the same Russian name — Mihail Kolesnikov, a name that is somewhat synonymous with recent phishing domains tied to malicious Google ads.
Kolesnikov could be a nod to a Russian general made famous during Boris Yeltsin’s reign. Either way, it’s clearly a pseudonym, but there are some other commonalities among these domains that may provide insight into how Snatch and other ransomware groups are sourcing their victims.
DomainTools says there are more than 1,300 current and former domain names registered to Mihail Kolesnikov between 2013 and July 2023. About half of the domains appear to be older websites advertising female escort services in major cities around the United States (e.g. the now-defunct pittsburghcitygirls[.]com).
The other half of the Kolesnikov websites are far more recent phishing domains mostly ending in “.top” and “.app” that appear designed to mimic the domains of major software companies, including www-citrix[.]top, www-microsofteams[.]top, www-fortinet[.]top, ibreoffice[.]top, www-docker[.]top, www-basecamp[.]top, ccleaner-cdn[.]top, adobeusa[.]top, and www.real-vnc[.]top.
In August 2023, researchers with Trustwave Spiderlabs said they encountered domains registered to Mihail Kolesnikov being used to disseminate the Rilide information stealer trojan.
But it appears multiple crime groups may be using these domains to phish people and disseminate all kinds of information-stealing malware. In February 2023, Spamhaus warned of a huge surge in malicious ads that were hijacking search results in Google.com, and being used to distribute at least five different families of information stealing trojans, including AuroraStealer, IcedID/Bokbot, Meta Stealer, RedLine Stealer and Vidar.
For example, Spamhaus said victims of these malicious ads would search for Microsoft Teams in Google.com, and the search engine would often return a paid ad spoofing Microsoft or Microsoft Teams as the first result — above all other results. The malicious ad would include a logo for Microsoft and at first glance appear to be a safe and trusted place to download the Microsoft Teams client.
However, anyone who clicked on the result was whisked away instead to mlcrosofteams-us[.]top — yet another malicious domain registered to Mr. Kolesnikov. And while visitors to this website may believe they are only downloading the Microsoft Teams client, the installer file includes a copy of the IcedID malware, which is really good at stealing passwords and authentication tokens from the victim’s web browser.
The founder of the Swiss anti-abuse website abuse.ch told Spamhaus it is likely that some cybercriminals have started to sell “malvertising as a service” on the dark web, and that there is a great deal of demand for this service.
In other words, someone appears to have built a very profitable business churning out and promoting new software-themed phishing domains and selling that as a service to other cybercriminals. Or perhaps they are simply selling any stolen data (and any corporate access) to active and hungry ransomware group affiliates.
The tip about the exposed “server status” page on the Snatch darkweb site came from @htmalgae, the same security researcher who alerted KrebsOnSecurity earlier this month that the darknet victim shaming site run by the 8Base ransomware gang was inadvertently left in development mode.
That oversight revealed not only the true Internet address of the hidden 8Base site (in Russia, naturally), but also the identity of a programmer in Moldova who apparently helped to develop the 8Base code.
@htmalgae said the idea of a ransomware group’s victim shaming site leaking data that they did not intend to expose is deliciously ironic.
“This is a criminal group that shames others for not protecting user data,” @htmalgae said. “And here they are leaking their user data.”
All of the malware mentioned in this story is designed to run on Microsoft Windows devices. But Malwarebytes recently covered the emergence of a Mac-based information stealer trojan called AtomicStealer that was being advertised through malicious Google ads and domains that were confusingly similar to software brands.
Please be extra careful when you are searching online for popular software titles. Cracked, pirated copies of major software titles are a frequent source of infostealer infections, as are these rogue ads masquerading as search results. Make sure to double-check you are actually at the domain you believe you’re visiting *before* you download and install anything.
Stay tuned for Part II of this post, which includes a closer look at the Snatch ransomware group and their founder.
Further reading:
@HTMalgae’s list of the top Internet addresses seen accessing Snatch’s darknet site
Ars Technica: Until Further Notice Think Twice Before Using Google to Download Software
Bleeping Computer: Hackers Abuse Google Ads to Spread Malware in Legit Software
The password manager service LastPass is now forcing some of its users to pick longer master passwords. LastPass says the changes are needed to ensure all customers are protected by their latest security improvements. But critics say the move is little more than a public relations stunt that will do nothing to help countless early adopters whose password vaults were exposed in a 2022 breach at LastPass.
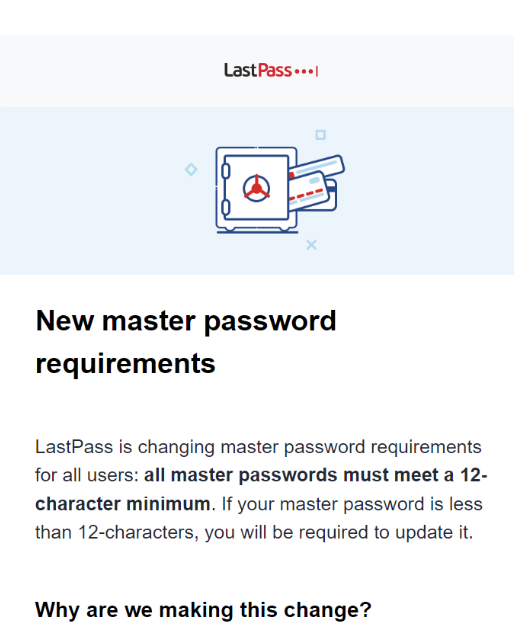
LastPass sent this notification to users earlier this week.
LastPass told customers this week they would be forced to update their master password if it was less than 12 characters. LastPass officially instituted this change back in 2018, but some undisclosed number of the company’s earlier customers were never required to increase the length of their master passwords.
This is significant because in November 2022, LastPass disclosed a breach in which hackers stole password vaults containing both encrypted and plaintext data for more than 25 million users.
Since then, a steady trickle of six-figure cryptocurrency heists targeting security-conscious people throughout the tech industry has led some security experts to conclude that crooks likely have succeeded at cracking open some of the stolen LastPass vaults.
KrebsOnSecurity last month interviewed a victim who recently saw more than three million dollars worth of cryptocurrency siphoned from his account. That user signed up with LastPass nearly a decade ago, stored their cryptocurrency seed phrase there, and yet never changed his master password — which was just eight characters. Nor was he ever forced to improve his master password.
That story cited research from Adblock Plus creator Wladimir Palant, who said LastPass failed to upgrade many older, original customers to more secure encryption protections that were offered to newer customers over the years.
For example, another important default setting in LastPass is the number of “iterations,” or how many times your master password is run through the company’s encryption routines. The more iterations, the longer it takes an offline attacker to crack your master password.
Palant said that for many older LastPass users, the initial default setting for iterations was anywhere from “1” to “500.” By 2013, new LastPass customers were given 5,000 iterations by default. In February 2018, LastPass changed the default to 100,100 iterations. And very recently, it upped that again to 600,000. Still, Palant and others impacted by the 2022 breach at LastPass say their account security settings were never forcibly upgraded.
Palant called this latest action by LastPass a PR stunt.
“They sent this message to everyone, whether they have a weak master password or not – this way they can again blame the users for not respecting their policies,” Palant said. “But I just logged in with my weak password, and I am not forced to change it. Sending emails is cheap, but they once again didn’t implement any technical measures to enforce this policy change.”
Either way, Palant said, the changes won’t help people affected by the 2022 breach.
“These people need to change all their passwords, something that LastPass still won’t recommend,” Palant said. “But it will somewhat help with the breaches to come.”
LastPass CEO Karim Toubba said changing master password length (or even the master password itself) is not designed to address already stolen vaults that are offline.
“This is meant to better protect customers’ online vaults and encourage them to bring their accounts up to the 2018 LastPass standard default setting of a 12-character minimum (but could opt out from),” Toubba said in an emailed statement. “We know that some customers may have chosen convenience over security and utilized less complex master passwords despite encouragement to use our (or others) password generator to do otherwise.”
A basic functionality of LastPass is that it will pick and remember lengthy, complex passwords for each of your websites or online services. To automatically populate the appropriate credentials at any website going forward, you simply authenticate to LastPass using your master password.
LastPass has always emphasized that if you lose this master password, that’s too bad because they don’t store it and their encryption is so strong that even they can’t help you recover it.
But experts say all bets are off when cybercrooks can get their hands on the encrypted vault data itself — as opposed to having to interact with LastPass via its website. These so-called “offline” attacks allow the bad guys to conduct unlimited and unfettered “brute force” password cracking attempts against the encrypted data using powerful computers that can each try millions of password guesses per second.
A chart on Palant’s blog post offers an idea of how increasing password iterations dramatically increases the costs and time needed by the attackers to crack someone’s master password. Palant said it would take a single high-powered graphics card about a year to crack a password of average complexity with 500 iterations, and about 10 years to crack the same password run through 5,000 iterations.
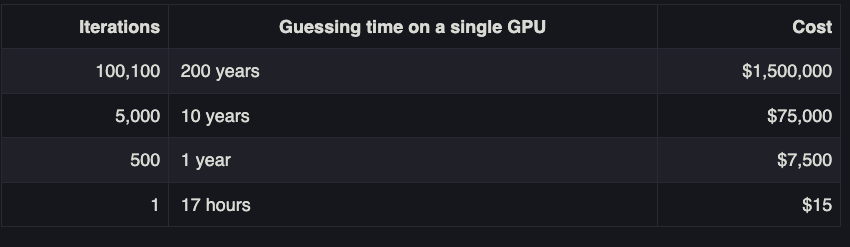
Image: palant.info
However, these numbers radically come down when a determined adversary also has other large-scale computational assets at their disposal, such as a bitcoin mining operation that can coordinate the password-cracking activity across multiple powerful systems simultaneously.
Meaning, LastPass users whose vaults were never upgraded to higher iterations and whose master passwords were weak (less than 12 characters) likely have been a primary target of distributed password-cracking attacks ever since the LastPass user vaults were stolen late last year.
Asked why some LastPass users were left behind on older security minimums, Toubba said a “small percentage” of customers had corrupted items in their password vaults that prevented those accounts from properly upgrading to the new requirements and settings.
“We have been able to determine that a small percentage of customers have items in their vaults that are corrupt and when we previously utilized automated scripts designed to re-encrypt vaults when the master password or iteration count is changed, they did not complete,” Toubba said. “These errors were not originally apparent as part of these efforts and, as we have discovered them, we have been working to be able to remedy this and finish the re-encryption.”
Nicholas Weaver, a researcher at University of California, Berkeley’s International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) and lecturer at UC Davis, said LastPass made a huge mistake years ago by not force-upgrading the iteration count for existing users.
“And now this is blaming the users — ‘you should have used a longer passphrase’ — not them for having weak defaults that were never upgraded for existing users,” Weaver said. “LastPass in my book is one step above snake-oil. I used to be, ‘Pick whichever password manager you want,’ but now I am very much, ‘Pick any password manager but LastPass.'”
Asked why LastPass isn’t recommending that users change all of the passwords secured by the encrypted master password that was stolen when the company got hacked last year, Toubba said it’s because “the data demonstrates that the majority of our customers follow our recommendations (or greater), and the probability of successfully brute forcing vault encryption is greatly reduced accordingly.”
“We’ve been telling customers since December of 2022 that they should be following recommended guidelines,” Toubba continued. “And if they haven’t followed the guidelines we recommended that they change their downstream passwords.”
In December 2022, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that a cybercriminal using the handle “USDoD” had infiltrated the FBI‘s vetted information sharing network InfraGard, and was selling the contact information for all 80,000 members. The FBI responded by reverifying InfraGard members and by seizing the cybercrime forum where the data was being sold. But on Sept. 11, 2023, USDoD resurfaced after a lengthy absence to leak sensitive employee data stolen from the aerospace giant Airbus, while promising to visit the same treatment on top U.S. defense contractors.
In a post on the English language cybercrime forum BreachForums, USDoD leaked information on roughly 3,200 Airbus vendors, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses. USDoD claimed they grabbed the data by using passwords stolen from a Turkish airline employee who had third-party access to Airbus’ systems.
USDoD didn’t say why they decided to leak the data on the 22nd anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, but there was definitely an aircraft theme to the message that accompanied the leak, which concluded with the words, “Lockheed martin, Raytheon and the entire defense contractos [sic], I’m coming for you [expletive].”
Airbus has apparently confirmed the cybercriminal’s account to the threat intelligence firm Hudson Rock, which determined that the Airbus credentials were stolen after a Turkish airline employee infected their computer with a prevalent and powerful info-stealing trojan called RedLine.
Info-stealers like RedLine typically are deployed via opportunistic email malware campaigns, and by secretly bundling the trojans with cracked versions of popular software titles made available online. Credentials stolen by info-stealers often end up for sale on cybercrime shops that peddle purloined passwords and authentication cookies (these logs also often show up in the malware scanning service VirusTotal).
Hudson Rock said it recovered the log files created by a RedLine infection on the Turkish airline employee’s system, and found the employee likely infected their machine after downloading pirated and secretly backdoored software for Microsoft Windows.
Hudson Rock says info-stealer infections from RedLine and a host of similar trojans have surged in recent years, and that they remain “a primary initial attack vector used by threat actors to infiltrate organizations and execute cyberattacks, including ransomware, data breaches, account overtakes, and corporate espionage.”
The prevalence of RedLine and other info-stealers means that a great many consequential security breaches begin with cybercriminals abusing stolen employee credentials. In this scenario, the attacker temporarily assumes the identity and online privileges assigned to a hacked employee, and the onus is on the employer to tell the difference.
In addition to snarfing any passwords stored on or transmitted through an infected system, info-stealers also siphon authentication cookies or tokens that allow one to remain signed-in to online services for long periods of time without having to resupply one’s password and multi-factor authentication code. By stealing these tokens, attackers can often reuse them in their own web browser, and bypass any authentication normally required for that account.
Microsoft Corp. this week acknowledged that a China-backed hacking group was able to steal one of the keys to its email kingdom that granted near-unfettered access to U.S. government inboxes. Microsoft’s detailed post-mortem cum mea culpa explained that a secret signing key was stolen from an employee in an unlucky series of unfortunate events, and thanks to TechCrunch we now know that the culprit once again was “token-stealing malware” on the employee’s system.
In April 2023, the FBI seized Genesis Market, a bustling, fully automated cybercrime store that was continuously restocked with freshly hacked passwords and authentication tokens stolen by a network of contractors who deployed RedLine and other info-stealer malware.
In March 2023, the FBI arrested and charged the alleged administrator of BreachForums (aka Breached), the same cybercrime community where USDoD leaked the Airbus data. In June 2023, the FBI seized the BreachForums domain name, but the forum has since migrated to a new domain.
Unsolicited email continues to be a huge vector for info-stealing malware, but lately the crooks behind these schemes have been gaming the search engines so that their malicious sites impersonating popular software vendors actually appear before the legitimate vendor’s website. So take special care when downloading software to ensure that you are in fact getting the program from the original, legitimate source whenever possible.
Also, unless you really know what you’re doing, please don’t download and install pirated software. Sure, the cracked program might do exactly what you expect it to do, but the chances are good that it is also laced with something nasty. And when all of your passwords are stolen and your important accounts have been hijacked or sold, you will wish you had simply paid for the real thing.
Microsoft today issued software updates to fix at least five dozen security holes in Windows and supported software, including patches for two zero-day vulnerabilities that are already being exploited. Also, Adobe, Google Chrome and Apple iOS users may have their own zero-day patching to do.

On Sept. 7, researchers at Citizen Lab warned they were seeing active exploitation of a “zero-click,” zero-day flaw to install spyware on iOS devices without any interaction from the victim.
“The exploit chain was capable of compromising iPhones running the latest version of iOS (16.6) without any interaction from the victim,” the researchers wrote.
According to Citizen Lab, the exploit uses malicious images sent via iMessage, an embedded component of Apple’s iOS that has been the source of previous zero-click flaws in iPhones and iPads.
Apple says the iOS flaw (CVE-2023-41064) does not seem to work against devices that have its ultra-paranoid “Lockdown Mode” enabled. This feature restricts non-essential iOS features to reduce the device’s overall attack surface, and it was designed for users concerned that they may be subject to targeted attacks. Citizen Lab says the bug it discovered was being exploited to install spyware made by the Israeli cyber surveillance company NSO Group.
This vulnerability is fixed in iOS 16.6.1 and iPadOS 16.6.1. To turn on Lockdown Mode in iOS 16, go to Settings, then Privacy and Security, then Lockdown Mode.
Not to be left out of the zero-day fun, Google acknowledged on Sept. 11 that an exploit for a heap overflow bug in Chrome is being exploited in the wild. Google says it is releasing updates to fix the flaw, and that restarting Chrome is the way to apply any pending updates. Interestingly, Google says this bug was reported by Apple and Citizen Lab.
On the Microsoft front, a zero-day in Microsoft Word is among the more concerning bugs fixed today. Tracked as CVE-2023-36761, it is flagged as an “information disclosure” vulnerability. But that description hardly grasps at the sensitivity of the information potentially exposed here.
Tom Bowyer, manager of product security at Automox, said exploiting this vulnerability could lead to the disclosure of Net-NTLMv2 hashes, which are used for authentication in Windows environments.
“If a malicious actor gains access to these hashes, they can potentially impersonate the user, gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems,” Bowyer said, noting that CVE-2023-36761 can be exploited just by viewing a malicious document in the Windows preview pane. “They could also conduct pass-the-hash attacks, where the attacker uses the hashed version of a password to authenticate themselves without needing to decrypt it.”
The other Windows zero-day fixed this month is CVE-2023-36802. This is an “elevation of privilege” flaw in the “Microsoft Streaming Service Proxy,” which is built into Windows 10, 11 and Windows Server versions. Microsoft says an attacker who successfully exploits the bug can gain SYSTEM level privileges on a Windows computer.
Five of the flaws Microsoft fixed this month earned its “critical” rating, which the software giant reserves for vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malware or malcontents with little or no interaction by Windows users.
According to the SANS Internet Storm Center, the most serious critical bug in September’s Patch Tuesday is CVE-2023-38148, which is a weakness in the Internet Connection Sharing service on Windows. Microsoft says an unauthenticated attacker could leverage the flaw to install malware just sending a specially crafted data packet to a vulnerable Windows system.
Finally, Adobe has released critical security updates for its Adobe Reader and Acrobat software that also fixes a zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2023-26369). More details are at Adobe’s advisory.
For a more granular breakdown of the Windows updates pushed out today, check out Microsoft Patch Tuesday by Morphus Labs. In the meantime, consider backing up your data before updating Windows, and keep an eye on AskWoody.com for reports of any widespread problems with any of the updates released as part of September’s Patch Tuesday.
Update: Mozilla also has fixed zero-day flaw in Firefox and Thunderbird, and the Brave browser was updated as well. It appears the common theme here is any software that uses a code library called “libwebp,” and that this vulnerability is being tracked as CVE-2023-4863.
“This includes Electron-based applications, for example – Signal,” writes StackDiary.com. “Electron patched the vulnerability yesterday. Also, software like Honeyview (from Bandisoft) released an update to fix the issue. CVE-2023-4863 was falsely marked as Chrome-only by Mitre and other organizations that track CVE’s and 100% of media reported this issue as “Chrome only”, when it’s not.”